A person's lower back, even if he is not overweight, always bears a very large load. After all, upright walking is the only way for a person to move. Most often, acute pain in the lumbar spine and the problems of its treatment are associated with pathology of the deep muscles of the back and with hernias and protrusions of discs.
However, when acute back pain first occurs, it is unclear what caused it. Back pain can occur due to:
- osteochondrosis and its complications, that is, with protrusions and hernias of the lumbar spine;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- inflammation of the nerve roots, or radiculitis;
- spondylolisthesis and scoliosis, when the vertebrae are connected to each other at abnormal angles;
- inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, brucellosis.
Finally, the cause of acute lower back pain may be a paravertebral tumor or metastases to the spine. And if it is known that the cause is a hernia, then how does the lower back hurt?
Mechanism of formation of intervertebral hernia
The spine is designed to withstand loads. It supports and stabilizes the body in a standing position, providing complete freedom of movement. When lifting weights, uncomfortable positioning of the body, strong and stressful loads, it takes on the main effort. The load is especially severe when lifting heavy objects with outstretched arms. The heaviest load and, accordingly, wear falls on the lumbar region. When age-related or pathological changes begin in the body, tissues change structure and can no longer fully perform shock absorption functions. Under force, they can become deformed and crumble, which disrupts the functions of the spine and can disrupt the functioning of the entire body.
Features of anatomy
The entire spine is formed by more than 30 vertebrae of different sizes and is divided into 5 sections:
- cervical - formed by 7 vertebrae (C1–C2), which are the smallest and most mobile in the body;
- thoracic - formed by 12 vertebrae (Th1–Th12), least likely to be susceptible to degenerative-dystrophic changes;
- lumbar – consists of the 5 largest vertebrae (L1–L5), which bear the greatest load during physical work;
- sacral – has 3 vertebrae (S1–S3);
- coccyx – formed by 1–3 fused vertebrae.
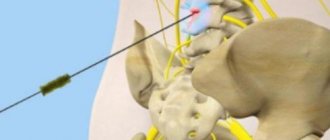
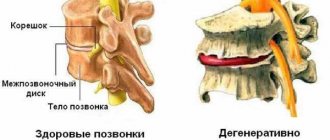
Between all the vertebrae there are cartilaginous structures that provide shock absorption when walking and the natural flexibility of the spine. They are called intervertebral discs. Each disc has a pulpous nucleus pulposus and a tough outer shell called fibrous. It is protected on the sides by end plates.
How does a hernia appear?
The formation of protrusion occurs in several stages:
- Protrusion. The beginning of pathological changes. The fibrous ring becomes less elastic and can shift and become deformed.
- Partial loss of a section of the disc. This is the second stage in which tissue destruction can occur. This process is inevitably followed by displacement of the gel-like core of the disc.
- Prolapse. The nucleus emerges from the disc ring and begins to influence the nerve endings located nearby.
- Sequestration. The process by which a semi-liquid substance from the nucleus penetrates the cavity of the spinal column. This is accompanied by allergic reactions, nerve connections and blood flow in the tissues are disrupted. Due to constant pressure in an area that is not designed for it, there is a loss of sensitivity and the threat of paralysis.
If help is sought in a timely manner, when the process does not involve the nerves and spinal cord, conservative treatment is used and the patient can be completely cured.
Stages of the disease
Lumbar spinal hernia is characterized by different signs at certain stages of disease progression. Currently, each patient has the opportunity to stop the development of the disease and prevent the risk of serious consequences, as well as to treat a hernia of the lumbar spine without surgery , for this it is necessary to visit a competent specialist in a timely manner. Below we will talk about the main stages characteristic of this pathology:
- Prolapse. In this case, there is a slight change in the position of the disk. There is a possibility of its return to its usual place, subject to the cessation of the negative impact;
- Protrusion. There is a strong displacement of the location of the disc, but it does not protrude beyond the boundaries of the vertebrae;
- Extrusion. The nucleus is displaced beyond the boundaries of the vertebrae;
- Sequestration. It is characterized by the appearance of cracks in the area of the fibrous ring. In this case, there is a displacement of the pulp beyond the line marked by the vertebrae.
How does a hernia manifest?
At the very beginning of the development of the pathological process, the patient does not feel serious pain, symptoms are few. The more tissue protrudes, the more the patient feels it. There are three groups of symptoms for intervertebral hernia:
- The main symptom of a herniated disc is pain. At first it is not sharp, may be aching, and go away with a change in body position. The more serious the stage of the process, the stronger the pain. Shooting sensations appear, it is painful for the patient to turn the body, the sensations intensify with physical activity.
- Spinal syndrome. Constant pain causes spasms in the lower back muscles. The patient cannot move fully and is forced to tilt the body in order to relieve some of the load and reduce pain.
- Damage and death of nerve roots due to constant compression. The compression that occurs due to tissue protrusion constantly affects the nerve fibers. This disrupts blood flow, their functions, and later death occurs altogether. The manifestations of this process are: weakness, decreased tone, loss of sensitivity, the appearance of body asymmetry, decreased sensitivity and tone of the skin.
If the protrusion occurs in the posterior direction, any physical work is highly likely to cause severe compression and paralysis.
Rehabilitation
After any surgical intervention, each patient goes through a recovery period. But its duration and complexity depend on the type of operation performed and its volume. Therefore, after nucleoplasty or hydroplasty, postoperative pain is completely absent or patients experience minor discomfort, and discharge is carried out on the same day.
When performing endoscopic surgery, the hospitalization period is on average 5 days. And after microdiscectomy, you will only be allowed to get out of bed after 5–7 days. At the same time, the most difficult recovery period awaits patients who have undergone microdiscectomy, since this is the most traumatic operation. But even after it, the pain is most pronounced only at first, and then the patient’s condition progressively improves.
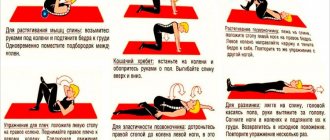
As part of rehabilitation, the following may be prescribed for different periods:
- drug therapy;
- exercise therapy;
- orthopedic corset;
- physiotherapy;
- massage.
Thus, lumbosacral hernias are a widespread problem that is easiest to deal with in the earliest stages of formation. Then you can solve the problem using conservative methods or using the most gentle operation - nucleoplasty.
Manifestations depending on the location of the hernia
The characteristics of a hernia are determined by its location. In this area, the nerve roots are pinched and a characteristic clinical picture occurs. The nerve that is pinched during the formation of the lumbar protrusion of the spine runs along the inner surface of the leg from the hip to the ankle. The pain is not necessarily localized along the entire length; it can be reflected in the leg, foot, buttock, or outer side of the thigh. The lower back may also hurt at one point. As the situation develops, the pain may move lower - to the lower leg, heel and toes. In intensity, it can be a constant aching pain or lumbago that occurs when moving.
Basically, the pain becomes more intense with prolonged walking, standing, turning the body, and bending. It is also painful to lift your leg, do a number of exercises, and also drive on uneven roads.
At the beginning of the development of a hernia, pain can be relieved by lying down, bending one leg at the chest. This will help relieve tension and pressure on the nerve endings. In a more complex situation, this method will not help. Movements are constrained, their amplitude is greatly reduced, and the leg gets tired.
Basically, the patient feels compression of the spinal cord as tingling, burning, and numbness. It dulls the pain. The main symptom that the specialist will pay attention to during the examination is muscle tension on the side of the back, painful when pressed.
First aid for pain syndrome without drugs
Let's consider the principles of first aid, which can be carried out without taking medications and try to get rid of pain, and then - medications used in the first days, and even in the first hours after the onset of such acute pain.
Attention! You should be careful about one very common mistake. On the first day, and especially in the first hours, any warming up is strictly prohibited, and especially with the use of heating pads and physiotherapeutic devices that create excess heat. In the first day, swelling of the nerve roots and muscle tissue only increases, and an attempt to relieve pain by adding heat, according to the laws of physiology, only increases the blood flow to the area of inflammation, complementing and increasing the volume of hyperemia. Treatment of acute lower back pain in the first day with heat will only lead to increased pain.
Therefore, instead of intensive heating, you can, on the contrary, use cooling. If the patient does not have chronic inflammatory diseases of the kidneys or female genital organs, then an ice pack or some cold object can be applied to the lower back for a short time (5-10 minutes) several times a day through dense tissue. This will reduce swelling and relieve pain.
The second thing to do is to try to immobilize the patient by putting a semi-rigid corset on him. It will maintain the necessary distance between the lumbar vertebrae and reduce the risk of acute pain.
The third non-medicinal first aid method is the use of home physiotherapeutic devices, which do not heat, but distract and irritate. These are Lyapko and Kuznetsov applicators. The needles and thorns on which the patient lies, on the contrary, allow the volume of blood to flow from the area of inflammation into the subcutaneous tissue and deep layers of the skin. Thus, the pain syndrome is reduced, and the patient, at least while he lies still, experiences less discomfort. These simple remedies make it possible to alleviate the patient’s condition before using medications.
All other methods of treating acute lower back pain when protrusion and hernia occur or worsen are associated with the use of appropriate medications. Let's take a closer look at them.
Establishing diagnosis
The diagnosis is made after examination and examination of the patient. First of all, instrumental diagnostics are carried out to help determine whether the tendon reflexes are normal. The patient is asked to raise his straightened leg. Tests are also carried out for sensitivity to vibration, the ability to sense temperature and pain. If there is a hernia, there will be certain manifestations:
- The doctor will determine the sensitivity disorder.
- The patient's movement biomechanics will be changed.
- Tendon reflexes will deviate from normal.
Also, to diagnose protrusion, CT or MRI diagnostics of the spine is performed. These studies will help not only visualize the hernia, but also determine the condition of the surrounding tissues and diagnose narrowing of the spinal canal, if any. If indicated, contrast myelography may be prescribed. After the examination, the degree of pathological changes can be determined and adequate treatment can be prescribed. If the nerves are not affected, the patient complains only of pain, conservative therapy is used.
Which doctor should I contact?
Spinal diseases are treated by vertebrologists and neurologists, who often also work as chiropractors. They should be contacted if the slightest of the above-described deviations occurs. They are also the ones who interpret MRI, CT and X-ray images.
But due to their own workload, and often laziness, when symptoms of hernias and, in particular, back pain occur, people delay seeing a doctor. Painkillers in the form of tablets or ointments are often used on their own. But they only temporarily eliminate the symptom that is key to the disease.
This allows you to continue to lead your usual lifestyle, but has a negative impact on the prognosis, as the protrusion continues to increase. Therefore, over time, the pain syndrome intensifies, then neurological disorders in the form of numbness of the limbs or even paralysis join it, and internal organs corresponding to the level of damage also suffer.
Often in such situations people say that they are “falling apart.” And the reason lies in the intervertebral hernia. Therefore, in order to prevent this from happening, you should consult a doctor if the slightest manifestations of the disease appear. This specialist will be able to choose the right treatment tactics and assess the prospects for conservative therapy. Indeed, in advanced cases, the situation can only be corrected through surgery.
Prolonged ignoring of the problem can lead to the development of severe complications, including:
- spinal canal stenosis;
- disorders of the pelvic organs, up to loss of control over urination and defecation, as well as persistent erectile dysfunction;
- complete paralysis of the limbs.
Therefore, we recommend not to delay and contact a vertebrologist, chiropractor or neurologist as early as possible. Otherwise, conservative therapy will not bring results and the patient will have to muster the courage, as well as material resources, to perform a neurosurgical operation. Moreover, no neurosurgeon can give a 100% guarantee that it will be effective.
The specialist will prescribe the necessary studies, based on the results of which he will select the correct treatment tactics, taking into account the nature of the existing changes, the size of the hernia, its location and the clinical picture.
Why is a lumbar hernia dangerous?
Any hernia brings not only pain, but also a serious risk of disruption of the body and paralysis. Vertebral protrusion in the lumbar region has a number of dangerous accompanying manifestations:
- Blood circulation in the pelvis is disrupted, due to which the organs do not receive proper nutrition. This provokes problems with the excretory system and disruption of the internal genital organs.
- The spine is curved due to muscle tone. This causes compression of internal organs and can provoke other pathologies not directly related to the spine.
- Sensitivity decreases, numbness and limited body mobility are observed.
- Shooting appears - severe sharp pain during physical activity or movement.
- Knee reflexes may disappear, and mobility of the ankle and foot may change.
- The most serious consequence is paralysis.
Kinds
All hernias can be divided into anterior and posterior (dorsal). The former are rare and have a very favorable prognosis, while the latter pose a danger to a person’s physical capabilities because they fall into the lumen of the spinal canal. Depending on their location they are divided into:
- central (median) – located in the central part of the spinal canal, so they can provoke the appearance of pain, both on the right side of the body and on the left;
- paramedian - formed on the left or right side relative to the central axis of the spine, therefore causing the appearance of characteristic symptoms on the corresponding side of the body;
- circular - the entire posterior surface of the disc protrudes, which leads to filling of the entire spinal canal and the development of severe neurological symptoms, as well as severe pain;
- foraminal - a hernia forms in the area of very narrow openings of the spine formed by the vertebral body and articular processes, and causes burning, excruciating pain.
Depending on the size of the hernia they are divided into:
- small – the size of the protrusion does not exceed 5 mm;
- medium – the hernia reaches 5–7 mm;
- large - the formation increases to 8 mm or more.
But, unlike popular belief, the size of the intervertebral hernia is not strictly related to the severity of the observed symptoms. Even very large hernias can exist for a long time completely asymptomatically and are discovered by chance, while small ones can so infringe on the spinal root that not only severe pain syndrome occurs, but also serious disruptions in the organ innervated by it. Therefore, treatment tactics for each patient are chosen to a greater extent in accordance with the severity of complaints, rather than the size of the formation.
Operation
Radical intervention is used when it is necessary to free the spinal cord and nerves from the pressure of protruding tissues. The most popular methods are:
- Endoscopy is an operation through an incision in the spine using a probe. A camera and instruments are inserted through a small hole, and displaced tissue is removed.
- Disc endoprosthetics. Damaged elements are removed. A prosthetic structure is installed in their place.
- Percutaneous discectomy. Access is made through a puncture, the deformed core is removed and replaced with a special compound.
- Laser reconstruction – the hernia is removed by evaporating moisture from the tissue.
Possible complications
Among the most serious dangers posed by a lumbar hernia is a disruption in the supply of nerves to the pelvic region and lower extremities. In this case, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- Significant deterioration of sensitivity in the legs and perineum;
- The pain becomes too intense;
- Muscle weakness in the lower extremities and a noticeable change in gait;
- Severe disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system;
- Development of impotence in men, lack of sexual activity in women.
If you have one or more of the above symptoms, you should seek help from a neurosurgery specialist as soon as possible. In this case, the effectiveness of conservative methods is considered zero. The possibility of restoring the health of the lumbar spine depends on how seriously you take this problem and how promptly you visit a medical clinic.
Preventive measures
Spinal herniation can be prevented. There are a few simple rules for this:
- Nutrition and weight control. Excess weight increases the load on the spine.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Regular physical activity - morning exercises, warm-up during sedentary work.
- Sleep on a hard mattress, choose the right pillow.
- Preventive examinations with a doctor, timely seeking medical help if alarming symptoms appear.
By contacting a neurologist at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in a timely manner, you can avoid complications and return to a normal lifestyle as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
Today, the only research method that can provide comprehensive information about the condition of intervertebral discs is magnetic resonance imaging or MRI. It is safe for the patient and at the same time makes it possible to identify the slightest deviations in the “shock absorbers” of the spine, including minor protrusions.
The study can be carried out using two types of devices:
- Closed - classic MRI machines with a retractable couch and a hollow tube in which a magnetic field with a power of 1.5 to 3 Tesla is created. They are not suitable for patients suffering from claustrophobia.
- Open - the device does not have a solid tube, which increases the level of comfort for patients who are afraid of closed spaces, but at the same time reduces the information content of the study, since in such devices the magnetic field power does not exceed 0.2–1.2 Tesla.
During the procedure, it is important to remain completely still, otherwise it will not be possible to obtain a clear image, and the information content of the study will be reduced. On average, an MRI takes 20 minutes, but the method cannot be used to examine people with metal structures or elements in the body (with the exception of titanium).
Sometimes, to qualitatively assess the condition of bone structures, patients are also prescribed an X-ray or CT scan of the spine. They are also used when it is impossible to perform an MRI for one reason or another. With the help of CT and X-rays, it is possible to assess the height of the discs, detect signs of osteoporosis, osteophytes, spinal fractures, including fused ones, instability of spinal motion segments and anomalies.
In our clinic, you can also learn in more detail about the composition of your body and the state of the vascular system, which is involved in the blood supply to internal organs, skeletal muscles, and the brain. Our experienced doctors will explain the data obtained to you in detail. Bioimpendansometry calculates the ratio of fat, muscle, bone and skeletal mass, total fluid in the body, and basal metabolic rate. The intensity of recommended physical activity depends on the state of muscle mass. Metabolic processes, in turn, affect the body's ability to recover. Based on the indicators of active cell mass, one can judge the level of physical activity and nutritional balance. This simple and quick test helps us identify disturbances in the endocrine system and take the necessary measures. In addition, it is also very important for us to know the condition of blood vessels for the prevention of diseases such as heart attacks, hypertension, heart failure, diabetes and much more. Angioscan allows you to determine such important indicators as the biological age of blood vessels, their stiffness, stress index (which indicates heart rate), and blood oxygen saturation. Such screening will be useful for men and women over 30, athletes, those undergoing long-term and severe treatment, as well as everyone who monitors their health.
In this case, body composition analysis gives us information that adipose tissue predominates in the body, and the musculoskeletal component is in relative deficiency. These data will help the rehabilitation doctor competently draw up a physical activity plan, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Drug treatment
The doctor will most likely prescribe medication. The drugs can eliminate unpleasant symptoms, so taking anti-inflammatory or painkillers is required. For example, a doctor may prescribe Diclofenac or Ibuprofen. With the help of these drugs it will be possible to relieve pain and also prevent muscle tissue atrophy.
If the patient feels stiffness of movement or suffers from spasms, then the doctor will prescribe Mydocalm and Sirdalud. These are relaxing remedies that will quickly improve the patient’s well-being.
There are other answers to the question of how to cure a hernia of the lumbar spine. It is necessary not only to take medications, but also to undergo some other procedures.