What it is?
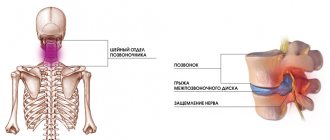
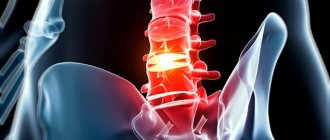
Cervical spondylosis is the name given to dystrophic-degenerative changes occurring in the cervical spine . As it progresses, special bone growths appear on the edges of the vertebrae, at the attachment points of the vertebral longitudinal ligaments, which look like spikes or hooks. These growths are called osteophytes. Typically, osteophytes grow in the direction of each other.
Osteophytes, when growing, have the ability to grow together
But in advanced cases of spondylosis, the vertebrae themselves are deformed. The disease most often occurs in the cervical region, because this part of the spine is characterized by increased mobility. Intervertebral discs and the vertebrae themselves wear out faster.
Clinical picture
In old age, the vertebrae and the discs that are located between them begin to gradually deteriorate. As a result, the spine loses its flexibility. In response, the body begins to intensively build bone tissue. This is how osteophytes are formed.
When bone growths appear, patients experience characteristic symptoms. After all, osteophytes begin to put pressure on the spinal nerve endings , causing pain.
At the first stage, when degenerative processes just begin, there are no characteristic symptoms. Problems appear at the stage of formation of growths.
Classification
Experts distinguish 3 stages of the disease . An accurate diagnosis is established after examining the patient by a vertebrologist and conducting appropriate diagnostics.
- At stage 1 there is practically no pain . Some patients may experience aching sensations in the neck area, which have little effect on the quality of life. At this time, degenerative-dystrophic changes begin.
- If the patient did not monitor the condition of the spine and missed the moment when cervical spondylosis just began to develop, or he was not prescribed suitable treatment, then the disease goes into the second stage. The resulting processes begin to increase, they grow towards each other . With exertion and hypothermia, the pain intensifies. The second stage can last several years, and the patient periodically experiences exacerbations.
- As the disease progresses, osteophytes begin to fuse with each other . Bone arches are formed. At the third stage, the muscles are constantly under great tension, and the neck can become completely immobilized. Some patients even partially lose control of their limbs.
The exact stage is determined after an X-ray examination.
Prevalence and significance
Most people over 50 years of age are diagnosed with spondylosis . For some, by the age of 55, the first signs of deformation only appear, for others, bone arches are already forming. Therefore, doctors recommend regularly examining the condition of the spine, because this will avoid many problems. The seriousness of cervical spondylosis cannot be underestimated, because this disease in its advanced form leads to negative consequences. In patients, the blood supply to the spinal column deteriorates, arteries and nerve endings are compressed.
Video: “Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine”
Anatomical structure of the spinal column
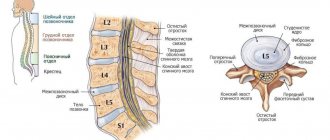
The spine is a part of the skeletal system of the human body, consisting of vertebrae connected to each other by a large number of ligaments and cartilage. The dimensions, as well as a number of individual characteristics of the structural elements of the skeleton of the human body are determined by the department in which they are located. So, they distinguish:
- cervical
– 7 cervical vertebrae of relatively small size with openings in the transverse processes through which a channel for blood vessels (arteries and veins) runs;
- chest
– 12 vertebrae of relatively large size, increasing towards the bottom. On the transverse processes there are depressions into which the heads of the ribs enter, which makes it possible to limit the area of the chest of the human body;
- lumbar
– 5 massive vertebrae with a relatively small arch;
- sacral
– 5 vertebrae, which over time transform into a single bone (sacrum).
The key function of the spine is to support and protect the human body. However, in addition, there are also such functions as:
- supporting;
- protective;
- depreciation;
- motor.
Transformations of the structure of the spine during the natural maturation of the body
The spine of a newborn and an adult differs somewhat in a number of features, the most striking among which is the degree of flexibility (in infancy it has excessive flexibility, which does not allow one to maintain posture). In addition, as a person grows older (from birth to 25 years), the spine undergoes a number of consistent changes:
- the first stage (up to 7 years) - during this period, intensive growth is observed, which contributes to an increase in the volume and weight of the vertebral body and connective tissues. There is a gradual replacement of cartilage with bone, the arches fuse with the body and the natural curves of the musculoskeletal system are formed;
- second stage (7-15 years) – the mass of the vertebrae continues to increase, ossification nuclei are formed in their body, which arise in the thickness of the vertebral growth zone;
- the third stage (15-25 years) – thorough formation of the ossification nucleus, which leads to deterioration of flexibility and limited range of movements. The length of the spinal column gradually decreases, and flexibility and elasticity are significantly reduced.
Risk factors, causes
Spondylosis develops in older people . The main risk factor is age-related changes in the spine, as a result of the progression of which flexibility is lost and osteophytes begin to form.
The causes of cervical spondylosis include:
- general wear and tear of the body;
- flat feet;
- spinal overload (observed during prolonged sitting);
- traumatic lesions;
- osteochondrosis;
- inflammation of the joints between the vertebrae (arthritis);
- regular hypothermia;
- violation of metabolic processes, in which the process of supply of nutrients to organs and tissues is disrupted.
Since osetophytes grow due to overload of the back, pay attention to what loads the spine experiences in different body positions
Sometimes cervical spondylosis occurs at a younger age in patients who are diagnosed with instability of the cervical vertebrae.
Preventive measures
Treatment of spondylosis of the thoracic spine is not considered complete until the patient has undergone prevention or correction. Spondylosis is a complex disease that can return at any time if it is not completely treated in a timely manner. Any element of the thoracic spinal column can become deformed at the most inopportune time.
First of all, the entire therapeutic course must be completed, down to the last pill or procedure. During the time that the doctor has determined for treatment, the injury that caused spondylosis must be eliminated. But no one bothers you to take certain preventive measures during and after therapy.
Here are some recommendations:
- Adjust your diet. With age, consumption of junk food can become a “starter” for the development of spondylosis. This is especially true for salty foods, because salt accumulates in joints and cartilage, dehydrating them and making them more fragile.
- Get yourself in good physical shape. If you are overweight, it is advisable to get rid of it, because obesity creates additional stress not only on the spinal column, but also on the entire body.
- Continue physical exercise. If you keep the back muscles in the appropriate condition, they will act as a “support” for the spine and will not allow it to collapse prematurely.
For several months after completion of treatment, you need to continue monitoring with a specialist. If changes are noticed, it is advisable to correct them immediately so that a minor problem does not turn into full-fledged spondylosis. Accordingly, you need to avoid physical activity, strength exercises and follow your doctor’s recommendations.
Consequences
If left untreated, spondylosis can lead to the following problems::
- formation of intervertebral hernias;
- neurological disorders (pain in various areas, numbness of the limbs, malfunction of internal organs);
- vascular problems;
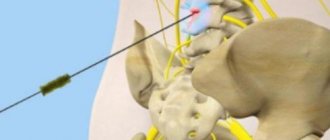
- pinching of nerves and blood vessels.
Osteophytes can put pressure on the roots of nerve endings or compress blood vessels. The patient experiences severe pain, dizziness, blurred vision, and pressure surges. Patients often complain of noise and ringing in the ears. Some even lose control of their limbs.
In the third stage, patients may experience pinching of the spinal column . This leads to spasms in the limbs and difficulty walking. Some complain of urinary problems. Bladder control becomes more difficult.
General information
As the body ages, the structures of the spine wear out. Joints, ligaments, and intervertebral discs are especially susceptible to negative changes. All changes that occur in the spinal column are purely individual and depend on many factors.
For some people, this disease is not age-related; its development can be triggered by other reasons. The symptoms of the disease are also highly individual. In some people, the clinical manifestations of degenerative changes are more pronounced, in others they are moderate. Also, the appearance of pain is directly influenced by the location of the pathology, its effect on the spinal cord or spinal roots.
Spondylosis deformans can develop in all parts of the spinal column. And the symptoms are determined by the localization of the pathological process. Doctors often diagnose osteoarthritis or osteoarthritis.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Patients who are subsequently diagnosed with cervical spondylosis come to doctors with such complaints:
- persistent headaches of varying intensity, localized mainly in the occipital region;
- feeling of weakness;
- noise and ringing in the ears;
- numbness of the limbs, feeling of “pins and needles”;
- frequent pressure changes;
- blurred vision;
- neck stiffness, decreased mobility;
- crunch in the cervical spine.
To establish a diagnosis, a neurological and physical examination is necessary. Particular importance is given to collecting the patient's medical history. But the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after performing hardware diagnostics.
Pay attention to the methods for diagnosing spondylosis. Spondylosis can be detected using the following methods:
- X-ray: X-ray will show bone processes along the edges of the cervical vertebrae;
- myelography: it is performed to assess the condition of the spinal canal;
- computed tomography, which provides a three-dimensional image;
- electromyelography: the study makes it possible to assess the condition of nerve endings;
- magnetic resonance imaging: the diagnostic method is considered the most informative; it allows you to see the vertebrae and intervertebral discs layer by layer.
Treatment tactics are selected depending on the established stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
Lumbar spondylosis
Lumbar spondylosis most often affects the sacral vertebrae, which indicates the need to use a more precise formulation of the diagnosis - sacrolumbar spondylosis.
Symptoms of lumbar spondylosis
The following symptoms are usually identified as manifestations of a disease localized in the sacrolumbar region:
- pain of varying intensity
– unpleasant sensations are concentrated in the lumbosacral region, but can also affect the coccygeal region;
- feeling of stiffness in the lower back
– significantly limits the mobility of the spinal column, which negatively affects the patient’s quality of life;
- partial or complete loss of sensation
– a symptom of this kind occurs due to compression (squeezing) of nerve fibers and manifests itself in numbness, tingling or even a local decrease in temperature;
- lameness
– pain while walking, forcing you to stop for short breaks, accompanied by pain in the calf muscles and a feeling of weakness.
Treatment of lumbar spondylosis
It is implemented using an integrated approach, including various types of physiotherapeutic procedures, attending massage sessions, taking medications, as well as interaction with a chiropractor and following the general recommendations of the treating specialist.
Treatment
Did you know that...
Next fact
There is no single method for treating cervical spondylosis . The tactics of therapy are determined in each case individually: the doctor takes into account the patient’s condition, the degree of damage to the vertebrae, and the size of osteophytes. Treatment is aimed at reducing pain and preventing progression of the disease.
But the patient must be committed to long-term therapy ; it is impossible to quickly get rid of spondylosis and instantly minimize the manifestations of this disease.
Drugs
Drug therapy is prescribed if necessary to relieve acute pain. Doctors recommend medications to patients that are designed to relieve inflammation and minimize pain.
The most commonly prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Diclofenac;
- Ibuprofen;
- Movalis;
- Amidopyrine;
- Celecoxib;
- Voltaren.
But they cannot eliminate cervical spondylosis itself and stop its progression, so limiting yourself to just taking pills will not work. Even while taking NSAIDs, pathological osteosynthesis does not stop : bone tissue continues to form.
Surgery
If there is no effect from conservative therapy for 2-3 months, surgery is recommended. But surgical treatment is resorted to in extreme cases.
It is recommended when:
- persistence of pain for a long time that cannot be stopped;
- the appearance of instability of the spinal column, increasing the risk of injury to the spinal cord and its roots;
- the appearance of herniated intervertebral discs;
- compression of the spinal cord, in which characteristic symptoms appear: the functioning of the bladder and intestinal sphincter is disrupted, paralysis and paresis of the limbs occur.
The operation is prescribed to eliminate pinched nerve roots and stabilize the spinal column . The type of surgical intervention is determined by the doctor depending on the degree of spondylosis, the patient’s condition and his age.
Video: “3 myths in spine treatment”
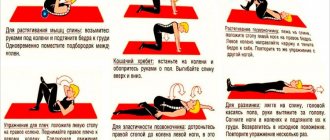
Exercises, exercise therapy, massage
When cervical spondylosis is detected, therapeutic exercises are necessarily prescribed . It must be carried out under the mandatory supervision of a physiotherapist. After the patient understands the tactics of physical therapy, he can continue performing the therapeutic set of exercises independently at home.
For spondylosis, massage of the collar area will be effective. It is important to perform all exercises carefully and smoothly . Overloads must be avoided. With regular exercise, it is possible to normalize blood flow in the cervical spine and increase muscle tone. Thanks to this, the physiological mobility of the spine is maintained normally.
Good results for spondylosis can be achieved using manual therapy . But this technique only relieves pain, reducing discomfort, it helps reduce the intensity of compression of the nerve roots. It is impossible to stop the process of bone tissue growth with its help.
A regular massage of the collar area helps normalize blood circulation . Thanks to this, the flow of blood and nutrients to the affected area is restored.
Treatment at home
Each patient can do exercises daily aimed at improving blood circulation in the cervical spine. But a physiotherapist should select them.
At home, patients can do self-massage daily with moderate intensity . Standard massage techniques are used: rubbing, stroking, kneading.
In addition to exercises and massage, warm compresses and rubbing have worked well for spondylosis. It is also useful to take relaxing baths.
HOW SPINAL DEFORMATIVE SPONDILOSIS APPEARS
It is believed that the spine begins to age after 20 years. The nutrition of tissues deteriorates, including the cartilaginous tissues of the vertebrae, designed to protect bones during movement. Posture worsens - the vertebrae are displaced and this leads to an increase in the load on them when moving. Even mild, minor injuries and micro-bruises destabilize the spinal column. Added to the negative factors are bad habits, excess weight, weak muscles, systemic diseases, and even unsuccessfully placed fillings and flat feet.
Spondylosis develops as a response to increased stress, aging and wear of the vertebrae. To increase the area of worn vertebrae, the spine “grows” osteophytes. These bone growths serve a good purpose:
- compensate for uneven load caused by spinal curvature;
- limit mobility, which means reducing the risk of injury and strain.
The other side of the coin is the narrowing of the intervertebral lumen and deterioration of blood flow. The situation is aggravated by calcification of the canal, pinching and injury of the nerve root by sharp thorns. Ultimately, fusion and blockade of mobility.
Prevention
Treatment of cervical spondylosis is a long and complex process . It is easier to prevent a disease than to figure out in the future how to normalize the condition.
Basic methods of prevention:
- use of orthopedic mattresses for sleep and rest;
- yoga classes;
- swimming;
- maintaining correct posture.
It is important to walk more, while keeping your back and head straight. People working at a computer should warm up their neck and shoulders at least once every 1-2 hours: make circular movements with their shoulders, tilt their heads in different directions.
Benefits of MBST Therapy
Among the methods that can be considered revolutionary, MBST therapy (nuclear magnetic resonance therapy) stands out. Its peculiarity and at the same time its advantages lie in its effect on the patient’s cells, which begin to regenerate and renew themselves.
The technique has been refined and is used for the treatment of spondylosis of the thoracic spine, even in chronic degenerative diseases of the joints or intervertebral discs. Today, nuclear magnetic resonance therapy is the only way to influence the patient’s cells.
The result of the procedure is the easing of pain, a decrease in symptomatic manifestations, and the healing of crushed or deformed bones. Meniscal rupture, injuries received as a result of vigorous physical or sports activity, intervertebral disc protrusion - all this can be cured using MBST therapy.
Why is MBST therapy so popular and in demand among patients? The methodology involves treating the spine without the intervention of surgeons. There is no risk for the patient, and the therapy has no side effects or complications.