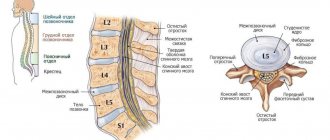
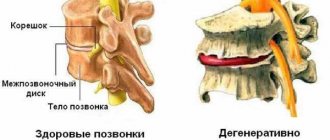
Probable causes
Among the probable causes of the pathology, it is customary to highlight:
- increased or insufficient load on the muscles due to non-physiological factors;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- suffered injuries, in particular not only acute, but also chronic microtrauma received in the process of playing sports;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- genetic predisposition to pathological processes occurring in bone and cartilage tissue;
- poor posture;
- lack of physical activity;
- features of human professional activity.
It is worth noting that uneven distribution of load along the spinal column can cause a deterioration in the quality of blood supply to the intervertebral discs, which sooner or later leads to their degeneration and final destruction.
Risk factors
Lifestyle factors that affect overall health can affect intervertebral discs. Risk factors for degenerative disc disease (osteochondrosis) include:
- Family history of back pain or musculoskeletal disorders
- Excessive stress on the lower back due to sports or the nature of work
- Prolonged static loads on the discs due to prolonged sitting and/or poor posture
- Lack of disc support due to weak back muscles
- Obesity
- Smoking or any form of nicotine consumption
Disc degeneration is part of the aging body, but not all people develop pain or any specific symptoms. Symptoms tend to occur when there is instability, muscle tension, and possibly nerve root irritation.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Considering the clinical picture of lumbosacral osteochondrosis, one can trace certain symptoms characteristic of this type of pathology.
The main symptom of lumbar osteochondrosis is pain of varying intensity, often aching in nature, but sharp pain can also occur. Symptoms manifest themselves in static conditions and are especially noticeable in the morning, after rest.
The variability in the nature of pain is due to different mechanisms of its occurrence. Pain can be caused by poor circulation in tissues, swelling of muscles and ligaments, as well as compression of nerve roots.
Clinical practice involves identifying a set of symptoms that accompany lumbar osteochondrosis.
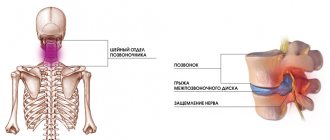
Symptoms characteristic of vertebral syndrome
Vertebral syndrome is a complex of pathological conditions caused by various disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Characteristic features are:
- in particular, flattening or deepening of the curves of the lumbar region;
- decreased mobility of the location of the disease, impaired muscle tone;
- pain of varying intensity when performing movements that require the use of the lumbar region;
- increased lumbar sensitivity.
Symptoms characteristic of extraverbal syndrome
Extraverbal syndrome is divided into two groups:
- reflex - syndromes, the manifestation is associated with irritability of nerve endings, caused by compression of the spinal nerves, provoking swelling of nearby tissues, spasms and the onset of the inflammatory process. Accompanied by intense pain, which can be acute, sharp or prolonged, as well as paresthesia (sensitivity disorder, burning/tingling).
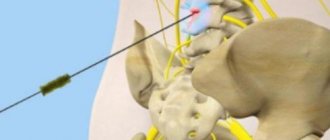
- compression syndromes - caused by compression of tissues in the condition of destruction of vertebral bodies, as well as the formation of herniated intervertebral discs. They are determined by systematic fatigue of the lower extremities and disruption of the usual gait.
Forecast
The chance of a complete recovery in the presence of lumbosacral osteochondrosis is very favorable . Competent therapy relieves pain and relieves inflammation if treatment is started at the initial stage of the disease.
It’s another matter when a patient is irresponsible about his health. This will certainly lead to complications that will significantly worsen the prognosis. Without treatment, there is a threat not only to loss of ability to work, but also to the life of the patient. But with timely consultation with a doctor, the disease is successfully treated, and the person gets rid of this problem forever.
Degree of development of lumbar osteochondrosis
The extent of damage to the intervertebral discs allows us to determine the degree of clinical development of the pathology:
- 1st degree – a characteristic manifestation is a decrease in the elasticity of the intervertebral discs. When performing sufficiently sudden movements, cracks may appear in the annulus fibrosus, the formation of which is accompanied by sharp pain. With osteochondrosis of the lumbar region of the 1st degree, a spasm of the muscular frame surrounding the lumbar location of the disease can be traced;
- 2nd degree – loss of stability at the site of pathology, formation of protrusions (swellings) of the intervertebral disc. Increased chronic pain in the lower back and lower extremities. Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region of the 2nd degree is often accompanied by paresthesia, swelling and fatigue in the lower extremities;
- 3rd degree – the beginning of the manifestation of intervertebral hernias. It is expressed in pain from a pinched nerve root, numbness of the lower extremities. In rare cases, “distant” symptoms may occur, namely diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys.
- Grade 4 – the properties of the intervertebral disc are completely lost. The vertebral bodies come closer together and, as a result, their destruction occurs. Compression syndrome is observed. “Remote” symptoms become persistent.
Diagnostic features
Only a specialist can make a diagnosis after a thorough examination.
It is important to remember that the symptoms of a degenerative-dystrophic disease are nonspecific, which implies the need to consult a doctor who can rule out the presence of other ailments, in particular various neoplasms that can provoke similar symptoms.
In order to determine the localization of the pathology, an x-ray examination is prescribed. Clarification and confirmation of the presumptive diagnosis is carried out using magnetic resonance imaging, which provides high-quality images of each layer of the spinal column.
A wide range of nonspecific symptoms often leads to a false diagnosis and, as a consequence, incorrect treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis. Based on this, we can come to the conclusion that it is important to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis by visiting different specialists, including: vertebrologist, neurologist, nephrourologist, gastroenterologist and surgeon.
Non-drug methods for treating lumbar osteochondrosis
Destructive processes in lumbar osteochondrosis occur to a greater extent in the cartilaginous tissues of the intervertebral discs. Due to the peculiarities of the clinical picture, complete regeneration of destroyed tissues is impossible, and therefore it is important to begin treatment in a timely manner, namely, from the moment the first moderate pain in the lumbar region appears.
With a timely diagnosis and the development of a competent treatment regimen, pathological processes can be significantly slowed down or stopped altogether.
Before embarking on non-drug treatments, it is important to consult with a specialist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out in order to eliminate pain and improve blood circulation in tissues, eliminate the inflammatory process. Among the most popular methods of physiotherapy are:
- electrophoresis (exposure to direct electric current in combination with the administration of various drugs);
- diadynamic therapy (exposure to currents of varying intensity);
- ultrasound therapy (exposure to ultrasound along the affected part of the spine);
- magnetotherapy (exposure to an alternating magnetic field).
Massage
The most common and one of the most beloved methods of prevention and treatment. Not applicable during the acute phase.
The massage should be performed by a specialist with a medical education who knows the specifics of the pathological process and is proficient in therapeutic massage techniques.
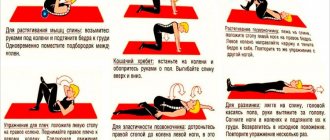
Exercise therapy
Physical therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is the most important component of treatment.
The type of gymnastics and exercises for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine are determined strictly on an individual basis, taking into account the characteristics of the body and help eliminate spasms, strengthen the muscle frame, and stimulate blood circulation.
Exercise therapy for lumbar osteochondrosis is an important component of treatment, because exercise has a beneficial effect, stimulating blood circulation and normalizing the functioning of all body systems.
Characteristics of the disease
Osteochondrosis of this department is characterized by the fact that the pathological process causes dystrophic and degenerative changes in the structure of the intervertebral discs. As a result, the disease provokes the occurrence of hernias and pinching, which is accompanied by severe pain and can even lead to disability. Sometimes it happens that osteochondrosis in the lumbosacral spine is polysegmental in nature. This means that several parts of the spine are affected, rather than just one. This disease is detected in almost 80% of people who complain to a neurologist
for pain in the back. As a rule, most patients are over 35 years of age. But the disease is “getting younger”, which is associated with the unhealthy lifestyle of the younger generation. Many people spend a lot of time sitting in front of computers.
Drug treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis with medications is best started from the appearance of the first symptoms, after confirmation of the diagnosis by the attending physician.
Depending on the degree of lumbar osteochondrosis, different groups of drugs can be used. So, to relieve swelling in the tissues surrounding the lesion, diuretics are used, and antispasmodics are used to eliminate muscle spasms.
It is worth noting that self-medication can aggravate the situation and lead to negative consequences, and therefore only the attending physician should prescribe medications.
Gels and ointments for osteochondrosis
May have an analgesic or warming effect. The composition often uses components that have a cooling or warming effect (menthol, snake venom), which helps eliminate muscle spasms and significantly alleviate pain.
The most prescribed are:
- Nise;
- Capsicam;
- Voltaren.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for lumbar osteochondrosis
They are used to eliminate pain in the primary stages of pathology development. NSAIDs are available as ointments, gels or injections.
In case of intense pain, the attending physician may prescribe a novocaine blockade, which allows pain relief for a long time.
Among the most effective NSAIDs are:
- Artradol;
- Aertal
Chondroprotectors
The primary stages of the development of the disease, due to the peculiarities of the progression of the pathology, require pathogenetic treatment, in particular the normalization of metabolic processes occurring in cartilage tissue. Chondroprotectors come to help in solving this issue.
The key direction of action of the drugs is the normalization of the structural and functional state of cartilage tissue.
Some of the most effective are:
- Artakam;
- Don;
- Alflutop.
Glucocorticosteroid drugs
Prescribed for progressive lumbar osteochondrosis, in case of insufficiency of treatment with chondroprotectors and NSAIDs.
Active substances contribute to the effective elimination of inflammatory syndrome.
Among the most effective and frequently used is the drug Flosteron.
Surgical intervention
A radical method of treating the disease, used only in severe cases.
During surgery, the doctor eliminates the cause of pain and stabilizes the spine.
Nutritional Features
In order to prevent and treat pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, a balanced diet is an important component.
The diet for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine involves a varied, low-calorie diet, enriched with vitamins and essential microelements.
Proper nutrition for degenerative-dystrophic diseases prevents further development of the disease. It is important to come to a diet that will not become a one-time event, but will develop into a way of life.
Main goals of the diet
Planning a healthy diet should primarily be driven by goals such as:
- maintaining optimal body weight;
- saturating the body with all necessary substances;
- eliminating the possibility of dehydration;
- preventing the progression of pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Basic nutrition rules
A menu developed for feeding people with osteochondrosis should be formed taking into account the following rules:
- daily calorie intake should not exceed energy expenditure;
- The frequency of meals is determined individually. The interval between each of them should not exceed 4 hours;
- food products must be enriched with vitamins and beneficial elements;
- proteins, fats and carbohydrates must be present;
- limiting fast sugars, animal fats and synthesized oils;
- compliance with the drinking regime.
By adhering to the basic rules of nutrition, it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathology, but there is a possibility of progression of the disease.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
The patient may be prescribed a special diet that will improve metabolic processes and help saturate the body with vitamins, nutrients and minerals. For osteochondrosis, it is recommended to eat in small portions, about 5-6 times a day. The diet of those suffering from osteochondrosis should include fermented milk and dairy products, lean meat, fish and poultry, as well as jellied meat, olive oil and jellied dishes.
You should limit your intake of flour and confectionery products, and also eat less salty and sweet foods. During the day, it is important to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid: preferably water. You should drink less strong tea, coffee, carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
Measures to prevent lumbar osteochondrosis
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a serious chronic disease that significantly reduces a person’s quality of life. Timely treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis allows you to slow down the course of pathological processes and avoid radical measures and the development of dangerous complications.
The best treatment for lumbar osteochondrosis is its prevention. In order to prevent degenerative-dystrophic processes, it is important:
- determine and maintain a moderate schedule of physical activity;
- take systematic breaks from work (5-7 minutes per hour);
- sleep only on a flat surface or an orthopedic mattress;
- wear suitable shoes;
- Healthy food;
- to refuse from bad habits.
Remember that a healthy body is an integral component of a full life for every person. Prevention and timely treatment of many diseases ensure the elimination of the disease and improve the quality of life.