Causes
Depending on the cause of occurrence, traumatic and pathological fractures are distinguished. The cause of traumatic bone fractures is a sharp, sudden action of a mechanical shock force on the bone. Pathological fractures appear when a certain pathological process affects bone tissue. This may be the result of a cyst or the development of a malignant tumor. In this case, the structure of the bone tissue is gradually destroyed and even small loads can lead to a fracture. With the second type, the risk of fracture increases several times. It even gets to the point where a person can also break a leg while walking. Here the reason is that this is a pathology of the bone itself, and not an external influence on it.
What is a fracture: causes and types
Bones are susceptible to a variety of injuries, but not all of them are fractures. This concept refers to a violation of the integrity of the bone, which occurs due to external strong mechanical influence. If the force of the impact exceeds the strength of the bone, a fracture will inevitably occur.
In practice, there are several types of fractures:
- congenital - occur during intrauterine development of the fetus, against the background of pathologies of bone skeleton growth, as well as during childbirth (if additional force is used);
- acquired - arise during life, from falls, impacts, etc.;
- traumatic - against the background of injury;
- pathological - occur against the background of various pathologies, including syphilis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis and other diseases.
The main factors leading to fractures are compression, impacts, lifting weights, twisting and turning, as well as twisting and falling from a height.
There is another classification of fractures:
- open – with skin damage;
- closed - without them.
It is quite obvious that the former are more dangerous; they are associated with damage to soft tissue and may be accompanied by bleeding, mixing of bone fragments, infection and other complications.
Fractures are also divided into 2 types:
- Epiphyseal - the most severe, they lead to confusion of the joint surface and dislocation. A type of epiphyseal fractures are intra-articular fractures, when they affect only the joint capsule itself.
- Metaphyseal – fixed by the common connection of two fragments.
Symptoms
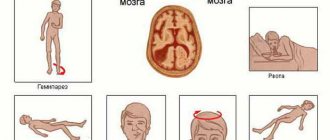
Bone fractures have characteristic symptoms that make it possible to identify pathology when it occurs, which is very important to exclude complications. The following main relative signs of a fracture can be distinguished: - Pain syndrome: sharp pain when a bone ruptures and aching pain in the future, which intensifies with longitudinal load or its imitation. - Swelling: Swelling in the affected area develops gradually. — Hematoma: of different sizes on the affected area; in this case, a hematoma with pulsation indicates continued bleeding. The absolute sign of a fracture occurs as a result of direct destruction of the bone and indicates the completion of the process. These signs of a fracture are: - A characteristic crunch (crepitus): occurs when bone tissue ruptures, and is subsequently audible with a phonendoscope due to the friction of the fragments. — Unnatural direction of a limb or other bone. — Increased mobility in case of joint rupture. — Bone fragments are visible visually during an open fracture. - Shortening of the limb when fragments are displaced, protrusion of the broken bone. Some signs of a fracture without displacement or an incomplete fracture may not appear, which will complicate the diagnosis. The symptoms of a fracture are clearly determined by radiography - the location, type and degree of destruction are recorded.
Signs of a fracture
A fracture can be diagnosed based on a number of signs:
- sharp, severe pain in the corresponding area;
- swelling of the tissue;
- swelling;
- clearly visible deformation of the damaged area;
- limited body movements or inability to do so;
- forced adoption of a certain posture to overcome severe pain;
- shortening of limbs;
- pain when tapping;
- sounds of bone fragments crunching under the surface of the skin.
Diagnostics
For most closed fractures, X-ray diagnosis plays a leading role. This study is necessary not only to confirm the diagnosis of the fracture and document it. It is very important for the traumatologist, based on radiographs, to get an idea of the nature of the displacement of the fragments, the direction of the fracture lines and the presence of additional cracks indicating splitting of the fragment. This information is needed to determine treatment tactics and select the type of osteosynthesis. X-ray examination is also important during the treatment process. It determines the completeness of reposition, the correct position of the fixing structure, the absence of secondary displacement (as swelling subsides), the appearance and formation of callus. The surgeon and traumatologist must follow the rules for taking radiographs for fractures.
Treatment of fractures at the MedikCity clinic
If you need emergency and professional help, then contact the paid emergency room of the MedicCity clinic!
We work every day from 9.00 to 21.00. X-rays work for you in the same mode, and we perform MRIs around the clock!
Experienced traumatologists use in their work all the advanced methods of treating fractures, as well as modern, high-quality materials, in particular plastic plaster, which is lightweight, does not deform from water and is comfortable to wear.
Types of modern plastic plaster
One of the easiest is Scotchcast . The patient practically does not feel its weight, and the body breathes in it. Scotch tapes are available in various colors, which slightly “brightens up” not the easiest period in a person’s life. Among the disadvantages, it can be noted that the plaster cannot be exposed to water (it is put on with a special cotton-rag stocking, which serves as a layer between the rough material and the skin), and it can only be removed with the help of a specialist.
Softcast is a bandage made of a very flexible, elastic material, which allows it to be used for sprains and sprains. In cases of fractures, the bandage is worn together with adhesive tape. This plaster is made from fiberglass fabric impregnated with polyurethane resin and is therefore water resistant. In this case, the cast ensures the flow of air to the injured limb.
HM-cast is a synthetic mesh with large cells, made in the shape of a sleeve. It is very light, but you only need to wear it with a special synthetic stocking. This product can be used for water procedures; it is very light in weight and is available in various sizes, which makes it convenient for treating limb fractures of different locations. This cast allows X-ray penetration, allowing specialists to monitor bone healing without removing the cast.
Turbocast is the most common plastic gypsum with high strength. A cotton stocking is not worn under this cast, so you can take water procedures in the turbocast. Another plus is that this material has a working memory, so it can be heated and used repeatedly. A turbocast plaster cast looks aesthetically pleasing and is easy to use (it can be hygienically treated with a soap solution).
In our clinic you can replace the uncomfortable old plaster cast with a modern lightweight turbocast bandage. Follow our promotions! Very often there is a discount on the plaster replacement procedure.
If necessary, the doctor will quickly and professionally install an orthosis for you and remove the Ilizarov apparatus. If you need to remove an Ilizarov apparatus, you can find out the cost of the service by phone.
Treatment
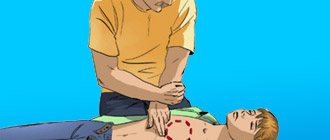
The main objectives of treating a victim with a fracture are saving his life and preserving the limb, restoring the integrity of the bone and the anatomical shape of the joint, the function of the damaged limb and the working capacity of the victim. First aid is aimed at preventing displacement of bone fragments, damage to soft tissues, wound infection, the development of traumatic shock and massive blood loss. Necessary actions: immobilize the damaged area of the skeleton using a splint that captures the joints above and below the site of injury. Stop the bleeding with a tourniquet and apply a sterile bandage to the wound. Give an anesthetic: analgin or promedol. Transport the victim to the emergency room. In case of multiple fractures and spinal injuries, it is not recommended to move the patient until the ambulance arrives. Conservative treatment consists of immobilization and the use of plaster casts after closed reduction of the fracture or without it (if there is no displacement). When applying plaster, the limb must be in the physiologically correct position. Its distal parts (for example, fingers in case of a fractured limb) must be open to be able to determine swelling and prevent disruption of tissue trophism. Sometimes traction is necessary for a fracture—the use of skeletal, cuff, adhesive, or adhesive traction. This method helps to neutralize the action of muscle layers that are attached to bone fragments, prevent their displacement and create conditions for bone tissue regeneration. Skeletal traction gives the greatest effect. A weight attached to a wire that is passed through the bone ensures that the bone fragments are maintained in a position that is optimal for tissue restoration. The disadvantage is the forced immobilization of the patient, leading to a deterioration in his general condition. For cracks in long bones and fractures of small bones, functional methods are used. They involve the absence of immobilization or minimal immobilization of the damaged area and are reduced to providing it with rest. Surgical treatment is necessary for jaw fractures (installation of an external fixation device), restoration of spongy bones (cranial vault), excessive formation of callus, etc. In the postoperative period, the fracture site is immobilized. Recovery time ranges from several weeks to several months. If bone restoration does not occur and a false joint is formed (persistent abnormal mobility at the fracture site), endoprosthetics methods are used (replacement of elements of the musculoskeletal system with implants). After the cast is removed, rehabilitation therapy begins. This is, first of all, a massage. Prescribed 10-45 days after the fracture. It accelerates the process of callus formation, improves blood circulation and tissue nutrition, and prevents muscle atrophy. CRM therapy is a passive development of joints (without the participation of muscles) using a specially tuned mechanical device. Physiotherapy. In the first 10 days, exercises are done for intact joints and limbs. They prevent muscle weakness and joint stiffness. After removing the cast, exercise therapy helps restore the mobility of damaged joints and muscle strength. It is recommended to increase the load gradually, completing rehabilitation with active gymnastics, which helps neutralize the consequences of the fracture.
How to distinguish a fracture from a dislocation
A fracture is a break in the integrity of the bone, while a dislocation is a rupture of the joint capsule and ligaments. This can lead, for example, to sprains. In this case, movements are completely blocked. At the same time, during a fracture, the damaged bones are quite mobile and therefore require immediate immobilization.
If a dislocation occurs, severe pain is felt in the joint, it swells, and a change in shape and unevenness of the surface are visually noticeable. Moreover, during a dislocation, the length of the limb and its shape never change, but the joints themselves are displaced. If a fracture occurs, the length of the bone, on the contrary, may change.
First aid for a closed fracture
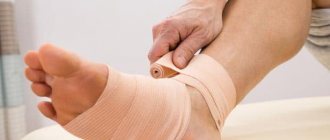
When providing first aid for a closed fracture, you should immediately contact an ambulance. After this, it is necessary to immobilize the broken limb and, if possible, apply ice or a cold object to the injury site. The person may be given a painkiller. When transporting independently, a splint is applied using available items: board, stick, ski, etc.
In the absence of available means, the injured limb is bandaged to the uninjured one. During transportation, the victim must lie down - the broken limb should be slightly raised.