Hemoglobin level is an important indicator of a man’s health, and its decrease is a good reason to see a doctor. After all, this protein performs a number of vital functions, including ensuring tissue respiration. Therefore, when its concentration in the blood decreases, changes in well-being of varying degrees occur, and in severe cases, low hemoglobin can cause the development of serious complications.
What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a complex protein containing iron. Its main task is to add oxygen diffusing into the blood from the lungs and distribute it throughout the body. Giving oxygen to cells, hemoglobin attaches carbon dioxide formed by them in the process of vital activity. Then getting through the bloodstream to the lungs, it gives it away, again making room for oxygen. This is how gas exchange and tissue respiration occur. But, in addition, hemoglobin is involved in maintaining the acid-base balance, in DNA synthesis, and in the occurrence of a number of redox reactions.
To synthesize hemoglobin, the body uses iron, which comes from food and accumulates in the form of ferritin in the liver, lungs, and spleen. There is also a small amount of iron present in the intestinal mucosa. If the diet does not meet the body's iron needs, ferritin is activated. This helps maintain normal hemoglobin levels and organ function. But with prolonged deficiency, its reserves are depleted, and the concentration of hemoglobin decreases.
In men, critically low hemoglobin levels are rare, since they, unlike women, do not experience regular physiological bleeding. For the same reason, the increase in hemoglobin in men occurs faster and more effectively. But if left untreated, there is a serious risk of complications, especially if you have bad habits:
- thrombosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- decreased immunity;
- deterioration of cognitive functions (memory, attention);
- hypoxic coma.
Often, when low hemoglobin persists for a long time, the presence of chronic fatigue syndrome is observed.
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin levels
The main reasons for a decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood in men are:
- reduction in the amount of iron entering the body;
- disturbances in the absorption and transport of iron throughout the body;
- a decrease in the number of red blood cells as a result of a violation of their production by the bone marrow or a shortening of life due to various circumstances.
In this case, most often a decrease in hemoglobin is due to iron deficiency in the body. The fact is that the absorption of this microelement from food is limited. Even with proper nutrition, no more than 1-1.5 mg can be absorbed per day, and if there are errors in the diet, the amount of iron entering the body cannot cover the need for it. In such cases, iron depots in the form of ferritin are used to maintain normal life functions. But its reserves are limited, and therefore, when they are depleted, the intensity of bone marrow erythropoiesis decreases. As a result, the number of red blood cells, as well as the level of hemoglobin, decrease, which indicates the development of anemia and is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
Thus, the causes of low hemoglobin in men can be:
- malnutrition;
- insufficient consumption of foods that are sources of iron:
- adherence to a vegetarian diet;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- severe bleeding during injuries, operations, including hidden ones (observed with peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, kidney pathologies, pulmonary siderosis, etc.);
- haemorrhoids;
- malignant tumors;
- chronic intoxication;
- vasculitis;
- systemic scleroderma;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- helminthiasis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
Statistics show that men are more likely than women to have gastrointestinal diseases caused by Helicobacter pillory, which leads to impaired absorption of iron in the intestines and a decrease in hemoglobin.
What is dangerous about increased hemoglobin in men?
Excess Hb leads to thickening of the blood due to the large number of red blood cells. Which, as a result, causes a deterioration in the blood supply to all cells and tissues. The nervous system, brain and cardiovascular system are primarily affected.
It was noted that there was a gradual increase in the size of the kidneys, spleen and liver. The risk of blood clots forming in blood vessels increases significantly, which can break off at any time and lead to death.
A combined disruption of the functioning of several internal organs leads to the fact that the body’s compensatory systems cannot cope. If a man does not attempt to lower hemoglobin for a long time, this can result in serious health problems, even death.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms largely depends on the level of hemoglobin: the lower it is, the more severe the anemia. Therefore, in mild cases, men may not notice changes in their well-being or not attach importance to them, since they are little expressed. In such situations, periodic weakness or increased fatigue may occur, but many attribute this to stress, age and other life circumstances. With a further decrease in hemoglobin, the situation becomes more complicated, the existing symptoms become more intense, and others appear.
Sometimes even a decrease in hemoglobin to 90 g/l is asymptomatic.
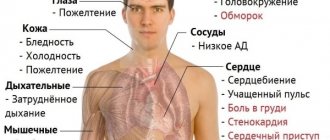
In general, a decrease in hemoglobin levels in men may appear:
- drowsiness, weakness, decreased performance;
- shortness of breath, which initially occurs due to physical exertion;
- feeling of heartbeat;
- dizziness that can lead to loss of consciousness;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- increased irritability, aggressiveness;
- headaches of varying degrees of intensity;
- decreased appetite;
- increased brittleness of nails, the appearance of white spots and bumps on them;
- perversion of taste preferences with the emergence of a desire to eat inedible food, in particular raw meat, chalk, clay;
- developing an addiction to the smells of acetone, gasoline, perfume, etc.;
- ringing in the ears, flickering of spots before the eyes.
A symptom of decreased hemoglobin that is typical for men may be impaired erectile function.
Frequently asked questions and doctor's answer
General practitioner Victoria Druzhikina answered questions
1. What is Hemoglobin indicated in a blood test?
- “In a general blood test, hemoglobin is abbreviated as Hb, measured in grams per liter.” 2. Why is low Hemoglobin dangerous?
– “Low hemoglobin levels are dangerous due to anemia and its consequences:
- oxygen starvation of organs and tissues, primarily nervous;
- muscle weakness;
- fainting due to decreased blood pressure;
- decreased immunity;
- wear and tear of the heart muscle due to the development of compensatory tachycardia in conditions of lack of oxygen;
- heart attacks;
- retardation in mental and physical development.
In severe cases, untreated anemia can lead to hypoxic coma and death due to brain or heart failure.”
3. Blood transfusion for low hemoglobin
– “To treat severe forms of anemia, blood or red blood cell transfusions are used. The procedure is indicated in 2 cases:
1. With a hemoglobin level of 70 g/l and below.
2. In case of poor tolerance to anemia and the threat of hypoxic coma at any level of hemoglobin. This can occur in people whose lives involve high oxygen consumption - pregnant women, athletes, scuba divers playing wind instruments.
The standard regimen is 2 doses (1 dose – 200 ml) twice a week. Before and after the procedure, general urine and blood tests and temperature must be monitored.
Before the manipulation, the patient’s blood type and Rh factor are determined, and donor blood is selected based on these indicators. Next, the compatibility of the blood samples is checked. If the reaction proceeds normally, a transfusion is performed. If flakes or clots form, this blood is not transfused, but other samples are tested for compatibility.” 4. Hemoglobin norm in children under one year old
– “The hemoglobin norm in children under one year of age is determined by physiological factors. By the end of the 1st month, the numbers are higher than in adults and amount to 160–200 g/l.”
5. How to increase Hemoglobin in a child?
“If anemia is detected, it is important to increase hemoglobin levels as soon as possible, especially in children. The main role in this belongs to drugs. Unfortunately, nutrition will not significantly increase the numbers. With the help of food, you can only slightly improve your performance and maintain it at this level.
Foods to increase hemoglobin in children:
- beef;
- buckwheat;
- cocoa;
- liver;
- apples;
- pomegranate;
- walnuts.
Drugs for the treatment of anemia in children:
- Maltofer;
- Ferrum Lek;
- Totema;
- Ferlatum and others"
6. How to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy?
“During pregnancy, it can be difficult for a woman to follow a diet with foods rich in iron. However, their list is quite wide, you can choose what you like:
- beef;
- wheat bran;
- hazelnuts;
- cabbage, including broccoli;
- chocolate;
- rabbit;
- liver;
- cocoa;
- apples;
- pears;
- parmesan, etc.
How to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy - the most used drugs:
- Maltofer;
- Sorbifer Durules;
- Ferrum Lek;
- Gyno-tardiferon;
- Totema;
- Ferlatum and others."
7. Iron supplements to increase hemoglobin in adults
– “To treat anemia in adults, the same drugs are used as for pregnant women. Can also be used:
- Venofer;
- Ferlatum protein;
- Cosmopher;
- vitamin complexes with iron (Ferro-Folgamma, Fenyuls, etc.).”
8. Normal Hemoglobin in Newborns? – “The hemoglobin norm varies slightly from month to month, the generally accepted average values are 120–160 g/l.
Immediately after birth, the mother’s blood circulates in the baby, so values from 180 to 240 g/l are considered normal for the 1st week of life.”
For information on hemoglobin levels, see also the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. The norms of indicators are indicated in Appendix No. 3 of Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated 09/14/2001 364 (as amended on 06/06/2008)
Rate how useful article
4.7 was. 29 people voted, average rating 4.7
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Diagnostics
If the symptoms described above appear, especially if this is accompanied by the presence of factors predisposing to a decrease in hemoglobin, you should take a general blood test and consult a physician with its results. To confirm anemia, a repeat clinical blood test is usually prescribed. This eliminates the possibility of mistakes being made in the laboratory.
If a decrease in hemoglobin levels is confirmed, treatment for anemia is immediately prescribed. And in parallel with this, a comprehensive examination of the body is carried out in order to identify the causes of its development. This is especially important in cases where there are no obvious prerequisites for this, for example, having undergone surgery in the recent past, injuries with large blood loss, etc. For this, the following may be prescribed:
- blood chemistry;
- stool test for occult blood;
- colonoscopy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys.
How to increase low hemoglobin
Even a slight decrease in hemoglobin levels requires treatment. Otherwise, the man’s well-being will progressively deteriorate. Therefore, from the moment a general blood test is performed and low hemoglobin levels are established, it is necessary to make adjustments to the daily diet and start taking iron-containing medications. It is impossible to cope with the problem only by changing the diet and increasing the amount of iron sources in the body, since at best, as much of this trace element is absorbed from food per day as is consumed. This will not allow the formation of the necessary depots and eliminate the risk of re-development of anemia in the near future.
It is imperative that in combination with the treatment of anemia, therapy for the disease that provoked its development is prescribed. Accordingly, it will be strictly specific in each individual case.
Nutrition correction
With low hemoglobin, men are advised to increase the amount of iron-rich foods in the daily menu, as well as those containing folic acid, vitamin B12 and ascorbic acid, as they increase the quality of its absorption. These include:
- beef tongue, liver;
- white chicken, turkey, veal;
- various seafood, as well as red and black caviar;
- buckwheat, rice;
- leafy greens, cabbage, broccoli, green beans, spinach;
- legumes;
- pumpkin, tomatoes, beets;
- berries, especially black currants, blueberries, cranberries;
- fruits, in particular pomegranate, persimmon, dried apricots;
- peanut.
But when drawing up a menu, it is worth taking into account the peculiarities of iron absorption. So, you should not combine meat dishes with pasta, bread and cereals. They are recommended to be consumed with vegetable side dishes. It is also necessary to consume fermented milk products and nuts separately from other meals.
Normal hemoglobin level in blood during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s amount of enzyme in her blood will differ from the values indicated in the table above. Also, pregnant women should know what medications can and cannot be taken during pregnancy. These deviations are associated with various changes that occur in the body.
Approximate indicators of enzyme content in pregnant women are shown in the table:
| Trimester | Amount of hemoglobin g/l. |
| 1 | 115 — 165 |
| 2 | 110 — 145 |
| 3 | 110 — 140 |
These differences are associated with the end of menstruation and the subsequent growth of the placenta, which requires constant nutrition. Therefore, it is important for the expectant mother to systematically undergo blood tests, since a critical decrease/increase in hemoglobin can become a source of dangerous complications (hypoxia, abnormal fetal development, early birth, underweight of the baby, retardation in mental/physical development, etc.).
Doctor's advice
Often the cause of increased hemoglobin is non-compliance with the drinking regime. The body receives little fluid (less than 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day, tea, coffee and other liquids do not count), this causes the blood to thicken. In this condition, not only hemoglobin, but other indicators also increase - hematocrit, red blood cells, platelets. Hematologists advise that if you have anemia, your diet should focus on meat. Liver and buckwheat are in second place in importance. Next are apples, nuts, cocoa. These same principles apply not only to adults, but also to children.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist