What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells. This element acts as a connecting link in metabolism, as it transports oxygen to all internal structures of the body and removes carbon dioxide from them. In addition to helping tissues “breathe,” the protein performs a pigment function, in other words, it gives the blood fluid a red tint.
Fluctuations in the required level of hemoglobin in the blood may indicate a pathological or some kind of stressful condition.
If any changes in the amount of hemoglobin are detected, patients are sent for additional studies, which help to reconstruct a complete clinical picture, and also allow one to diagnose/refute the presence of possible diseases.
Table of hemoglobin norms in the blood of women by age
Women experience many different hormonal changes throughout their lives, which are treated by an endocrinologist. They may be associated with physical overexertion, frequent stress, pregnancy, menstruation or menopause. For these reasons, enzyme concentrations may vary throughout the month and do not indicate the presence of any pathological processes in the body. In addition, depending on the age of the patient, protein levels will also vary.
Nowadays you can find a lot of information on the Internet regarding the norms of various blood parameters, including hemoglobin. The figures indicated there are far from the real situation. The medical guidelines used by doctors indicate clear ranges - the minimum and maximum of each indicator. There is "from and to" for all ages. To treat the patient and determine the further prognosis. For hemoglobin, both the upper and lower limits of normal are important
The standard hemoglobin level in women varies from 120 to 150 g/l. You can evaluate the results of the analyzes by checking the indicated values with the tabular data.
Hemoglobin norm in women - table by age:
| Woman's age | Hemoglobin norm, g/l. |
| 17 — 20 | 120 — 150 |
| 21 — 30 | 120 — 150 |
| 31 — 40 | 120 — 145 |
| 41 — 50 | 120 — 140 |
| 51 — 60 | 120 — 140 |
| 61 — 65 | 120 — 140 |
| more than 65 | 120 — 150 |
Normal hemoglobin level in women aged 30–40 years
The norm at 40 years is at its highest level, after which it gradually begins to decline. Such modifications are associated with hormonal changes in the body that begin to occur during this period. The process of minimizing the concentration of the enzyme in the blood continues throughout subsequent years. Compared to thirty-year-old women, at 40 years old the protein content decreases by 5 g/l.
Normal after 50 years
After 50 years, the norm of hemoglobin in the blood of women decreases noticeably . These modifications can be clearly seen in the table; the indicated indicators do not correspond to normal values. Such disorders are associated with hormonal and emotional instability. Women at this age are susceptible to depression, various experiences) and quickly get tired even with minimal physical exertion (the help of a psychologist can help cope with such conditions.
Normal for women after 60
As indicated in the table, the hemoglobin level in women after 60 years of age becomes critical. This situation is associated with the end of menopausal changes and the minimization of metabolic processes in the body. Hemoglobin in women after 65 years of age has critical indicators, as internal metabolism in tissues slows down.
Table of hemoglobin norms in men by age
In men, the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood differs significantly from the normal values of the enzyme in women. So, in the male half, its content should not decrease to 130 g/l. and rise above the level of 170 g/l.
Such differences are associated with the production of testosterone in men, which can further enrich blood cells with oxygen.
In addition, the energy costs of the stronger sex are larger, which means the need for air exchange increases.
The norm of hemoglobin in the blood of men, depending on age, is shown in the table:
| Age | Normal hemoglobin g/l. |
| 15 — 18 | 120 — 155 |
| 18 — 30 | 130 — 170 |
| 30 — 40 | 130 — 155 |
| 40 — 60 | 130 — 160 |
The hemoglobin level in men after 30 years gradually begins to decrease. These differences can be analyzed using the table. Such changes are directly related to testosterone production.
As you know, after 40 years, the production of the hormone decreases, and therefore, male libido is gradually suppressed (consultation with a sexologist can solve this problem)
Against the background of ongoing processes, the physical activity of a man is similarly minimized.
In men after 50–60 years, the concentration of the enzyme is minimized, since testosterone virtually ceases to be produced. Therefore, it is regularly necessary to monitor the indicators of blood components and undergo tests. Any deviation from normal values (as indicated in the table) should be immediately eliminated, since at this age there is a high risk of developing anemia and other pathologies associated with the abnormal composition of the blood fluid.
Indications for the purpose of the study
Hemoglobin is a complex protein, the main component of red blood cells, which carries oxygen from the lungs to all tissues of the body and is involved in the removal of carbon dioxide from the body's cells.
The hemoglobin molecule consists of heme (the non-protein part) and globin (the protein part, which contains four polypeptide chains in its molecule: two alpha chains and two beta chains). Each of the four globin subunits has a heme group with an iron atom attached to it.
Normally, several forms of hemoglobin can be found in the blood, differing from each other in the protein part (quantitative or qualitative composition of the amino acids that make up the globin):
- embryonic (occurs in the fetus up to 2 months of intrauterine development);
- fetal (formed from the 2nd month of intrauterine development, circulates before birth, is destroyed in the first week of life);
- mature hemoglobin.
When hemoglobin interacts with various substances that can bind to its active center, hemoglobin derivatives arise. Depending on what hemoglobin has attached, the following forms are distinguished:
- HbO2 – compound with oxygen (oxyhemoglobin);
- HbCO2 – hemoglobin with carbon dioxide (carbohemoglobin);
- HbMet – hemoglobin with oxidized iron (methemoglobin);
- HbCO – carboxyhemoglobin formed during carbon monoxide poisoning;
- HbA1C – glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetes mellitus.
Along with normal forms of hemoglobin, there may be mutant or pathological ones. More than 300 forms of pathological hemoglobins are known.
Most often found:
- HbS – hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia;
- Kempsey hemoglobin for polycythemia;
- hemoglobin Hammersmith et al.
Derivatives and pathological forms of hemoglobin are determined for the purpose of diagnosing various diseases and during dynamic monitoring of their course (for example, the glycosylated hemoglobin indicator reflects the average blood glucose level over the previous three months).
The lifespan of red blood cells, the dry matter of which is 90-95% hemoglobin, is 110-120 days. The destruction of red blood cells occurs in the spleen, a small part of the hemoglobin breaks down in the red bone marrow and stellate cells of the liver.
Determination of hemoglobin concentration as part of a clinical blood test is one of the most important diagnostic methods. A calculated indicator reflecting the average hemoglobin content in 1 cell (erythrocyte) is used for the differential diagnosis of anemia.
Hemoglobin concentration is determined as part of preventive, dispensary observation during the initial examination to identify diseases, during hospitalization in therapeutic and surgical hospitals.
Determination of the quantitative content of hemoglobin is used in combination with other hematological indicators (hematocrit value, number of red blood cells, red blood cell indices) to diagnose a number of pathological conditions: anemia, erythremia and secondary erythrocytosis, to assess the degree of dehydration of the body, determine the severity of blood loss in hemorrhagic conditions, and assess the effectiveness of blood transfusions in the process of therapy, determining the severity of the patient’s condition in inflammatory, infectious diseases, as well as for monitoring the therapy and the course of various diseases.
Table of hemoglobin norms in children by age
In newborns, the density of hemoglobin in the blood has maximum values. Then its content gradually decreases, a certain stability of indicators appears only at 6 months. This condition persists until the child reaches 5 years of age, after which the concentration of the enzyme begins to increase again.
It is also worth considering that when a child reaches the age of 12 years, it is necessary to analyze protein indicators based on his gender. They will be different for boys and girls.
The norm of hemoglobin in the blood of children by age is shown in the table:
| Age | Boys | Girls |
| from 0 to 15 days. | 160 — 200 | 160 — 200 |
| 1 - 3 months | 120 — 160 | 120 — 160 |
| 4 - 6 months | 95 — 140 | 95 — 140 |
| 6 – 12 months | 110 — 145 | 114 — 150 |
| 1 - 2 g. | 110 — 130 | 110 — 130 |
| 2 - 5 l. | 105 — 150 | 105 — 145 |
| 5 - 11 l. | 110 — 140 | 110 — 140 |
| 12 - 14 l. | 120 — 140 | 120 — 140 |
| 15 - 17 l. | 120 — 155 | 120 — 150 |
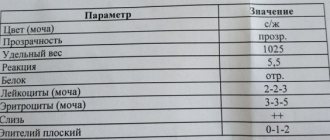
Norms and deviations of hemoglobin as a result of analysis
The normal level of hemoglobin in the blood is a guarantee of good health for adults and children. The indicator for each person up to a certain age is approximately at the same level. In 2-week-old babies it is 135-200 g/l, at 1 year old it is 100-140, and at 12 years old it is already 114-145 g/l. The concentration of hemoprotein in the blood of strong healthy children is always higher.
The norm is different for men and women. The strong half of humanity is characterized by a hemoglobin test value of 130-160 g/l, for girls and women over 18 years old - 120-155. During menstruation it can drop to a level of 100 g/l. After 45 years, the hemoprotein content in both sexes may change upward.
An increased level of hemoglobin, recorded as a result of the analysis, in some cases indicates the presence of cancer problems, heart and intestinal pathologies.
A low rate is often associated with malnutrition, low-carbohydrate diets, hidden blood loss and blood diseases. It is observed in people suffering from diabetes, pancreatic tumors, and occurs in pregnant women.
Important! Whatever the results of a blood test for hemoglobin, it is strictly not recommended to make a diagnosis on your own and self-medicate. An experienced specialist from the Health of the Nation medical center will conduct a thorough examination, determine the exact cause of the ailment, and prescribe competent treatment.
Health is the main wealth that nature has awarded to humans. It should be taken care of by professionals.
Normal hemoglobin level in blood during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s amount of enzyme in her blood will differ from the values indicated in the table above. Also, pregnant women should know what medications can and cannot be taken during pregnancy. These deviations are associated with various changes that occur in the body.
Approximate indicators of enzyme content in pregnant women are shown in the table:
| Trimester | Amount of hemoglobin g/l. |
| 1 | 115 — 165 |
| 2 | 110 — 145 |
| 3 | 110 — 140 |
These differences are associated with the end of menstruation and the subsequent growth of the placenta, which requires constant nutrition. Therefore, it is important for the expectant mother to systematically undergo blood tests, since a critical decrease/increase in hemoglobin can become a source of dangerous complications (hypoxia, abnormal fetal development, early birth, underweight of the baby, retardation in mental/physical development, etc.).
Doctor's advice
Often the cause of increased hemoglobin is non-compliance with the drinking regime. The body receives little fluid (less than 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day, tea, coffee and other liquids do not count), this causes the blood to thicken. In this condition, not only hemoglobin, but other indicators also increase - hematocrit, red blood cells, platelets. Hematologists advise that if you have anemia, your diet should focus on meat. Liver and buckwheat are in second place in importance. Next are apples, nuts, cocoa. These same principles apply not only to adults, but also to children.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Hemoglobin level in women during menstruation
During the menstrual period, protein content decreases sharply. This feature of the female body is associated with loss of blood fluid and is not a sign of pathology. It is for this reason that women feel unstable during menstruation:
- dizziness occurs (about other causes of dizziness here);
- appetite increases;
- there is a persistent feeling of fatigue, etc.
At the same time, experts recommend refraining from taking blood tests a few days before/after menstruation, as the information will be distorted. The normal level of hemoglobin after menstruation is restored within 2 – 3 days (with correct nutrition and lifestyle).
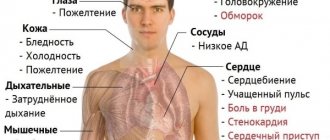
Causes and symptoms of low hemoglobin
Iron deficiency anemia is a fairly dangerous and common condition in which the blood cell content is less than the lower limit of normal.
In this case, the patient may have the following symptoms:
- vertigo;
- severe fatigue;
- change in taste preferences;
- frequent headaches (read how to get rid of headaches in this article);
- dyspnea;
- decreased blood pressure;
- decreased muscle tone;
- brittle nails/hair.
The danger of decreasing hemoglobin levels is that the brain and other internal structures do not receive the required amount of oxygen, and therefore cease to function correctly. As a result, associated health problems appear that significantly affect the quality of life.
The main reasons for a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood:
- poor nutrition (frequent diets, lack of vitamins, etc.);
- chronic gastritis (here you can find effective tablets for stomach pain)
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- arthritis;
- hepatitis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- tuberculosis;
- blood loss (after operations, injuries).
What functions does hemoglobin perform in the body?
A normal level of hemoglobin in the blood of men is necessary for the transfer of oxygen to the cells of tissues and organs. Protein has several functions; it not only provides oxygen to tissues and organs, but also absorbs carbon dioxide. It is quite difficult to detect hemoglobin in plasma in its free form, since this protein has its own role and functions.
In addition to the fact that protein delivers oxygen and promotes the utilization of carbon dioxide, it is involved in metabolic processes and cellular nutrition processes. And also the combination of protein with oxygen allows the blood to acquire the proper consistency. In this state, it can easily move through the vessels, carrying oxygen and nutrients.
Any deviation from the norm, increase or decrease in hemoglobin content in plasma leads to various health problems. May cause a disease or pathological condition.
Plasma erythrocyte protein levels depend on several factors, but increases or decreases can vary within a certain range. Minor deviations are not considered a pathology; with age, the level of protein in the plasma decreases, and its norm undergoes certain, but not dramatic changes.
What affects the level of hemoglobin in the body:
- taking medications;
- age indicator;
- lifestyle and amount of physical activity;
- the presence of pathologies in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels;
- race;
- Country of Residence.
If a man lives in a hot climate, then there is a high probability of developing dehydration. If the rules of drinking regime are not followed, the body regularly faces dehydration, which as a result leads to an increase in the level of iron in the blood and an increase in its viscosity. The role of hemoglobin in the body is clear, but it is worth noting that in its free form this protein is toxic.
The fact is that the molecular bond with oxygen reduces the toxicity of the protein; in this form it is not dangerous for the human body. But if the connection is broken and the substance enters the blood in a free form, then there is a high risk of developing intoxication. It is worth giving an example to support this statement. Examples include internal bleeding, blood loss due to hemolytic anemia, etc.
How to increase hemoglobin in the blood
It is important to control the ratio of all components of the blood fluid. Since its minimization is a pathological condition that will require certain treatment, and it does not always go away quickly and successfully. As therapy, doctors can take measures such as:
- blood transfusion (used in extreme cases, when the level is greatly reduced and drug treatment fails);
- prescription of vitamins (B9 and B12);
- taking iron-containing medications (in the form of tablets, suspensions or injections);
- drawing up a special menu (iron-enriched foods are added to the diet - meat, liver, herbs, vegetables, buckwheat, dried fruits, seafood, chocolate, etc.)
Therapy to increase hemoglobin levels in the blood is prescribed by a doctor during a personal appointment or online consultation. You can consult online or consult with a service doctor.
How to determine the amount of hemoglobin in the blood
All methods for determining the amount of protein come down to clinical studies. To begin with, the patient should donate blood for analysis, and after a few hours he will be informed of the result of the study.
The Govars method in a modification of Sali is considered widespread in medicine. During the procedure, biological fluid is exposed to hydrochloric acid. As a result, hydrochloric acid hematin appears, its level is compared with standards, which ultimately make it possible to obtain an accurate result.
Whatever the norm of hemoglobin in a person’s blood, one should not draw premature conclusions. Only a doctor can judge what is considered normal and what is pathology.
If there is a deviation from the norm, you can take on the task of correcting the condition on your own, but it is advisable to coordinate the actions with a doctor.
The iron-containing protein hemoglobin is an important element in the blood that performs certain functions in the body. If its level decreases or increases, disruptions in the body’s functioning occur and a person’s well-being deteriorates. To avoid serious consequences, it is worth monitoring the level of protein in the body and regularly donating blood for analysis.
High hemoglobin: causes, treatment
If hemoglobin levels in the blood exceed the norm indicated in the table, then this condition is also a reason to consult a doctor. In this case, the patient may have symptoms such as:
- problems in the functioning of the genitourinary system;
- drowsiness;
- yellowish skin;
- poor appetite;
- decreased vision;
- oncology;
- chronic heart failure;
- high fatigue.
The reasons for such a violation include:
- diabetes mellitus (the disease is treated by an endocrinologist);
- increased blood viscosity;
- erythrocytosis;
- excess vitamin B12/B9;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases.
Causes of elevated hemoglobin
What can increased hemoglobin indicate? The fact that certain processes occur in a person’s body that are difficult to characterize as normal.
Most often, increased levels are diagnosed in people:
- with heart and vascular disease;
- with problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- with overwork (mainly of a physical nature);
- with a “lack of” oxygen (often diagnosed in those who like to travel to the mountains).
If the amount of iron-containing protein in the blood is increased, the doctor may prescribe drug therapy to the patient. Drugs that reduce iron levels in the blood and lower blood viscosity. One of the most commonly prescribed drugs to reduce hemoglobin is Curantil.
How to lower hemoglobin without taking medications:
- you should give up heavy physical activity;
- normalize nutrition (reduce the amount of protein consumed);
- lose excess weight (if any);
- contact a cardiologist for help (to treat heart failure);
- drink enough liquid per day.
Frequently asked questions and doctor's answer
General practitioner Victoria Druzhikina answered questions
1. What is Hemoglobin indicated in a blood test?
- “In a general blood test, hemoglobin is abbreviated as Hb, measured in grams per liter.” 2. Why is low Hemoglobin dangerous?
– “Low hemoglobin levels are dangerous due to anemia and its consequences:
- oxygen starvation of organs and tissues, primarily nervous;
- muscle weakness;
- fainting due to decreased blood pressure;
- decreased immunity;
- wear and tear of the heart muscle due to the development of compensatory tachycardia in conditions of lack of oxygen;
- heart attacks;
- retardation in mental and physical development.
In severe cases, untreated anemia can lead to hypoxic coma and death due to brain or heart failure.”
3. Blood transfusion for low hemoglobin
– “To treat severe forms of anemia, blood or red blood cell transfusions are used. The procedure is indicated in 2 cases:
1. With a hemoglobin level of 70 g/l and below.
2. In case of poor tolerance to anemia and the threat of hypoxic coma at any level of hemoglobin. This can occur in people whose lives involve high oxygen consumption - pregnant women, athletes, scuba divers playing wind instruments.
The standard regimen is 2 doses (1 dose – 200 ml) twice a week. Before and after the procedure, general urine and blood tests and temperature must be monitored.
Before the manipulation, the patient’s blood type and Rh factor are determined, and donor blood is selected based on these indicators. Next, the compatibility of the blood samples is checked. If the reaction proceeds normally, a transfusion is performed. If flakes or clots form, this blood is not transfused, but other samples are tested for compatibility.” 4. Hemoglobin norm in children under one year old
– “The hemoglobin norm in children under one year of age is determined by physiological factors. By the end of the 1st month, the numbers are higher than in adults and amount to 160–200 g/l.”
5. How to increase Hemoglobin in a child?
“If anemia is detected, it is important to increase hemoglobin levels as soon as possible, especially in children. The main role in this belongs to drugs. Unfortunately, nutrition will not significantly increase the numbers. With the help of food, you can only slightly improve your performance and maintain it at this level.
Foods to increase hemoglobin in children:
- beef;
- buckwheat;
- cocoa;
- liver;
- apples;
- pomegranate;
- walnuts.
Drugs for the treatment of anemia in children:
- Maltofer;
- Ferrum Lek;
- Totema;
- Ferlatum and others"
6. How to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy?
“During pregnancy, it can be difficult for a woman to follow a diet with foods rich in iron. However, their list is quite wide, you can choose what you like:
- beef;
- wheat bran;
- hazelnuts;
- cabbage, including broccoli;
- chocolate;
- rabbit;
- liver;
- cocoa;
- apples;
- pears;
- parmesan, etc.
How to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy - the most used drugs:
- Maltofer;
- Sorbifer Durules;
- Ferrum Lek;
- Gyno-tardiferon;
- Totema;
- Ferlatum and others."
7. Iron supplements to increase hemoglobin in adults
– “To treat anemia in adults, the same drugs are used as for pregnant women. Can also be used:
- Venofer;
- Ferlatum protein;
- Cosmopher;
- vitamin complexes with iron (Ferro-Folgamma, Fenyuls, etc.).”
8. Normal Hemoglobin in Newborns? – “The hemoglobin norm varies slightly from month to month, the generally accepted average values are 120–160 g/l.
Immediately after birth, the mother’s blood circulates in the baby, so values from 180 to 240 g/l are considered normal for the 1st week of life.”
For information on hemoglobin levels, see also the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. The norms of indicators are indicated in Appendix No. 3 of Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated 09/14/2001 364 (as amended on 06/06/2008)
Rate how useful article
4.7 was. 29 people voted, average rating 4.7
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Causes of low hemoglobin
Reduced hemoglobin in men is a rather rare phenomenon; increased levels are more common. A low level of hemoglobin is called anemia; with this phenomenon, the patient most often experiences the following symptoms:
- frequent headaches and dizziness;
- nausea, loss of appetite;
- pale skin;
- general weakness, high fatigue;
Some of the most common causes of anemia are:
- blood loss (traumatic injury, surgery, bleeding, colon cancer or stomach ulcer);
- nutritional deficiencies (iron, vitamin B12, folic acid);
- bone marrow problems (bone marrow replacement for cancer);
- suppression of red blood cell synthesis by chemicals;
- renal failure;
- abnormal hemoglobin structure (sickle cell anemia or thalassemia).
Lack of iron in the blood is an important sign of pathology. Often, low levels of iron-containing protein occur due to depletion of the body.
How to increase hemoglobin:
- It is worth including animal products in the diet, mainly meat and liver;
- regularly take walks in the fresh air;
- exercise;
- take appropriate medications.
If the cause of iron deficiency is not a consequence of poor and inadequate nutrition, but a consequence of the disease. Attention should be paid to the treatment of the underlying disease, compensating for the lack of erythrocyte protein with approved drugs.
Tardiferon is a drug that can be prescribed to a patient with low iron levels in the blood. The medication is available in tablet form and has minimal contraindications.