Symptoms of high hemoglobin
Initially, it is necessary to sort out what complaints does a woman have with increased hemoglobin?
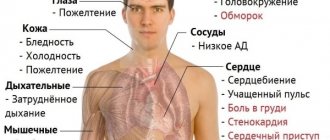
The condition of increased hemoglobin is called hyperhemoglobinemia and very often occurs without the manifestation of clinical signs. In most cases, high hemoglobin in women and men is detected only during a routine general clinical examination. In some cases, hyperhemoglobinemia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased blood pressure and swollen veins;
- a feeling of aching in bones and joints;
- decreased performance;
- weakness and drowsiness;
- shortness of breath even when walking calmly;
- slight blueness of the fingertips;
- pallor or flushing of the face;
- losing weight for no apparent reason;
- decreased concentration and absent-mindedness;
- long and painful menstruation;
- neurotic disorders, psychoses, insomnia, depression.
Often the causes of high hemoglobin levels in women and men are a concomitant disease. In this case, the symptoms of hyperhemoglobinemia are similar to the clinical manifestations of the underlying pathology. This fact explains the difficulties for differential diagnosis of hyperhemoglobinemia itself and identifying its causes.
Hemoglobin during pregnancy
During pregnancy, elevated hemoglobin is extremely rare. As a rule, a single increase in Hb concentration is not significant, since the levels of all indicators change during the day against the background of physical or emotional activity. However, consistently high levels may indicate a lack of B vitamins or the development of a pathological process. In this case, a comprehensive examination of the patient is prescribed to eliminate the hyperhemoglobinemia condition as quickly as possible. This is necessary to reduce the risk of developing thrombosis and fetal hypoxia.
Pregnant women are more often characterized by a state of hypohemoglobinemia - a deficiency of hemoglobin levels against the background of blood thinning, as a result of an increase in its volume.
For early diagnosis of deviations from the norm when planning to conceive a child, a course of preventive measures is recommended to prevent a decrease in Hb concentration. This will significantly reduce the risk of developing any type of anemia.
Read further: What is hemoglobin in the blood, its types, how is it tested. How does alcohol affect? The influence of periodic women's days
Anemia during pregnancy
According to WHO, approximately half a billion women of reproductive age in the world suffer from anemia. According to Rosstat, the course of pregnancy is complicated by the development of anemia in every third patient.
“You’re doing well, but your hemoglobin is a bit low.” - Oh, is that scary? - No, it’s not scary at all. I'll prescribe you a pill, and everything will be fine.
In fact, not everything is so simple - issues of iron deficiency are under the close attention of WHO experts, who recommend considering iron deficiency anemia as a significant risk factor for the death of children in the perinatal period.*
"I have low hemoglobin"
The norms of hemoglobin content in pregnant women differ from the population. From 1972 to the present, during pregnancy, the lower limit of normal for pregnant women is considered to be 110 g/l.
— My hemoglobin was 99 g/l, I took the drug, and after a week my result was 112 g/l. Tell me, doctor, should I continue taking the drug or is it enough?
Cases of “magical” healing are not uncommon. In such situations, it is important to understand how the study was conducted. Unfortunately, in the Russian Federation, a general blood test is still taken “from a fingertip”; the hemoglobin concentration is determined manually, using the obtained capillary blood samples. With this sampling technique, the hemoglobin level can be significantly reduced due to the presence of tissue fluid (the finger was massaged well or pressed hard). The maximum error can be obtained in pregnant women with edema - on average ±10 g/l.
The most accurate results are obtained from an automated venous blood analysis result. This is the method that should be used in everyday practice.
“We treat hemoglobin with iron”
Of course, you want to minimize drug exposure during pregnancy. Moreover, iron supplements are not always well tolerated - nausea, constipation, or diarrhea do not add loyalty to therapy even for the most disciplined patients.
— My hemoglobin is 110 g/l. During the consultation, the gynecologist insists on taking iron supplements, but the therapist says that it is too early. Who is right?
The one who makes the correct diagnosis will be right. A low hemoglobin level requires confirmation of iron deficiency, since anemia can be associated with various factors, and we only treat iron deficiency with iron supplements.
The “gold standard” for diagnosing iron deficiency is to determine serum ferritin levels. Even with a normal number of red blood cells, “good” hemoglobin and hematocrit, a ferritin level of less than 30 ng/ml clearly indicates latent (hidden) iron deficiency. It is at this moment that it is necessary to provide iron subsidies in a prophylactic dose in order to prevent a full-blown anemia. Prophylactic doses of iron are usually well tolerated and can be included in vitamin and mineral complexes.
High hemoglobin in women - what does it mean and what should be done
Doctors are often asked the question - what does it mean if a woman has increased hemoglobin? As a rule, this condition is caused by a lack of oxygen in the blood. In order to compensate, the body begins to actively produce red blood cells containing Hb molecules.
To prevent the risk of developing complications in the form of thrombosis, mandatory correction of high hemoglobin levels is necessary. If such a condition is caused by external factors, then when they are eliminated, the Hb value returns to normal. In a situation where hyperhemoglobinemia is a concomitant symptom of the disease, initial elimination of the underlying pathology is necessary.
Reasons for the increase
Factors that cause an increase in hemoglobin levels can be exogenous (external) or endogenous (internal).
Exogenous causes. An increase in hemoglobin levels may be associated with a person’s type of activity. Thus, pilots, residents of high mountains and climbers who spend significant time at high altitudes experience hypoxia. Therefore, immediately after the flight, the Hb concentration will be higher than normal. Taking certain medications, such as steroids, also affects this laboratory indicator.
During long-term training with heavy loads, a huge amount of oxygen is consumed, which, with the correct technique, is compensated by frequent and deep breathing. If technology is violated, an increase in hemoglobin levels is observed in the body.
Endogenous causes. Diabetes mellitus and mental disorders accompanied by stress reactions can also cause Hb deviations from the norm. And in the case of a benign tumor process of the circulatory system (Vaquez disease), an increase in the concentration of red blood cells becomes malignant.
When taking medications that lead to excessive absorption of iron ions in the blood against the background of malfunctions of the enzymatic system, the Hb level increases.
Reasons for the downgrade
Low Hb concentrations are observed against the background of the following pathological conditions:
- anemia of various types;
- failures of hemoglobin synthesis processes;
- liver diseases;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
- chronic kidney disease, which results in a decrease in the concentration of the hormone erythropoiesin, the main role of which is the activation of the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- blood hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells;
- oncological diseases accompanied by metastases to the bone marrow;
- chronic pathologies of connective tissue;
- infectious process.
Read further: Tables of norms with explanations of indicators in a biochemical blood test
What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells. This element acts as a connecting link in metabolism, as it transports oxygen to all internal structures of the body and removes carbon dioxide from them. In addition to helping tissues “breathe,” the protein performs a pigment function, in other words, it gives the blood fluid a red tint.
Fluctuations in the required level of hemoglobin in the blood may indicate a pathological or some kind of stressful condition.
If any changes in the amount of hemoglobin are detected, patients are sent for additional studies, which help to reconstruct a complete clinical picture, and also allow one to diagnose/refute the presence of possible diseases.
Treatment methods for high hemoglobin
High hemoglobin in women poses a serious threat, especially during pregnancy. Therefore, when diagnosing a pathological condition, mandatory treatment is necessary. How to reduce hemoglobin?
Treatment and correction methods for elevated hemoglobin in women are aimed at thinning the blood and reducing the concentration of red blood cells. For this purpose, for example, the following drugs are prescribed:
- aspirin®;
- cardiomagnyl®;
- chimes®.
Important: independent selection of medications and dosages for treatment is prohibited. Such behavior can lead to a worsening of the condition and severity of the disease.
It is acceptable to prescribe hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches. When a leech bites, the enzyme hirudin contained in their saliva enters the human bloodstream. Hirudin has a bidirectional effect on the blood: on the one hand, it slows down the processes of blood clotting, and on the other, it reduces the risk of blood clots. It should be noted that for therapy it is necessary to use only medicinal leeches sold in pharmacies and diluted in laboratory conditions. For one session, 5 leeches are enough, each of which sucks no more than 15 ml of human blood when biting.
Menu for women with high hb
In combination with drug treatment and hirudotherapy, it is necessary to adhere to a certain menu:
- the amount of red meat in the diet should be reduced, and offal (liver, tongue, kidneys) should be completely excluded;
- the diet should be dominated by white meat and low-fat fish;
- the consumption of legumes (peas, beans, lentils) is allowed, since iron, which predominates in their composition, is poorly absorbed by the human body;
- vitamin complexes containing folic acid and B vitamins are excluded;
- It is forbidden to consume juices and rosehip decoctions;
- You need to drink clean water without gas often and in small portions: every half hour - 1 glass of water.
Preparation and delivery of glycated hemoglobin analysis
Analysis for glycated hemoglobin does not require special preparation. There is no need to donate blood on an empty stomach. Before blood sampling, the patient does not need to limit himself to drinks or refrain from physical or emotional stress. It will not affect the results of the study and taking medications (except for drugs that reduce blood glucose levels).
The test is more reliable than a blood sugar test or a “load” glucose tolerance test. The analysis will reflect the concentration of glycated hemoglobin accumulated over three months. The form that the patient receives will indicate the results of the study and the norm of glycated hemoglobin. The interpretation of the test results at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out by an experienced endocrinologist.
Diagnostic methods and preparation
Diagnosis of hemoglobin level is mandatory when conducting a general blood test. The duration does not exceed 1 day. The biomaterial for analysis is venous or capillary blood. To obtain the most reliable results, you must follow the preparation recommendations:
- eliminate fatty and fried foods for 1 day;
- blood is donated strictly on an empty stomach, the last meal taken at least 8 hours before;
- within half an hour, physical and emotional stress is limited;
- You must not smoke for 1 hour.
Interpretation of results and norm
Important: the interpretation of the data obtained should only be carried out by the attending physician.
Otherwise, the risk of incorrect diagnosis and selection of treatment methods that will worsen the patient’s condition cannot be excluded.
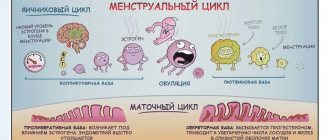
Reference (normal) values are selected individually for each patient, taking into account gender, age and menstrual cycle.
| Floor | Age | Hemoglobin norm, g/l |
| Both | 0 – 14 days | 135-200 |
| Up to 1 month | 100-170 | |
| 1-2 months | 95-130 | |
| 2-4 months | 100-140 | |
| 4-6 months | 110-140 | |
| 6-9 months | 100-150 | |
| 9-12 months | 115-145 | |
| 1-5 years | 110-150 | |
| 5-10 years | 115-145 | |
| 10-12 years | 120-160 | |
| Man | 12-15 years | 120-160 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-170 | |
| 18-45 years old | 130-170 | |
| 45-60 years | 140-175 | |
| Over 60 years old | 120-175 | |
| Woman | 12-15 years | 110-150 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-155 | |
| 18-45 years old | 115-160 | |
| 45-60 years | 120-160 | |
| Over 60 years old | 110-170 |
It should be noted that even with a normal quantitative content of red blood cells in the blood, a deviation from the reference values of the Hb indicator may be observed.
A small one-time deviation from the norm is not a cause for concern. In other words, if hemoglobin 160 is detected in a patient under the age of 18, then there is no need for additional laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Despite the difference in normal values for different sexes, hemoglobin 150 g/l is considered the optimal value for both women and men.
Table of hemoglobin norms in men by age
In men, the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood differs significantly from the normal values of the enzyme in women. So, in the male half, its content should not decrease to 130 g/l. and rise above the level of 170 g/l.
Such differences are associated with the production of testosterone in men, which can further enrich blood cells with oxygen.
In addition, the energy costs of the stronger sex are larger, which means the need for air exchange increases.
The norm of hemoglobin in the blood of men, depending on age, is shown in the table:
| Age | Normal hemoglobin g/l. |
| 15 — 18 | 120 — 155 |
| 18 — 30 | 130 — 170 |
| 30 — 40 | 130 — 155 |
| 40 — 60 | 130 — 160 |
The hemoglobin level in men after 30 years gradually begins to decrease. These differences can be analyzed using the table. Such changes are directly related to testosterone production.
As you know, after 40 years, the production of the hormone decreases, and therefore, male libido is gradually suppressed (consultation with a sexologist can solve this problem)
Against the background of ongoing processes, the physical activity of a man is similarly minimized.
In men after 50–60 years, the concentration of the enzyme is minimized, since testosterone virtually ceases to be produced. Therefore, it is regularly necessary to monitor the indicators of blood components and undergo tests. Any deviation from normal values (as indicated in the table) should be immediately eliminated, since at this age there is a high risk of developing anemia and other pathologies associated with the abnormal composition of the blood fluid.
Consequences of increased hemoglobin in women
High hemoglobin levels are dangerous for women due to complications that affect the functioning of various systems and organs. Thus, an increase in blood viscosity leads to the formation of clots, which can cause bleeding, pulmonary thromboembolism, stroke, heart attack or thrombosis. Any of these conditions requires immediate assistance from medical personnel, since it threatens the life and health of the patient.
Hyperhemoglobinemia is especially dangerous for people with chronic diseases of the lungs and cardiovascular system, since their risk of developing thrombosis increases several times. Timely monitoring of Hb level concentrations is necessary during and after treatment of pathologies.
Indications for analysis of glycosylated hemoglobin
Analysis for glycated hemoglobin is performed for the following purposes:
- Diagnosis of carbohydrate metabolism disorders (with a glycated hemoglobin level of 6.5%, the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is confirmed);
- Monitoring diabetes mellitus (glycated hemoglobin allows you to assess the level of disease compensation over 3 months);
- Assessment of patient adherence to treatment - the degree of compliance between the patient's behavior and the recommendations he received from the doctor.
A blood test for glycated hemoglobin is prescribed to patients who complain of extreme thirst, frequent excessive urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and increased susceptibility to infections. Glycated hemoglobin is a criterion for retrospective assessment of glycemic levels.
Depending on the type of diabetes and how well the disease responds to treatment, glycated hemoglobin analysis is carried out 2 to 4 times a year. On average, patients with diabetes are recommended to donate blood for testing twice a year. If a patient is diagnosed with diabetes for the first time or the control measurement is unsuccessful, doctors prescribe a glycated hemoglobin test again.
Prevention of elevated hemoglobin
Preventive measures against increasing the concentration of Hb in the blood consist of maintaining a healthy lifestyle:
- cessation of alcohol abuse, smoking and psychotropic drugs;
- maintaining a proper diet;
- drinking large amounts of clean water without gas;
- limiting physical and emotional overload;
- health status monitoring – annual scheduled examinations and maintenance therapy for chronic diseases.
Table of hemoglobin norms in children by age
In newborns, the density of hemoglobin in the blood has maximum values. Then its content gradually decreases, a certain stability of indicators appears only at 6 months. This condition persists until the child reaches 5 years of age, after which the concentration of the enzyme begins to increase again.
It is also worth considering that when a child reaches the age of 12 years, it is necessary to analyze protein indicators based on his gender. They will be different for boys and girls.
The norm of hemoglobin in the blood of children by age is shown in the table:
| Age | Boys | Girls |
| from 0 to 15 days. | 160 — 200 | 160 — 200 |
| 1 - 3 months | 120 — 160 | 120 — 160 |
| 4 - 6 months | 95 — 140 | 95 — 140 |
| 6 – 12 months | 110 — 145 | 114 — 150 |
| 1 - 2 g. | 110 — 130 | 110 — 130 |
| 2 - 5 l. | 105 — 150 | 105 — 145 |
| 5 - 11 l. | 110 — 140 | 110 — 140 |
| 12 - 14 l. | 120 — 140 | 120 — 140 |
| 15 - 17 l. | 120 — 155 | 120 — 150 |
Norms of glycated hemoglobin
Normally, the level of glycated hemoglobin varies from 4.8 to 5.9%. The closer the level of glycated hemoglobin in a diabetic patient is to 7%, the easier it is to control the disease. As glycated hemoglobin levels increase, the risk of complications increases.
Endocrinologists interpret the glycated hemoglobin indicator as follows:
- 4-6.2% – the patient does not have diabetes;
- From 5.7 to 6.4% - prediabetes (impaired glucose tolerance, which is associated with an increased risk of diabetes);
- 6.5% or more – the patient has diabetes.
Several factors may affect the indicator. In patients with abnormal forms of hemoglobin (patients with sickle erythrocytes), the level of glycated hemoglobin will be underestimated. If a person suffers from hemolysis (decomposition of red blood cells), anemia (anemia), severe bleeding, then his test results may also be underestimated. Increased levels of glycated hemoglobin occur with a lack of iron in the body and with a recent blood transfusion. Analysis for glycated hemoglobin does not reflect sudden changes in blood glucose levels.
Table of correspondence of glycated hemoglobin to the average daily plasma glucose level for the last three months.
| Glycated hemoglobin (%) | Average daily plasma glucose level (mmol/l) |
| 5,0 | 5,4 |
| 6,0 | 7,0 |
| 7,0 | 8,6 |
| 8,0 | 10,2 |
| 9,0 | 11,8 |
| 10,0 | 13,4 |
| 11,0 | 14,9 |
Increased and decreased levels of glycated hemoglobin
An increased level of glycated hemoglobin indicates a long-term gradual but steady increase in the concentration of glucose in a person’s blood. These data do not always indicate the development of diabetes mellitus. Carbohydrate metabolism may be impaired as a result of impaired glucose tolerance. The results will be incorrect if the tests are performed incorrectly (after meals, not on an empty stomach).
A glycated hemoglobin content reduced to 4% indicates a low level of glucose in the blood - hypoglycemia in the presence of tumors (pancreatic insulinoma), genetic diseases (hereditary glucose intolerance). The level of glycated hemoglobin decreases with inadequate use of drugs that reduce blood glucose levels, a low-carbohydrate diet, and heavy physical activity leading to exhaustion of the body. If the level of glycated hemoglobin is increased or decreased, consult an endocrinologist at the Yusupov Hospital, who will conduct a comprehensive examination and prescribe additional diagnostic tests.
How to reduce glycated hemoglobin
You can reduce the level of glycated hemoglobin using the following measures:
- Add more vegetables and fruits to your diet that contain a lot of fiber, which helps stabilize blood glucose;
- Consume more skim milk and yogurt, which contain a lot of calcium and vitamin D, which help normalize blood glucose levels;
- Increase your intake of nuts and fish, which contain Omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce insulin resistance and regulate blood glucose levels.
To reduce glucose resistance, season your dishes with cinnamon, add cinnamon to your foods, add it to tea, sprinkle it on fruits, vegetables and lean meats. Cinnamon helps reduce glucose resistance and glycated hemoglobin levels. Rehabilitation specialists recommend that patients perform a set of physical exercises daily for 30 minutes, which allow them to better control the level of glucose and glycated hemoglobin. During your workout, combine aerobic and anaerobic exercises. Strength training can temporarily lower blood glucose levels, while aerobic exercise (walking, swimming) helps automatically lower blood sugar levels.
In order to do a blood test for the content of glycated hemoglobin and get advice from a qualified endocrinologist, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital. The price of the study is lower than in other medical institutions in Moscow, despite the fact that laboratory assistants use the latest automatic glycated hemoglobin analyzers from the world's leading manufacturers.