Symptoms of high hemoglobin
Initially, it is necessary to sort out what complaints does a woman have with increased hemoglobin?
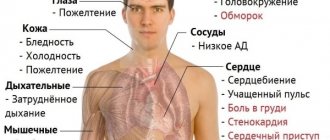
The condition of increased hemoglobin is called hyperhemoglobinemia and very often occurs without the manifestation of clinical signs. In most cases, high hemoglobin in women and men is detected only during a routine general clinical examination. In some cases, hyperhemoglobinemia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased blood pressure and swollen veins;
- a feeling of aching in bones and joints;
- decreased performance;
- weakness and drowsiness;
- shortness of breath even when walking calmly;
- slight blueness of the fingertips;
- pallor or flushing of the face;
- losing weight for no apparent reason;
- decreased concentration and absent-mindedness;
- long and painful menstruation;
- neurotic disorders, psychoses, insomnia, depression.
Often the causes of high hemoglobin levels in women and men are a concomitant disease. In this case, the symptoms of hyperhemoglobinemia are similar to the clinical manifestations of the underlying pathology. This fact explains the difficulties for differential diagnosis of hyperhemoglobinemia itself and identifying its causes.
Hemoglobin during pregnancy
During pregnancy, elevated hemoglobin is extremely rare. As a rule, a single increase in Hb concentration is not significant, since the levels of all indicators change during the day against the background of physical or emotional activity. However, consistently high levels may indicate a lack of B vitamins or the development of a pathological process. In this case, a comprehensive examination of the patient is prescribed to eliminate the hyperhemoglobinemia condition as quickly as possible. This is necessary to reduce the risk of developing thrombosis and fetal hypoxia.
Pregnant women are more often characterized by a state of hypohemoglobinemia - a deficiency of hemoglobin levels against the background of blood thinning, as a result of an increase in its volume.
For early diagnosis of deviations from the norm when planning to conceive a child, a course of preventive measures is recommended to prevent a decrease in Hb concentration. This will significantly reduce the risk of developing any type of anemia.
Read further: What is hemoglobin in the blood, its types, how is it tested. How does alcohol affect? The influence of periodic women's days
Functions of hemoglobin
Red blood cells are important because they enable the “respiration” of cells and tissues of the body. But they only serve as a kind of transport that helps carry vital oxygen; in fact, the main respiratory function is performed by protein - hemoglobin, which red blood cells are saturated with. It is he who gives them their color and interacts with oxygen, attaching it to itself and delivering it to the tissues, and then taking carbon dioxide from the cells. It also plays a significant role in maintaining the acid-base balance in the body. It is noteworthy that immediately after their creation, red blood cells are not yet saturated with hemoglobin; this happens after they enter the blood. Normally, a mature red blood cell contains about 400 million hemoglobin molecules.
Since hemoglobin is responsible for one of the most important functions - respiratory, its indicators are very important; in case of deviations, hypoxia begins - oxygen starvation, which has a very negative effect on the body as a whole. At the same time, it must be remembered that the deviation of its indicators beyond the norm is not an independent disease, but at the same time serves as its consequence; this always prompts a more in-depth study of the state of health to identify the real cause of such a deviation and prevent possible consequences.
Separate studies of hemoglobin are not carried out; its quantity is studied as part of a general (clinical) blood test, where other blood components - red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets - are analyzed in combination with hemoglobin.
High hemoglobin in women - what does it mean and what should be done
Doctors are often asked the question - what does it mean if a woman has increased hemoglobin? As a rule, this condition is caused by a lack of oxygen in the blood. In order to compensate, the body begins to actively produce red blood cells containing Hb molecules.
To prevent the risk of developing complications in the form of thrombosis, mandatory correction of high hemoglobin levels is necessary. If such a condition is caused by external factors, then when they are eliminated, the Hb value returns to normal. In a situation where hyperhemoglobinemia is a concomitant symptom of the disease, initial elimination of the underlying pathology is necessary.
Reasons for the increase
Factors that cause an increase in hemoglobin levels can be exogenous (external) or endogenous (internal).
Exogenous causes. An increase in hemoglobin levels may be associated with a person’s type of activity. Thus, pilots, residents of high mountains and climbers who spend significant time at high altitudes experience hypoxia. Therefore, immediately after the flight, the Hb concentration will be higher than normal. Taking certain medications, such as steroids, also affects this laboratory indicator.
During long-term training with heavy loads, a huge amount of oxygen is consumed, which, with the correct technique, is compensated by frequent and deep breathing. If technology is violated, an increase in hemoglobin levels is observed in the body.
Endogenous causes. Diabetes mellitus and mental disorders accompanied by stress reactions can also cause Hb deviations from the norm. And in the case of a benign tumor process of the circulatory system (Vaquez disease), an increase in the concentration of red blood cells becomes malignant.
When taking medications that lead to excessive absorption of iron ions in the blood against the background of malfunctions of the enzymatic system, the Hb level increases.
Reasons for the downgrade
Low Hb concentrations are observed against the background of the following pathological conditions:
- anemia of various types;
- failures of hemoglobin synthesis processes;
- liver diseases;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
- chronic kidney disease, which results in a decrease in the concentration of the hormone erythropoiesin, the main role of which is the activation of the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- blood hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells;
- oncological diseases accompanied by metastases to the bone marrow;
- chronic pathologies of connective tissue;
- infectious process.
Read further: Tables of norms with explanations of indicators in a biochemical blood test
Reasons for increasing protein
An increase in hemoglobin levels can be caused by two main reasons:
- exposure to external factors and lifestyle;
- pathological deviations.
Lifestyle
In the first case, the metabolism in the body is not disturbed, the number of red blood cells does not increase, but for some reason the body needs oxygen more, so the hemoglobin level automatically increases. This situation is temporary, and the body will return to normal as soon as the cause of the lack of oxygen is eliminated. This group of temporary factors that contribute to an increase in hemoglobin includes:
- living in mountainous areas: for people living in high mountainous areas, high hemoglobin in the blood is the norm;
- features of the profession: climbers and pilots (lack of oxygen in the blood is a consequence of high altitude), bodybuilders (taking anabolic steroids and steroids and excessive physical activity cause oxygen starvation);
- excessive nicotine consumption: smoking increases blood viscosity, increasing iron levels in the blood;
- non-compliance with the drinking regime: if the body lacks fluid, the amount of protein in the blood automatically increases;
- unhealthy diet: predominance of protein foods in the diet.
Pathological deviations
The second group of reasons causing an increase in protein includes pathological disorders in the body. With such disorders, the body's metabolism is disrupted and red blood cells are reduced. To compensate for the lack of red blood cells, the body begins to increase the production of hemoglobin. The pathological group includes:
- kidney dysfunction;
- hormonal disorders;
- pulmonary fibrosis;
- congenital heart defects;
- intestinal obstruction;
- diabetes;
- cancer;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- poisoning;
- liver pathologies;
- stress;
- dehydration;
- pernicious or hemolytic anemia;
- bone marrow dysfunction;
- hereditary hemoglobinemia.
Hemoglobin levels may increase in response to an increase in platelets in the blood. The number of these blood cells increases with serious disturbances in the functioning of the body and a number of dangerous diseases.
The general causes of increased protein are the same for all sexes and ages, but some factors in the development of the disorder are unique to certain categories of patients.
Among women
Previously, it was believed that women did not face the problem of high hemoglobin levels. But doctors have refuted this opinion and found that an increase in iron-containing protein in women is most often caused by:
- pneumonia;
- infectious infections;
- asthma;
- malignant neoplasms;
- mental and emotional overload.
Sometimes an increase in hemoglobin-containing proteins is associated with a woman’s lifestyle or is a consequence of taking certain medications.
During pregnancy, increased hemoglobin in women, the causes and consequences of which are unpredictable, is considered a dangerous condition. With this disorder, pregnant women may experience disturbances in the functioning of the liver or kidneys, and may cause developmental abnormalities in the unborn child. In this case, doctors recommend that the pregnant woman follow a certain diet and take a course of vitamins to maintain normal hemoglobin levels.
In men
The stronger sex is more often susceptible to excess iron-containing protein in the blood. This is due to the fact that men are more prone to bad habits, and they often eat unhealthy “cholesterol” foods. Also, men are more often diagnosed with heart and vascular diseases, which contribute to an increase in hemoglobin levels in the blood.
Among men, more often there are representatives of professions in which disorders are associated with the implementation of their activities: miners, pilots, submariners, climbers, bodybuilders. In order to avoid the development of the disorder, doctors recommend that the stronger sex adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
In children
During intrauterine development, the fetus cannot breathe through the lungs on its own, but takes in air from the mother’s blood. The pregnant woman and the baby may not have enough oxygen between them, which is why the fetus's body begins to adapt to low oxygen levels by increasing protein levels.
In a newborn, according to recent studies, intrauterine hypoxia with placental insufficiency is often the cause of high hemoglobin. Over time, with the development and growth of the baby, the situation stabilizes, and by the age of two, the protein concentration returns to normal. If this does not happen, then the baby may have serious health problems: heart defects, blood diseases, neoplasms.
In adolescence, the reasons for elevated protein levels are the same as in adults. But more often in adolescents, the pathological condition is caused by pulmonary fibrosis, dehydration, intestinal obstruction, and blood diseases. Parents of boys involved in sports should pay attention to the use of anabolic steroids by teenagers, which increase the level of transport protein in the blood.
Treatment methods for high hemoglobin
High hemoglobin in women poses a serious threat, especially during pregnancy. Therefore, when diagnosing a pathological condition, mandatory treatment is necessary. How to reduce hemoglobin?
Treatment and correction methods for elevated hemoglobin in women are aimed at thinning the blood and reducing the concentration of red blood cells. For this purpose, for example, the following drugs are prescribed:
- aspirin®;
- cardiomagnyl®;
- chimes®.
Important: independent selection of medications and dosages for treatment is prohibited. Such behavior can lead to a worsening of the condition and severity of the disease.
It is acceptable to prescribe hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches. When a leech bites, the enzyme hirudin contained in their saliva enters the human bloodstream. Hirudin has a bidirectional effect on the blood: on the one hand, it slows down the processes of blood clotting, and on the other, it reduces the risk of blood clots. It should be noted that for therapy it is necessary to use only medicinal leeches sold in pharmacies and diluted in laboratory conditions. For one session, 5 leeches are enough, each of which sucks no more than 15 ml of human blood when biting.
Menu for women with high hb
In combination with drug treatment and hirudotherapy, it is necessary to adhere to a certain menu:
- the amount of red meat in the diet should be reduced, and offal (liver, tongue, kidneys) should be completely excluded;
- the diet should be dominated by white meat and low-fat fish;
- the consumption of legumes (peas, beans, lentils) is allowed, since iron, which predominates in their composition, is poorly absorbed by the human body;
- vitamin complexes containing folic acid and B vitamins are excluded;
- It is forbidden to consume juices and rosehip decoctions;
- You need to drink clean water without gas often and in small portions: every half hour - 1 glass of water.
Interpretation of test results (increased leukocytes)
Despite the fact that the level of hemoglobin depends on many factors (age, food intake, gender, physiological state), there are certain limits for the content that have already been given above.
A deviation of the hemoglobin level from the norm that is not caused by any disease is called physiological and, often, either does not require any treatment at all, or everything is corrected by diet, iron supplements or lifestyle changes. Thus, a physiological increase in hemoglobin can occur in people who consume insufficient amounts of water. Plasma production is reduced, more red blood cells are produced, and blood viscosity increases. Of course, this condition cannot be called normal; it is dangerous to health, but it can be easily corrected by consuming more clean drinking water.
Increased hemoglobin is observed in people who smoke. Their body experiences serious oxygen starvation, as strong compounds of hemoglobin and carbon monoxide arise. Quitting a bad habit will solve everything. The place of residence also influences, for example, people living in high mountains, where the air is thin and has a relatively low oxygen content, or pilots and flight attendants have an increased level of hemoglobin, which is not a deviation and does not require any treatment methods.
High hemoglobin can occur in professional athletes; this is also a normal variant. An increased protein level for women and children is above 150 g/l, and for men above 180 g/l.
A hemoglobin level is considered low if it is 20 g/l less than normal. A physiological decrease in hemoglobin can be caused by poor diet: a person eats little meat, dairy and iron-containing products. In this case, everything is corrected with an appropriate diet and vitamins, but it is important not to let the situation get worse and adhere to all the doctor’s instructions, because with a further decrease in hemoglobin, you can develop anemia.
Diagnostic methods and preparation
Diagnosis of hemoglobin level is mandatory when conducting a general blood test. The duration does not exceed 1 day. The biomaterial for analysis is venous or capillary blood. To obtain the most reliable results, you must follow the preparation recommendations:
- eliminate fatty and fried foods for 1 day;
- blood is donated strictly on an empty stomach, the last meal taken at least 8 hours before;
- within half an hour, physical and emotional stress is limited;
- You must not smoke for 1 hour.
Interpretation of results and norm
Important: the interpretation of the data obtained should only be carried out by the attending physician.
Otherwise, the risk of incorrect diagnosis and selection of treatment methods that will worsen the patient’s condition cannot be excluded.
Reference (normal) values are selected individually for each patient, taking into account gender, age and menstrual cycle.
| Floor | Age | Hemoglobin norm, g/l |
| Both | 0 – 14 days | 135-200 |
| Up to 1 month | 100-170 | |
| 1-2 months | 95-130 | |
| 2-4 months | 100-140 | |
| 4-6 months | 110-140 | |
| 6-9 months | 100-150 | |
| 9-12 months | 115-145 | |
| 1-5 years | 110-150 | |
| 5-10 years | 115-145 | |
| 10-12 years | 120-160 | |
| Man | 12-15 years | 120-160 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-170 | |
| 18-45 years old | 130-170 | |
| 45-60 years | 140-175 | |
| Over 60 years old | 120-175 | |
| Woman | 12-15 years | 110-150 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-155 | |
| 18-45 years old | 115-160 | |
| 45-60 years | 120-160 | |
| Over 60 years old | 110-170 |
It should be noted that even with a normal quantitative content of red blood cells in the blood, a deviation from the reference values of the Hb indicator may be observed.
A small one-time deviation from the norm is not a cause for concern. In other words, if hemoglobin 160 is detected in a patient under the age of 18, then there is no need for additional laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Despite the difference in normal values for different sexes, hemoglobin 150 g/l is considered the optimal value for both women and men.
Hematologist: who is he, for what symptoms and diseases should you make an appointment with a doctor?
Table of contents
- Hematologist: what does it treat?
- Pediatric hematologist: who is he and what does he treat?
- Help from a hematologist during pregnancy
- When to go to a hematologist?
- Preparing for a consultation
- Blood tests to be taken before consultation
- Stages of consultation with a hematologist
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Advantages of visiting a hematologist at MEDSI
A hematologist is a doctor who deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the blood and hematopoietic organs.
This specialist works with children and adults and uses both traditional and modern techniques in his practice. It can successfully identify even hidden pathologies that do not manifest significant symptoms.
Hematologist: what does it treat?
These specialists provide therapy for the following diseases:
- Anemia.
This pathology is characterized by a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin. Anemia is not a separate disease! This is a symptom of mycosis, pyelonephritis, tuberculosis and other dangerous conditions. It is usually accompanied by weakness, general malaise, appetite and sleep disturbances, shortness of breath even with moderate exertion, and poor concentration. - Lymphocytic leukemia.
This disease is malignant and is characterized by the proliferation of atypical B lymphocytes that accumulate in the bone marrow, spleen, liver and lymph nodes. A predisposition to the pathology is inherited, and its main symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, excessive sweating, weakness and sudden weight loss. As lymphocytic leukemia develops, an enlarged spleen and liver, anemia, dizziness, and spontaneous bleeding are detected - Multiple myeloma.
This pathology is malignant and is distinguished by the ability of tumor cells to synthesize homogeneous immunoglobulins or their fragments. The tumor is formed predominantly in the bone marrow and can be focal, diffuse or focal-diffuse - Myeloid leukemia.
This form of leukemia is characterized by the rapid division of special cells in the bone marrow and their accumulation in the blood. Usually it is diagnosed only during a clinical analysis, since often the pathology does not manifest itself in any way. In some cases, patients complain of a slight increase in body temperature, decreased immunity and general malaise. It is also possible to detect anemia and an enlarged spleen - Lymphomas.
This pathology is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes. The primary tumor site usually metastasizes and spreads throughout the body. There are several forms of lymphoma, which differ in symptoms and degree of malignancy.
Specialists also treat other diseases.
Pediatric hematologist: who is he and what does he treat?
This specialist deals with the treatment and prevention of diseases that occur in both children and adults. Working with patients under 18 years of age, he takes into account all the features of their age and development.
They are referred to such doctors if they suspect various forms of anemia, thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count), hemorrhagic vasculitis (inflammation of microvessels), hemophilia and other congenital hereditary disorders.
Important! If blood diseases are detected at an early age, the patient should be under medical supervision for as long as possible. It is very important not only to detect pathology, but also to control it. Only in this case can the correct growth and development of the child be ensured.
Help from a hematologist during pregnancy
A large number of blood diseases are inherited, for this reason it is very important to visit a doctor when planning a child and during pregnancy. The specialist will provide the necessary genetic tests and determine the likelihood of developing abnormalities. It is especially important to contact a hematologist if one or both future parents have pathologies.
In addition, it is very important for a pregnant woman to monitor all blood parameters, since the supply of oxygen and other nutrients to the fetus largely depends on them. Consultation with a doctor is required for various deviations from the norm. It is especially important to quickly seek medical help if you suspect the development of iron deficiency anemia. This problem is one of the most common and needs correction and observation until birth.
When to go to a hematologist?
Consultation with a doctor is required for the following signs of various disorders:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Weakness and drowsiness
- Increased body temperature (not due to colds and inflammatory processes)
- Weight loss
- Sleep disorders
- Excessive sweating
- Pale skin
- Decreased appetite
- The appearance of bruises on the body without objective reasons
- Dizziness
Help is required for patients who complain of joint pain, itching, dry skin, tingling and numbness of the fingers. You should make an appointment with a hematologist if you have a hereditary predisposition to blood diseases and low hemoglobin detected as part of a general diagnosis. Both general practitioners, gastroenterologists, neurologists and other doctors can refer you to this specialist.
Preparing for a consultation
No special preparation is required for the standard appointment. Some restrictions are imposed only if the patient must first undergo tests.
Before research you must:
- Try to quit drinking alcohol and smoking for a few days
- Limit fluid intake (per day)
- Refuse to eat (10-12 hours before)
- Avoid the use of medications. If this is not possible, you should tell your doctor what medications are being taken, on what schedule and in what dosages. This will allow you to correctly decipher the diagnostic results
Blood tests to be taken before consultation
Before visiting a hematologist, you should undergo the following tests:
- Common with determination of the number of reticulocytes
(“young” red blood cells). This test will reveal the rate of red blood cell production in the bone marrow - For HIV, hepatitis and other infections
- For ferritin.
Such a study will determine the content of a protein in the blood that preserves iron in cells. - Percentage of transferrin saturation.
This test identifies a protein that binds to iron and distributes it throughout the body.
The research results will allow the specialist to immediately make a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment. If necessary, other examinations will be recommended.
Stages of consultation with a hematologist
Conversation
It is aimed at collecting anamnesis. The patient is asked about the symptoms of the disease that have arisen. The doctor clarifies the time of appearance of signs of pathologies, their intensity and other features. The specialist also finds out hereditary predisposition to various diseases.
Inspection
The doctor assesses the condition of the skin and mucous membranes. During the examination, signs of disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic system may be revealed, such as pale skin, rashes, hematomas, cyanosis (bluish coloration).
Making a diagnosis or ordering additional examinations
If a patient contacts a hematologist with the results of blood tests, a diagnosis can be made immediately. If studies have not been carried out, the doctor will refer you to them. In some cases, not only laboratory but also instrumental examinations are required. The doctor writes out directions for them.
Diagnostics
Blood diseases have a variety of manifestations that are similar to other pathological conditions. Therefore, a wide range of examination techniques are used to identify them. The patient is required to undergo blood tests.
Also held:
- Urine tests
- Coagulogram
- Lymph node puncture
- Scintigraphy
- CT and MRI (computer and magnetic resonance imaging)
- X-ray of flat bones
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and lymph nodes
- Bone marrow puncture, etc.
Comprehensive diagnostics makes it possible to identify even hidden pathologies that have not yet manifested themselves.
Treatment
The treatment regimen and program are developed depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, general current condition, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The main areas of treatment include:
- Antibacterial.
It is required for patients who suffer from a general decrease in immunity and are more susceptible to various infections than others. - Transfusion.
This therapy involves transfusion of blood and its components. - Supportive.
It is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and improving the general well-being of the patient. - Chemotherapy.
Prescribed to disrupt the processes of growth and reproduction, as well as necrosis of malignant cells - Medication.
This treatment is carried out to replenish the deficiency of various elements, correct the functioning of the blood coagulation system and accelerate metabolic processes - Radiation therapy.
Prescribed in combination with other manipulations to combat cancer pathologies
Doctors can also resort to hormonal treatment, bone marrow cell transplantation, and surgical interventions.
Important! As a rule, therapy is complex.
Advantages of visiting a hematologist at MEDSI
- Experienced doctors.
Our specialists have all the knowledge and skills necessary to treat pathologies even in advanced cases. If necessary, endocrinologists, gastroenterologists, etc. are involved in the work. - Comprehensive expert-level diagnostics.
We have modern equipment to conduct any examinations. Laboratory research can be performed in Cito mode (urgent) - Application of modern methods of treatment of various identified diseases.
This increases patients' chances of a full recovery. - Comfort of visiting a doctor.
We have ensured that there are no queues and offer to make an appointment for a consultation at a convenient time.
If you want to consult a hematologist, just contact us in any convenient way.
Consequences of increased hemoglobin in women
High hemoglobin levels are dangerous for women due to complications that affect the functioning of various systems and organs. Thus, an increase in blood viscosity leads to the formation of clots, which can cause bleeding, pulmonary thromboembolism, stroke, heart attack or thrombosis. Any of these conditions requires immediate assistance from medical personnel, since it threatens the life and health of the patient.
Hyperhemoglobinemia is especially dangerous for people with chronic diseases of the lungs and cardiovascular system, since their risk of developing thrombosis increases several times. Timely monitoring of Hb level concentrations is necessary during and after treatment of pathologies.
Blood test for hemoglobin at MedArt
The laboratory of the MedArt medical center is equipped with an automatic hematology analyzer DxH 500 Beckman Coulter, manufactured in the USA. This equipment is characterized by increased accuracy when conducting research. The medical staff of our center is highly qualified and well prepared for their work. The result of a general blood test will be 100% reliable and will not raise any doubts in you.
With us, you can take a general (clinical) blood test without spending a lot of time and effort on getting a referral, and then finding out the test results. We guarantee fast and high-quality hematological diagnostics. You can get results within a day, and in emergency situations, according to indications, within 1 hour.
A comfortable and calm environment will help you relax, in this case the test results will not be distorted due to stress or nervousness.
Prevention of elevated hemoglobin
Preventive measures against increasing the concentration of Hb in the blood consist of maintaining a healthy lifestyle:
- cessation of alcohol abuse, smoking and psychotropic drugs;
- maintaining a proper diet;
- drinking large amounts of clean water without gas;
- limiting physical and emotional overload;
- health status monitoring – annual scheduled examinations and maintenance therapy for chronic diseases.