Vaginal candidiasis (better known by its popular name - thrush) is a disease that affects a large number of women. Despite the disease being sufficiently studied, the chronic form of thrush in women is often observed.
Thrush occurs due to an imbalance of microflora in a woman’s vagina, and the causative agent of this disease is the yeast fungus Candida albicans, which belongs to the opportunistic microflora.
Thrush can also affect other parts of the body: the mucous membrane of the mouth, skin and even nails. But the most common is vaginal candidiasis. The fact is that the female vagina, by its nature, is not a sterile environment and serves as a habitat for many microorganisms that maintain normal microflora in a woman’s body. The fungus Candida albicans, the causative agent of vaginal candidiasis, is normally present in the vagina of every woman and maintains its pH balance along with other microorganisms. Under unfavorable conditions, fungi actively multiply, and thrush in women is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms.
This disease also occurs in men, but due to the anatomical features of the structure of the genital organs, female thrush is a more common occurrence.
Risks of getting sick
Candida mushrooms are natural inhabitants of the microflora of the human body. Therefore, there is always a chance of contracting thrush. However, due to physiological characteristics, women are at greater risk of developing candidiasis than men. Above you can see the symptoms of vaginal thrush in women.
Causes
Why thrush occurs is one of the most common questions among women. After all, this problem is very common. Unpleasant sensations arise at the most inopportune moment. This fungal disease destroys intimate relationships and ruins everyday life.
You can become infected with candidiasis from a sexual partner. Especially if a man has obvious signs of this disease or is a carrier of fungi. However, this reason is far from the most common. Much more often, thrush occurs as a consequence of decreased immunity and disruption of the natural balance of the microflora of the genital organs.
There are many factors that provoke the development of vaginal candidiasis in women.
- Changes in hormonal levels during menopause.
- Use of hormonal contraceptives.
- A decrease in the body's defenses as a result of chronic diseases or after infections.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy and before menstruation.
- Use of intimate hygiene products: intimate gels, soaps, shower gels containing a lot of alkali and fragrances.
- Long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids and cytostatic drugs.
- Intestinal dysbiosis, in which fungi can be introduced into the vagina.
- Deodorized tampons and pads cause allergic reactions and disrupt the condition of the mucous membrane.
- Climate change, which entails adaptation to new conditions and water composition.
- Using panty liners. They interfere with air access to the genitals, increasing humidity.
- Vitamin deficiency entails a decrease in the body's resistance and a deterioration in the condition of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics, narrow and tight. The most common culprit for thrush is thongs.
- The diet is rich in confectionery and carbohydrate dishes, strong coffee, carbonated drinks, yeast baked goods, spicy and fatty delicacies, ketchup and mayonnaise.
- Metabolic disorders. A striking example is diabetes mellitus. It not only weakens local immunity, but also increases the amount of carbohydrates in cells, which is a good breeding ground for microorganisms.
- Obesity - favorable conditions for the proliferation of fungi are created in the folds of the body.
- Chronic stress, severe mental and physical stress, overwork, lack of sleep.
- Sexual intercourse with a dry vagina and other actions that can lead to microtraumas on the genital mucosa. Through them, Candida can penetrate deep into the tissues.
- Chronic stress, severe mental and physical stress, overwork, lack of sleep.
- Smoking causes vasospasm and impairs blood circulation, including in the genitals.
The action of these factors leads to a decrease in the number of lactobacilli that create a protective microfilm. They produce less lactic acid, and an alkaline environment is formed in the vagina. Fungi and other bacteria penetrate the cells of the mucous membrane and thin skin of the external genitalia. There they begin to actively reproduce, feeding on glycogen and destroying host cells. If left untreated, the inflammatory process gradually spreads.
Treatment of candidiasis in women
The treatment regimen for candidiasis in women is always individual and depends on the degree of neglect of the fungal infection, the state of the immune system and test results. It is possible to repeat the treatment course, in combination with antibacterial and antiprotozoal drugs for combined infections.
Preparations for the treatment of candidiasis in women at home:
- Natamycin (Pimafucin) is No. 1 for pregnant women with thrush.
- Nystatin (tablets, vaginal suppositories) has fairly low antifungal activity. Included in combined local remedies (for example, Terzhinan), suitable for combined fungal/bacterial infections.
- Miconazole (combined drug Klion-D) is a fast-acting drug (recovery in 1 week), used for candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis.
- Clotrimazole - for topical use (ointment, suppositories, vaginal tablets). Use at the very beginning of the disease or in combination with oral medications is recommended. Treatment course - 2-4 weeks.
- Fluconazole (Mikosist) - one 150 mg tablet is sufficient for acute manifestations. For prolonged candidiasis, take three times a week.
- Ketoconazole is an effective new generation remedy (ointment, tablets). Treatment of the acute form is 5 days, chronic - 10 days.
Local treatment with home remedies may also include:
- Douching with soda is effective with antifungal therapy, but the duration of use is limited to 7 days (dries out the mucous membrane);
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs with an anti-inflammatory effect (chamomile, sage), when used judiciously (no more than a week), will speed up recovery, but are not a panacea for thrush.
During treatment, abstinence from sexual intercourse is required. If a partner has symptoms of a fungal infection, mutual treatment is necessary.
Symptoms of candidiasis in women
The pathology is characterized by specific manifestations that allow the disease to be quickly and accurately diagnosed.
As a rule, a woman herself can determine the presence of candidiasis (see photo) by the following symptoms:
- Pain and discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse. This symptom is due to a decrease in the protective functions of the mucus of the urethra and vagina;
- Burning itching in the genital area. It is worth noting here that experts categorically prohibit scratching the affected area too much, as there is a risk of damaging the inflamed layer of the mucous membrane. In this case, favorable conditions are created for the penetration of fungi into deep tissues. In addition, when scratching, vaginal discharge can fall on a healthy surface, which will cause additional inflammation and spread of the disease;
- Vaginal discharge, which can be described as “cheesy” (hence another name for the disease “Thrush”). The discharge is usually clearly visible on dark-colored underwear and consists of mucus with many white dense lumps;
- A specific smell from the genitals, which has a slight sour milk tint. As a rule, the smell is noticeable only by the patient herself, but this is enough to become a tangible problem for a woman. On a subconscious level, the patient is afraid that the people around her may also feel it, hence the symptom of candidiasis in women such as emotional imbalance.
If a woman, having suspected the development of candidiasis, promptly sought help from a specialist and faithfully followed all his recommendations, the prognosis of the disease is very favorable. But, if the patient does not pay attention to the symptoms of the disease for a long time or ignores the doctor’s instructions, the fungi continue to actively multiply.
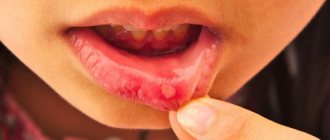
How and with what to treat thrush in the mouth
Since candidiasis often develops as a secondary disease1, treatment of oral thrush requires an individual approach. What do we have to do?
1. Eliminate the factors that contributed to the appearance of oral mycosis
To do this you need:
- cure diseased teeth and gums, relieve exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- replace old “outdated” removable dentures with new ones, follow the rules for using and processing dentures;
- every time after using inhalers with steroid drugs (for bronchial asthma), rinse the mouth and gargle with water6;
- take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- use toothbrushes with soft bristles, toothpastes, and mouthwashes with an anti-inflammatory effect1;
- follow the rules of caring for a newborn and feeding hygiene (if the disease manifests itself in an infant);
- use formulas that do not contain sugar for artificial feeding of a newborn.
2.Keep a diet
Meals include:
- limiting the daily intake of simple carbohydrates: sweets, flour products, potatoes, rice, legumes, boiled beets and carrots, sweet fruits and dried fruits;
- supplementing the diet with fresh vegetables with a lot of fiber, which contribute to the formation of normal microflora in the intestines and the formation of immunity9;
- consumption of sour berries and lactic acid products, which, due to their acid content, hinder the spread of fungi1;
- taking vitamins1 necessary for the normal functioning of the immune system;
- eating enough easily digestible meat and eggs for the normal functioning of the immune system.
3. Carry out local treatment
For oral thrush in both adults and children, treatment may include topical use of drugs with antifungal activity. Moreover, if the fungus affects only the oral cavity, local therapy may be sufficient5 to cope with the problem.
To treat the oral mucosa, today it is recommended5 to use hexetidine preparations, for example, HEXORAL® solution and HEXORAL® aerosol .
HEXORAL® with hexethidine:
- is active against biofilms[7] that are resistant to other drugs, and is harmful to fungi of the genus Candida, which cause oral candidiasis;
- has a high safety profile;
- can be used not only in adults, but also in children from 3 years old8;
- eliminates discomfort and relieves pain7;
- lasts for a long time, up to 12 hours[8];
- Available in the form of a solution and an aerosol, for comfortable use in any situation (for fungal laryngitis in children, it is especially convenient to use the aerosol form of the drug)2.
Important: doctors prescribe general antifungal drugs only if local treatment is ineffective and multiple relapses of candidiasis occur against the background of severe immunodeficiency and/or severe concomitant diseases. In these cases, HEXORAL® can be an addition to the main therapy1, 2, 5.
When treating oral thrush in newborns, there is often no need to use systemic antifungal agents1, 2, 5.
Up to contents
Prevention
To reduce the risk of thrush, you should follow your doctor's recommendations:
- Wear comfortable cotton underwear.
- It is not advisable to use tampons for more than three hours at a time. Panty liners should be changed every two to three hours.
- Maintain intimate hygiene regularly (wash yourself at least twice a day). In this case, it is also advisable to use special gels for the intimate area based on lactic acids. These products will create favorable microflora on the mucous membranes.
- You should not use colored, much less scented, toilet paper or napkins.
- When treating with antibiotics, it is important to take special bifidobacteria to maintain intestinal microflora.
- You should minimize the consumption of sweets and starchy foods.
- In hot weather, you should not stay in a wet swimsuit for a long time.
- Avoid casual sex. If this happens, be sure to use a condom.
- Enrich your diet with fruits and vegetables, as they contain healthy vitamins. You can also take additional vitamin complexes.
- If you notice the first signs of candidiasis, you should immediately consult a doctor before the disease progresses to a more advanced form.
- Visit your gynecologist regularly for preventative check-ups. At the same time, it is also important that the sexual partner undergoes all tests.
- Avoid stress and severe nervous tension.
- Control your weight and prevent obesity.
- You should not self-prescribe oral contraceptives (pills). They must be selected by a doctor. The same applies to taking hormonal medications.
You should not douche unless urgently necessary, so as not to once again wash out the microflora from the vagina. In general, gynecologists do not recommend that women often douche. This is an extreme measure permissible in case of serious inflammatory processes.
Will folk remedies help?
Folk remedies for candidiasis can only provide temporary relief; they cannot fight the causes of the disease. Traditional methods should be used exclusively as auxiliary and only on the recommendation of a doctor.
For vaginal candidiasis, you can wash yourself with a weak soda solution, water with the addition of tea tree oil, eucalyptus, or chamomile decoction (douching is not recommended, especially for expectant mothers). You can use the same products to rinse your mouth if candida has become active in it, or wipe the skin affected by the fungus. For intestinal candidiasis, you can drink a decoction of wormwood root or tincture of juniper fruits.
Allergic forms of the disease
When the disease occurs, a high degree of sensitization of the body to yeast-like fungi and their metabolic products is recorded. Candidamicids (levurides) appear on the skin - a secondary allergic rash. The rashes are polymorphic, often in the form of erythematous-squamous edematous spots, less often - bullous or urticarial. Sensitization develops during disease, candidate carriage, and penetration of fungal metabolic products into the human body through the respiratory tract. The condition is aggravated by irrational antibiotic therapy and hypovitaminosis.
- With the development of candidal allergy of the respiratory system, patients experience laryngospasm and laryngeal edema, leading to acute stenosis.
- With allergic bronchopulmonary candidiasis, patients develop bronchial asthma and asthmatic bronchitis.
- Gastrointestinal allergies occur in the form of enterocolitis, spastic or ulcerative colitis, and damage to the biliary tract.
Candida carrier
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida are opportunistic flora. They occur in 60 - 80% of healthy people. Candidiasis can be transient, short-term, long-term and chronic. No clinical symptoms are noted.
- Transient candidiasis lasts for several days. Fungi are released once. In crops, colonies are found in small numbers - from single to several dozen.
- Short-term candidiasis is considered to be 3-4 weeks. The number of colonies in crops ranges from several tens to hundreds.
- Candida carriage for more than 3 months is considered long-term.
- Candidiasis that continues for many years is considered chronic.
Individuals with long-term and chronic candidiasis may develop candidiasis.