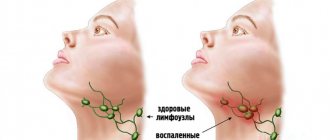
To the reference book Enlarged lymph nodes signal the development of an inflammatory pathology in the body or may be a consequence of excessive growth of lymphoid tissues (lymphoproliferative diseases, hyperreactivity of the immune system).
Author:
- Oganesyan Tigran Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
3.83 (Votes: 6)
Lymph nodes are peripheral organs of the lymphatic system, the main task of which is to provide a natural filter for lymph and the body's immune defense. In the lymph nodes, lymphatic fluid is filtered from microorganisms, atypical cells and other antigenically foreign particles. In this case, an immunological reaction develops, during which the formation and maturation of immune cells that are capable of destroying foreign agents (bacteria, fungi, viruses, parasites, malignant cells, foreign inclusions) occurs.
Enlarged lymph nodes signal the development of an inflammatory pathology in the body or may be a consequence of excessive growth of lymphoid tissues (lymphoproliferative diseases, hyperreactivity of the immune system).
Inflammation of the lymph nodes can be purulent and non-purulent, depending on the duration of the course - acute and chronic. It can be local (when only a certain group of nodes increases) and generalized (inflammation affects several unrelated groups at once).
Depending on their location, all lymph nodes are combined into the following regional groups:
- cervical, widely scattered along the front and side surfaces of the neck;
- mental, located behind the chin;
- occipital, located at the junction of the neck and skull;
- submandibular, lying in the middle of the lower jaw;
- parotid and behind the ear, located in front and behind the ears;
- axillary, one group of which is located in the thickness of the fiber of the axillary region, and the other is adjacent to the inner surface of the pectoral muscles;
- elbow – on the front surface of the elbow joint;
- inguinal, located in the inguinal folds;
- popliteal, localized on the back surface of the knee joints.
Thus, there are quite a lot of areas where enlarged lymph nodes can be detected. Moreover, with different diseases they increase in different ways. The following may differ: consistency, surface structure, mobility, pain on palpation, and the condition of the skin over them. It is very important to diagnose and identify the root cause of the development of the inflammatory process, which only a certified doctor can handle.
What are lymph nodes
Lymph nodes play the role of biological filters and perform the main task of the lymphatic system to protect the body. Lymph nodes can be called a border post on the path of infection spreading throughout the human body.
Washing all cells and at the same time absorbing fungal infections, viruses and harmful bacteria, lymph is collected in the lymphatic ducts, which, like the circulatory system, are located throughout the body. Moving strictly from bottom to top, the lymph one by one enters the plexus of nodes, where the infection is recognized and urgent measures are taken to eliminate it.
The structure of the lymph nodes
The human body, as an autonomous biological system, is capable of not only functioning, but also protecting itself independently. Lymph nodes located along the lymph flow have a complex structure.
| Node capsule | It consists of connective tissue, permeated with smooth muscle fibers, which give the node the ability to move lymph through contractions. |
| Trabeculae (bars) | They are located like crossbars from the outer capsule to the center of the lymph node. They play the role of a frame together with the fibers. Made up of dense connective tissue |
| Stroma | Reticular connective tissue of the node with cells in the form of processes, the fibers of which form a three-dimensional network. It consists of phagocytes - macrophage cells. |
| Cortex | Divided into superficial and parakarthical (deep subcortical zone). Contains lymphoid nodules and internodular lymphoid tissue. |
| Parocartic zone | Boundary between the cortex and medulla. Contains T lymphocytes and plasmacides. |
| Brain matter | It consists of two structured parts - the medullary sinuses and cords. |
| Sinuses | The space divided by the medullary cords and overlapped by the reticular cells. Contains lymph and macrophages |
| Brain cords | Consist of dense lymphoid tissue of the inner cortex. Contains B lymphocytes and plasma cells with macrophages. |
| Blood vessels | Enter through the entrance gate of the node. From the main artery, capillaries supply capsules, nodules and trabeculae |
| Afferent lymphatic vessels | Lymph is supplied to the lymph node using valves on the curved side of the node. |
| Efferent lymphatic vessels | Located in the hilum area on the concave side, the valves support the unidirectional flow of lymph. |
Macrophages are cells that are capable of capturing and digesting foreign bacteria, dead cell formations, and toxic enzymes harmful to the body. It is in the lymph node that they are trained to recognize foreign components, and retain the memory of them throughout a person’s life.
Lymphocytes are white blood cells found in large numbers in the body of the lymph node. When an infection comes through the lymph flow, lymphocytes immediately begin to eliminate it.
In case of lack of strength, lymphocytes receive a signal from the brain matter to reproduce. In this situation, the node may increase in size, become red, or become inflamed if the infection has affected a large part of the lymphatic system.
Rules for preparation before performing an ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes
Special preparation is not needed, however, there are general rules regarding the days of the menstrual cycle when the study will show the most informative and objective results. At the end of menstruation, the ducts are restored, and at the beginning of the cycle, glandular structures develop and branch. During ovulation, the gland begins to prepare for possible conception, so there is a noticeable swelling and increase in size. Experts recommend performing an ultrasound before ovulation. It is at this time that the mammary glands do not swell (not edematous), and the structure and tissues are best visible.
Optimal schedule for:
- 7-14 days with a menstrual cycle that lasts more than 28 days;
5-12 days with a 28-day cycle.
When there are urgent indications for diagnosis, ultrasound examination is performed regardless of the day of the menstrual cycle.
What do lymph nodes look like?
In the human body, the number of lymph nodes is strictly individual, but their number is more than 600 and groups of lymph nodes are more than 150. Lymph nodes can be single (in the knee joint), in the form of a chain (cervical region) or a cluster of 10 - 20 pieces at a time (armpit) .
The shape of lymph nodes can change not only due to the presence of diseases, but also as the body ages. If at a young age the lymph node normally has an oval shape closer to a circle, then over the years it stretches out and has an oblong appearance.
Also, over the years, the number of lymph nodes itself decreases. Some die off due to damage to the lymphatic ducts, others grow together into one large or several medium-sized nodes after illness. Only the lymph nodes located in the abdominal cavity do not change in their number, and throughout life they carry out their load, supporting a person’s vital functions.
Upon palpation, the lymph node is difficult to detect. Normally, its size does not exceed 0.5 cm. In a healthy state, they are soft, mobile and do not cause pain to the touch.
Benefits of breast ultrasound
Among the main advantages of this diagnostic method:
- affordable price;
- the ability to adjust and control the treatment process at any stage;
- no absolute contraindications;
- painlessness;
- high information content and safety;
- efficiency of carrying out and obtaining results.
The absence of restrictions on the number of tests (can be used an unlimited number of times) is another significant advantage of this diagnostic method. And due to the absence of radiation exposure, the procedure is indicated for use by people of absolutely any age.
Groups of lymph nodes
The location of lymph nodes on the human body is the key to the safety of his health. Collected in groups, they have the opportunity to more thoroughly cleanse the lymph, and at the same time increase the body’s immunity. Based on their location, they are classified as external and internal.
Location of lymph nodes on the human body by group
The largest of them are:
- In the groin area, symmetrically on both sides of the pubic bone.
- In the armpits.
- Submandibular zone.
- Cervical region.
- Sternal region.
- Abdomen.
External lymph nodes
The lymph nodes of the outer group are located directly under the skin, and can be palpated when they become enlarged when fighting infection or inflammation.
- The lymph nodes in the neck and head most often attract attention since viral infections primarily affect the larynx, trachea or ears. Severe caries can also be the root cause of enlarged submandibular lymph nodes. All of them guard brain activity and can significantly increase in size in the fight against viral infection.
- Superficial lymph nodes located in the groin can be detected by palpation after hypothermia, viral or sexually transmitted infections of the pelvis.
- The axillary lymph nodes have many branches. They are responsible for several areas and require great care when hygienizing the armpits. Associated with a large group of lymph nodes in the chest area, back and arms. One of the main places for removing waste.
- The elbow and knee lymph nodes are located at the junction of the muscles. At the movable part of the joints. Since human limbs are the most traumatic places in the body, they are the first to become susceptible to infections and bacteria.
Internal lymph nodes
The nodes of the internal group play an important role in the functioning of the abdominal organs. Lymph nodes located in the cavity along the abdominal aorta, next to the spleen and liver, are responsible for their cleansing function. They cannot be palpated, and diagnosis is carried out using MRI or ultrasound for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and suspected lymphadenitis.
The most important of them:
- Mesenteric - a group of lymph nodes in the area of the connection between the intestine and the peritoneum.
- Intrathoracic – responsible for the outflow of lymph from the trachea, bronchi, lungs and heart.
- Pelvic - internal and external lymph nodes of the iliac zone, including lymph nodes of the sacral part.
The nodes located on the walls of various cavities are called pariental, and the surrounding internal organs are called visceral.
Classification
Acute lymphadenitis is accompanied by pain in the area of the cervical lymph nodes
Regional lymph nodes are classified by location:
- Inguinal: legs, abdominal wall, buttocks.
- Axillary: arms.
- Cervical: head, face, neck.
- Mediastinal: breast (breast).
- Para-aortic: abdominal organs.
According to the clinical course, lymphadenitis is distinguished between acute (up to 4 days) and chronic (4-6 days). Acute inflammation of the upper respiratory tract is usually often accompanied by inflammatory swelling of the cervical lymph nodes. Chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract can also cause its enlargement. Inflammation in other organs is less often manifested by enlarged lymph nodes.
Lymphoma is staged according to the Ann Arbor classification. There are 4 stages, which are characterized by varying involvement of lymph nodes and organs outside the system in the malignant process. There are also asymptomatic and symptomatic forms of lymphoma.
What functions do lymph nodes perform?
The location of lymph nodes on the human body ensures the widespread movement of lymph, while performing vital functions in the human body:
- Protective - lymph with foreign elements collected from a certain area of the body enters the lymph node. In the lymph node it is destroyed with the help of lymphocytes and macrophages.
- Immune – in the lymph nodes, not only the fight against harmful formations occurs, but also the recognition of viruses, bacteria and infections. It is in the lymph nodes that their genetic code is stored, and lymphocytes learn to recognize these types of infections for their further destruction.
- Barrier – cancer cells are not only suppressed in their development, but also remain in the node for storage, preventing them from entering the bloodstream.
- Hematopoietic - it is in the lymph nodes that lymphocytes are formed that can resist various infections. Immune cells formed in the medullary space of the lymph node participate in the process of bone marrow hematopoiesis.
- Metabolic - a large number of lymph nodes located on the intestinal walls absorb the lipid components of food with the help of villi.
- Drainage – collects excess fluid from the intercellular space and removes it from the body.
Layout of lymph nodes
The location of lymph nodes on the human body corresponds to the following scheme: moving from the tips of the toes, lymph drains the entire body, while the lymph nodes contribute to its movement, cleansing the lymph and filling the blood with immune cells.
Lymph nodes of the head and neck
The cervical lymph nodes are the border on the threshold of the movement of infection into the brain. The oral cavity is the place where the majority of viruses, bacteria and infections enter the body.
In the cervical region, the lymph nodes are located in different groups, which are separately classified:
- Submandibular - increase in case of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
- The chin are protected by the cranial bone and cannot be palpated.
- Parotid (posterior and anterior) - painful and enlarged with otitis, chickenpox, ENT diseases.
- Tonsillar – with inflammation of the tonsils and tonsillitis, they increase at the end of the lower jaw.
- Superficial and deep cervical nodes - the posterior ones, when inflamed, are palpated along the cervical vertebrae, the anterior ones in the area of the larynx.
- Occipital - at the site of attachment of the spine to the skull.
- Jugular - surround the jugular vein in the interclavicular cavity.
The salivary glands are the excretory duct of the lymphatic system. With the help of the submandibular lymph nodes, waste enters the oral cavity for further processing in the intestines. Adenoids are also lymph nodes that become inflamed in the presence of not only viral manifestations, but also staphylococcal infections.
Group of axillary lymph nodes
Responsible for cleansing and circulating lymph in the chest area. They are located deep in the armpit.
They are located in the form of a group of nodes connected to each other, but at the same time:
- the anterior ones, located closer to the pectoral muscle, filter lymph from the thoracic region and mammary glands;
- the posterior ones cover the subscapular area of the back and its superficial lymphatic vessels;
- The lateral lymph nodes in this group encircle the axillary vein and filter lymph coming from the upper extremities.
Enlarged axillary lymph nodes in women are often an indicator of the development of mastopathy of the mammary glands. It is known that with the help of the sweat glands of the armpits, up to 50% of toxins are removed from the body by the lymph nodes.
Inguinal lymph nodes
One of the groups of lymph nodes that guard the spread of infection from the genitals, lower extremities and pelvic organs. They are located in the folds of the groin area and can be palpated; if they increase, they indicate an inflammatory process, a viral infection, or an exacerbation of a herpetic infection of the genital organs.
They actively participate in the process of excretion through the vagina in women and the urethra in men.
Popliteal lymph nodes
Large lymph nodes located at the attachment point of bones and muscles under the kneecap. The first from the beginning of the movement of lymph on the human body. Responsible for the lower limbs.
Stagnation of lymph from a sedentary lifestyle can cause swelling of the legs and bursitis. When the popliteal lymph nodes are blocked and inflamed, the inflammatory process spreads to the joints and becomes the cause of arthritis.
Lymph nodes of the chest
The group of lymph nodes of the mediastinum (chest) is divided into two subtypes:
- parietal – rear and anterior;
- intrathoracic visceral - anterior and posterior mediastinal nodes.
The posterior group of parietal nodes includes intercostal nodes, as well as nodes located on the anterior and lateral parts of the spine. The anterior ones surround the thoracic artery.
The outflow of lymph from the heart muscle and lungs is controlled by tracheobronchial groups of nodes. In the thoracic region, the purified lymph mixes with the blood, flowing into the superior vena cava. The thoracic duct is the main one; lymph flows through it up to 6 times a day.
Lymph nodes in the abdominal cavity
The intestine is the site of a large concentration of lymph nodes, which are interconnected and located so closely that inflammation of one inevitably leads to complications in the functionality of the neighboring one.
United in the retroperitoneal subgroup (mesenteric nodes), they intertwine all vital organs and support their vital functions:
- Mesenteric nodes - filter lymph from the area of the posterior abdominal wall.
- Paraaortic - entwines the abdominal aorta.
- Paracaval - located along the entire path of the vena cava.
- Parapancreatic - a group of lymph nodes that support the functioning of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
The intestinal lymph nodes actively participate in lipid metabolism, and also dump neutralized toxins and poisons into it to remove them from the body. It is in the lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity that 90% of immune cells are formed, so diseases of the gastrointestinal tract cannot be ignored. The intestinal lymphatic system reacts acutely to digestive problems.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes: symptoms and causes
The location of the lymph nodes on the human body is so organic that it allows the lymphatic system to keep under control all the vital organs and functions of the human body. If the threat is great and the spread of viruses or infections has become threatening, the lymph nodes may increase in size and become inflamed due to overload.
Inflammation may be accompanied by:
- High temperature.
- Enlargement of one or the entire group of lymph nodes.
- Redness of the skin at the location of the lymph node.
- Aching pain and itching.
- Aches all over the body.
The main causes may be not only acute respiratory diseases, but also sluggish chronic processes. Experts first of all recommend removing the source of infection to cause inflammation of the lymph node.
For example:
- with tonsillitis, the submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged;
- behind the ears the nodes become inflamed due to otitis media, severe caries, sinusitis and sinusitis;
- at the same time, inflamed nodes in front and behind the auricle can indicate to the doctor the symptoms of rubella;
- with herpes type 2, the lymph nodes in the groin become inflamed;
- inflamed lymph nodes above the collarbone require immediate examination of the lungs and chest organs;
- axillary nodes can become inflamed with mastopathy.
- enlarged nodes in the abdominal cavity may be a consequence of viral intestinal infections.
If the lymph nodes are enlarged for several days or are painful to the touch, you should consult a doctor and get tested to rule out diseases of the lymphatic system.
Enlargement of deep internal lymph nodes (especially the abdominal cavity) is difficult to diagnose. Their symptoms are often similar to respiratory diseases or poisoning, so timely diagnosis (ultrasound, biochemical blood test) helps make a diagnosis in a timely manner.
Contact our clinic!
“Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic” offers you consultations with doctors of the highest category, constantly developing in their specialization and working with advanced diagnostic and therapeutic equipment. A quick and competent diagnosis of enlarged lymph nodes is a guarantee of successful recovery with minimal risk of exacerbations. To make an appointment, you can leave an online application on our website or call us by phone. You should not postpone a visit to the doctor, as a protracted inflammatory process can lead to negative health consequences.
How to keep lymph nodes healthy
The movement of lypha in the human body is many times slower than that of blood in blood vessels (blood completes a full circle in 25 seconds). Taking care of the lymphatic system is the key to health.
- The skin helps the lymph remove toxins from the body, so any water procedures that cleanse its surface help the functioning of the lymph nodes. This especially applies to bath procedures.
- Lymph nodes under the kneecap and on the elbow joint are the first barrier to infection and bacteria in case of injury to the arms and legs. For this reason, even minor injuries should not be ignored. Disinfection will make it easier for the lymphatic system to work.
- The axillary lymph nodes are one of the places where infection and waste are removed from the body into the external environment. Long-lasting deodorants clog pores and interfere with the functioning of lymph nodes. Upon returning home, it is necessary not only to remove makeup from cosmetics, but also to wash off the deodorant without interfering with the lymphatic system to cleanse the body.
- With viral or chronic diseases of the throat, the submandibular lymph nodes often become inflamed in an attempt to prevent the spread of infection throughout the body. Applying compresses or heating enlarged lymph nodes with a lamp is strictly prohibited.
- Lymph needs water. When the body is dehydrated, protozoa, fungi and infections can progress in the lymph. To facilitate the functioning of the lymph nodes, it is necessary to maintain water balance.
- Having mastered the methods of deep breathing with the diaphragm and abdomen, you can remove congestion in the lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity.
The well-known expression that movement is the key to life has a scientific basis. Lymph does not have its own heart, and it moves depending on the physical activity of a person. Its stagnation allows the development of various infections to progress. Long hours of sedentary work at a computer must be interrupted by breaks with physical activity.
The location of lymph nodes in all particularly important areas of the human body helps the immune system maintain the vital activity of the body. They require careful treatment.
Article design: Mila Friedan