Lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space and pelvis - treatment of advanced cancer
If the tumor was not detected at an early stage, it begins to spread to other parts of the body. One of the most common “targets” of metastasis are lymph nodes. Moreover, most malignant tumors of the abdominal organs give metastases to nearby parts of the lymphatic system.
This means that, with a high degree of probability, the patient, simultaneously with treatment of the primary tumor, will have to treat metastases to the lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneum and pelvis . In modern conditions, treatment tactics include simultaneous treatment of the primary tumor and metastases to the lymph nodes with CyberKnife ( radiosurgery ), or surgical removal of the affected lymph nodes (if surgical treatment of the primary tumor was performed), as well as radiation therapy of the affected lymph nodes, or those that are highly likely to be affected the tumor process spreads. Chemotherapy is also widely used as a treatment for metastases (including to lymph nodes) .
1.What are lymph nodes?
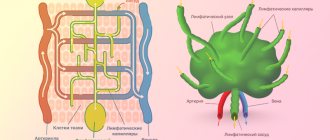
Lymph nodes
- These are small glands that resemble beans in shape and are located throughout the human body. Lymph nodes are part of the lymphatic system, through which fluid (lymph), nutrients move, and substances that the body does not need are removed into the bloodstream.
Lymphatic system
– an important part of the immune system that protects the body from disease. Lymph nodes filter lymphatic fluid (lymph) as it passes through them, trapping bacteria, viruses and other harmful and foreign substances, which are then destroyed by lymphocytes - white blood cells.
Lymph nodes can be single or in groups. The size of lymph nodes can range from very small - the size of a pinhead, to quite large - the size of a large grape. Lymph nodes can be felt in the neck, groin and armpits. In general, lymph nodes are usually not noticeable and do not cause pain when pressed on them. Most lymph nodes in the body cannot be felt at all.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Combined treatment of lymph node metastases
Traditionally, local spread of primary tumor cells into nearby lymph nodes is quite common. If surgery , the patient is recommended to remove nearby lymph nodes . If the lymph nodes are affected by distant metastases (lymphogenous metastasis), their surgical treatment (second surgery) may be difficult due to the severity of the patient's condition or the large volume of intervention required.
In the case of multiple metastases, the patient is indicated for chemotherapy, and for the treatment of single metastases, high-precision radiation therapy IMRT is widely used in world practice. Also, radiation therapy is combined with surgical treatment of the primary tumor, after which most world protocols provide for irradiation of the removed tumor bed and lymph nodes.
Metastases to the lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum, plan for IMRT radiation therapy on a modern linear accelerator
Treatment of metastases in the lymphatic system with CyberKnife
The CyberKnife radiosurgical system is the most effective method of combating cancer metastases
In many cases, in order to treat metastases to the lymph nodes, it is not necessary to use surgical intervention, which is associated with the need for anesthesia, damage to healthy tissue during access to the metastasis, as well as a recovery period during healing. Such a bloodless alternative to traditional surgery is stereotactic radiosurgery, implemented using the CyberKnife system.
There is no clear recommendation that any lymph node metastasis should be treated with CyberKnife. In some cases, treatment of metastases in the lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space and pelvis, greater effectiveness can be achieved by radical treatment using a high-precision linear accelerator (IMRT). Therefore, like any other treatment, radiosurgery on CyberKnife for lymph node metastases is prescribed after an interdisciplinary consultation, at which doctors of various specializations consider all aspects of a particular case in order to determine the most effective treatment regimen.
If the patient is indicated for radiosurgery on the CyberKnife, preliminary planning is carried out, during which, based on CT and MRI diagnostic data, a three-dimensional model of the relative position of the affected lymph node, surrounding healthy tissues will be created, and also the nearby body structures into which it is unacceptable will be taken into account. supply of ionizing radiation.
During each of the treatment sessions (fractions), CyberKnife, based on the treatment plan, will deliver many single beams of ionizing radiation, at the intersection of which a high-dose zone will be formed, corresponding to the shape and volume of metastasis in the lymph node. In addition, treatment of metastases using CyberKnife may be included in a fraction (session) for the treatment of the primary tumor or other metastases.
As a rule, the cost of treatment with CyberKnife is lower than with surgery, because there is no need for anesthesia or recovery period.
2. Why does lymph node enlargement occur?
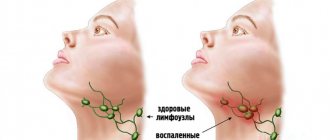
Often, single lymph nodes become painful and swollen due to various injuries, infections, or tumors developing in or near the lymph nodes. Depending on which lymph nodes are inflamed and swollen, the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes
:
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, under the jaw, or behind the ears
usually occur due to a cold or sore throat. Enlarged cervical lymph nodes can occur after injury - a cut or bite near the gland, or due to swelling and infection of the mouth, head and neck; - Inflammation of the lymph nodes under the arm
(axillary lymph nodes) occurs due to injury or infection of the arm. In rare cases, the lymph node under the arm becomes enlarged due to breast cancer or lymphoma; - Lymph nodes in the groin
become inflamed, painful, and enlarged from injury or infection of the leg, groin area, or genitals. In rare cases, the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin is testicular cancer, lymphoma or melanoma; - Inflammation of the lymph nodes above the collarbone
(supraclavicular lymph nodes) can occur due to an infection or tumor in the lungs, chest, neck, or abdomen.
Visit our Therapy page
general characteristics
Enlarged lymph nodes are soft, tight-elastic or dense round formations that can be felt under the lower jaw, in the neck, axillary area, groin and other places.
The surface of the lymph nodes can be smooth or bumpy. Often the increase is preceded by acute infectious and inflammatory processes (ARVI, sore throat, pulpitis), trauma with skin damage, vaccination. Sometimes changes in the lymph nodes are detected by chance by the patient or doctor during a preventive or advisory examination. Lymph nodes are said to be enlarged when their density, surface and mobility change, and their dimensions exceed 1 cm (for elbow formations - 0.5 cm, for inguinal formations - 1.5 cm). When palpated, the nodes can be both painful and painless. In addition to lymphadenopathy, skin manifestations (elements of rash, redness of the skin), fever up to 38 ° C and above, prolonged low-grade fever, complaints of fatigue, sweating, heaviness in the left or right hypochondrium caused by an enlarged spleen and liver are possible.
The reason for contacting a doctor is the independent detection of large painless lymph nodes, sharp pain in the lymphoid tissue when trying to palpate, a combination of lymphadenopathy with other pathological signs - rash, hyperthermia, weight loss, fatigue. Particular concern should be caused by lymph nodes measuring 2-3 cm, which have enlarged for no apparent reason, are located in several zones and persist for more than 2 months.
3. Diseases leading to inflammation of the lymph nodes
If the lymph nodes become inflamed and enlarged in more than one area of the body, it is called generalized lymphadenopathy.
This inflammation of the lymph nodes is caused by:
- Viral diseases such as measles, rubella, chickenpox or mumps;
- Mononucleosis, the symptoms of which are fever, sore throat, fatigue, as well as the viral infection cytomegalovirus that causes similar symptoms;
- Bacterial diseases such as strep throat (caused by streptococcus bacteria) or Lyme disease (a bacterial infection spread by certain types of ticks);
- Side effects from taking phenytoin, a medicine used to prevent seizures;
- Side effects from the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine;
- Cancer - leukemia, Hodgkin's disease and lymphoma;
- AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome;
- Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Classification
When determining the forms of lymphadenopathy, the location of enlarged lymph nodes is primarily taken into account. Lymphoid tissue is the main protective barrier against the spread of infectious pathogens and tumor cells. Therefore, the location of altered lymphatic formations facilitates the diagnosis of the disease that caused the lymphadenopathic reaction. Depending on the localization of the process, the following are distinguished:
- Enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes
. Characteristic of pathological processes in the head and neck area - diseases of the eyes, ENT organs and paranasal sinuses, skin damage. Submandibular lymphadenopathy often signals dental problems and chronic tonsillitis. - Enlarged cervical lymph nodes
. Usually observed with respiratory infections, oral pathology, infectious mononucleosis, late stages of tuberculosis. Cervical nodes can be affected by lymphomas, lymphogranulomatosis, metastasis of thyroid cancer, lung cancer. - Enlarged supraclavicular lymph nodes
. Most often due to tumor causes. Detection of an enlarged node on the right is pathognomonic for cancer of the esophagus and lungs. The left lymph node is affected by malignant processes in the abdominal cavity, pelvis, and retroperitoneal space. - Enlarged axillary lymph nodes
. Inflammatory lesions are possible in the presence of wound infections, cat scratch disease, and brucellosis. Damage to the nodes of the axillary group is typical for breast cancer, melanoma of the upper extremities, and the installation of silicone breast implants. - Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes
. As a rule, nodes in the groin react to the development of syphilis, gonorrhea, chancroid, and other genital infections. Inguinal lymphadenopathy is also a sign of malignant lesions of the pelvic organs, lymphoma, and bubonic plague.
Somewhat less frequently, lymph nodes of other groups are involved in the process - submental, cubital (in the area of the elbow), parotid, occipital, jugular. During a routine instrumental examination, an increase in internal lymph nodes can be determined - intrathoracic (mediastinal), bronchopulmonary, para-aortic, splenic, mesenteric, retroperitoneal.
In the diagnostic plan, it is important to take into account other criteria for the classification of lymphadenopathy - the characteristics of altered lymphoid formations, the extent of the lesion. This approach allows us to assume the type of pathological process occurring in the involved nodes and the body as a whole. Important criteria for the classification of enlarged lymph nodes are:
- Dimensions
. With I degree lymphadenopathy, the diameter of the affected formations is 0.5-1.4 cm, with II degree - 1.5-2.4 cm, and with III degree - 2.5 cm or more. A significant and prolonged increase in the size of lymph nodes is more typical for malignant processes. - Soreness
. Intense pain is often caused by inflammation of the lymph nodes, especially acute purulent lymphadenitis. Formations that have undergone malignant degeneration are often painless, except in cases of hemorrhage into the necrotic center. - Density
_ Enlarged, inflamed lymph nodes are usually soft; when they suppurate, fluctuation (fluctuation of fluid) is felt during palpation. The stony consistency of the formations is typical for the metastatic process, and tight elasticity is typical for lymphomas. - Communication with each other
. A pathological formation of lymph nodes that can be felt as a single unit and move together is called a conglomerate. Lymph nodes fused together are detected in tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, lymphogranuloma venereum, lymphomas and metastasis. - Quantity
. It can affect either one or two or several nodes in one zone. In the first case, they talk about single enlarged nodes, in the second - about local lymphadenopathy. The more active the process, the more formations are affected, however, with metastasis, one large node is often detected. - Prevalence
. With local lymphadenopathy, single nodes are identified in one area, with regional lymphadenopathy - several formations in 1-2 adjacent zones. A generalized (widespread) process is characterized by damage to lymphatic structures in three or more areas.
Taking into account the pathogenesis, enlargement of lymph nodes can be primary (systemic), secondary (reactive) and inflammatory. Primary polyadenopathies develop with systemic malignancy of lymphoid tissue (leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma) and benign processes (sinus histiocytosis). Reactive lesions are a response to another pathology (infection, immune disease, proliferation of tumor cells, metabolic disorders). Inflammation (lymphadenitis) occurs when infectious agents multiply in the tissue of the node.
4.Treatment of lymph nodes
Treatment of swollen lymph nodes involves treating the cause of their enlargement, swelling and pain. For example, a bacterial infection is usually treated with antibiotics, but a viral infection often goes away on its own. A more serious case is cancer. If there is reason to suspect that enlarged lymph nodes are associated with oncology, a biopsy may be performed and, of course, a full examination by a good doctor is necessary.
In any case, if the enlarged lymph nodes do not go away in about a month and their size does not decrease, you should consult a doctor. In general, lymph nodes may remain swollen long after the infection has passed. This is especially common in children.
What are the reasons?
Among the infections that can cause mesadenitis in a child are bacteria such as:
- coli;
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- salmonella;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
These may also be the following viruses:
- enterovirus;
- adenovirus;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- cytomegalovirus.
Doctors often associate the development of mesadenitis in children with the presence of diseases such as:
- pneumonia;
- flu;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- tonsillitis;
- bronchitis.
After severe infectious diseases, a child is often diagnosed with reactive mesadenitis. In addition, this pathology often occurs in children as a specific reaction to vaccinations or uncontrolled use of certain types of medications.
Causes and features of enlarged lymph nodes in various diseases
Most often, enlarged lymph nodes are a marker of immune or infectious diseases, including:
- acute respiratory viral infections (pharyngitis, tonsillitis) are the most common cause of enlarged lymph nodes; they are moderately painful, dense to the touch, their mobility is preserved;
- lymphadenitis - develops in the presence of a purulent process in the body, the lymph nodes are significantly enlarged, motionless and sharply painful on palpation, the skin over them turns red;
- tuberculosis - most often changes become noticeable in the lymph nodes of the chest cavity, less often in the neck; at first, the lymph nodes are moderately painful, but as the underlying disease develops, they adhere to each other and to the surrounding tissues, threatening to form a serious fistula;
- rubella – the cervical, parotid, and occipital nodes may enlarge; they are moderately painful and do not adhere to surrounding tissues;
- syphilis - an increase in nodes in the groin, not always painful, which is later replaced by the development of hard chancre on the genitals;
- HIV infection – lymph nodes of all groups enlarge, while for a long time other symptoms of pathology in the body may not be detected;
- autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis, autoimmune thyroiditis) - lymph nodes of all regional groups can enlarge;
- oncological pathologies - lymph nodes enlarge either due to metastasis from malignant neoplasms, or from diseases that attack the lymphatic system itself (Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas).
Taking certain medications (for example, hydralazine) can also cause changes in the size of lymph nodes. Another reason may be the presence of silicone prostheses in the body, which the lymphatic system perceives as a foreign body and gives a signal about the development of an inflammatory process. We can talk about both breast implants and prosthetic arms, legs and other parts of the body.