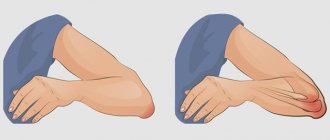
The hand is a part of the human hand, which consists of the bones of the wrist, metacarpus, fingers (phalanx) and the soft tissues that are located around them. Complaints that the hands hurt are very common, since they are susceptible to injury, infection, and disease.
If you are bothered by pain in your hand, you don’t have to endure it! Contact the CELT Pain Clinic!
Pain in the left or right hand can be caused by a disease of the musculoskeletal system or nerves, and if its cause is not addressed in a timely manner, the consequences may be irreversible.
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic - 4,500
Make an appointment
Types of pain in the hands
- Constant and periodic pain.
Pain may always be present or develop under certain circumstances. So, with injuries, discomfort is most often felt when pressing on the hand or moving the joint. And in case of inflammatory or degenerative processes, it can last for hours even after the cessation of exposure.
- The discomfort may be mild or severe.
The nature of burning unbearable pain is usually noted with gout. For carpal tunnel syndrome, dull pain is more typical.
- Painful sensitivity may appear on one hand or be felt symmetrically in both hands.
Pain in the left hand is often characteristic of coronary heart disease. With gout, painful sensations on the right hand will eventually spread to the left limb.
But it is impossible to determine the cause of pain only by its nature or location, since symptoms for various diseases can be similar. For example, pain in the bend of the wrist can be both a consequence of injuries and a symptom of pathologies of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Because of this, it is difficult for a person to know which doctor to contact about pain. In such cases, you should start with a therapist.
How to understand that you have arthrosis of the hand
The disease goes through several stages. To detect it as early as possible, you need to know the signs of each of them:
Stage 1 – there are periodic aching pains at night, you will feel tension in the muscles, and you may notice slight swelling. Fingers move without difficulty.
Stage 2 – the pain bothers you both at night and during the day, especially after putting pressure on your fingers. When moving, a crunching sound appears. The muscles of the affected fingers begin to atrophy and increase in volume. Bone growths are formed - Heberden's nodes.
Stage 3 – the affected fingers are already severely limited in mobility. The surface layer of the interphalangeal joints is completely destroyed, osteophytes merge into a single whole, pain is constantly present.
Arthrosis and arthritis of the hands have many common symptoms, but they are completely different diseases. What are their differences? Comment from the famous doctor, Professor Bubnovsky:
Treatment
Pain in the hand is a symptom, not a separate disease, so treatment is not limited to the use of painkillers and ointments. These methods only temporarily reduce pain, but do not get rid of their cause. As a result, the disease progresses, leading to loss of mobility and joint deformation. Dr. Bubnovsky’s centers help relieve pain and restore joint mobility.
The basis for the treatment of pain in the hands is the unique method of Professor Bubnovsky - modern kinesitherapy. Such treatment not only eliminates discomfort, but also normalizes blood circulation, relieves inflammation and restores affected functions.
Exercises using the Bubnovsky method are simple, accessible and have virtually no contraindications. Thanks to gymnastics, blood flow in the tissues of the joint improves, its mobility increases, and stiffness and tension in the hand go away.
The treatment program is prescribed by a kinesiotherapist after examining the patient and a series of myofascial tests. In this case, not only the state of hand function is assessed, but also the general condition of the musculoskeletal system. This approach makes it possible to prescribe personalized and most effective treatment. Classes are conducted under the guidance of an instructor. He controls the technique of movement and breathing, monitors the body’s reaction.
Exercises are performed in a certain sequence using various exercise equipment and devices. For narrow-local exercises, a decompression wrist simulator is used. Exercises on it strengthen your fingers, help eliminate excess tension in the hand and restore tissue nutrition. As a result of stretching the hand, the pain goes away.
The treatment is complemented by exercises on the Bubnovsky multifunctional simulator (MTB) and rehabilitation simulators. Exercises on them increase blood circulation in the muscles of the arm, strengthen the joints, and restore their mobility. Strength loads can be supplemented with massage, cryotherapy, electrophoresis and magnetotherapy.
Such an integrated approach affects the root cause of the disease and has a beneficial effect on the entire body as a whole.
Diagnostics
The causes of pain are determined by orthopedic traumatologists. To make a diagnosis, the results of a survey, physical examination, instrumental and laboratory techniques are used. May be assigned:
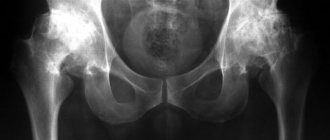
- X-ray of the hand.
Performed in 2 or 3 projections, it makes it possible to diagnose fractures, dislocations, arthrosis, arthritis, osteomyelitis, and neoplasms. - CT scan of the hand.
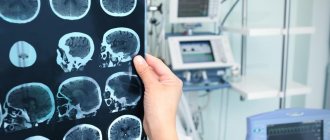
More informative when studying solid structures. Recommended for complex fractures and fracture-dislocations, arthritis, arthrosis, osteoporosis. Allows you to accurately localize the area of damage, assess the nature and extent of the pathological process. - MRI of the hand.
Indicative when studying soft tissue formations. It is prescribed to study the condition of muscles, ligaments, tendons, blood vessels, and nerves. It is used for tendinitis, arthrosis, arthritis, purulent processes, and carpal tunnel syndrome. - Electrophysiological techniques.
They are used for neurological causes of pain in the hand to determine the level of nerve damage, assess nerve conduction, and the condition of muscle tissue. - Lab tests.
They are performed to identify signs of inflammation, specific markers, assess the activity of various organs in systemic pathologies, and study the structure of tissue during histological or cytological analysis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, an examination by a specialist is required.
Prevention
To prevent pain in the hands, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid injury to the upper extremities. Before playing sports, you need to warm up well and do not neglect wrist protection during physical activity.
- Wear mittens or gloves during the cold season. Frequent hypothermia negatively affects the small joints of the hands and can cause the development of arthritis and pain in the hands.
- Do hand exercises. This is not necessarily a complex of physical therapy. It is enough to make normal rotational movements with your hand and stretch your fingers, hands, and wrist from time to time. Use wrist expanders.
- Avoid physical overexertion. For example, when working at a computer for a long time, it is recommended to use special pads for your hands, as well as take breaks during monotonous work.
- Regularly undergo medical examinations and monitor concomitant diseases. Even in the absence of complaints, it is necessary to undergo an examination of the body once a year. Do not wait for complications to develop, but seek medical help at the first symptoms of discomfort.
- Give up bad habits and eat a balanced diet. Caffeine and cigarettes constrict blood vessels, limiting blood supply to the joint tissues of the extremities. Alcohol increases the risk of developing osteoporosis. A lack of vitamins reduces the body's protective functions.
Following these recommendations does not require much effort and helps maintain mobility of your fingers and hands and overall health. Therapy for any disease in its early stages is easier, and the risk of complications is minimal. With an integrated approach and the support of doctors at the Dr. Bubnovsky Center, you can achieve lasting results in treatment - forget about pain in your hands and restore joint mobility.
Surgery for arthrosis of the thumb
Conservative treatment of deformity of the joints of the fingers may be ineffective, then the question of surgical intervention arises.
The most common surgical technique for treating arthrosis deformans of the thumb is trapezectomy. During this operation, the trapezium bone is removed, the same one on which the first metacarpal bone rests and presses. The technique has proven itself all over the world and is one of the most common procedures in hand surgery.
This operation can be performed under local anesthesia, without general anesthesia. It is not painful and there are no risks associated with general anesthesia.
After the operation, there will be a pin fixing the first metacarpal. The arm will be in a cast. After 12-14 days, you can remove the sutures, remove the pin, and replace the plaster with a light and comfortable plastic orthosis. Development of the joint begins after 6 weeks from the date of surgery.
Restoration of function should be expected 2-3 months after surgery. Working with a hand therapist will certainly make your recovery easier.
Symptoms - what are they?
Symptomatic manifestations are determined by the specific ailment that led to wrist pain. The most common manifestations include situations when:
- palms and hands become swollen and numb;
- the affected area burns and itches;
- fingers tremble and tingle, there is a sensation of “goosebumps”;
- The pain intensifies at night or is provoked by excessive physical activity;
- fingers turn out to be weak for simple manipulations of grasping a simple, light object;
- limited movement is felt in the wrist area of the hand.
Such manifestations of the disease are more rarely observed when:
in general, your health worsens and your temperature rises, accompanied by muscle weakness;- redness of the skin of the hands is observed (mainly observed with injuries);
- the hand is in an unnatural position. The consequence of a dislocation may be the presence of articular instability of the joint;
- subcutaneous hematoma, which is often caused by an open fracture;
- there is severe pain during flexion and extension;
- joint destruction is observed;
- it is impossible to perform simple manipulations with the affected hand;
- there is shortness of breath, pain in the chest and heart, tingling, burning and itching in the arm.
The above manifestations are the most common. They may appear in both acute and chronic pain syndrome of the wrist joint. The exact clinical symptoms are determined by the specific disease causing the pain.
Tendonitis in pregnant women and its features
This disease is a frequent “guest” of women who are expecting a child. If there are suspicions, then it is preferable not to do an x-ray or computed tomography during the examination. Any medications that a pregnant woman will take must be prescribed by the attending physician and also agreed with the gynecologist. In this case, self-medication will be dangerous not only for the patient, but also for her unborn child.
When the first symptoms of tendinitis appear, doctors advise limiting yourself to physical therapy, rest, and applying cold compresses to the affected area. If you need to relieve inflammation and reduce pain, ointments based on painkillers are prescribed.
If the problem enters an acute phase, the doctor may resort to immobilization of the joint. Antibiotics may be prescribed, but only if a bacterial infection is found and other treatments have been ineffective. In the most extreme cases, surgery is performed on the joint.