Dislocations, sprains, bruises and ruptures (ligaments, for example) - injuries with damage to muscles and joints.
Such injuries are common companions for people who lead an active lifestyle and play various sports. Often the cause of these injuries is a person’s unpreparedness for a given physical activity - which is why it is recommended to specially prepare for each sports achievement.
1
Treatment of dislocations, sprains, ligament tears
2 Treatment of dislocations, sprains, ligament tears
3 Treatment of dislocations, sprains, ligament tears
However, dislocations, bruises, sprains and ligament tears can also be caused at home. Dislocations of the shoulder and knee joints are most often recorded. A dislocation of the ankle joint, for example, is much less common (usually this is an injury to lovers of high-heeled shoes).
Let's try to figure out how to properly treat dislocations and other injuries.
Symptoms of dislocation
Depending on the type of injury, be it, for example, a dislocated hip, a dislocated leg, or a dislocated shoulder, the manifestations of the disease may differ from each other. So, with a similar problem with the hip joint, received at birth, the gait is often disturbed, the posture is bent, and one leg may even become shorter than the other.
However, there are still general symptoms of dislocation, based on which one can assume a dislocation of a certain part of the body:
- redness of the skin in the affected area;
- intense pain that intensifies when moving the dislocated limb;
- external change in the shape of the joint, an increase in its size;
- increased swelling in the injured area;
- loss of sensation in the limbs (this symptom is possible due to injury to nerve endings);
- difficulty in motor activity;
- increase in body temperature, high fever, chills.
Sprains
Sprains occur in a person if he performs sudden movements with a force exceeding the permissible load on the joint. When a ligament is sprained, there is partial damage or incomplete rupture of the capsule of the ligaments that strengthen the joint.
The ligaments most often affected by sprains are the ankle ligaments (especially when the foot rolls in) and the wrist joint. Somewhat less commonly, this injury affects the ligaments of the knee joint. When wearing high-heeled shoes, a woman often gets her legs turned inward and the Achilles tendon stretched.
Degrees of sprain
The following degrees of ligament damage can be distinguished:
- 1st degree , preservation of the mechanical integrity of the ligament with rupture of individual fibers. The presence of slight edema without hemorrhage is characteristic. The patient may feel moderate pain, with limited movement and support;
- Grade 2 , accompanied by partial damage to the articular capsule of the ligaments, the appearance of multiple fiber ruptures, frequent blood loss and moderate swelling. Difficulty in support, movements are quite painful and limited. Some instability of the joint is revealed.
- Grade 3 , complete rupture of the ligaments, which is marked by severe pain, significant swelling and bruising. When moving, joint instability is felt.
For grade 1 and 2 sprains, conservative treatment may often be sufficient.
For complete ligament ruptures, surgical treatment is used.
Causes
The main cause of dislocation, whether it is a dislocation of the shoulder joint or jaw, is indirect trauma. So, for example, if a person accidentally falls directly on his hand, stretching it forward, then, most likely, it is not the hand itself that will suffer, but his shoulder joint.
Often, damage occurs along with a number of severe bone diseases, as additional complications. These include:
- tuberculosis;
- arthritis;
- osteomyelitis;
- arthrosis and others.
Ligament tears
Ligament rupture is a fairly common type of injury for people whose work involves prolonged physical activity. Most often, ligament rupture accompanies a dislocation or fracture, but it can also be an independent injury.
In accordance with the reasons that caused the injuries, traumatic and degenerative ligament ruptures are distinguished. If the first type of damage can be obtained as a result of injuries, then the second occurs during the aging process of the body.
Symptoms of ligament rupture:
- pain and limitation of joint function (impossibility to straighten and lift the injured arm or leg);
- the appearance of edema, hematoma;
- change in the external contours of the damaged joint (joint instability);
- the occurrence of numbness and tingling in the affected limb.
A special place is occupied by ligament ruptures such as meniscus damage.
When should you see a doctor?
If you suspect you have a dislocated hip or dislocated hip joint, you should immediately seek qualified medical help. Otherwise, there is a risk of aggravating the condition of an already damaged joint.
It is necessary to provide first aid for a dislocation. The joint should be immediately immobilized and a cooling compress applied to it to reduce swelling. If the injured person feels unbearable pain, it is necessary to give him an anesthetic drug. Then you need to transport the victim to the hospital to provide him with proper medical care by an experienced trauma surgeon.
Specialists with many years of qualifications and enormous work experience are ready to accept patients at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) at any time. The multifunctional medical institution is located in the center of Moscow, at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, 10, close to the Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Tverskaya, Novoslobodskaya and Chekhovskaya metro stations.
Diagnostics.
After an accident, the victim must be immediately taken to the traumatology department, and he must not make any leg movements (active or passive). Upon admission of the patient, the doctor performs a detailed examination of the injured limb and takes a complete anamnesis. The main method for diagnosing foot dislocations remains radiography. Only with the help of X-rays can a traumatologist make an accurate diagnosis (determine the type of dislocation) and begin appropriate treatment. In the case of complicated dislocations with fractures, surgical intervention may be required.
Treatment of injury
It includes mandatory repositioning of the displaced joint and returning it to its previous position. The manipulation can be performed under both general and local anesthesia. Finally, a plaster cast is applied to the damaged area.
In addition, there is often a need for additional procedures:
- therapeutic massage;
- recreational gymnastics;
- acupuncture sessions.
In particularly difficult situations, surgery may be indicated. If the cause of the dislocation is a bone disease, you should definitely give it due attention and carefully treat it, otherwise the injuries will recur again and again.
Treatment of joint dislocations and reduction
Treatment of traumatic dislocations consists of reduction (relocation) and fixation of the articular elements. This procedure should be carried out immediately if the patient is in satisfactory condition.
If the dislocation is not corrected as soon as possible, this can lead to a number of complications:
- development of contracture due to contraction of muscle fibers;
- the formation of scar tissue in the joint cavity - usually at the site of a dense blood clot (fibrin).
There are two options for joint realignment:
- open;
- closed.
The open method is used if the closed method is contraindicated for medical reasons. Its essence lies in joint arthroscopy. Through surgery, the doctor removes from the joint cavity coagulated blood and articular elements destroyed due to injury. He then returns the displaced parts to their original position using lever-like movements. This is a painful procedure, so it is performed under general anesthesia. Anesthesia allows not only to achieve pain relief, but also has a relaxing effect on muscle fibers, facilitating the operation.
The closed method involves returning the articular heads to their place without surgical intervention. After reduction, the joint must be immobilized. To do this, a plaster fixing bandage is applied to it for 14–20 days. After reduction, a control x-ray is taken, which shows whether the displaced structures are in the correct position.
Rehabilitation after injury
After the dislocation has been treated at the proper level and the patient has gone home with the doctor’s recommendations, the recovery period begins.
In order to strengthen muscles and bones and quickly return them to their previous condition, it is recommended:
- take a course of restorative massage;
- physical therapy course;
- take up regular swimming;
- do not avoid long walks in the fresh air;
- balance your own diet by consuming enough proteins, fats and carbohydrates required by the body.
Prevention of dislocation of the shoulder joint, jaw or other part of the body consists, first of all, of taking good care of your own health, proper nutrition and regular exercise.
Meniscal tears
The menisci of the knee (internal and external) are a kind of cartilage pads between the bones that protect the articular cartilage and ensure smooth movements when walking.
A meniscus tear is a damage to the cartilage formation, which is accompanied by injury to the structures of the knee joint. Injuries such as cruciate ligament injury and rupture of the collateral ligaments (the lateral ligaments of the knee) often occur simultaneously with a meniscus tear. Meniscal tears are common among athletes, especially representatives of contact sports.
The second reason for damage to the meniscus of the knee joint is degenerative disorders in cartilaginous formations. If the meniscus is damaged, the function of the entire joint deteriorates, pain, swelling, cracking and popping appear when bending the knee.
1 Treatment of dislocations, sprains, ligament tears
2 Treatment of dislocations, sprains, ligament tears
3 Treatment of dislocations, sprains, ligament tears
Carrying out the reduction
The essence of any method of reversing a dislocation is to restore the articular limbs and return them to a physiological position.
At our GMS Hospital center, treatment is performed under anesthesia (depending on the type of injury, scale, location and severity).
The specialist approaches the dislocation carefully and only after complete immobilization of the injured limb. Does not perform any sudden or unnecessary movements, so as not to aggravate clinical symptoms.
Treatment after joint repair should include:
- massage treatments;
- therapeutic exercises;
- acupuncture.
If the dislocation occurs along with a rupture of the vascular or tendon bundle, or a bone fracture, then surgical treatment is indicated; reposition may be necessary to fully restore the functions of the joint.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana
What indications to use
Very often, even before the appearance of pronounced clinical symptoms, you can notice joint deformation during an objective examination. But in most cases, clinical dislocation is manifested by the following symptoms:
- loss of movement and sensation in the injured joint;
- severe pain when performing simple movements, rotation, which intensifies over time;
- feeling of numbness at the site of injury;
- tingling sensation;
- joint deformation, forced position;
- redness in the area of damage, increased local temperature, swelling;
- fever, chills, general condition disturbance;
- pale, cold skin.
If there are several symptoms, the patient should go to a medical clinic for consultation with a doctor.
More about reduction
Dislocation occurs due to physical impact. The complexity of treatment depends on the nature of the dislocation - complete or incomplete, fresh or more than 1 week, with rupture of the vascular or tendon bundle.
Dislocation can occur in any joint - shoulder, knee, elbow, ankle, etc.
According to statistics, the problem is more common in men between 20 and 50 years old. But a dislocation can happen to anyone, in 90% of cases the main cause is an injury (sports, work, industrial, accident).
Trauma (from the Greek trauma - wound) is damage in the human body caused by the action of environmental factors.
There are different types of injuries:
depending on the type of traumatic factor:
1) mechanical,
2) thermal (burns, frostbite),
3) chemical,
4) barotrauma (due to a sharp change in atmospheric pressure),
5) electrical injuries, etc.
6) combined, for example a combination of mechanical trauma and burn;
on the duration of exposure to the traumatic factor:
1) sharp;
2) chronic injuries;
from the circumstances under which the injury occurred:
1) household,
2) production,
3) sports;
Mechanical injuries can be open (wounds) and closed, that is, without violating the integrity of the skin; uncomplicated and with the development of complications - suppuration, osteomyelitis, sepsis, traumatic toxicosis, etc.; isolated (within an organ or segment of a limb), multiple (damage to several organs in one cavity or several segments of a limb) and combined (simultaneous damage to internal organs and the musculoskeletal system).
There are bruises, sprains, dislocations, fractures, compression of tissues and internal organs, concussions, ruptures. They may be accompanied by bleeding, swelling, inflammatory reaction, necrosis (death) of tissue. Severe and extensive injuries are accompanied by shock and are life-threatening.
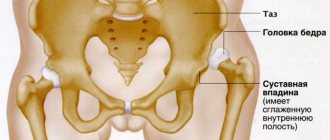
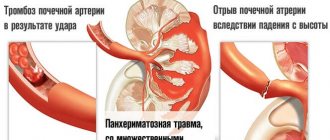
Dislocations
Dislocations are a complete displacement of the articular ends of bones, in which the contact of the articular surfaces in the articulation area is lost. Dislocation occurs as a result of injury, usually accompanied by rupture of the joint capsule and ligaments. This displacement of the ends of the bones occurs more often in the shoulder, less often in the hip, elbow and ankle joints. Even more rarely as a result of bruise.
Signs of dislocation:
Displacement of bones from their normal position in the joint, sharp pain, inability to move in the joint.
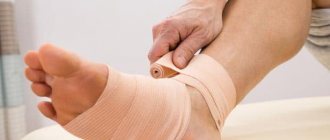
First aid for a sprain:
1) cold on the area of the damaged joint;
2) use of painkillers;
3) immobilization of the limb in the position it assumed after the injury;
4) contact a surgeon.
On the first day after injury
Reduction of a dislocation is a medical procedure ( ! ). You should not try to straighten a dislocation, as it is sometimes difficult to determine whether it is a dislocation or a fracture, especially since dislocations are often accompanied by cracks and fractures of bones.
Bruises
Bruises are injuries to tissues and organs in which the integrity of the skin and bones is not damaged. The degree of damage depends on the force of the blow, the area of the damaged surface and the significance of the bruised part of the body for the body (a bruised finger, naturally, is not as dangerous as a bruised head). Swelling quickly appears at the site of the injury, and bruising is also possible. When large vessels rupture under the skin, accumulations of blood (hematomas) can form.
Signs:
Soft tissues are damaged without compromising the integrity of the skin. Bruise (bruise), swelling (edema).
First aid for bruise:
1) first of all, it is necessary to create rest for the damaged organ.
2) a pressure bandage must be applied to the area of the bruise, giving this area of the body an elevated position, which helps stop further hemorrhage into the soft tissues.
3) to reduce pain and inflammation, cold is applied to the site of the injury - an ice pack, cold compresses.
Sprains and ligament tears
Sprains and ruptures of joint ligaments occur as a result of sudden and rapid movements that exceed the physiological mobility of the joint. The cause may be a sudden twisting of the foot (for example, when landing unsuccessfully after a jump), or a fall on an arm or leg. Such injuries are most often observed in the ankle, knee and wrist joints.
Signs:
1) the appearance of sharp pain;
2) rapid development of edema in the area of injury;
3) significant dysfunction of the joints.
Unlike fractures and dislocations, with sprains and ruptures of ligaments, there is no sharp deformation and pain in the joint area when there is a load along the axis of the limb, for example, when pressure is placed on the heel. A few days after the injury, a bruise appears, and sharp pain subsides at this point. If the pain does not disappear after 2-3 days and you still cannot step on your foot, then a fracture of the ankle joint is possible.
First aid for sprains:
First aid for sprains is the same as for bruises, i.e.
1) first of all apply a bandage,
2) tight bandaging that fixes the joint,
3) applying a cold compress to the joint area, pressure and splint bandages, creating a motionless state.
When a tendon or ligament ruptures, first aid consists of creating complete rest for the patient and applying a tight bandage to the area of the damaged joint.
Fractures
A fracture is a partial or complete disruption of the integrity of a bone as a result of its impact, compression, crushing, bending (during a fall). Fractures are divided into closed (without damage to the skin) and open, in which there is damage to the skin in the fracture area.
Signs:
1) sharp pain, intensifying with any movement and load on the limb;
2) change in the position and shape of the limb;
3) dysfunction of a limb (inability to use it);
4) the appearance of swelling and bruising in the fracture area;
5) shortening of the limb;
6) pathological (abnormal) bone mobility.
First aid for bone fractures:
1) creating immobility of bones in the fracture area;
2) taking measures aimed at combating shock or preventing it;
3) organizing the fastest delivery of the victim to a medical facility.
Rapid immobilization of the bones in the fracture area - immobilization - reduces pain and is the main point in preventing shock. Immobilization of the limb is achieved by applying transport splints or splints made from available hard material. The splint must be applied directly at the scene of the incident and only after that the patient must be transported. In case of an open fracture, an aseptic bandage must be applied before immobilizing the limb. When bleeding from a wound, methods of temporarily stopping bleeding should be used (pressure bandage, application of a tourniquet, etc.).
Tires come in three types:
1) Hard
2) Soft
3) Anatomical
Boards, strips of metal, cardboard, several folded magazines, etc. can serve as rigid tires. Folded blankets, towels, pillows, etc. can be used as soft splints. or support bandages and dressings. With anatomical splints, the victim’s body is used as a support. For example, an injured arm can be bandaged to the victim’s chest, a leg to a healthy leg.
When carrying out transport immobilization, the following rules must be observed:
1) the splints must be securely fastened and well fix the fracture area;
2) the splint cannot be applied directly to a naked limb; the latter must first be covered with cotton wool or some kind of cloth;
3) creating immobility in the fracture zone, it is necessary to fix two joints above and below the fracture site (for example, in case of a tibia fracture, the ankle and knee joints are fixed) in a position convenient for the patient and for transportation;
4) in case of hip fractures, all joints of the lower limb (knee, ankle, hip) should be fixed.
Fractures
Fractures can be closed (without damage to the skin), open (with disruption of the integrity of the skin) and complicated (bleeding, crushing of surrounding tissues). With open fractures (bone fragments are visible in the wound), microbes enter the wound, causing inflammation of the soft tissues and bones, so these fractures are more severe than closed ones.
Signs:
pain, swelling, change in shape and shortening of the limb, the appearance of mobility at the site of injury, crunching of fragments.
First aid for fractures:
fragments, when displaced, often damage blood vessels, nerves and internal organs, so do not move a broken leg or arm under any circumstances. Everything should be left as is, but the damaged bones should be given maximum rest.
In victims with open fractures, do not try to set protruding fragments into the wound or remove fragments from the wound. You need to stop the bleeding, apply a sterile bandage, a clean handkerchief or towel to the wound. Then, carefully, so as not to increase the pain, you should apply a ready-made splint (cardboard, plywood, wood or wire) or one made from improvised means - boards, sticks, pieces of plywood, branches, umbrella, gun) and create rest for the victim and the limbs. The splint must be applied to clothing, having previously covered it with cotton wool, wrapped with a bandage, towel or soft material. After application, the splint must be bandaged or tied with something in three or four places to the body. If a large tubular bone (femur or humerus) is broken, three joints must be fixed with a splint at the same time, and if smaller bones are damaged, it is enough to immobilize the above and underlying joints.
Femur fracture
First aid:
To create rest for the injured leg, splints are bandaged on the outside, from the foot to the axillary region, and on the inner surface - from the sole to the perineum. If the hospital or first aid station is far from the crash site, you need to bandage another splint on the back, from the foot to the shoulder blade. If there are no splints, you can bandage the injured leg to the extended healthy one.
Fractures of the shin bones
First aid:
The splint is applied along the back surface of the injured leg, from the foot to the buttocks, and secured with a bandage in the area of the knee and ankle joints.
Fractures of the bones of the hand and fingers
First aid:
Damaged bent fingers (giving a grasping position to the hand) are bandaged to a cotton roll, hung on a scarf or splinted. Fixing your fingers in a straight position is unacceptable.
Clavicle fracture
Occurs when falling. Damage to large subclavian vessels caused by displaced bone fragments is dangerous.
First aid:
Deso bandage. To create peace, hang the hand on the side of the injury on a scarf or on the raised hem of the jacket. Immobilization of clavicle fragments is achieved with a Deso bandage or by bringing the hands together behind the back using cotton-gauze rings (you can also tie the hands behind the back with a belt).
Fractures of the forearm and humerus
First aid:
bending the injured arm at the elbow joint and turning the palm towards the chest, apply a splint from the fingers to the opposite shoulder joint on the back. If there is no splint, you can bandage the injured arm to the body or hang it on a scarf, on the raised hem of the jacket. Fractures of the spine and pelvis.
A spinal fracture is an extremely serious injury.
Signs:
Severe pain appears in the damaged area, sensitivity disappears, paralysis of the legs occurs, and sometimes urination is impaired.
First aid:
It is strictly forbidden to sit down or put a victim with a suspected spinal fracture on his feet. Create peace by laying it on a flat, hard surface - a wooden board, boards. The same items are used for transport immobilization.
If there is no board and the victim is unconscious, transportation is least dangerous on a stretcher in a prone position. The victim cannot be placed on a soft stretcher. You can - only on a shield (a wide board, plywood, a door removed from its hinges), covered with a blanket or coat, on your back. It must be lifted very carefully, in one step, so as not to cause displacement of fragments and more severe destruction of the spinal cord and pelvic organs. Several people can lift the victim by holding his clothes and acting in concert, on command. If there are no boards or shields, the victim is placed on the floor of the car and driven carefully (without shaking). A person with a fracture of the cervical spine should be left on his back with a bolster under his shoulder blades, and his head and neck should be supported by placing soft objects around their sides. If the pelvic bones are damaged, the victim’s legs are slightly spread apart (the “frog” position) and a thick cushion of folded blanket or rolled up clothing is placed under the knees.
Rib fractures
First aid:
You need to tightly bandage the chest at the fracture site.
Fractures of the foot bones
First aid:
A board is bandaged to the sole.
Damage to the skull and brain
The greatest danger from head injuries is brain damage.
is classified as follows :
1) concussion;
2) bruise (concussion);
3) compression.
Brain injury is characterized by general cerebral symptoms:
1) dizziness;
2) headache;
3) nausea and vomiting.
The most common are concussions, in which the main symptoms are loss of consciousness (from several minutes to a day or more) and retrograde amnesia (the victim cannot remember the events that preceded the injury). When the brain is bruised and compressed, symptoms of focal damage appear: disturbances in speech, sensitivity, limb movements, facial expressions, etc. First aid is to create peace. The victim is placed in a horizontal position. To the head - an ice pack or a cloth moistened with cold water. If the victim is unconscious, it is necessary to clear the oral cavity of mucus and vomit, and place him in a fixed, stabilized position.
Transportation of victims with head wounds, damage to the bones of the skull and brain should be carried out on a stretcher in a supine position. Unconscious victims should be transported in a lateral position. This provides good immobilization of the head and prevents the development of asphyxia from retraction of the tongue and aspiration of vomit.
Fractures of the skull bones
Broken bones often damage the brain, which is compressed as a result of hemorrhage.
Signs:
violation of the shape of the skull, a break (dent), leakage of cranial fluid and blood from the nose and ears, loss of consciousness.
First aid:
To fix the neck and head, a cushion is placed on the neck - a collar made of soft fabric. For transportation, the victim’s body is placed on his back, on a shield, and his head is placed on a soft pillow.
Jaw fractures
Signs:
pain, displacement of teeth, mobility and crunching of fragments. When the lower jaw is fractured, its mobility is limited. The mouth doesn't close well. Due to severe injuries, tongue retraction and breathing problems may occur.
First aid:
Before transporting victims with damaged jaws, the jaws should be immobilized: for fractures of the lower jaw - by applying a sling bandage, for fractures of the upper jaw - by inserting a strip of plywood or a ruler between the jaws and fixing it to the head.
Information prepared by: Paramedic on strengthening preventive work among healthy children Dmitrieva I.A. 2021
joint
joint
- unsuccessful attempts at treatment make further reduction difficult, so surgery may be required;
- you can further damage the joint by significantly damaging the soft tissue, making the dislocation irreducible;
- there are no opportunities for adequate pain relief at home;
- there are no diagnostic devices at home to assess the degree of damage to intra-articular structures;
- the lack of adequate treatment leads to an old dislocation, which cannot be reduced in a closed way, but is treated with surgery.