Ligaments connect the tissues of joints and bones and consist of connective fibers. Despite their elasticity and strength, they can suddenly become damaged as a result of injury. This is fraught not only with stretching, but also with partial or complete rupture. A minor sprain can be cured on your own, but in case of ruptures you should definitely visit a doctor. Considering that after an injury it is difficult for a lay person to understand how serious the injury is, it is advisable to immediately go to the emergency room and undergo an examination.
A sprain is not considered a serious injury, and proper care will ensure a quick recovery without complications. But if you underestimate the seriousness of the injury and do not provide timely first aid for a sprained ligament, complications may occur. You can understand that the measures taken are not enough by the following symptoms that appear in the first 3 days:
- the temperature has increased;
- the pain increases;
- restriction of mobility persists or increases;
- swelling and redness of the skin appears.
The listed symptoms are a reason to urgently consult a doctor!
sprain
sprain
Damage to the structures of the knee develops when exposed to excessive mechanical force. Usually it occurs during rotation of the thigh around its axis with the lower leg fixed in one position (twisting the leg). In addition, sprains of the meniscus of the knee joint occur due to direct mechanical impact on the knee.
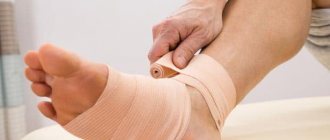
First aid for ankle ligament injuries
Sometimes an ankle sprain is compared with injuries resulting from a twisted foot. However, in this case it is wrong to talk about a sprain, since bruising and swelling occur. At the time of injury, tears occur in the area of the ligamentous apparatus. In turn, when stretched, the integrity of some fibers is disrupted, but the functional characteristics remain unchanged.
If signs of injury are detected in the ankle area, the person should receive immediate assistance. First of all, it is necessary to minimize the load on the ankle joint. This will prevent deterioration of the ligaments and tendons in the future. The following measures should also be applied to the victim:
- Apply a cold compress. This will make it possible to prevent increased swelling and the spread of bruising to nearby tissues. In this case, the patient notes a loss of sensitivity in the affected area, which helps eliminate pain. Moreover, by using a cold compress immediately after injury, it is possible to reduce the duration of the treatment process. Apply the bandage to the painful area for 20 minutes;
- Using an elastic bandage. To ensure immobility of the damaged joint, it is recommended to use a fixing bandage. Experts recommend avoiding tight bandaging, as it can cause loss of sensation in the fingers and increased swelling. However, such a bandage will prevent the occurrence of ruptures in the future;
- Placing the leg in an elevated position. The injured limb should be placed on pillows or on a chair (in a sitting position). This will relieve pain in the ankle joint and eliminate swelling in nearby tissues.
The use of warming agents is strictly prohibited during the period of first aid. It is not recommended to do alcohol rubbing and take a hot shower. It should be remembered that the fixing bandages are removed before resting at night.
Knee sprain - classification
Knee joint injury and sprain are classified based on the location and extent of the damage. Based on the location of the injured area, there are:
- Sprain of the medial ligament of the knee joint.
- Sprain of the lateral ligament of the knee joint.
- Sprain of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint.
- Sprained posterior cruciate ligament of the knee.
Several degrees of tissue trauma are classified by severity, based on the severity and number of injured fibers.
Feelings at different degrees of stretching
Treatment is prescribed depending on the degree of sprain. Knowing the symptoms, you can roughly determine the severity of the injury, provide first aid and decide on the urgency of calling doctors.
Taking into account the number of damaged ligaments and muscle tissue, 3 degrees are distinguished:
- A minor injury with little pain and virtually no swelling. Stretching does not prevent you from moving and doing your usual activities. No special treatment is required, but it is advisable to reduce the load until recovery.
- Moderate severity of damage with single tissue ruptures. The pain is constant, there are hematomas and swelling. Treatment will take about 1–2 months at home under the supervision of a traumatologist.
- Complete tissue rupture, severe pain, numerous hematomas and swelling. Urgent medical care is required in a hospital. Severe sprains have a poor prognosis. Recovery will take a long time.
knee ligaments - symptoms
knee ligaments - symptoms
- Painful sensations in the area of trauma, the severity and localization of which depend on how severe the sprain of the knee joint is and how many structures were involved in the pathological process.
- Swelling of tissues and hyperemia of the skin resulting from the development of an inflammatory reaction.
- Limitation of joint movements or, conversely, the appearance of instability.
Signs of knee sprain also depend on the severity of the violation of the anatomical integrity of the connective tissue fibers and the involvement of other structures (bone base, menisci). Severe sprain of the knee joint may be accompanied by the appearance of pathological mobility in it.
Advice from traumatologists
Sprains often occur in athletes, so their first aid kit is constantly stocked with tools to eliminate pain, immobilize the joint and speed up recovery. Traumatologists recommend that all people replenish their first aid kit with special medical products that may be useful in case of injury.
Self-fixing elastic sprain bandage is an excellent solution for treating damaged tendons. The product is made from fabric of a special structure and does not contain latex (only polyamide, cotton and viscose). All that remains is to choose the appropriate width of the bandage and always have it at hand. Unlike conventional elastic bandages, new medical dressings are resistant to sterilization, X-ray treatment, high temperatures (can be ironed), allow air to pass through and remove moisture from the skin.
Traumatologists recommend not only athletes, but also all active people to buy a self-fixing modern bandage. The costs will be repaid by its long service life - even with repeated use, the material retains its shape. In case of sprained ligaments, this bandage will help out both an adult, a child, and an elderly person.
Sprained collateral ligament of the knee joint - signs
A sprain of the collateral ligament of the knee usually occurs when a mechanical force is applied, resulting in abnormal flexion in the frontal plane. It is accompanied by severe pain sensations developing in the area of the internal or external surface.
Sprains of the medial collateral ligament of the knee develop somewhat less frequently, but can lead to pathological mobility. Sometimes damage to the lateral connective tissue cords and sprain of the cruciate ligaments of the knee can be combined. In this case, the symptoms are more pronounced, and the pain becomes more intense.
Features of the clinical picture
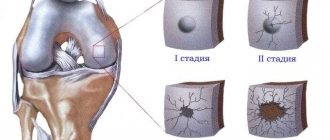
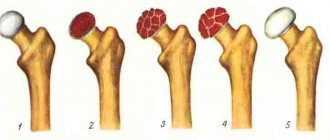
Experts distinguish three main degrees of severity of joint ligament damage, the type of which determines the characteristics of the clinical picture of the pathological condition:
- I degree or mild damage is the occurrence of minimal ruptures of individual fibers with the formation of a small zone of tissue damage. This condition is characterized by pain of moderate intensity and preservation of the ability to move the joint. With a mild degree of ligament rupture, there is no hematoma.
- II degree (medium) or so-called incomplete ligament rupture. In practice, the injury is manifested by the development of severe pain in the area of the affected joint, pronounced swelling of the soft tissues, and a sharp limitation of movements.
- III degree or severe rupture - complete separation of the fibrous elements, which is characterized by sharp, intense pain, severe swelling in the area of the injured joint, hemorrhage with the formation of a hematoma and impaired motor function. In such a joint, when performing movements, a specific click and pain occurs, as well as pathological mobility or instability.
Symptoms of these injuries may vary from patient to patient depending on the characteristics of their body. When a sprain is severe or completely torn, some people have severely limited mobility, while others can move around despite pain. This depends on the pain threshold of a particular person, his hardening and sports training.
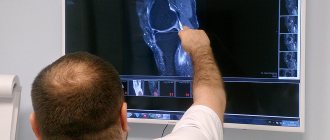
Diagnostics
Clinical signs of sprain of the knee joint do not make it possible to accurately determine the location and severity of the violation of the anatomical integrity. For this purpose, additional objective research methods are used, which include:
- Radiography is a technique that allows you to visualize gross violations of the anatomical integrity, in particular, a pronounced stretch of the internal ligament of the knee joint. To do this, it is carried out in direct and lateral projection.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging - these imaging methods make it possible to detect even minor injuries, in particular a sprain of the collateral ligament of the knee or a violation of the integrity of the cruciate connective tissue cords.
- Ultrasound examination – a knee sprain is often accompanied by an inflammatory reaction with an increase in the amount of synovial fluid, which can be detected by ultrasound.
- Arthroscopy is a method that makes it possible to visualize the sprain of the internal ligaments of the knee by introducing a special optical device, an arthroscope, into the cavity.
Arthroscopy is a low-traumatic invasive procedure that makes it possible to restore the correct structure of the structures of the musculoskeletal system.
Physical therapy: basic principles of exercises
You can start physical therapy only with the permission of a traumatologist. In some cases, simple exercises can be performed as early as 3 days after the injury, but active training begins approximately a month after the injury. Exercises are selected by the instructor taking into account the nature and extent of the injury. The goal is to improve blood circulation, strengthen muscles and ligaments. If pain occurs during class, the exercises are stopped and transferred to the next day. Exercise cannot be completely excluded from rehabilitation: muscles and ligaments will be replaced by connective tissue, which will limit their mobility.
Stretching is a vital part of physical therapy. It is necessary to avoid spasms of injured muscles and ligaments. As a rule, the exercise lasts 15 seconds, and you need to repeat it 2-3 times a day. For chronic injuries, the duration of stretching is increased to 30 seconds, and the number of repetitions is increased to 3-5 times per day. If you do everything correctly, you will not feel pain the next day. If discomfort occurs, this indicates muscle overstrain, and the intensity of stretching is reduced.
Sprained knee ligaments - treatment
If during diagnostic procedures a sprain of the ligaments of the knee joint was determined, the symptoms and treatment are determined only by a traumatologist. Based on the data obtained during an objective diagnosis of such a condition as a knee injury, treatment includes the following:
- drug therapy;
- non-pharmacological therapeutic measures;
- surgery.
The main directions of treatment for the pathological process are determined by the doctor, based on the specific clinical situation.
Proper first aid
In case of sprained ligaments, first aid is reduced to the following measures:
- Provide rest to the victim - sit or lay him down so that the injured limb does not move. To reduce swelling, it is advisable to slightly elevate your arm or leg.
- Apply cold. This will reduce swelling and pain. Pour ice into the bag; if there is none, use a heating pad with cold water. Apply to the damaged area for 15 minutes, take a half-hour break and repeat. It is good if there is a special cooling bandage that provides safe cold for 2 hours.
- Protect against overload. The diseased joint is fixed with an elastic bandage.
- Ointments and anti-inflammatory drugs for pain and swelling should be used only as prescribed by a specialist.
The listed measures for sprains are quite enough to reduce pain. In the next 2 days, it is important to provide fixation and rest to the injured limb. During this time, pain and swelling should decrease to a minimum. Next, it remains to begin to gradually and little by little load the limb. Full recovery occurs in 2–3 weeks.
physiotherapy
physiotherapy
- NSAIDs;
- analgesics;
- multivitamin preparations;
- chondroitin sulfate;
Non-drug measures are prescribed, mainly physiotherapy (electromagnetic fields, mud, ultraphonophoresis with non-steroidal analgesics).
The nature of the injury and its location influence how long a knee sprain takes to heal. Typically, the average duration of conservative therapy is about a month. If a severe knee sprain has been diagnosed, treatment includes surgery. The operation is performed with an open approach or using arthroscopy.
Help with grade 3 ankle sprains
More serious injuries may result in complete rupture of the ankle ligaments. In this case, signs identical to a bone fracture appear. The patient loses the ability to move because he feels severe pain and the inability to step on a limb. Such symptoms are caused by changes in the anatomical relationship of the component parts of the joint. Characteristic features of the disease also include the rapid spread of hematoma and swelling over the entire area of the ankle.
In case of rupture of the ankle ligaments, conservative treatment is practically not prescribed, which is due to the following points:
- There is a weak ability of damaged fibers to fuse;
- It may not be possible to fully restore the functional characteristics of the foot;
- If surgical intervention is refused, there is a risk of recurrent ankle injury due to ankle instability.
Planned surgical intervention is performed in case of complete separation of the ligament from the bone. To restore its continuity, bone and tendon sutures are applied. After completion of the surgical procedure, the patient is recommended to wear a bandage made of plaster for 21-28 days. During the entire rehabilitation period, the patient must take medications that improve blood supply to the tissues in the ankle joint. Medicines that expand the vascular lumens are also prescribed: Venarus, Detralex and Phlebodia.
Make an appointment Online booking
- Clinic on Krasnopresnenskaya +7 (499) 252-41-35 Volkov lane, 21
- Clinic on Varshavskaya +7 (499) 610-02-09 Varshavskoe highway, 75, building 1
- Clinic in Annino +7 (495) 388-08-08 Varshavskoe highway, 154, building 1
Sprain: how to treat
A sprain is a closed mechanical injury that disrupts the integrity of individual muscle or connective tissue fibers. If the range of motion of the ligament exceeds its capabilities, it may tear or partially rupture. Most often, the ligaments of the shoulder, knee, wrist and ankle joints are sprained.
0 Symptoms:
• Pain is a characteristic sign of spraining, often acute. Sometimes in the first moments after an injury a person does not feel pain. After some time, the pain increases, as if spreading throughout the limb, becoming strong and painful. • Fluid may accumulate in the tissues and severe swelling may occur. If blood vessels are damaged, bluish bruises and hematomas occur. • The site of injury often becomes swollen and painful even when touched. • The mobility of the injured limb naturally worsens, sometimes the victim cannot even move independently.
First aid
- Ensure rest and elevation of the affected limb.
- Secure it with a bandage - an elastic bandage, scarf, scarf.
- Immediately apply cold - an ice pack or a briquette from the freezer.
- Take the patient to a specialist to rule out fractures and ruptures.
Treatment occurs in 2 stages.
Acute period. Usually takes 1-2 weeks. The main point is immobilization, i.e. restriction of joint mobility using a tight bandage or orthopedic splint. Sometimes a plaster splint is necessary. For the first few days, cold application to the sore spot and elevated position of the limb are recommended.
Already 12 hours after the injury, you can begin physiotherapeutic procedures - magnetic therapy, since its active factor helps relieve swelling, inflammation, reflex spasms and pain. High-quality blood microcirculation around the injured area is the key to successful and quick rehabilitation. Moreover, a bandage, even a plaster cast, does not interfere with therapy! When the condition improves, you need to prepare to return to work - that is, to normal physical activity, and it’s time to add massage and exercise therapy to physiotherapeutic procedures.
The second period is recovery. It is necessary to devote energy and time to myorelaxation (relaxation of muscles that have become accustomed to improper functioning during illness), myocorrection - the formation of the desired motor stereotype, and myotonization - consolidation of the correct attitudes.
Exercises on special exercise machines, swimming in the pool, and taking baths with brine - a saturated saline solution - are considered useful. Physiotherapeutic procedures should be continued until completion of the course to promote accelerated rehabilitation after ligament injuries.
An excellent physiotherapeutic device is ALMAG+. The device allows magnetic therapy to be carried out not only in the hospital, but also in a familiar home environment.
When stretched, ALMAG+ makes it possible to: • reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings and relieve pain; • suppress inflammation; • accelerate the resorption of hematomas; • increase capillary permeability and eliminate swelling; • activate tissue regeneration, restore muscle strength; • reduce immobilization time and reduce muscle atrophy caused by inactivity; • quickly restore your ability to work and return to your favorite activities.
How to avoid ankle ligament injuries?
In order to minimize the risk of joint injury, experts recommend adhering to the following measures:
- Ensure sufficient and regular physical activity to maintain the necessary elasticity of the ligaments;
- Provide moderate loads on the limb;
- Use comfortable shoes with low heels (no more than 7 cm);
- Perform a special set of exercises to strengthen the ankle joint and ligaments;
- Try to maintain normal weight;
- Timely treat pathologies that have a negative impact on the musculoskeletal system.
2. Why muscle strain occurs
In the process of life, when we are awake, certain muscle groups are almost constantly working, making numerous contractions. For the most part, they are safe and do not lead to negative consequences. In this case, the muscles adjacent to the contracting muscle tissues are stretched. The elongation limit is quite high, but in extreme situations, during overloads or sudden movements, a mismatch occurs - adjacent muscles contracting simultaneously cause harm to each other. The muscles most often subject to excessive stretching are the back, neck, legs, and forearm. Regular training and warming up before heavy exercise can minimize the risk of such injury. Also important here:
- natural flexibility of the body and elasticity of tissues;
- general physical fitness;
- individual characteristics of the musculoskeletal frame;
- posture.
Factors and situations that increase the likelihood of getting a sprain are very diverse and sometimes unexpected:
- practicing sports involving monotonous movements (rowing, tennis), as well as contact team sports (football, basketball);
- long periods of static body position in an uncomfortable, monotonous position (sitting at a table, embroidering, painting and some crafts);
- sudden loss of balance, falling on ice, jumping over an obstacle/puddle/stream;
- sharp sudden cough;
- lifting weights without bending your knees;
- catching a thrown object (volleyball);
- inconsistency when performing heavy work with the participation of a partner.
Visit our Traumatology and Orthopedics page
Physiotherapy for ankle ligament injuries
For those wondering how to treat an ankle sprain, undergoing physical therapy is a must step. When implementing such measures, you can get a more tangible positive effect than after taking medications.
In case of first and second degree injuries, physiotherapy should be resorted to within 72 hours after the start of treatment. They can also be performed after surgery, during the rehabilitation period. An experienced specialist will help you choose the most effective physiotherapy procedures. At the same time, he takes into account the individual nuances of each patient, as well as:
- Intensity of damage;
- The ability of tissues to regenerate;
- Presence in the anamnesis of pathologies caused by malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
Initially, the patient is recommended to undergo a procedure that involves exposure to direct electric current and special medications. For this purpose, a cotton swab soaked in a special medicine is applied to the damaged area, and metal plates are placed on it. By using electrical impulses, the medicine can reach the deepest layers of tissue. As a rule, during the procedure, agents with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects are used. In some situations, to speed up the process of fusion of ligaments that were previously torn from the base, it is recommended to use chondroprotectors.
Also during the recovery period, the following techniques can be used: ultrasound exposure, paraffin baths, magnetic therapy and shockwave therapy.
1.Types of muscles
All muscles of the human body are divided into three groups: skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Only skeletal muscles are at risk of being stretched, since only they contract consciously. The other two groups are responsible for the work of internal organs and contract unconsciously, so the load on them is always proportionate to what is natural and physiological.
The muscles that support the skeleton and are responsible for our movements work at the will of our thoughts, and it is not always possible to calculate a safe load. In everyday life we sometimes set ourselves impossible tasks, in sports we strive for high results, in critical situations we make sudden movements that go beyond the resources and training provided by nature.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!