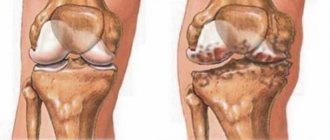
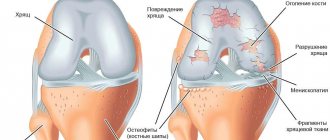
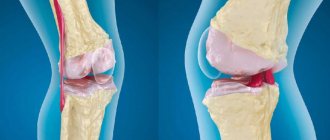
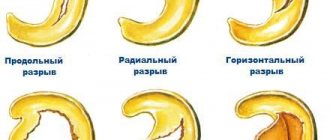
Gonarthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic pathology of the knee joint that affects the cartilaginous tissue lining the condyles (thickenings or protrusions) of the tibia and femur. At the initial stage of the disease, a small part of the hyaline cartilage is involved in the destructive process.
Clinically, grade 1 gonarthrosis is manifested by mild pain, aggravated by physical activity, swelling of the knee, which disappears on its own. The absence of pronounced symptoms at this stage of the pathology often becomes the reason for the patient’s delay in seeking medical help.
The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, medical history, and the results of instrumental studies - radiography, MRI, arthroscopy. Patients are prescribed conservative treatment of gonarthrosis: taking chondroprotectors, exercise therapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures. The prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Causes and provoking factors
The pathogenesis of gonarthrosis is based on a violation of the trophism of cartilage tissue. They receive nutrients not from the systemic bloodstream, but from the synovial fluid. With grade 1 gonarthrosis, a circulatory disorder is observed in small vessels. Nutrient deficiency occurs in the synovial fluid and hyaline cartilage. Radial cracks form on the surface, it loses its smoothness, strength and elasticity. Now, during sliding, the cartilages do not smoothly move relative to each other, but begin to “cling.” And this leads to their microtrauma, further thinning and loss of shock-absorbing properties.
Gonarthrosis develops under the influence of several provoking factors. In approximately a third of patients, the impetus for destructive-degenerative changes in cartilaginous tissue was previous knee injuries - intra-articular fractures, damage to the ligamentous-tendon apparatus, including the menisci.
Knee injury is one of the causes of gonarthrosis.
The following external and internal negative factors also become the cause of the manifestation of gonarthrosis:
- intense sports training, heavy lifting, professional overload of the knee;
- systemic pathologies of the musculoskeletal system - rheumatoid, psoriatic, gouty arthritis, osteoporosis, lupus erythematosus;
- endocrine and metabolic disorders, such as diabetes mellitus or adrenal insufficiency;
- hypermobility of the joints, which causes weakness of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus;
- congenital abnormalities of the knee, postural disorders, flat feet, clubfoot, hallux valgus.
The United States holds the record for knee replacement surgery. Relatively recently, a relationship was discovered between the frequent replacement of joints with prostheses and the craze of Americans for running.
Running is America's favorite sport.
During jogging, the knee is subjected to severe stress that exceeds the strength of hyaline cartilage. In the case of young people, everything is not so dangerous - the speed of recovery processes in them prevails over destruction. After 30-35 years, cartilage does not have time to regenerate, so several years after regular physical activity, gonarthrosis manifests itself.
Prevention of gonarthrosis of the knee joint
Any disease can be prevented through the use of preventive measures, which include:
- Regular swimming and other sports.
- Compliance with safety precautions to prevent injuries.
- Body weight control.
- Following a diet that involves limiting the consumption of fatty and spicy foods, smoked foods, and other foods that are not healthy.
- Quitting bad habits.
- Timely consultation with a doctor if you receive an injury and complete a full course of treatment.
- Systematic preventive courses of therapy using chondroprotectors after 35 years.
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Providing joint protection from overheating/hypothermia.
Having problems with your joints? Do not delay your visit to the doctor, take care of your health and enjoy a full life!
Clinical picture
Gonarthrosis develops slowly over several years. Even with grade 1 pathology, the clinical picture may lack specific signs of cartilage destruction. At the initial stage of gonarthrosis, mild discomfort appears, which was preceded by intense physical activity. Pain occurs when going up or down stairs, after long walks or cycling.
Knee pain when climbing stairs is a sign of gonarthrosis in the initial stage.
In most cases, a person attributes them to muscle fatigue and is in no hurry to see a doctor. The following symptoms are characteristic of gonarthrosis of the 1st degree:
- slight stiffness of the knee joint in the morning, disappearing within 30-40 minutes;
- knee stiffness (sometimes combined with pain) that occurs after prolonged stay in one body position;
- crepitus (crunching, clicking, crackling) when flexing or extending the joint, usually manifesting itself at the end of the initial stage of gonarthrosis;
- slight morning swelling of the joint, disappearing within a few hours under the influence of hormone-like substances produced in the body.
Swelling of the knee in the morning.
A specific symptom of this disease of the knee joint is “starting pain”. It occurs during the first steps that a person takes after rising from a chair or armchair. There are no external signs of the degenerative-dystrophic process yet. But even at the initial stage of gonarthrosis, there have been cases of the development of synovitis - inflammation in the synovial membrane, accompanied by the accumulation of fluid (effusion) in the joint cavity. The knee increases in size, a feeling of heaviness appears, and range of motion decreases. Upon palpation, a small rounded compaction is detected. Often synovitis of the knee is accompanied by malaise and a slight increase in general and local temperature.
Gonarthrosis of the second and third degrees of severity is characterized by much more pronounced symptoms, including due to the formation of osteophytes.
Osteophytes in the knee joint.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease are determined by the degree of development of pathological processes.
The development of pathology is gradual. Grade 1 knee joint gonarthrosis is characterized by symptoms such as:
- superficial pain when performing movements;
- stiffness, a tightening sensation in the popliteal region;
- “starting pain” that occurs when taking the first steps after a long static stay (standing/sitting/lying).
Grade 2 knee joint gonarthrosis has symptoms such as:
- increased intensity of pain;
- localization of pain in the anterior internal articular surface;
- decreased motor function;
- visually noticeable deformation, expansion of the knee.
Grade 3 knee joint gonarthrosis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- constant pain of varying intensity;
- loss of mobility;
- increased volume of the knee, noticeable x-shaped or o-shaped deformity;
- unsteady gait.
Diagnostics
When examining a patient with grade 1 gonarthrosis, the doctor usually does not detect external signs of changes in the knee joint. Therefore, the diagnosis is made based on the results of radiography, anamnesis and complaints of the patient. A definite clue is the presence in the medical history of previous injuries, systemic inflammatory or degenerative pathologies.
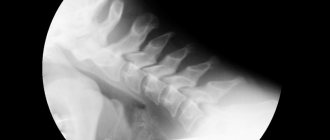
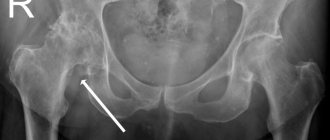
The most informative way to make a diagnosis is an X-ray examination. But at the initial stage of gonarthrosis, pronounced destructive changes in cartilage may not be observed. Only at its final stage are the following revealed:
- slight fusion of the joint space;
- changing its contours;
- compaction of the subchondral region;
- sharpening of the edges of the condyles;
- widening of the ends of the bones.
The image on the right shows fusion of the joint space.
The study of radiographic images helps to determine the cause of the development of gonarthrosis (injury). The study is also informative for excluding certain pathologies (for example, malignant neoplasms in the tibia or femur).
Certain difficulties in identifying grade 1 gonarthrosis arise due to natural changes in the knee joint in elderly patients. They are not accompanied by any clinical manifestations. The doctor makes a diagnosis of gonarthrosis if radiological signs are combined with specific symptoms.
If radiography is uninformative, a CT scan of the knee joint is performed for a detailed study of pathological changes in bone tissue. And MRI and ultrasound can detect destruction of connective tissue structures located near the joint.
Symptoms
Arthrosis is a slowly progressive disease that in itself never causes changes in blood counts (for example, ESR), an increase in body temperature or other clearly noticeable characteristic signs. It is noteworthy that the degree of pain and limitation of joint mobility does not directly depend on morphological changes. That is, one patient may have severe pain even with minor cartilage degeneration, while another may have virtually no pain even with pronounced changes, clearly visible on X-rays, MRI or CT, or ultrasound. The fact is that there are no nerve endings or blood vessels in cartilage. Therefore, symptoms appear only when changes begin in other tissues.
Treatment tactics
Grade 1 gonarthrosis responds well to treatment. The main tasks of orthopedists are to prevent the progression of the degenerative-dystrophic process and restore joint mobility. The therapy uses methods aimed at improving the blood supply to the knee joint with nutrients and biologically active substances. This can be done with the help of physical therapy, massage and physiotherapy.
The doctor examines the patient before prescribing diagnostic measures.
Drug therapy
Pharmacological drugs are usually used only in external dosage forms - ointments, gels, creams, balms. Painkillers are used when necessary, and not for a course of treatment. The use of tablets or injection solutions is not practiced, since there are no pronounced symptoms at the initial stage of gonarthrosis.
The exception is chondroprotectors - the only group of drugs, a course of which stimulates the restoration of cartilage tissue. Patients are prescribed the following tablets, capsules, dragees, solutions for parenteral administration:
- Alflutop;
- Rumalon;
- Don;
- Chondrolone;
- Mucosat;
- Structum;
- Teraflex.
Chondroprotectors are clinically effective specifically for grade 1 gonarthrosis. As the disease progresses, the cartilage tissue wears out greatly, and it is impossible to regenerate it with the help of drug therapy. There are chondroprotectors in the form of ointments and gels, but there is no evidence base for their therapeutic activity. During a course of taking tablets, their ingredients accumulate in the joint cavity and after 2-3 weeks begin to have an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect. This allows you to completely abandon the use of ointments with NSAIDs and warming components.
| Clinical and pharmacological group of drugs for external use used for the treatment of grade 1 gonarthrosis | Names of medicines | Pharmacological action and clinical effect |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Fastum, Voltaren, Artrosilene, Indomethacin, Nurofen, Ketorol, Nise | Inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which stimulates the biosynthesis of mediators of pain, inflammation, fever, prostaglandins and bradykinins. Increasing range of motion, preventing morning swelling and stiffness of the knee joint |
| Preparations with a warming effect | Capsicam, Viprosal, Apizartron, Nayatox, Finalgon | Irritation of receptors located in the subcutaneous tissue, providing a distracting and analgesic effect. Stimulation of blood circulation and microcirculation, acceleration of metabolic processes and regeneration of connective tissue structures |
| Chondroprotectors | Teraflex, Chondroxide, Chondroitin-Acos, Arthro-Active, Honda | Inhibition of enzymes that cause the destruction of cartilage tissue, inhibition of the development of the inflammatory process, slowing down the degeneration of hyaline cartilage. Reducing the severity of pain, increasing the mobility of the knee joint by accelerating the resorption of swelling |
Non-drug therapy
Immediately after diagnosing grade 1 gonarthrosis, the patient is referred to a physical therapy doctor. The doctor selects exercises individually for each patient, taking into account his physical fitness. Daily exercises allow you to completely stop using painkillers. When performing exercises in the knee joint, blood circulation significantly improves, stimulating recovery processes.
The first training must be carried out under the supervision of a physical therapy doctor. You should not perform movements too intensely, as this will cause even more damage to the hyaline cartilage. They should be smooth, slow, with low amplitude. This helps speed up blood circulation, but eliminates any stress on the sore knee.
Physiotherapeutic procedures help speed up the regeneration of cartilage tissue. The greatest therapeutic effectiveness is typical for the following health activities:
- UHF therapy;
UHF session.
- electrophoresis with chondroprotectors;
- laser therapy;
- amplipulse therapy;
- interference therapy;
- applications with therapeutic mud, ozokerite, paraffin;
- magnetotherapy.
Magnetic therapy session for damage to the knee joints.
Overweight patients are advised to lose weight. Otherwise, neither taking chondroprotectors nor engaging in physical therapy will help stop the spread of pathology. Doctors advise wearing orthopedic devices - elastic knee pads - before physical activity or long walks.
Elastic knee pads for fixing the knee joint.
The use of folk remedies (compresses, rubs, infusions) is possible only after the main treatment and in agreement with the orthopedist.
Treatment for grade 1 gonarthrosis should be started immediately after diagnosis. Compliance with all medical recommendations will allow you to avoid the development of complications and completely restore all functions of the knee joint.
List of sources
- Loginov S.I., Solodilov R.O. The influence of gonarthrosis on the kinematics of the knee joint. Bulletin of Siberian Medicine. 2016;15(3):70-78.
- Kashevarova NG, Alekseeva LI, Anikin SG, et al. Osteoarthritis of the knee joints: risk factors for the progression of joint disease in a five-year prospective disease. Materials of the III Eurasian Congress of Rheumatologists, (Minsk, Republic of Belarus, May 26-27, 2021). Issues of organization and informatization of healthcare. 2021.
- Kosareva M.A., Mikhailov I.N., Tishkov N.V. Modern principles and approaches to the treatment of gonarthrosis // Modern problems of science and education. – 2021. – No. 6.
- Bagirova G.G. Osteoarthrosis: epidemiology, clinic, diagnosis, treatment / Bagirova G.G., Meiko O.Yu. - M., 2005. - 224 p.
- Badokin V.V. Main symptom-modifying slow-acting drugs in the treatment of osteoarthritis // Breast Cancer. 2011. No. 12. pp. 72–79.
Self-help is a way to improve your quality of life
Self-help has a huge impact on the outcome of gonarthrosis treatment. Be active in the fight against the disease: watch your weight, stay physically active and eat healthy foods.
medi products
Orthoses that correct the position of the knee joint can be an effective alternative to endoprosthetics and pain medications.
Knee braces and orthoses: Genumedi, Collamed OA, M.3s OA and M.4s OA can be used to treat gonarthrosis at different stages.
Therapeutic exercises for arthrosis
Considering the cause of the development of the disease (wear and tear of cartilage), many people wonder what is better: doing exercises or resting more without putting stress on the joints? There is a one-word answer to this question: exercises are extremely useful both for those suffering from gonarthrosis and for the prevention of this disease! Usually, when pain occurs, people try to give their joints rest, but this is the wrong way. Lack of mobility is the main risk factor for arthrosis in general and gonarthrosis in particular.
Performing special exercises can increase muscle strength and improve coordination. In addition, joint movement promotes the formation of synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant and reduces friction between the joint surfaces.
Sports and gonarthrosis
What really helps? Does exercise help or is it better to rest? One thing is for sure: sports and exercise are invaluable both for those who already suffer from gonarthrosis and for those who want to prevent it! When people experience pain, they try to move the affected knee as little as possible. This is a fundamentally wrong approach, since insufficient physical activity is one of the main factors in the development of arthrosis.
Targeted training of joints affected by arthrosis helps strengthen muscles and improve coordination. When you move, more synovial fluid is produced, which contributes to less wear and tear on the articular cartilage.
The most preferred sports for patients with osteoarthritis
Preferred sports that are gentle on joints:
- Swimming
- Water aerobics
- Cycling
- Golf
- Skiing
- Walking
Undesirable “contact” sports:
- Football
- Skiing
- Tennis
- Volleyball
Determine the type of sports activity that suits you best. Avoid strenuous exercise associated with sports. If you are unsure whether you can participate in any sport, seek advice from your doctor.