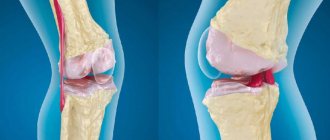
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint is a deforming type pathology, localized in the tissues of the lower extremities. The progression of the pathology is accompanied by damage to cartilage tissue and has a predominantly progressive course.
Clinical symptoms suggest the presence of pain of varying intensity, intensifying when performing various types of movements, as well as limitation of motor activity of the joint and excessive accumulation of fluid inside its cavity (synovitis).
The disease is diagnosed in patients of different ages; the most common location is the inside of the knee. The problem often occurs in athletes or people over 40 years of age.
Treatment is predominantly conservative, but if there is significant tissue damage, surgery is indicated.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint: what is it?
Osteoarthritis of the knee is the second name for a disease of a pathological nature, suggesting the presence of degenerative processes localized in the joint of the lower limb.
There are several classifications of the disease:
1.According to the development mechanism:
- primary;
- secondary.
2. By the nature of the lesion:
- right-sided;
- left-handed;
- double-sided
It is important to note that regardless of the characteristics of the pathology, the disease can lead to disability.
Surgery for stage 4
Some people definitely want to become disabled in order to be guaranteed to receive financial assistance from the state every month. And there are good reasons for this, because a person with such orthopedic disorders is not only able to go to work, but is simply unable to take care of himself at the everyday level. We have already found out whether it is possible to obtain a document in Russia and Ukraine confirming the status of “disabled person” with deforming arthrosis of the knee of 3-4 degrees. Yes, of course, you can count on a positive decision from the local medical and social examination authorities. These are the two most difficult degrees of severity by the standards of a person’s physical condition.
But still, as observations show, no benefits and benefits can replace the patient’s desire to get rid of persistent chronic impairment of static-dynamic functions, hellish pain and, of course, disability status. Everyone dreams of returning to a normal lifestyle. And if an old woman of 85 years old may still come to terms with her condition, but not people who still have time to live. No one would like to be disabled, suffering from their inferiority and feeling defective for the rest of their life, while giving up worldly joys. There is a way out, despite the incurability of a serious disease! And we talked about it several times in this article. Yes, this solution is endoprosthetics. And, fortunately, it copes well with the three most important tasks, and these are:
- relief from deformities and pain;
- restoration of healthy knee mobility;
- return of a person to a working state.
No operation other than endoprosthetics will relieve you of disability. And replacing a knee joint with an endoprosthesis will put even the most seemingly hopeless person back on his feet. And he will not only provide, but also open all the doors to a normal existence, the same as that of healthy people. A unique artificial joint transplant is a real chance to become a full-fledged person who does not evoke pity and sympathy from strangers.
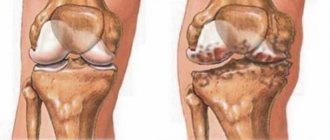
On the left is partial endoprosthetics, on the right is total.
With a new knee joint, you will be able to walk independently without depending on aids, do physical exercise, travel, realize yourself in a professional field, calmly do housework, and much more. In a word, such treatment for stage 3-4 gonarthrosis, such as endoprosthetics, will relieve disability. Successful restoration of function is observed in approximately 98% of cases.
Knee replacement process
For anesthesia, specialists mainly use epidural anesthesia - the introduction of a special anesthetic drug through a catheter into the epidural space of the spine. This type of anesthesia blocks nerve impulses in the spinal cord, making the lower body completely insensitive to pain. The person remains conscious and tolerates all surgical procedures on the lower limb well. After the administration of the anesthetic, the surgical process begins, which, with such a severe diagnosis, mainly involves the complete replacement of the problematic knee joint with a total prosthesis.
On the front side of the knee, the surgeon makes a small incision in the soft tissue structures, its length is approximately 10 cm. The non-viable joint is carefully resected, after which the doctor makes several sawdusts on the femur bone and tibial component. In turn, the tibia is subjected to perforation, that is, a special depression is made in order to tightly immerse the leg of an artificial metal platform (the tibial component of the endoprosthesis) into it.
When the bones are prepared, the installation of the prosthesis begins. The specialist first installs a test endoprosthetic system to be sure that the corrected axis is correct and the corresponding section is stabilized. Next, the prepared ends of the femur and tibia are covered with permanent functional components of the prosthetic structure. Their strong fixation is carried out using medical cement or by hammering. Then the knee cavity is thoroughly washed with saline, drainage is placed on the wound, and the surgical incision is sutured in layers. The limb is immobilized using orthopedic devices.
Pathogenesis
The pathology develops over a fairly long period of time. The whole process can be defined in the following sequence:
- The emergence of causes of disruption of natural metabolic processes provokes the destruction of cartilage tissue.
- Destructive processes destroy the structure of the fibers responsible for the shock-absorbing effect. Not only the elasticity of the tissues gradually decreases, but also the stability of the joint.
- Due to the constant increased load on the joint membrane, an inflammatory process occurs, causing a decrease in mobility.
Development mechanism
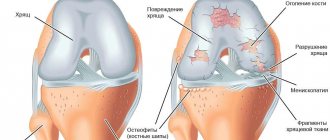
Initially, gonarthrosis affects hyaline cartilage. It becomes thinner, thicker, and less smooth. When sliding, the cartilage lining the bone surfaces now “clings” to each other, which further accelerates their destruction. The joint capsule gradually degenerates, and the synovial fluid thickens. Due to lack of nutrients, cartilage disappears from a large surface of the bones. Increasing loads leads to their deformation and pressing into each other. Multiple bone growths (osteophytes) are formed, constantly injuring soft tissues and synovial membranes.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint: causes
Any pathological process has reasons that provide the basis for its development. In most known cases, it is impossible to identify any cause of gonathrosis. However, among the most likely factors provoking the pathological process, it is customary to highlight:
- injuries – more than 20% of cases are caused by previous injuries. The most likely occurrence of pathology after an injury is already after 3 years, however, its early development is also possible, within a few months;
- Excessive physical activity provokes pathological processes. Running and squats are considered especially dangerous;
- Excess body weight – lack of body weight control provokes a negative impact on the knees, which causes injuries.
It is also worth noting that among the causes of gonarthrosis may be previous arthritis of various groups, as well as genetic predisposition and metabolic disorders within the body.
Degrees of gonarthrosis of the knee joint
The degree of gonarthrosis is determined by the severity of pathological changes. Let's look at each of them in detail.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint 1st degree
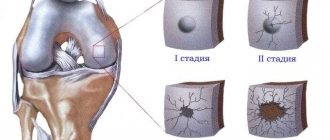
Grade 1 knee joint gonarthrosis is the beginning of the disease. This period is characterized by dull, periodic pain, occurring mainly after exercise.
From time to time, there is a slight swelling of the affected area that disappears on its own, but there is no visible deformation.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint 2nd degree
With grade 2 gonarthrosis of the knee joint, symptoms increase. The painful sensation becomes longer and more intense, and a crunching sensation occurs. The classic course of the pathology involves the occurrence of slight or moderate limitation of mobility, as well as slight deformation.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint 3rd degree
The peak of clinical manifestations occurs in grade 3 gonarthrosis of the knee joint. The pain is severe and constant, and the patient’s gait is impaired. The limitation of mobility becomes pronounced, and the deformation becomes noticeable.
Diagnosis of the disease
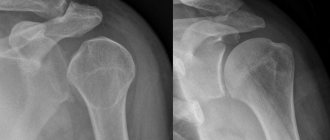
The diagnosis is made based on medical history, patient complaints, and external examination. With grade 3 gonarthrosis, the knee is deformed and enlarged. Synovitis often accompanying the pathology leads to its smoothing due to the formation of inflammatory edema. Of the instrumental studies, the most informative are radiography and MRI. According to indications, arthroscopy is performed - examination of the internal surfaces of the joint.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease are determined by the degree of development of pathological processes.
The development of pathology is gradual. Grade 1 knee joint gonarthrosis is characterized by symptoms such as:
- superficial pain when performing movements;
- stiffness, a tightening sensation in the popliteal region;
- “starting pain” that occurs when taking the first steps after a long static stay (standing/sitting/lying).
Grade 2 knee joint gonarthrosis has symptoms such as:
- increased intensity of pain;
- localization of pain in the anterior internal articular surface;
- decreased motor function;
- visually noticeable deformation, expansion of the knee.
Grade 3 knee joint gonarthrosis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- constant pain of varying intensity;
- loss of mobility;
- increased volume of the knee, noticeable x-shaped or o-shaped deformity;
- unsteady gait.
Consequences and prognosis
The course of grade 3 gonarthrosis is complicated by spontaneous hemarthrosis, the development of secondary reactive synovitis, and external subluxations of the patella. But the most serious consequence is ankylosis. The joint space is completely fused and the knee is immobilized. This leads to disability of the patient due to the inability to move independently. This development of events can only be avoided by knee replacement.
Diagnostic methods
Today, there are several diagnostic methods used to make a diagnosis. The effectiveness of the methods used is determined solely by the complexity of the approach.
Medical examination
An orthopedic surgeon can diagnose pathological processes of a degenerative-dystrophic nature. To get an appointment with him, you can take a direct coupon or contact a therapist for a referral.
An examination by an orthopedist is a key step in making a diagnosis, which involves activities such as:
- palpation of the composition;
- linear measurements of bone tissue;
- determining the mobility of the affected joint from different angles.
Clinical researches
To confirm the diagnosis, a number of tests are required, including:
- blood test (determining the formula and erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- determination of biochemical parameters of blood and urine.
X-ray studies
X-ray allows you to identify pathological processes, however, it is ineffective in identifying the initial degree of the degenerative-dystrophic process.
Using X-rays, you can detect narrowing of the joint space, destruction of cartilage and bone tissue, as well as the presence of salt deposits in the later stages of the pathology.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound of the affected tissue gives better results, but cannot completely replace x-ray examination.
Magnetic resonance imaging
A progressive diagnostic method that allows you to examine parts of the joint layer by layer and determine changes in cartilage and bone tissue.
The main advantage of the diagnostic method is high accuracy rates, but the disadvantage is the relatively high cost.
How to treat stage 3?
At the very beginning of this section, we have already given important information on how to treat severe pathology in the late course. Lost mobility and normal anatomical proportions will have to be restored to the knees through endoprosthetic surgery. This is the only medical and orthopedic technology that is capable of maximally or completely returning to a person the quality of life that was before he fell ill with insidious gonarthrosis.
The essence of endoprosthetics is to remove a joint distorted by the disease and install an endoprosthesis in its place - an artificial joint structure that replicates the functions and structure of a healthy knee joint. The unnatural organ takes root well because its structural parts are made from high-tech nanomaterials with a high degree of biocompatibility with the human body. Modern endoprostheses, subject to high-quality implantation and ideal step-by-step postoperative care, last for an average of 20-25 years.
What the surgeon sees during joint surgery.
Prosthetics are performed in a specialized clinic that practices this type of surgery. It is better to undergo it abroad, where the complex surgical process is carried out by highly qualified specialists who brilliantly master all the intricacies of knee implantation. Today, as reviews from world experts and patients show, medical centers in the Czech Republic have great opportunities.
If for some reason the patient cannot undergo high-quality surgical treatment, he will be recommended classical conservative therapy. It is aimed primarily at relieving pain and swelling, which are persistent and pronounced at this phase. Conventional anti-inflammatory compounds from the NSAID class have little or no effect, so often, to help feel relief, the question arises of the need for intra-articular injections based on corticosteroids. However, steroid therapy cannot be used for a long time, since the hormonal substances included in such medications are dangerous due to severe side effects.
It is too late to slow down the degenerative process with chondroprotectors, hyaluronic acid and any other stimulators of metabolism in joint tissues. There is no need for them at all now. It is recommended to wear special orthopedic devices (knee pads, insoles, orthoses, etc.), a kind of exercise therapy without stress on the joint, movement is allowed only with a cane or crutches. Sometimes limb traction is prescribed in combination with physiotherapy procedures.
If there is pathological fluid inside the knee, the patient is periodically sent for puncture (removal of its excess). If prosthetics are contraindicated or impossible due to certain circumstances, the surgeon advises to undergo arthrodesis (complete closure of the knee) or tibial osteotomy (axis correction), but these methods, despite their aggressiveness, have a short-term effect and do not restore full range of motion.
Key methods for treating knee gonarthrosis
Before starting treatment for gonarthrosis of the knee joint, it is important not only to identify the symptoms of the existing disease, but also to establish the probable causes of its occurrence.
Eliminating the causes of pathological processes will allow you to prescribe the most effective treatment.
Drug treatment
Treatment with medication involves the use of drugs such as:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- vasodilators, which make it possible to reduce muscle tone;
- anti-enzyme, neutralizing the action of certain enzymes;
- intra-articular injections that relieve inflammation and severe pain;
- chondroprotectors that promote the restoration of cartilage tissue. It is worth paying special attention to the benefits of using this group of drugs, which help speed up treatment methods and provide effective prevention of complications. One of these drugs is Artracam.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
The use of physiotherapeutic procedures in complex treatment gives very good results. Among the widely used methods are:
- electrophoresis;
- diadynamic currents;
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser exposure;
- mud therapy.
Healing Fitness
A useful and very effective method of treatment, which is an integral part of complex therapy. The use of exercises promotes the development of mobility.
The type and intensity of the exercise complex is determined by the attending physician and dosed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Surgical intervention
In cases where traditional therapeutic treatment does not produce a positive result or the disease is at the last stage that cannot be treated, surgical intervention is indispensable.
Today there are several types of surgical intervention:
- arthrodesis – removal of deformed tissues and the affected joint without maintaining mobility;
- arthroscopy – removal of affected tissue through small punctures using modern equipment;
- periarticular osteomy - filing of bones and their subsequent connection at a certain angle, which allows you to distribute the load;
- endoprosthetics – complete replacement of elements, installation of a prosthesis.
It is important to remember that surgery is always accompanied by risks.
Main characteristics
Most often, this disease appears in people after the age of 45, since it is during this period that age-related changes occur in the body. The tissues begin to thin out and become vulnerable to injury and damage. In younger people, such negative changes occur as a result of active participation in professional sports.
Treatment of the disease in the initial stages of development involves the use of conservative methods. Men over 45 years of age, as well as women over 55 years of age are at risk. Also, the risk of developing gonarthrosis is present in people who have a genetic predisposition to diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a non-inflammatory disease; it progresses slowly. As it develops, the quality and quantity of cartilage tissue changes. The main symptoms include pain. Most often they appear in the following cases:
- during joint flexion;
- when climbing stairs;
- after prolonged sitting.
In the initial stages of development, stiffness and pain occur in the morning after waking up. After some time, these symptoms go away on their own. As the disease progresses, the duration of unpleasant symptoms increases.
If irreversible changes occur in the cartilage tissue, inflammatory processes may develop in the joint. In this case, the disease, which is initially non-inflammatory in nature, is complemented by an inflammatory process. The main goal of therapy is to reduce the frequency and duration of the period of inflammation.
Articular cartilage gradually wears out, and its amount between the rubbing surfaces of the bones decreases. Gonarthrosis is one of the most common diseases in the world among older people. Age is considered a significant risk factor.
Prevention of gonarthrosis of the knee joint
Any disease can be prevented through the use of preventive measures, which include:
- Regular swimming and other sports.
- Compliance with safety precautions to prevent injuries.
- Body weight control.
- Following a diet that involves limiting the consumption of fatty and spicy foods, smoked foods, and other foods that are not healthy.
- Quitting bad habits.
- Timely consultation with a doctor if you receive an injury and complete a full course of treatment.
- Systematic preventive courses of therapy using chondroprotectors after 35 years.
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Providing joint protection from overheating/hypothermia.
Having problems with your joints? Do not delay your visit to the doctor, take care of your health and enjoy a full life!
Why is complex treatment at East Clinic more profitable and effective?
To make gonarthrosis a thing of the past as quickly as possible, we offer a range of treatment procedures. This saves you time, money and speeds up your recovery. Treatment of gonarthrosis works faster when combining massage, osteopathy, gentle manual therapy, acupuncture with laser, moxotherapy, and homeosinology. These procedures are included in the course of treatment sessions, the combination of which is selected by the doctor.
During one visit to the clinic, you can undergo two or more procedures, and if you pay for a course of treatment at a time, you will receive a pleasant bonus - a 10% discount. The cost of one treatment session depends on the set of procedures.
The rate of cure using non-medicinal methods depends on the person’s life potential, but in most cases, in stage 2, one comprehensive course of treatment is sufficient.