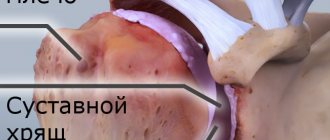
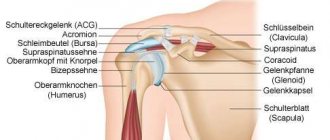
The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in the human body because it can move in all three planes. The joint itself consists of the articular surface of the scapula (glenoid cavity), the head of the humerus, which absolutely matches the shape of the cavity, and the clavicle. The head of the humerus is held in position by the cartilage cushion that lines the edge of the glenoid cavity and the connective tissue that forms the joint capsule. The muscles and tendons surrounding the joint provide it with stability and strength.
But it is precisely this mobility that is responsible for shoulder dislocations and injuries (due to the fact that the area of contact of the articular surfaces is small). A shoulder dislocation is a instability in which the head of the humerus falls out of the glenoid socket as a result of physical force. Dislocations of the humerus in the shoulder joint are anterior (most common), posterior and inferior (depending on the direction of displacement of the head of the humerus).
Diagnostics.
Diagnosis of a dislocation includes a detailed examination of the patient, palpation of the damaged joint and the appointment of x-rays in two projections of the damaged joint. Using the obtained x-ray, the doctor identifies the type of dislocation, whether there is a fracture, and determines the method of reduction. In more serious cases, the doctor may prescribe computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging to clarify the diagnosis. If there are serious injuries, consultation with a surgeon is necessary.
The first dressing after arthroscopic Latarjet surgery.
The video shows the patient's first dressing after surgery. Small skin punctures, low trauma, moderate pain, and the ability to move the arm from the first day after surgery are the undeniable advantages of the arthroscopic intervention technique over the standard open method.
36 days after arthroscopic Latarget surgery.
36 days after arthroscopic Latarget surgery.
After Latarjet, first dressing
After Latarjet, X-ray control – the position of the bone block is ideal
Treatment of humeral dislocations.
To restore normal functioning of the shoulder joint, the victim must be urgently taken to the traumatology department, where he will receive qualified assistance.
When a shoulder is dislocated, treatment occurs in several stages.
- Anesthesia (local anesthesia or general anesthesia, determined by the doctor)
- Reduction of dislocation (conservative or surgical, according to indications)
- Immobilization (additional fixation of the reduced dislocation using bandages or a plaster cast, duration 3-6 weeks)
- Taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications
- Rehabilitation
Description and statistics
Among traumatic dislocations, shoulder dislocation is the most common. It accounts for about 55% of all injury cases. The shoulder joint makes a wide variety of movements, but it is very vulnerable to injury, because the contact area of its articular surfaces is quite small. For example, most often a shoulder dislocation is indirect: a person falls on an arm extended forward or to the side, its movement exceeds the physiological norm, the capsule is torn by the head of the humerus and falls out of the glenoid cavity.
Posterior dislocations are much less common. Statistics show approximately 2% of the case. These injuries occur due to fairly common situations when, for example, a fall occurred, but the arms were extended forward. Then the rupture occurs in the posterior region. Lower dislocations practically do not occur. This variety differs in that the head of the humerus bone moves downward. With such damage, motor function in the downward direction is noticeably reduced. Accordingly, victims face the need to hold the injured limb in such a position that the arm is raised and directed upward.
There is a risk of re-dislocation. It can occur within six months after the first one is corrected. Recurrences can happen more than once - up to ten times a year. Each time the changes will increase. This will provoke an increase in the diagnosis of repeated dislocations. Statistics show that such injuries usually occur in people under 20 years of age.
Recovery after a dislocated shoulder.
Rehabilitation measures take place in several stages. At the initial stage, in the first week after the injury, the patient is given rest with limitation of any actions in the shoulder joint, cold compresses are used, and the doctor prescribes electrophoresis. It is recommended to lightly warm up the hands and wrists (to prevent future atrophy of the arm muscles). At the next stages, exercises for developing the arm are gradually strengthened (a set of exercises is selected individually for each patient), and various physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. By strictly following all the recommendations of your doctor, continuing to do gymnastics to develop the joint and observing basic safety requirements, you can avoid serious consequences (for example, repeated dislocation, etc.)
kinds
Types:
Complete and incomplete dislocation are distinguished. With complete dislocation, the head completely comes out of the socket with loss of shoulder function, and it is almost impossible to perform any movements with the upper limb. With a partial dislocation, the function of the shoulder is not complete, but is preserved. Depending on how long ago the humeral head came out, the dislocation can be fresh or old (old dislocation is the result of the lack of provision of the necessary qualified medical care).
Clinical picture
The main problem with shoulder subluxation is instability of the glenohumeral joint. The anatomy of this joint allows for a large range of motion, which is accompanied by a loss of stability. A study conducted by Basmajian determined that the supraspinatus muscle and also the posterior fibers of the deltoid muscle play a key role in preventing humeral subluxation. Chaco and Wolf also confirmed in their study that the supraspinatus muscle is very important in preventing inferior subluxation of the humerus. Shoulder subluxation occurs during abduction and external rotation.
Other studies indicate that the most important ligamentous structure for maintaining proper alignment of the humerus and also for preventing shoulder subluxation is the inferior glenohumeral ligament. This ligament is most important in external rotation and abduction during the throwing movement.
Shoulder subluxation can lead to soft tissue damage because traction can occur due to gravitational forces and a weak shoulder provides poor protection. This is usually quite painful and may be accompanied by partial numbness in the shoulder, arm and hand.
Classification
Subluxation is classified into several forms, which depend on the mechanism of injury and the direction of displacement of the humeral head.
Currently, there are several types of subluxation:
- anterior - in this condition, the bone head, due to the fact that the articular lip has come off, moves slightly forward and falls under the coracoid process of the scapular region;
- posterior – occurs as a result of a fall on straight arms and, as in the first case, is accompanied by a rupture of the cartilaginous labrum;
- lower - with such a subluxation, the head of the joint extends beyond the boundaries of its cavity.
Three forms of subluxation of the shoulder region
In the case when the instability of the joint is determined exclusively by one direction, it is called single-plane. This type is most often caused by a rupture of the joint capsule, as well as the cartilaginous lip. With multiplanar instability, stretching of the tendon-ligamentous apparatus, as well as synovial membranes, occurs. In this case, characteristic mobility of the joint in several axes is manifested. The objective symptoms of the injury depend on the activity of negative manifestations of the shoulder joint.
Main types of shoulder surgery
Treatment of pathology includes up to 200 types of surgical intervention in the articular apparatus. In general, all types of operations for habitual shoulder dislocation can be divided into 4 main groups:
- strengthening the joint capsule;
- plastic interventions on muscles and tendons;
- osteoplastic procedures with implantation of grafts;
- mixed types of operations.
Basic shoulder joint intervention techniques
Most often, in surgery of the shoulder joints, doctors resort to several methods of intervention, which are named after the surgeons who proposed them - operations according to Seidel, according to Bankart, according to Weinstein, according to Boychev, Andreev, Latarge or Gendeson.
Seidel surgery
This treatment is based on cutting the tendon of the subscapularis muscle - in this way the surgeon achieves intermuscular balance. In addition, this method makes it possible to strengthen the anterior-inferior part of the capsule. It can be exposed by applying a longitudinal excision of the anterior internal humeral surface, from the acromion process to the deltoid muscle.
If the patient has external rotation of the shoulder, an incision is made in the subscapularis muscle in a transverse manner in the area where it attaches to the lesser tubercle of the humerus. A fascial flap from the thigh is taken in sizes up to 10 centimeters in length and up to 3 centimeters in width. This fascia is first fixed to the capsule in the area of the lower pole zone of the joint cavity with one of the ends, and then gradually laid on the capsule from the bottom up and from the inside outwards in an oblique direction. The fascia is fixed to the capsule along its entire length up to the outer upper edge of the dissected deltoid muscle, after which the free end of the tape is brought under the muscle bundle of the fascia and secured in the area of the humeral process of the scapula.
The wound is sutured in layers, and then a diverting plaster is applied to it - in this way it is possible to achieve immobilization of the joint during recovery and recovery.
After about a month and a half, the period of postoperative rehabilitation ends.
Operation Bankart
In this case, the capsule is strengthened by moving the long head of the biceps muscle to the anterior part of the head of the joint. The subscapularis muscle lengthens. This type of surgery is considered minimally invasive and makes it possible to qualitatively strengthen the articular apparatus by re-fixing the damaged lip of the joint. Using special anchors, a new lip is formed from the joint capsule, after which it is fixed to the bone with anchor clamps. Tears of the biceps muscle or the lip itself identified during the operation must be removed.
Weinstein's operation
In the process, the surgeon lengthens the subscapularis muscle and moves the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle to the anterior surface of the head of the bone. Access for the operation is formed along the groove separating the pectoralis major and deltoid muscles, and they must be moved apart. The deep fascia is subjected to longitudinal excision, after which the short head of the biceps muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle are displaced inward.
The intertubercular groove must be opened - in this way the tendon part is exposed along the length of the head of the biceps muscle. With external rotation of the shoulder, it is thrown over the lesser tubercle towards the inside and placed in front of the humeral head. The upper part of the tendon is fixed in the area of the proximal segment of the excised subscapularis muscle, the lower part is attached to the lesser tubercle. The subscapularis muscle is sutured and lengthened over the used tendon. The wound is sutured and a soft bandage is applied to it. A week later, the doctor removes the stitches, and after that the patient must gradually begin therapeutic exercises.
Surgical intervention according to Boychev
It is produced to create a thickening in the area of the anterior edge of the articular process. Thus, the tendons of the short head of the biceps muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle, as well as the outer region of the pectoralis minor, are cut off from the coracoid process. A tunnel is formed from top to bottom, through which the cut off muscles are passed behind the subscapularis. Next, they are fixed in place, strengthened on the coracoid process.
After suturing, the person must be provided with complete immobilization of the upper limb for 10-12 days.
Andreev's operation
Its essence is similar to the previous operation algorithm, except that the outer part of the pectoralis minor muscle in this case cannot be cut off.
Operation Latarget
It is prescribed if the patient has a loss of the bone lobe of the anterior edge of the glenoid cavity on the scapula. The operation is performed with the movement of the coracoid process and the muscle fixed on it to the anterior-inferior edge of the glenoid cavity. In this place it must be fixed. This way it is possible to replenish the missing bone mass in this place. The Latarge operation is considered one of the most effective - it is successful in 97-98% of cases.
Henderson operation
It is prescribed to form the tendon ligament between the shoulder and the acromion process. The incision in this case has an epaulette-like shape - through it the acromial clavicular joint and deltoid muscle are exposed. After muscle dissection, drilling is performed in the acromion process and the greater humeral tubercle through a canal into which the peroneus longus tendon is inserted. The tendon is taken at a length approximately half its thickness. It is pulled tight and the ends are sewn together. After suturing, it is necessary to ensure complete rest of the limb for 10-12 days.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Therapeutic measures
In case of subluxations, first aid should be provided to the victim in a timely manner, which is the key to successful treatment in the future.
After a preliminary examination, the patient is recommended to be given painkillers to reduce pain, and the injured arm must be securely fixed, pressing it tightly to the chest.
To prevent the increase in swelling, it is recommended to briefly apply a bag of cold ice or water to the injury, but it is important to remember that it is strictly forbidden to adjust the joint on your own, as this can significantly worsen the situation.
After the patient has been admitted to a medical facility and assessed the diagnostic results, the traumatologist decides on the need for medical intervention. Reduction of the joint is most often performed under general anesthesia, and all efforts are aimed at returning the humeral head to its anatomically correct position. After fixation, a plaster cast or orthosis is applied to the shoulder, which cannot be removed for 3 weeks until the scar connective tissue is restored.
Technique for reducing subluxation of the shoulder region
The rehabilitation period averages 1.5-2 months, during which the patient is advised to follow a gentle regimen, limiting loads and sudden movements on the shoulder joint. If necessary, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Forecast
The reliability of the joints directly depends on the condition of the muscle corset, therefore, to prevent dislocations and subluxations, you should pay attention to strengthening it with the help of special massage and dosed physical exercises. The best prevention of such manifestations is the regularity of sports activities, in the process of which all muscle groups should be involved.
In this case, the state of the body should be taken into account. In the event that, despite all the measures taken, it was not possible to avoid damage to the joint, it is necessary to promptly seek advice from a highly qualified specialist who will prescribe adequate treatment. It must be remembered that subluxations in the shoulder joint are quite common and the nature of further therapy depends on the mechanism of injury. With timely assistance, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Rating scales
Oxford Shoulder Instability Test (OISS)
The OISS is a 12-item questionnaire with five correct Likert responses for each question and has a range from 0 to 48 (with a score of 48 indicating better shoulder function). The OISS was developed and validated to assess shoulder instability and has also been tested to assess sensation in patients with shoulder instability.
Western Ontario Shoulder Instability Index (WOSI)
The WOSI is a 21-item questionnaire with a 100 mm horizontal visual analogue scale below each patient response question and ranges from 0 to 2100 as a percentage, with 100% representing the best possible shoulder-related quality of life. The WOSI is a carefully developed and evaluated instrument for patients with shoulder instability that has been demonstrated to have excellent sensitivity for posterior instability.
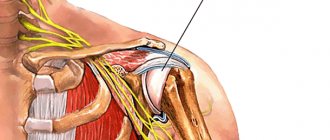
How the surgical procedure occurs: modern arthroscopy methods
Whenever possible, joint surgery is performed through arthroscopy. Arthroscopy refers to the surgeon's method of accessing the surgical field. It eliminates the need to make large incisions and, accordingly, significant tissue trauma. In addition, it takes into account the features of the complex structure of the articular apparatus more than classical open surgery.
The operating process looks like this: the patient is secured on a couch or in a special chair. It should take the most comfortable position, and to ensure complete immobility it is additionally secured with bolsters and belts.
After administering anesthesia, the surgeon treats the surgical field in accordance with aseptic requirements. When the anesthesia takes effect, the doctor makes a small incision and through it inserts an arthroscope into the shoulder - a flexible hollow tube with sensitive optics.
In order for the surgeon to have a better view of the field of activity, a sterile fluid is pumped through a tube into the joint, causing it to swell somewhat and make it easier to see. Several small incisions are made to allow instruments and cannulas to be inserted.
Having completed the necessary manipulations, the doctor removes the arthroscope and all his instruments, processes the incisions, and applies sutures or special patches to them.
Causes
Chronic shoulder dislocation is a polyetiological disease, the development of which can be caused by the influence of several provoking factors. These include:
- Traumatic or pathological damage to the soft structures of the shoulder that increases the depth of the glenoid cavity.
- Sprain of ligaments with a congenital decrease in their strength.
- Incorrect treatment of acute dislocation, accompanied by insufficient duration of immobilization (immobilization) of the joint or incorrect, insufficient reduction.
Acute shoulder dislocation, often leading to instability of the joint, occurs when the upper limb is sharply abducted posteriorly or is excessively rotated outward. As a result, habitual shoulder dislocation may develop. Rehabilitation and therapy necessarily take into account the causes of the pathology.
First aid
The speed of recovery and the number of complications that develop depend on whether first aid was provided to the victim. The person should be immediately placed on a hard surface and the injured shoulder should be kept at rest. This can be achieved by positioning the arm in an abducted position - the elbow needs to be slightly bent and a cushion or folded cloth placed under it. A bandage to support the upper limb in the abducted position will allow the joint to be completely fixed. This is a triangular scarf, in the middle of which the forearm is placed, and the ends are tied with a knot at the back of the neck. In addition to immobilizing the hand, the main task of first aid is to improve the well-being of the victim. What can be done to reduce the severity of pain:
- Apply an ice pack wrapped in thick cloth to your shoulder to prevent frostbite. The maximum time for applying a cold compress is 15 minutes every hour. The procedure not only helps eliminate pain, but also prevents the spread of inflammatory swelling to healthy joint structures;
A cold compress and immobilization of the affected arm are first aid measures.
- give the victim a tablet (1.5 for acute pain) of any anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drug - Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Nise, Ketorol. You can also dilute a Nimesil sachet in 100 ml of water.
In case of acute pain, you must call an ambulance. This is a characteristic symptom of combined joint damage, so the victim is hospitalized for examination and surgery. If a person complains of mild or moderate pain, then immediately after fixing the arm, he should be taken to the emergency room for realignment of the shoulder joint.
Habitual dislocation of the shoulder joint: injection of anesthetic before reduction.