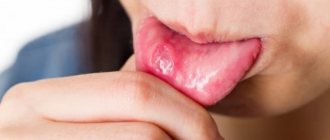
The norm is a small formation of light or white color. But a yellow coating on the tongue and bitterness already indicate disturbances in the functioning of the body.
Any changes in the oral cavity are always scary and cause discomfort. A slight coating on the tongue is normal for both adults and children. However, if the formation has acquired an atypical hue and is accompanied by bitterness, then this may indicate signs of illness.
Yellow coating on the tongue: when not to worry
If a strange tint appears on your tongue, do not immediately sound the alarm. The color of the plaque may vary depending on the time of year. For example, in summer in hot weather with a lack of water, the plaque may have a yellowish tint, in winter it can be white-yellow. Do not forget about coloring foods (citruses, apricots, coffee, strong tea), bad habits and medications - they can also cause yellow plaque.
Such plaque can usually be quickly removed with a toothbrush or scraper. If it is impossible to get rid of it with the help of hygiene products, and in addition there is an unpleasant odor from your mouth, then it’s time to see a doctor.
Yellow tongue or how to get rid of bad breath
Home Articles Popular information articles Nutrition and diets
Each of us, in the process of communicating with each other, notices that some people have bad breath, while others do not, some have bad breath and a tongue coated with a white-yellow coating, while others do not have this. And, interestingly, if there is a yellow coating on the tongue, there will definitely be bad breath!
Why does the tongue appear coated with a yellow coating and putrid odor from the mouth?
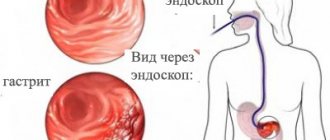
The cause of bad breath can be carious teeth, as well as diseases of the digestive system. Such diseases of the digestive system include, first of all, functional conditions of the valve apparatus of the stomach, when the contents of the stomach and intestines periodically reflux into the esophagus more than 2-3 times a day, especially at night, when you are in a horizontal position. This condition occurs when the sphincter apparatus of the stomach and esophagus is insufficient. The cause of episodes of reflux (or gastroesophageal reflux) of the contents of the stomach and (duodenogastric reflux) of the intestines can be observed due to poor nutrition (abuse of foods that cause a decrease in the tone of the sphincter apparatus of the stomach), taking medications of a similar effect (hypnotics, sedatives, antispasmodics, laxatives, etc.) frequent stress, prolonged physical activity, constipation, flatulence associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure. Reflux can also occur with alcohol abuse and smoking.
The presence of gastroesophageal functional reflux is a passing phenomenon, but when reflux is a consequence of organic disorders of the sphincter apparatus of the stomach and esophagus (esophagitis, gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer, etc.), or damage to the brain or spinal cord, congenital or acquired, then in these cases we speak of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The main signs of functional insufficiency of the lower esophageal sphincter are heartburn, belching of food, pain in the stomach or chest area, a yellow coating on the tongue, the appearance of stains on the pillow after sleep, and rotten breath. The yellow color of the tongue is associated with the reflux of bile into the oral cavity (duodenooral reflux). The frequency of reflux increases in the evening and night hours. It has been established that in healthy people duodenogastric reflux is practically absent.
The presence of reflux leads to the development of diseases of the digestive system and not only; the reflux of contents from the stomach into the oral cavity leads to microaspiration into the tracheal cavity, which can affect the health of the respiratory system. Long-term microaspiration of contents often leads to the appearance of an obsessive cough, and subsequently to the development of lung diseases (chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma...). Based on the above, it becomes clear that it is necessary to prevent functional diseases of the stomach and esophagus, and even more so to prevent the development of GERD, and when the first signs of gastroesophageal and duodenogastric reflux appear, it is necessary to take the most active measures to eliminate them.
Where to start, what should be recommended for patients with gastroesophageal reflux?
Nowadays, every person knows how to maintain health. Combating risk factors and preventing overstrain of the nervous system are not burdensome, truly accessible to everyone and highly effective. Physical education, proper nutrition, a rationally and intelligently structured lifestyle, work and rest schedule play an important role in them. Moreover, the final goal can be achieved only with comprehensive compliance with all recommendations throughout life. First of all, these include the complete abandonment of bad habits.
After eating at lunchtime, a walk is necessary and daytime sleep is allowed only after 1.5-2 hours. It is recommended to sleep with the head of the bed raised by at least 15-20 cm. You should avoid tight clothing, tight belts, and tight elastic bands of clothing. What happens if after a heavy meal a person lies down on his back? By the way, no animal sleeps on its back! With this position of the body, the gas bubble of the stomach moves to the front wall and not air, but acidic gastric contents are discharged into the esophagus. This is precisely the trigger mechanism for the development of gastroesophageal reflux.
Physical exercises should be with the exception of overstraining the abdominal muscles, deep bending, prolonged stay in a bent position, lifting weights of more than 6-7 kg on both hands. It is not recommended to inflate balloons or tubes with your mouth or engage in professional sports.
In terms of nutrition, you must adhere to a diet. You should limit or reduce the content of animal fats (cream, butter, fatty fish, pork, duck, lamb, cakes), increase the protein content, avoid irritating foods (strong broths, marinades, smoked meats, sour and irritating (pineapple) juices, tomatoes, citrus fruits, coffee, strong tea, chocolate, onions, garlic, alcohol, tobacco, spices), carbonated drinks. It is necessary to reduce the daily amount of food, and the number of meals can be increased. While eating, it is advisable not to be distracted or talk; food should be chewed thoroughly and not rushed. In addition, you should not eat before bed. Sleep is allowed 2-3 hours after the last meal. Patients with excess weight are recommended to reduce it.
The presence of reflux does not depend on age; it can also occur in children under one year of age. In the nutrition of children in the first months of life who are bottle-fed, special anti-reflux mixtures should be used, the peculiarity of which is a change in the ratio of casein and whey proteins towards casein, as well as the inclusion of thickeners in their composition (most often, carob gum.
Where to start drug therapy?
In children and adults in the initial stages of reflux development, it is necessary to start by taking a decoction of medicinal plants:
Oregano herb - 50.0 Plantain leaf - 40.0 Yarrow herb - 30.0 Linden blossom - 20.00
Brew 1 tbsp. for 250 water, leave for 2.5 hours, drink 1/2 cup 3 times a day 25 minutes before meals (dose for age 24 years). You need to take the herbal collection for 1 month. It is recommended to prescribe the collection for children from 2.5-3 months. Among medications, it is recommended to prescribe the drug Motilium. For adults (1 tablet x 3 times a day 15 minutes before meals for 10 days) and for young children in syrup, according to weight. This is the so-called symptomatic therapy; the main direction in treatment should be given to the disease that led to the appearance of pathological reflux. The presence of such complaints always requires contacting a gastroenterologist, who will prescribe the comprehensive necessary treatment. Functional disorders of the digestive system are a large group of diseases that are widespread in childhood and adulthood and have an ambiguous prognosis. In recent years, significant progress has been made in the treatment of functional disorders associated with the emergence of new effective drugs that regulate gastrointestinal motility. However, these remedies cannot provide a final solution to the problem: due to the significant role of the nervous system in the development of these diseases, their treatment must be comprehensive and carried out in collaboration with neurologists, psychologists, and psychoneurologists. Following our recommendations on this issue with a mandatory consultation with a gastroenterologist will help you get rid of bad breath and a coated tongue, and therefore improve your health.
Gastroenterological Center of the Chelyabinsk Region. Tel. to sign up for a consultation: 89026187717
Author: V.L.
Zemlyakov Printable version
Causes of yellow coating on the tongue
- Poor functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The most common reason for the appearance of an unpleasant plaque, which can indicate either a mild ailment or a serious illness. As a rule, the issue is resolved by correcting the diet, that is, switching to a more gentle regime and giving up fatty and fried foods.
If the plaque is dense and has an unpleasant odor, then the cause is diseases of the digestive system (pancreatitis, gastritis, ulcers).
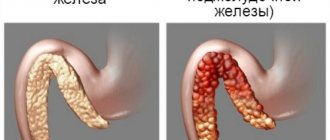
- Diseases of the liver, gall bladder, kidneys.
Excessive consumption of fatty and fried foods impairs the flow of bile, which disrupts liver function. Characteristic signs of liver and gallbladder diseases are a yellow coating on the tongue and a metallic taste in the mouth.
- Reaction to antibiotics.
Some medications increase the load on the liver and digestive organs. Since antibiotics kill not only harmful but also beneficial bacteria, to prevent dysbiosis, fermented milk products, prebiotics and probiotics are added to therapy.
- Viral and respiratory diseases.
Yellow plaque can be a consequence of infectious (whooping cough, scarlet fever, etc.) and respiratory (sore throat, pharyngitis, etc.) diseases. During illness, immunity decreases, which is why bacteria settle in the oral cavity, including on the tongue.
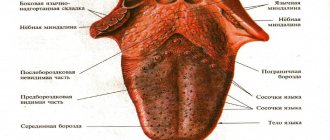
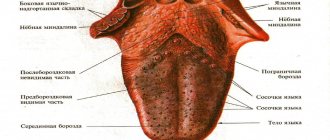
Anatomical structure of the tongue
The structure of human language corresponds to its multifunctionality, which lies in the fact that it participates in the processes:
- chewing;
- salivation;
- taste perception;
- speech.
The body of the tongue consists of striated muscle tissue, which is covered by a membrane of mucous tissue. Its surface, called the back, is conventionally divided into three parts:
- the last third, located near the pharynx, is called the root;
- the first two thirds are the body of the tongue.
A longitudinal groove runs in the middle, which is an external manifestation of the internal septum; it is, in fact, a reduced thyroglossal duct.
The mucous membrane, tightly adjacent to the muscle tissue, is covered on the outside with stratified squamous epithelium. It contains:
- salivary glands;
- taste buds;
- lymphatic ducts.
The mucous membrane of the posterior part forms three supraglottic folds, with the help of which the tongue is attached to the larynx:
- median;
- two lateral.
The tongue is abundantly covered with papillae, including:
- filamentous - act as organs of touch and, thanks to the rough surface, hold food on the tongue;
- cone-shaped – responsible for sensitivity to temperature and pain;
- mushroom-shaped - equipped with taste buds, thanks to them we distinguish many taste sensations;
- groove-shaped - located near the root, have serous glands and are also responsible for the sense of taste;
- leaf-shaped - equipped with lingual glands that secrete a mucous secretion.
The tongue is attached to the oral cavity by a fold of mucous membrane called the frenulum.
Yellow coating on the tongue: how to treat
Treatment of pathology should begin with clarification of the diagnosis. To do this, you need to consult a therapist and specialists, take the necessary tests and undergo appropriate diagnostics. Treatment may include not only taking medications, but also a special diet, rinsing with medicinal solutions, careful oral hygiene, etc.
To prevent the formation of a yellow coating on the tongue, experts recommend not to overuse coffee, fried and spicy foods, and to include more vegetables and fruits.
Treatment
To get rid of unsightly deposits, unpleasant odors and other symptoms, you need to determine their cause. To do this, you need to contact a therapist who will conduct an examination and prescribe additional tests and examinations (general analysis and blood biochemistry, throat culture, gastroscopy, ultrasound, coprogram, etc.). Based on the results, he will recommend therapy, diet and, if necessary, give a referral to a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, dentist or other specialist.
After treating the root cause of plaque, its intensity should decrease. But to speed up the process, doctors recommend paying more attention to oral hygiene, brushing the surface of the tongue twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush (but not a scraper, so as not to cause injury), drinking more water and rinsing your mouth with herbal decoctions.
Prevention
It is not always possible to prevent the formation of plaque on the tongue, especially if it is a symptom of an infectious, viral or fungal infection. But you can reduce the likelihood. The recommendations will not be new: you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, do not smoke, do not abuse alcohol, drink coffee and tea in moderation, exclude too fatty, spicy and fried foods, include more vegetables, fruits, whole grains in your diet, give preference to lean varieties of meat and fish and do not take medications (especially antibiotics) without a doctor's prescription.