What functions do the ovaries perform?
This body has only two main tasks:
- Reproductive.
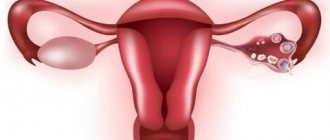
Each ovary contains follicles that contain eggs. Their number is maximum at the time of the birth of a girl. From the age of 12-14 years, the cyclical process of growth and maturation of follicles begins. During this process, one follicle with a mature egg becomes dominant. Then ovulation occurs - the process of releasing an egg from the follicle into the abdominal cavity. Throughout life, follicles are used up in each cycle, but their number is not replenished.
This is why women have a shorter reproductive capacity than men. Closer to 45-50 years of age, ovarian function declines. Their volume is reduced by 2 times. The number of cycles without ovulation increases. This period is associated with age-related changes and is called involution or menopause.
- Hormone synthesis.
The gonads mainly synthesize estrogen. It is this hormone that takes part in the formation of the female reproductive system. Thanks to it, the functional layer of the endometrium is regularly rejected, which leads to menstruation. In this way, estrogen controls the monthly ovulation cycle. Other sex hormones are also produced in smaller quantities in the ovaries - androgens and progesterone. Progesterone is important for maintaining pregnancy.
Any even minor deviations in the functioning of the female reproductive glands can lead to hormonal imbalance. This will not only affect the woman’s general well-being, but will also cause the development of many pathological processes.
The following ultrasound diagnostic indicators are considered normal:
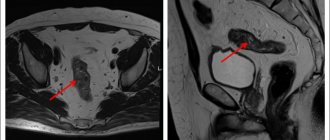
In women 16-40 years old, the sizes of both ovaries should not differ (length 30-41 mm, thickness - 14-22 mm, width - 20-31 mm). The normal volume of each of them is 12 cubic meters. ml. The outer surface of the ovary is lumpy and consists of many follicles. The degree of echogenicity of the stroma resembles the uterus. The total number of follicles must be at least 12; if there are less than 5, then we are talking about abnormal functioning of the follicular apparatus.
In the middle of the menstrual period, one dominant follicle of larger size should appear. Subsequently, an egg is released from it, and after 2 weeks a corpus luteum is formed in this area.
Types of ovarian diseases
All diseases can be divided into the following main groups:
- Benign formations.
This group includes various cysts (corpus luteum, follicular, paraovarian), teratomas, cystadenomas. They do not degenerate into malignant tumors and tend to grow slowly. They are often asymptomatic. Small formations require only medical supervision, while large ones are removed surgically.
- Inflammatory diseases of the ovaries.
In medicine, the inflammatory process in one or two ovaries at once is called oophoritis. It rarely occurs in isolation. It is often accompanied by inflammation of the fallopian tubes - salpingitis. The basis of these diseases is infection.
- Malignant tumors.
Ovarian cancer or carcinoma. The most malignant but rare tumors include hemangioendothelioma, leiomyosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. Treatment is complex and depends on the stage of development of the cancer process.
- Dysfunctions.
This is a pathological condition that is associated with a violation of any of the functions of the ovaries. These include premature menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome, anovulatory and juvenile (teenage) dysfunction. The main symptom is the absence of periods or changes in their duration. Dysfunction can cause infertility, amenorrhea (prolonged absence of menstruation), PMS, polymenorrhea (long and heavy menstruation).
All these diseases of the female ovaries can lead to serious and often irreversible consequences. Often the initial stage of the disease does not cause much concern, and the woman is in no hurry to see a doctor. In order to identify pathology in time, you need to be attentive to any changes in the body.
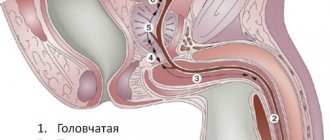
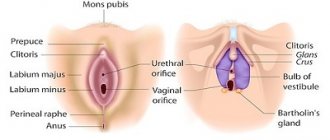
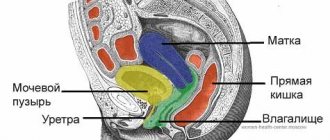
Structure
The female ovaries are a pair of glands (roughly the size and shape of an tonsil) in the female reproductive system that store eggs and produce estrogen. They are held in place by several ligaments on either side of the uterus. Eggs travel from the ovaries to the uterus through the fallopian tubes. Around the entrance to the fallopian tube are tiny fimbriae, or finger-like projections, that guide the egg into the tube to meet the sperm each month.
Ovarian sizes
The ovary of a female infant weighs less than 1 gram, its length is approximately 1.0 - 1.5 cm, its width is about 1.5 cm. When girls reach adolescence, the ovaries become larger and take on the shape of an almond, reaching approximately 3.0 - 3. 4 cm in length. The ovaries of a woman of reproductive age normally weigh 6.0 - 7.0 grams, have a length of 2.0 - 3.5 cm, and a width of about 2 cm. They are not always the same in size - the left ovary is often smaller than the right. Each of them has two rudimentary processes - the epididymis and the periovarian.
How the ovary works inside in women
When to see a doctor
All women should visit a gynecologist annually from the beginning of sexual activity. Some diseases, for example, neoplasms, can only be detected by examination using mirrors.
There is no need to hesitate to visit a doctor if you have the following symptoms from time to time or constantly:
- Menstruation did not occur until the age of 15-16. In this case, the girl must be shown to a pediatric gynecologist.
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen, worsening before menstruation.
- Cycle failure.
- Lack of menstruation for more than 2-3 months.
- Absence of pregnancy for a year with active sexual activity without protection.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Bloody discharge between periods.
- Heavy, prolonged and painful bleeding.
- Miscarriage.
All these symptoms indicate the presence of pathology in the reproductive system. With hormonal imbalance, a woman’s mood often changes. She becomes irritable, suffers from insomnia and chronic fatigue.
During inflammatory processes in the acute period, the ovaries enlarge. Therefore, when palpating the lower abdomen, a woman may feel pain or discomfort.
If the disease has become chronic, the symptoms are mild. Painful symptoms may only bother you before or during menstruation. Due to changes in hormonal levels, a decrease in libido may be observed.
The chronic form is more difficult to diagnose and treat. Therefore, if there are minor changes in women’s health, you should consult a gynecologist.
Research methods
Several types of ultrasound are common in diagnostic practice:
• With penetration of the sensor into the vagina (transvaginally).
• With penetration into the rectum (transrectal). It is prescribed to virgins for a more accurate assessment of the condition of the ovaries and to identify inflammatory processes and pathologies in them.
• Without penetration into the vagina, through the walls of the abdomen. This method uses a wider sensor that is placed over the woman's abdomen. In this way, only the most severe developmental anomalies can be seen.
To study the patency of the fallopian tubes, the ovaries and uterus are filled with a special fluid, and a monitor specialist observes its movement in the organs.
What treatment methods are there?
The gold standard for the treatment of menopausal syndrome is hormone replacement therapy (HRT). HRT is a pharmacological drug that compensates for the lack of estrogen in a woman’s body. Currently, HRT includes only “natural” estrogens and gestagens, which are obtained from plants (mainly soy and wild yam). HRT affects all components of the menopausal syndrome:
- vasomotor (hot flashes, sweating),
- psycho-emotional (anxiety, irritability, tearfulness),
- urogenital (dryness, itching and burning in the vagina),
- metabolic (weight gain, bone fragility, changes in skin turgor).
An alternative to hormone replacement therapy are herbal medicines . These are biologically active additives (BAA), which are obtained from the same plants, but using other technologies. As a result, such a supplement contains not only the active substance, which has an estrogenic effect on the body, but also other substances contained in plants. The effectiveness of herbal medicines in relieving the symptoms of menopausal syndrome is lower than that of HRT. Dietary supplements are used only for the treatment of hot flashes and do not affect bones, blood vessels, mood, skin and urogenital symptoms. Control over the production of herbal medicines is less strict and they are sold in pharmacies without a prescription. However, women who are contraindicated for hormone replacement therapy should be wary of taking herbal medicines and should consult a doctor.
For women for whom estrogen replacement therapy is contraindicated, the doctor can select non-hormonal drugs of central action , which will reduce the number and severity of hot flashes and regulate the psycho-emotional background. The main disadvantage of this therapy is that such drugs are prescribed in courses and not on a continuous basis, and during breaks the woman may experience hot flashes again. In addition, centrally acting drugs do not have a beneficial effect on the bones, urogenital disorders, skin and metabolism of women.
There is a set of measures aimed at changing lifestyle , which helps to survive the menopause. This includes special breathing exercises to control your condition during hot flashes, quitting smoking, proper nutrition, a diet containing soy products, exercise and walks in the fresh air.
Causes of pain in the ovaries
Painful manifestations in the ovaries can occur due to many reasons. Sometimes they are not dangerous, since they accompany physiological processes - menstruation, pregnancy, ovulation, intestinal motility. But sometimes the reason why the ovaries hurt is pathological changes occurring in the body:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- inflammatory process;
- cysts, including those with pedicle torsion;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- endometriosis;
- hemorrhage in the ovary (apoplexy);
- the condition of other organs and systems - kidney stones, appendicitis, depression, gastrointestinal problems and others.
What is menopausal syndrome?
Menopausal syndrome is a whole complex of symptoms associated with a lack of estrogen in a woman’s body. The first to appear are so-called vasomotor disorders - hot flashes, sweating, palpitations, dizziness. emotional background also depends on hormones: anxiety, depression, tearfulness, irritability, decreased libido and insomnia - this is how the body reacts to menopause. The severity and duration of these symptoms varies from person to person - for some they do not bother them at all, but for other women they continue for years. Over time, urogenital disorders : vaginal dryness, itching, burning, pain during sexual intercourse. The tone of the perineal muscles decreases, urination disorders may appear, including urinary incontinence when laughing or coughing. metabolism changes —weight may increase, adipose tissue accumulates in the waist area, bones become brittle (osteoprosis develops), appearance changes—the skin loses its elasticity, wrinkles appear. Of all these symptoms, only vasomotor symptoms (hot flashes and sweating) are temporary. Psychoemotional, urogenital disorders and metabolic changes will progress over time if left untreated.
What examination is prescribed before selecting HRT?
This is an examination that allows a woman to exclude contraindications for HRT. The minimum examination includes:
- Oncocytology of the cervix (screening for cervical cancer)
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
- Mammography (breast cancer screening)
- Blood chemistry
- Hormonal examination (usually an assessment of thyroid function).
This list can be expanded, especially if a woman suffers from chronic diseases.
The likelihood of pregnancy with inflammation of the right ovary
If the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner and treatment is prescribed adequately, the probability of successfully conceiving, carrying and giving birth to a healthy child is 70–80%. When right-sided orphitis has passed into a chronic stage, accompanied by frequent exacerbations, the probability of pregnancy does not exceed 20 - 25%.
Therefore, if a woman has not yet realized her reproductive function or is planning another pregnancy, she should closely monitor women’s health, and if there are any suspicious signs, seek professional medical help, and not self-medicate.
Mechanism of activation of immature follicles
For women suffering from infertility due to the disease discussed, the only option for motherhood is implantation of a fertilized donor egg. However, a group of specialists from Stanford University (USA) and the Faculty of Medicine of the University. St. Marianna (Japan) proposed an alternative - a method that eliminates known surgical interventions to stimulate ovulation, such as wedge resection of the ovaries or laser drilling. Doctors removed the ovaries from the study participants, divided them into several parts, and then treated the ovarian fragments with growth-stimulating drugs. A few days later, some of the tissue fragments were implanted into the women's fallopian tubes. Then the specialists observed the development of the follicles. Some study participants developed mature eggs, which allowed them to undergo the standard procedure of in vitro fertilization (IVF [3]). The results of the study were published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences [4].
It is important to note that the opportunity to carry out such treatment arose thanks to the study of a cell signaling pathway called Hippo [5], which is one of the key components of the regulation of such important processes as contact inhibition of cell growth and the associated control of the size of internal organs [6]. The Hippo protein complex was originally discovered in Drosophila. Flies in which its functioning was disrupted literally increased in size (which is why the regulator got its name: “Hippo” comes from the word “hippopotamus”). Then it was discovered in mammals.
A key component of the Hippo pathway is the Yap (Yes-activated protein) kinase, which in its active state is capable of binding a number of transcription factors, such as p73, p53-binding protein-2 (p53BP2), RUNX2, SMAD7, ERBB4, PEBP2a and TEAD/TEF [ 7]. Regulation of YAP activity is carried out mainly due to the inhibitory effect of LATS1 and 2 kinases (large tumor suppressor-1 and −2). They, in turn, are activated by MST1 and MST2 kinases (mammalian sterile-20-like kinases). For full activation of LATS and MST, it is also necessary that they be associated with the adapter proteins WW45 and MOB1, respectively. The above-described part of the Hippo signaling pathway is highly conserved in mammals, while the signals for activation or inhibition of LATS and MST can be quite diverse. The Hippo signaling pathway is summarized in Fig. 5.
Figure 5. Schematic representation of the operation of the Hippo signaling protein regulator.
The development of the embryo, the division of embryonic cells and the growth of tissues and organs are evolutionarily controlled by the work of various regulators. According to one of the study authors, Aaron Hsueh, an obstetrician-gynecologist at Stanford University in California, women with ovarian wasting syndrome have increased activity of the Hippo regulator [8]. In other words, it blocks the maturation of almost all ovarian follicles, which minimizes the possibility of ovulation and further fertilization.
Scientists disrupted the Hippo signaling pathway in the removed ovaries and thus prevented the premature arrest of follicle development. Next, the specialists stimulated the activity of another signaling pathway called Akt, which helped accelerate follicle growth [9], [10].
Clinical studies were conducted first on laboratory animals. At the next stage, 27 women suffering from primary ovarian dysfunction agreed to take part in the experiment. The study found that some women had no follicles in their ovaries. Immature follicles were found in the ovaries of 13 patients; Of these, in eight women, the use of the new treatment method contributed to the growth of viable follicles. For 14 women, treatment was ineffective.
As a result, mature eggs were obtained from five women and used for IVF. One of the patients, aged 29 years, gave birth to a child weighing 3.3 kg during the course of treatment at 37 weeks of pregnancy (Fig. 6). The scientific team hopes that the effectiveness of the new treatment will reach 30%. And, moreover, according to them, this method can also help women who have undergone radiation or chemotherapy, and patients aged 40–45 years with irregular menstrual cycles [11].
Figure 6. Kazuhiro Kawamura, one of the scientists involved in the study, holds a newborn boy born to an initially infertile woman.
Kazuhiro Kawamura
What changes with age?
A woman's ovaries contain a limited number of follicles, and over time these follicles are used up. At first, most cycles become anovulatory, that is, ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum do not occur, which means there is little progesterone hormone. A woman’s menstrual cycle begins to change - it becomes longer or shorter, the intensity of menstruation changes, and the menstruation itself comes irregularly. When there are very few follicles left, the ovary stops secreting estrogens. At first, menstruation becomes rare and irregular, then stops. The last menstruation is called “menopause”. Climacteric syndrome begins to develop.
Preparatory activities
It all depends on the type of ultrasound:
• Within 1-2 days before the transvaginal examination, the woman needs to take sorbent drugs and Espumisan. Before the ultrasound, the bladder must be emptied.
• Preparation for a transrectal examination, in addition to the above actions, also requires bowel cleansing 12 hours before the scheduled procedure. You can do this yourself, using an enema of laxative suppositories or medications. Before the study, you must empty your bladder.
• A transabdominal ultrasound will require a 3-day diet that excludes foods that cause bloating or gas. Take absorbents or Espumisan. 1 hour before the procedure, drink still water and do not urinate.
A routine ovarian examination is scheduled on days 5-7 of the cycle. If you need to control the changes occurring in the organ, you will need to undergo this procedure several times: at the beginning of the cycle (8-10 days), in the middle (14-16 days), at the end (22-24 days).
Possible complications and prognosis for various diseases
In women, ovarian disease should be treated by a doctor at a hospital location. Most of them are treatable with medication. The main complication is infertility. After salpingoophoritis, it is associated not only with blockage of the fallopian tubes, but also with changes in the endocrine and cardiovascular system.
Hormone therapy under the control of functional diagnostic tests and sanatorium-resort treatment are actively used. Tuberculosis has the same consequences. Viral diseases can cause early miscarriage and malformations of the fetus.
Diseases associated with acute conditions sometimes require surgical intervention. The result is usually removal of the ovary. If the second sex gland remains untouched, this will not affect the reproductive system. A woman may well become pregnant and bear a healthy fetus.
If for medical reasons it is necessary to remove both ovaries, then post-castration syndrome may occur. In young women, this syndrome develops much more severely.
The mammary glands begin to shrink, and sexual sensation decreases. Neuropsychic disorders occur in the form of depression, irritability, and memory loss. Somatic diseases are getting worse. Glaucoma and periodontal disease develop.
With the onset of menopause, the work of the ovaries gradually fades. For some women, this process occurs without pathological changes. However, a number of them may experience menopausal syndrome.
It is caused by disruption of the endocrine system. Women suffer from increased sweating, sleep disturbances, and tachycardia. General restorative therapy, physical therapy and hormonal medications help you get through this period comfortably.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Opinions and forecasts
According to Marcelle Cedars, a specialist in reproductive oncology at the University of California, San Francisco, researchers were quick to test a new method of treating infertility in humans: “Scientists demonstrated the birth of healthy offspring in preliminary studies on mice, but there was no evidence growth, development and/or fertility of this generation" [12].
The authors of the study believe that the method is suitable for infertile middle-aged women, as well as those who have been diagnosed with primary ovarian failure, as a result of which pregnancy does not occur in more than 50% of cases. However, not all experts share their optimism. The head of the medical group studying fertilization at the University of Southern California, Richard Paulson, is convinced that the key condition for the effectiveness of the developed mechanism of laboratory “activation” of the follicle is the presence of a healthy egg in it. In addition, Paulson draws attention to the fact that it is unreasonable to compare the results of treatment of a woman at the age of 29 with the results of treatment of a woman at 40, since hormonal stimulation of follicle growth and development occurs at different rates at different ages.
The considered conservative method of stimulating ovulation by blocking the Hippo signaling pathway in individual fragments of ovarian tissue may be useful for women with cancer or undergoing sterilization procedures. But still, the main achievement of scientists is the birth of a child to a woman who, without their participation, would never have been able to become a mother.
Are there any contraindications for HRT?
Yes, they exist, just like for any drug. These include:
- Vaginal bleeding of unknown origin
- Acute severe liver disease
- Acute deep vein thrombosis
- Acute thromboembolic disease, hereditary and acquired thrombophilias, previous thromboembolism or deep vein thrombosis.
- Porphyria
- Breast cancer and endometrial cancer.
In addition, there are a number of diseases for which the use of hormone replacement therapy is limited, therefore, before prescribing replacement therapy, a doctor’s consultation and examination are necessary.
Abnormal cystic formations
A dermoid cyst is considered a benign tumor and appears as a result of improper distribution of tissues in the body. The cavity of the cyst in this case consists of cells that should form the skin and other components, but end up in the ovaries. As a result, the cyst is filled with cells from hair, cartilage and nails. On an ultrasound machine it will look like a ball with very dense walls (up to 15 mm) and a high level of echogenicity. If this type of pathology is suspected, the doctor may prescribe an MRI or CT scan.
An endometrioid cyst is determined by ultrasound by the following signs:
• a round or oval formation is filled with liquid;
• located on one side, consists of one chamber;
• cystic walls are thin (up to 8 mm);
• the external structure is clear, the internal one is covered with irregularities;
• the ovary in the place where the cyst is found is not visible;
• the uterus is increased in size, but without changes in structure and shape;
• a healthy ovary contains many small follicles; up to 3 dominant follicles can mature in it;
• “honeycombs” are visible in the cavity - inclusions of an echo-positive nature of a linear, arc-shaped or ring-shaped shape, the thickness of which does not exceed 2 mm.
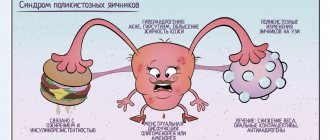
Polycystic disease can appear in girls and young women if their body produces too many male sex hormones. With this disease, the diameter of the ovaries reaches more than 10 cubic meters. cm with clearly visible cysts inside them with a diameter of up to 9 mm. The organ capsule becomes very thick
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor that most often occurs in women during menopause, and in more rare cases - in young girls or girls who have not yet started menstruation. The doctor should be wary if an ultrasound showed the presence of a multi-chamber cyst with poorly defined contents, which began to develop on organs located close to it. A symptom of cancer can be the appearance of fluid in the peritoneum and pelvis.
In this case, the woman is prescribed a series of repeated examinations. If she has reached the age of 45 years older, or this is discovered in a girl before the start of her menstrual period, the doctor sends the patient for a biopsy.
Risk factors for developing the disease
The reason for the development of pathology in a large number of women has not been established. Stopping long-term use of oral contraceptives may lead to premature ovarian failure. In some cases, the disease may develop immediately after pregnancy.
As a result of the studies, the presence of risk factors for the development of this disease has been proven:
- high blood glucose levels;
- age;
- smoking.
When to start HRT and how long can you continue taking it?
It is better to start HRT at the first signs of depletion of ovarian function and the appearance of menopausal syndrome. The more time has passed since the last menstruation, the fewer estrogen receptors remain in the body, which means that hormonal drugs will not be as effective as possible. It is considered optimal to prescribe HRT no later than 6-8 years after the last menstruation. If therapy was started on time, the effect of the drugs persists throughout the duration of administration and does not depend on age.
In the absence of contraindications, the duration of hormone replacement therapy is not limited. There is no need to take breaks in treatment. It must be remembered that a woman taking such drugs should regularly visit a gynecologist and undergo an examination at least once a year (usually the same as before selecting HRT).