- Possible complications
- Prevention of pathology
- Attending doctors
- Prices for services
Regulation of the normal menstrual cycle is carried out through the combined work of a cascade of levels, starting from the brain and ending with the endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterus).
When ovarian dysfunction develops, disturbances occur in the hypothalamic-pituitary system, after which the processes of physiological synthesis of pituitary hormones (follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones) are disrupted. When pathological levels of hormones influence the ovary, the mechanisms of its activity are disrupted. That is, the physiological process of ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum may be absent, which naturally leads to hormonal imbalance in the form of a disruption in the synthesis of the physiological level of estrogen and progesterone.
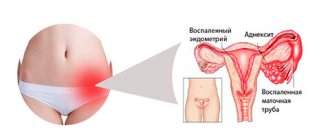
Insufficient synthesis of estrogen and progesterone affects the uterus and endometrium, forming the clinical manifestations of such a diagnosis as ovarian dysfunction.
Ovarian dysfunction refers to various pathological conditions, the development of which is caused by a violation of the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle, when the ovaries malfunction.
Symptoms of ovarian dysfunction
Dysfunction of the ovaries leads to the formation of certain characteristic clinical symptoms. The diagnosis of ovarian dysfunction can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- menstrual irregularities. This symptom is the most common complaint in women who have ovarian dysfunction. These disorders can be of a different nature: delays in menstruation, or, conversely, intermenstrual bleeding;
- amenorrhea: absence of menstruation may last for six months or more;
- Based on the fact that the ovarian-menstrual cycle is disrupted, the ovulation process may also be disrupted (the maturation of the follicle and the egg inside it, followed by its rupture and the release of the oocyte). If ovulation does not occur, then pregnancy is impossible. It is for this reason that when ovarian dysfunction occurs, the consequences can be of such a nature as infertility. Many couples turn to an obstetrician-gynecologist with just such a complaint, and the reason lies in the incorrect functioning of the ovaries;
- Violation of the hormonal function of the ovaries can result in miscarriage. This is a spontaneous abortion, a frozen (non-developing) pregnancy;
- severe course of premenstrual syndrome. Women begin to notice that PMS has become more severe and debilitating: irritability, mood swings, headaches develop, which can be combined with nausea;
- A violation of hormonal synthesis may develop in the direction of an increase in the amount of male sex hormones - hyperandrogenism. For this reason, women experience symptoms such as excess male-pattern hair growth (on the face, legs and arms, on the back and abdomen), rashes on the skin of the face, and increased greasiness of the hair and skin.
Complications and consequences
A disorder of the hormonal function of the ovaries in the absence of timely treatment can lead to serious consequences. Without correction, the pathology leads to a persistent disruption of the woman’s hormonal status, the most likely outcome of which will be infertility or the inability to bear a child. The risk of serious diseases of the reproductive system also increases significantly, especially in women of premenopausal age (40-45 years):
- fibroids;
- mastopathy;
- endometriosis;
- uterine fibroids;
- cancer of the uterus;
- breast cancer.
Causes
Ovarian dysfunction may be due to:
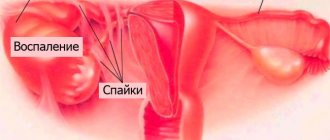
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ovaries themselves (oophoritis), as well as the mucous membrane of the uterus (endometritis) and fallopian tubes (salpingitis). In addition, the basis is often salpingo-oophoritis (adnexitis), when the pathological process affects both the ovaries and tubes;
- metabolic disorders and endocrine diseases (for example, thyroid dysfunction or obesity);
- termination of pregnancy (miscarriage or abortion);
- significant psycho-emotional or physical stress;
- inflammatory process associated with the installation of an intrauterine device;
- taking certain medications;
- exposure to radiation.
Why does amenorrhea occur?
According to statistics, 10% of women aged 17 to 45 experience secondary amenorrhea. Here the disorder occurs when the menstrual cycle has already established. Cases of primary amenorrhea, in which there was no menstrual bleeding initially during adolescence, are quite rare. This may be due to a delay in physical development, a debilitating diet, or a severe psycho-emotional state.
The menstrual cycle is regulated by different organs and systems: the cerebral cortex, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, the ovaries and the target organs of the reproductive system. Amenorrhea can be caused by a disorder at any level of regulation. Here a secondary form of pathology develops.
The most common causes of amenorrhea in women:
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- anorexia;
- ectopic and normal pregnancy;
- regular stress;
- premature menopause;
- early menopause;
- high levels of the hormone prolactin;
- imbalance of other sex hormones;
- exhaustion of the body.
The development of amenorrhea is also facilitated by the use of oral contraceptives, diet and fasting, infections and inflammation of the pelvic organs, and rapid weight gain.
Types of ovarian dysfunction
Hormonal ovarian dysfunction has several types:
- Juvenile dysfunction is abnormal functioning of the ovaries, which occurs during the early development of menstrual function. It is typical for teenagers aged 16-18 years. Irregular, painful and heavy menstruation may be bothersome;
- ovarian dysfunction during the reproductive period. Pathology manifests itself in the reproductive period of a woman’s life. Characteristic symptoms are: irregular cycle, delays or frequent periods, their scanty or large volume;
- premenopausal or menopausal ovarian dysfunction, which is characteristic of the period of extinction of hormonal activity of the ovaries.
Pathogenesis
The ovaries are part of a single system. The correct functioning of the gonads depends on the coordinated functioning of many structures; they themselves influence the hypothalamic-pituitary system and the activity of the adrenal glands.
Ovarian dysfunction can be a cause or consequence of a number of complications:
- proliferation of endometrial cells (the mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity), the appearance of hyperplasia, foci of endometriosis, polyps, adenomyosis of the uterus;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- mastopathy of the mammary glands;
- hormonal imbalance, increased androgen levels to concentrations typical for men;
- menstrual disorders;
- tumor formations in hormonally dependent female organs, cancer;
- vegetative-vascular disorders;
- anemia;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Diagnostics
At the initial appointment, the gynecologist-endocrinologist collects anamnesis, asking the patient leading questions, and also conducts an examination on the gynecological chair. The scope of the examination is determined individually and may include the following laboratory and instrumental studies:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and endocrine glands;
- blood tests for sex hormones, as well as thyroid and adrenal hormones;
- tests for STIs (sexually transmitted infections);
- CT and MRI of the brain to exclude pathology of the pituitary gland;
- smear on vaginal microflora;
- hysteroscopy, during which the doctor carefully examines the condition of the uterine cavity and removes a small piece of tissue for further histological examination;
- RDV (separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal).
Symptoms
The clinical picture of ovarian dysfunction is specific, so collecting complaints and studying anamnesis play a key role in making a diagnosis. The gynecologist will clarify the nature of the complaints, the time of their appearance, and the possible cause.
Women report the following symptoms:
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- lack of ovulation;
- severe premenstrual syndrome;
- uterine bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation;
- infertility;
- signs of anemia;
- pathological vaginal discharge, intoxication.
Changes in the menstrual cycle are accompanied by heavy (more than 80 ml) or excessively scanty discharge and irregular periods. This group also includes cycles that are too short (less than 21 days) and too long (more than 35 days). Lack of ovulation is diagnosed using functional tests or ovulation tests. The consequence of the disorder is infertility. Premenstrual syndrome is manifested by deterioration of well-being, mood swings, and severe pain. Uterine bleeding due to ovarian dysfunction occurs both in the middle of the cycle and during menstruation. Such women need emergency gynecological care.
Infertility is diagnosed when pregnancy does not occur within a year of active sexual activity. The main signs of anemia include general weakness, pale skin and mucous membranes, dizziness, brittle hair and nails. Anemia due to ovarian dysfunction is caused by long and heavy periods.
Vaginal discharge is mucous, purulent, watery or mixed. Intoxication symptoms include general weakness, increased body temperature, decreased appetite, and sweating. These signs occur when ovarian dysfunction is caused by an inflammatory process. Very often, the only complaint of a woman with ovarian dysfunction is intense uterine bleeding. Such patients are admitted to the gynecological department urgently. After the patient’s condition has stabilized and the bleeding has stopped, a full examination is recommended, the purpose of which is to find out the cause of the disorders.
After collecting complaints, an objective examination in a gynecological chair follows. The doctor examines the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix in the speculum, studies the position of the uterus in the pelvic cavity, evaluates its size and shape, and palpates the appendages. Already at this stage, the doctor may suspect ovarian dysfunction.
After an objective examination, the gynecologist draws up a plan for additional examination. It includes:
- general blood analysis;
- determination of the level of sex hormones;
- smears from the vagina, urethra and cervix;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- CT, MRI of the pelvic organs;
- hysteroscopy;
- laparoscopy.
In a general blood test, pathological changes may be absent, but anemia is more often detected as a consequence of prolonged and heavy bleeding.
The level of hormones in the blood depends on the type of disorder in a particular patient. This is the main method of assessing the state of hormonal balance in a woman. Determining the level of hormones in the blood helps to accurately determine the nature of the disorder and its possible cause. If ovarian dysfunction is suspected, doctors recommend donating blood for female and male sex hormones, hormones that characterize the functioning of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland. This approach will help the gynecologist choose the most appropriate treatment.
Flora smears help identify pathogenic bacteria as the cause of inflammatory processes.
Ultrasound scanning of the pelvic organs is a cheap and highly informative research method that is used as the primary method for diagnosing ovarian dysfunction. With the help of the study, the doctor can examine and evaluate the condition of the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, bladder, endocrine system, and determine the presence of ovulation. A gynecologist will easily detect congenital and acquired anomalies of the reproductive system, benign and malignant ovarian tumors, and signs of inflammatory diseases.
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is indicated when ultrasound does not show the expected results. These techniques are highly informative methods for visualizing internal organs. With their help, gynecologists identify the most minor ovarian disorders, which result in dysfunction. As a rule, CT and MRI are prescribed if tumor processes are suspected.
- Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic examination method with which a gynecologist examines the uterine mucosa. Using this method, polyps, benign and malignant tumors of the uterus, and other disorders that are the cause or consequence of hormonal dysfunction are diagnosed.
- Laparoscopy is also an endoscopic examination method in which an endoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity. Using the method, the doctor can examine the pelvic organs and identify the cause of ovarian dysfunction.
Treatment of ovarian dysfunction
The doctor develops the optimal therapeutic regimen only after assessing the results of the examination. In general, treatment for ovarian dysfunction is aimed at:
- eliminating the causes that provoked its development;
- normalization of a woman’s hormonal levels and menstrual cycle;
- cessation of dysfunctional bleeding, if any.
To achieve these goals, both conservative therapy and surgical treatment may be recommended.
In particular, if STIs are detected, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics, as well as anti-inflammatory and restorative drugs. In case of diagnosis of endocrine diseases, the function of the corresponding endocrine glands is restored. If a tumor is found, surgery will be required.
The use of traditional methods without prior examination and consultation with a doctor can be not only useless, but also harmful to a woman’s health. Therefore, if symptoms such as a change in the duration of the cycle, the appearance of intermenstrual discharge, pain before and during menstruation appear, you should definitely consult a gynecologist.
Probability of pregnancy
Ovarian dysfunction is not a death sentence for women who want to have a child. Pregnancy is possible, but only with medication support. Preparation and attitude towards it must be especially attentive.
The duration of treatment is about 6 months and is carried out under the close supervision of a gynecologist-endocrinologist. The woman is prescribed a course of hormonal therapy aimed at restoring the ovulatory menstrual cycle. When the mature follicle reaches 18 mm, and the thickness of the endometrium is 8-10 mm, the woman is injected with hCG, which provokes ovulation. Ovulation is monitored using ultrasound of the follicles, basal temperature measurements and blood tests.
According to statistics, therapy is successful for 90% of women and it is possible to achieve conception. Further pregnancy is carried out under careful supervision.
Prevention of pathology
To prevent the development of ovarian dysfunction, it is necessary to exclude those factors that can provoke this pathology.
You need to lead a healthy lifestyle, trying to eliminate stress, and also regularly visit an obstetrician-gynecologist for a preventive examination. This will allow timely detection of diseases of the pelvic organs. In addition, it should be remembered that the use of hormonal contraceptives should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
Proper nutrition and body weight control play an important role.
If there are pathologies of the endocrine glands, it is necessary to be under the supervision of an endocrinologist who will develop an optimal therapeutic regimen and monitor the patient’s condition.
Popular questions
I have inflammation of my left ovary.
The doctor prescribed me several injections and suppositories. Can I replace injections with tablets? I recommend that you consult your doctor regarding this issue to select adequate therapy and change the method of administration.
Good afternoon, polycystic ovary syndrome, the thyroid gland is normal, thyroid hormones too, hormones on days 2-4 of the cycle (it seems only DHEA-SO4 is increased): DHEA-SO4 354.8,
E2 28,
HFSH 2.46, HLH 2.19, PRL 10.99, TESTO 1.25, PROG 0.30, 25-OH 69.87, FT3 2.63, FT4 1.16, T3 1.65, T4 7.59,
TSH 1.790,
TP0AB 8.10, HSBG 28.6 26 years old, normal weight, I had my first menstruation at the age of 16 and came once every six months; I don’t plan to have children.
What treatment can you recommend? If, according to the result of ultrasound, there are more than 10 follicles in the ovaries and the volume is increased by more than 8.5 cm3, then it is recommended to take combined oral contraceptives. Considering the results of hormone levels, I would recommend taking a combination of ethinyl estradiol and cyproterone for at least 6 months.
How to treat an ovarian luteal cyst, if I’m pregnant, what should I do?
Hello! During pregnancy up to 16 weeks, such cysts require only dynamic monitoring and ultrasound control once a month.
Hello! For inflammation, can Reosorbylkat 200 be instilled?
Hello!
This drug is used only as prescribed by a doctor for severe, life-threatening conditions. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Treatment with folk remedies
Home remedies can be used in the treatment process as auxiliary methods. However, before doing this, you should definitely consult your doctor about this.
The most commonly used are infusions and decoctions of herbs, which take a long time to get the effect.
- Strawberry leaves . 1 tbsp. l. leaves pour 400 ml of water. After 6 hours, strain. Drink 1 tbsp every day. l. Similarly, you can prepare a healthy drink from raspberry leaves. These remedies are indicated for those who have heavy periods.
- Calendula . 10 g of dried flowers pour 200 ml of boiling water. Strain after 3 hours. Drink 2 tbsp. l. three times a day. The product helps regulate the monthly cycle.
- Viburnum bark . 1 tbsp. l. chopped bark, pour 250 ml of water and boil for 20 minutes. Add water so that you end up with the same amount of liquid as at the beginning. Drink 1 tbsp three times a day. l. The remedy is indicated for heavy bleeding.
- Red clover . Collect clover inflorescences, dry, 3 tbsp. l. Pour boiling water over this raw material and leave. Drink 2 tbsp. l. three times a day.
- Nettle . 1 tbsp. l. nettle pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, then boil for another 10 minutes. Drink this portion in small sips throughout the day. The product helps restore hemoglobin . However, it is important to consider that nettle increases blood clotting.
- Coltsfoot and sweet clover . Prepare a mixture of these herbs (10 parts coltsfoot and 1 part sweet clover), prepare an infusion by taking 1 tbsp. l. product in a glass of water and leave for 10 minutes. in a water bath. The product helps with heavy periods.
- Cinquefoil anseri . 20 g of the product should be poured into a tbsp. boiling water and cook for another 15 minutes. Cool, drink 4 r. 50 g per day before meals. The remedy is indicated for painful periods.
- Onion peel . Remove the skins from 1 kg of dry onion, pour in 2 tbsp. boiling water and cook for another 20 minutes. Drink half a glass in the morning after waking up. The remedy is indicated for scanty periods.
- Black radish juice . Grate the radish and squeeze out the juice. Add 1 tbsp to it. l. honey, stir. Drink 2 tbsp. l. before meals 4 times a day.
- Borovaya uterus . A decoction is prepared from 100 g of herb and 1.5 glasses of water. Boil the product for half an hour, drink 4 times a day, 1 tsp.
- Water pepper . 1 tbsp. l. herbs pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave. Drink 1 tbsp. l. three times a day. The infusion helps reduce blood loss during heavy periods and reduce the severity of pain.
- Ruta . Pour 5 g of rue leaves into 150 g of boiling water and cook for 15 minutes. so that the product does not boil, but simmers. Strain and drink the entire dose in the morning after waking up, then do not eat for 5 hours. Take the product once during scanty periods.
- Horsetail . 1 tsp. herbs pour 1 tbsp. boiling water Infuse and drink 1 tbsp. l. three times a day. Recommended for painful and heavy periods.
- Blueberry branches . This product is used for douching. 1 tbsp. l. means pour Art. boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Before douching, dilute the infusion with water.
For various disorders of the monthly cycle, it is also recommended to use herbal teas:
- First collection . Mix equal parts of birch leaves, mint, blackberry, yarrow herb, buckthorn bark, take 1 tbsp. l. means and pour boiling water (1 tbsp.). Strain and drink throughout the day. Take 3 months, the course can be repeated after 2 months. Indicated for irregular periods and pain.
- Second collection . Mix equal parts of buckthorn bark, lemon balm leaves, valerian root and cinquefoil herb, take 1 tbsp. l. product and pour 200 ml of boiling water over it. Strain after a few hours, drink a glass of the product 3 times a day for 5 days. Start treatment a few days before your period and stop on the first day.
- Third collection . Mix 2 tbsp. l. sweet clover, meadowsweet, meadowsweet, calendula, string, brew 1 tbsp. l. means Art. boiling water Drink the resulting infusion in the morning and evening. Start taking it on the last day of your period and continue treatment until the next one.
- The fourth gathering . Take 1 part wormwood, 3 parts oregano and lovage, 4 tbsp. l. garden quinoa. Stir, 3 tbsp. l. collection, pour 1 liter of boiling water. Take 100 g 6 times a day. Indicated for scanty periods.
- Fifth collection . Take 1 part each of fennel and juniper fruits, rue herb, St. John's wort, and cinquefoil; 2 parts each of parsley root, parsley seeds, rose hips, wormwood herb. Pour 2 tbsp. l. means 400 ml boiling water. After infusion, drink 100 ml twice a day. Take for 2 months. with scanty periods.
Treatment regimen for amenorrhea
The doctor determines how to treat ovarian dysfunction based on studies conducted, during which the cause of the disorder should be identified. If it is a tumor or adenoma, then they resort to surgical removal. Treatment of amenorrhea with hormones is necessary to restore the interaction between the ovaries and the pituitary gland. Regardless of the cause, vitamins and physical therapy are prescribed as an addition to the main therapy.
Methods for treating amenorrhea without hormones are used if menstruation has disappeared due to sudden weight loss or intense physical activity. In such situations, it is enough to organize a nutritious diet, a proper work and rest schedule, and also normalize the psycho-emotional state.
Other treatment options:
- Taking hormonal contraceptives for polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Taking dopamine agonist drugs that lower prolactin – for hyperprolactinemia.
- Neurosurgical intervention for pituitary tumors.
- Hormone replacement therapy – for premature menopause.
As you can see, there can be many reasons for the development of amenorrhea, and without it it is impossible to select competent therapy. Therefore, in such a situation, you should never resort to self-medication. Amenorrhea is dangerous for the development of infertility, which in the future will be very difficult to cure, and sometimes even impossible. To receive qualified medical care, contact Dr. Akner. We employ professional gynecologists with extensive experience in the diagnosis and treatment of female diseases. Sign up for a consultation on the website or call us at 8 (926) 497-44-44.
What it is
The state of ovarian dysfunction occurs due to the presence of infections in a woman, inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system, and endocrine diseases.
The duration of a normal menstrual cycle is 21-35 days. In this case, blood loss does not exceed 80-100 ml. Developing dysfunction of both ovaries leads to disruption of the cycle, due to which it can be longer (more than 35 days) or shorter (less than 21 days). Dysfunctional uterine bleeding may also indicate a hormonal imbalance.
Classification
Since the term “ovarian dysfunction” is a collective concept, it includes the following conditions:
- hyperfunction;
- ovarian hypofunction;
- too active production of female sex hormones;
- too active production of androgens ;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- primary failure;
- unspecified dysfunction.
There is also a classification according to the patient’s age:
- juvenile – develops in adolescents immediately after the first menstruation;
- reproductive - develops in patients of reproductive age;
- menopause – diagnosed in the period before menopause and directly during menopause.