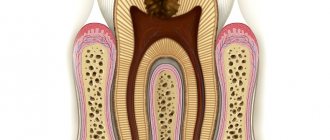
Dental granuloma is an inflammatory formation at the apex of the root. It is a proliferation of granulation tissue. Granuloma is formed as a result of the action of protective mechanisms in which the body localizes the source of infection and seeks to isolate it from other tissues. According to ICD-10, the disease was assigned code K04.5.
Typically, a granuloma is formed against the background of inflammation of the neurovascular bundle - the pulp. If pulpitis is not treated, its root part becomes inflamed, and the infection spreads beyond the boundaries of the tooth, into the peri-root tissue. As a result, a kind of pouch is formed, filled with decay products of dead cells.
A granuloma is considered to be a formation up to 0.5 cm in size, but it can grow, and as it grows, it transforms into a cystogranuloma, the size of which reaches 1 cm. With a diameter of more than 10 mm, we are talking about a tooth root cyst. There is no cavity in a granuloma; it is an area of tissue surrounded by a capsule. Due to the latter, the granuloma is firmly attached to the apex of the tooth root.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are two reasons for the development of granulomas on the root of a tooth.
1. Untreated pulpitis. The development of caries leads to the appearance of a deep cavity in the tooth. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the pulp, it becomes inflamed, and severe pain appears. Lack of medical care leads to the gradual death of the pulp. Bacteria penetrate beyond the tooth through root canals. A focus of inflammation appears at the apex of the root. We are talking about periodontitis.
A deep carious cavity in this case is not always observed. Inflammation can develop internally when secondary caries appears under the filling.
2. Poor quality endodontic treatment. Granuloma can develop at the root of a tooth in which root canal filling was previously performed. Usually there is underfilling: the doctor has not completely filled the canals with material. In the remaining voids, pathogenic bacteria develop, and the tissues surrounding the root react with inflammation.
These causes cause most cases of granuloma formation. But there are others, less common:
- poor quality orthodontic treatment;
- previous dental trauma;
- other inflammatory diseases - tonsillitis, abscess, etc.
In the latter case, the infection enters the tissues through the blood or lymph flow.
Ask a Question
Description
Granuloma is a focal growth of connective tissue cells accompanied by inflammation. Granulomas can be single or multiple, look like small nodules and are most often found in the presence of infectious pathologies in acute or chronic form.
Granuloma is an inflammatory formation on the skin that looks like a small plaque no more than three centimeters in diameter. The tissue on the surface of the formation may be rough and flat. As a result of the collision of connective cells with lymph and blood, an infiltrate is formed from the overgrown epithelium covering the body cavities and muscles.
Granuloma symptoms and complications
Symptoms of dental granuloma are nonspecific. Often the patient is unaware of the disease, since there may be no signs at all. Usually the tooth does not bother you, but moderate pain occasionally occurs when biting, drinking hot drinks or eating food. Such symptoms are characteristic of all forms of periodontitis.
It is worth noting that from time to time the disease may worsen. For example, in case of hypothermia, an infectious disease, surgery - in all cases when the body's defenses are reduced. During an exacerbation, the following symptoms appear:
- sharp pain, intensifying when biting, tightly closing the jaws;
- swelling of the gums in the projection of the root apex;
- pain in the gums when touched.
An exacerbation can go away on its own, and the disease returns to its chronic form. But sometimes inflammation develops before the appearance of purulent contents in the tissues - periostitis or gumboil.
Inflammation can cause resorption or dissolution of a section of jaw bone tissue. The appearance of purulent complications is dangerous due to its consequences: from tooth loss and damage to surrounding units to tissue melting and sepsis. Therefore, it is important to get timely help from a doctor. Treatment of dental granulomas is carried out by a dental therapist, and if removal is required, you need to contact a dental surgeon.
Diagnostics
The detection of granulomatous formations itself generally does not cause difficulties. Many patients, when contacting a specialist, complain about lumps that have appeared on the skin, under the skin or in the tissues. The process is somewhat more complicated when diagnosing a pathological phenomenon, when their formation is noted on internal organs, bones or deep in tissues.
To make a diagnosis, they most often turn to a therapist. In addition, if necessary, consultations with specialists such as:
- rheumatologist;
- dentist;
- radiologist;
- surgeon.
In medicine, there are several diagnostic research methods that can detect the problem:
- Ultrasound;
- CT scan;
- biopsy;
- radiography.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to make some efforts, since this task is not an easy one. In other words, it is not difficult to confirm the formation itself, but to determine the reason that contributed to its development is not so simple.
The most difficulties arise when you have one of the following diseases:
- granulomatosis ;
- sarcoidosis;
- listeriosis;
- annular or eosinophilic granuloma.
The problem is explained by the fact that such pathologies rarely appear, and specialists will rely on simpler diseases and look for the cause in them.
In addition to methods that help visualize the granuloma, the patient is also referred to undergo general blood and urine tests, which can help identify complications or other associated disorders.
In some cases, for example, if the development of a granuloma in the brain is suspected, a sample of cerebrospinal fluid is taken.
Laboratory and microbiological diagnostics do not help identify the neoplasm itself, but help determine the causes of its manifestation.
Conservative treatment
For granulomas, conservative treatment is more often used. It consists of mechanical treatment of the root canals. After this, they are filled with temporary healing material - pastes based on calcium hydroxide. After 2-3 weeks, a control image can be taken, and if the inflammation is eliminated, the canals are filled with a permanent material - gutta-percha. A new permanent filling is placed on the crown of the tooth.
There are two treatment tactics depending on the initial condition of the tooth.
1. Treatment of granuloma of a tooth in which the root canals are not filled. In this case, treatment involves the following steps:
- removal of carious tissues, old filling on the crown, if any;
- mechanical treatment of canals - with the help of special tools they expand, the walls are smoothed;
- antiseptic treatment of canals.
Further actions depend on the size of the granuloma. If it is small, up to 3 mm, simultaneous filling is allowed. If the formation is more than 3 mm, then the root canals are filled with temporary paste. It helps the granuloma shrink or disappear completely.
You will have to wear temporary material for no more than 3 weeks. At the end of the period, the doctor will order a repeat x-ray, and if he sees positive dynamics, he will fill the root canals with permanent material. The restoration of the tooth crown is also carried out.
2. Treatment of a tooth in which the root canals have already been filled. In this case, the doctor will first remove the old material. If a tooth has a crown, it must be removed. The root canals must be resealed, and the treatment tactics correspond to those described above: sometimes the installation of a temporary therapeutic filling is required.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes can be effective for skin granuloma. However, before starting treatment, you should know the type of granuloma. As we have found out, some skin manifestations are a consequence of systemic diseases, such as infectious diseases and autoimmune reactions; it is useless to treat granuloma caused by a foreign body with folk remedies.
Homemade recipes for granuloma can be used in parallel with the main therapy prescribed by the doctor.
Arnica ointment
Use for granuloma annulare.
Ingredients:
- Arnica roots 100 gr;
- Pork fat 100 gr.
How to prepare: Grind the roots and mix with melted fat.
How to use: Apply the ointment to the granuloma 3 times a day for 1 to 3 months.
Result: arnica perfectly relieves inflammation and helps in case of granuloma bleeding. Fat is a good base - it holds the composition on the skin for a long time. Granuloma can be treated in this way for a long time, from 1 to 3 months, but the first effect can be noticed after a couple of days of use.
Rosehip and elecampane root
Use for granuloma annulare, eosinophilic granuloma and granuloma of the mammary glands.
Since granuloma is often a consequence of poor immunity, restorative folk decoctions help well.
Ingredients:
- Dried rose hips 5 tbsp. l.
- Chopped elecampane root 1 tbsp. l.
How to prepare: Mix dry fruits and roots, pour 1 liter of boiling water. Simmer in a water bath for 20 minutes. Then leave for another 1 hour.
How to use: take twice a day, after diluting with boiling water, like tea for 1 month.
Result: elecampane root normalizes metabolism, which is especially necessary in case of immune system failures. Rose hips charge you with vitamin C and strengthen your general condition.
Vitamin balm
Use for immune granulomas.
Ingredients:
- Radish juice 0.5 cups;
- Carrot juice 0.5 cups;
- Honey 1 tbsp. L;
- Juice of 1 lemon.
How to prepare: Mix all ingredients thoroughly.
How to use: take 1 tbsp. l. balm three times a day before meals.
Result: this balm is a storehouse of vitamins - C, B, PP, E, A, K, calcium, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus and amino acids are present. The overall tone will improve within a week of regular use of the balm, which will prevent the formation of new granulomas and increase the body's resistance.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of dental granuloma may be required only in a few cases:
- obstruction of the root canals - complex, tortuous structure, too thin, narrow canals;
- impossibility of unsealing channels;
- the presence of a pin in the root canal - attempts to remove it may cause injury;
- patient's reluctance to remove the crown.
Many patients prefer granuloma removal because they do not want to resort to long-term treatment and remove a good crown. In this case, an apical resection operation is performed - part of the root is removed along with the granuloma through a small incision in the gums. Less commonly used is hemisection - removal of one root of a multi-rooted tooth along with part of the crown. In this case, further restoration of the crown of the tooth with a prosthesis will be required.
In rare cases, it is not advisable to preserve a tooth with granuloma. For example, if the crown is severely damaged and cannot be restored. In this case, when removing a tooth, the doctor must remove the granuloma from the socket in order to prevent the development of inflammation.
If purulent complications develop against the background of a granuloma, it is important to get help from a doctor immediately. The specialist will provide first aid: relieve acute pain by opening the tooth. Previously sealed canals are opened, and purulent contents are subsequently removed through them. In this case, relief comes instantly.
If severe swelling of the gums or cheeks appears, this may be due to the release of inflammatory contents under the periosteum or oral mucosa. In this case, a small incision is made to drain the pus. Further treatment is possible only after relief of acute symptoms. Drug therapy will also be required - the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics. You should not take them on your own. Moreover, it makes no sense to be treated only with antibiotics in the hope that the inflammation will go away - they are not able to eliminate the source of the disease or even reduce it, it is important to take local measures to eliminate the inflammatory process.
What to remember
- Skin granuloma is not a tumor or neoplasm, it is an inflammation of the skin. There are many types of granulomas, as well as the causes of their occurrence. They are often the result of a malfunction of the immune system, the body’s reaction to a foreign object, and the result of an infection in the body.
- Diagnosis of granuloma is difficult. It is necessary to first identify the root cause of inflammation.
- Treatment comes down to eliminating the underlying disease, or symptomatic therapy in case of autoimmune reactions.
- Some granulomas, such as pyogenic granulomas, are excised surgically.
Features of prevention
The main condition for the prevention of dental granulomas is timely assistance from a dentist when caries occurs. You should not allow severe tooth decay or the development of pulpitis. The peri-root tissues are healthy until the pulp becomes inflamed. Therefore, if symptoms of caries or pulpitis appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
Endodontic treatment also increases the likelihood of developing periodontitis. Therefore, it is better to eliminate caries in the early stages and avoid the need for root canal filling. If this is unavoidable, it is important to carefully choose a dental clinic - the professionalism of a specialist will help eliminate possible mistakes and prevent complications.
Stages
The development of granuloma (you can see its manifestations in the photo) can be divided into several stages:
- The initial stage is accompanied by an accumulation of newly formed cells with a tendency to phagocytosis. Cells of the immune system that tend to capture and process harmful particles such as viruses and bacteria are called phagocytes.
- At the second stage, the active phase of proliferation of accumulated phagocytes begins.
- In the third stage, phagocytes transform into epithelial cells.
- The final stage is characterized by the accumulation of epithelial tissue, from which a granuloma is formed.