Dry rhinitis, which should be treated with special medications under the supervision of a doctor, occurs with the same general symptoms as a common runny nose. The difference is the absence of liquid discharge due to drying out of the nasal passages.
Attention!
In the absence of nasal discharge (and this is the most characteristic symptom of ordinary rhinitis), diagnosis is often difficult. Determining the type of disease and selecting treatment methods is the prerogative of an experienced doctor.
How is allergic rhinitis different from a runny nose?
Allergy symptoms are similar to those of a cold. Common symptoms include runny nose, cough, and sore throat. Only an otolaryngologist can tell you how to distinguish an allergic runny nose from a cold.
Differences
| Possible manifestations | Allergic reaction | acute respiratory infections |
| Seasonality | Depends on the pathogen. Pollen has a clear seasonality. Household can be used year-round. | Mainly in autumn-winter and spring. |
| Signs of intoxication | Rarely | Almost always |
| Increased body temperature | Absent, occasionally rises to 37. | Almost always |
| Damage to systems other than the respiratory | Often | Rarely |
| Regular relapses of symptoms | Yes | No |
| Heredity | Genetic predisposition | No |
| Similarity of main symptoms | Almost always | Rarely |
| Blood analysis | There is an increase in the concentration of eosinophils | Signs of infectious etiology, including leukocytosis and increased ESR rate |
| Prick tests | Indicative | No signs of allergies |
| Indicators of the level of general IgE and specific IgE | Typical | No |
Symptoms
Since dryness and burning in the sinuses are most often provoked by diseases, it is quite normal that the main symptom will be accompanied by other clinical manifestations. These signs include:
- weakness and general malaise of the body;
- pain in the throat;
- the formation of crusts in the nose, which complicate the process of breathing through the nasal cavity;
- discomfort;
- severe itching in the nose;
- release of a sharp unpleasant odor when a person exhales air;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- inability to sneeze or, conversely, constant sneezing;
- increased tearfulness;
- feeling of stuffiness, like a cold;
- ulceration of the nasal mucosa;
- redness of the nose and eyes;
- labored breathing;
- pain in the ear canal;
- nosebleeds;
- cough, both dry and with sputum production;
- increase in body temperature.
It should be noted that the above symptoms are the most common, but this does not mean that all of them will be present in a particular person. The symptoms will fully correspond to the etiological factor.
Causes of atopic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis occurs upon contact with an allergen. The role of the provoking factor is:
- food (most often fish, milk and eggs);
- medicines;
- plant pollen:
- in spring: pollen of trees, especially hazel, birch and alder;
- in summer: pollen of grasses and flowers (the families of Poaceae, Chenopodiaceae, Asteraceae);
- fall: pollen from weeds, including ragweed and wormwood.
- house dust;
- insect allergens (cockroaches) and mold spores;
- animals. There is still no clear confirmation of the existence of hypoallergenic pets. This is due to the fact that allergies are provoked not so much by wool, but by saliva, urine and other biological fluids. Wool acts only as a carrier of allergens.
As a rule, increased sensitivity develops in people with a genetic predisposition. The family history of such patients often includes urticaria, bronchial asthma, diffuse neurodermatitis or other atopic conditions, which were confirmed in one or more close relatives. The basis of the disease is an immediate-type sensitization reaction, due to which symptoms appear both within a few seconds and within half an hour after contact with a potential allergen.
Methods for treating nasal diseases
The main goal of treatment carried out by a pediatric otolaryngologist is to relieve pain, relieve inflammation and restore patency of the nasal passages. It is also equally important to strengthen the local and general immunity of the body. Thus, treatment of diseases of the nose and its paranasal sinuses can be:
1. medicinal:
- antibacterial therapy;
- vasoconstrictors and antihistamines;
- immunostimulating drugs.
2. local:
- rinsing the nose and paranasal sinuses (cuckoo method);
- intranasal blockades (introduction of medicinal drugs into the side wall of the nose);
- physiotherapy (UHF and UV therapy).
3. surgical:
- puncture (puncture) of the maxillary sinus;
- surgical intervention.
Let us remind you that surgical methods are used in exceptional cases when conservative treatment is impossible or has not brought the desired result. In this regard, we note that a puncture is a radical measure, which is resorted to if the purulent contents of the paranasal sinuses are not eliminated by medication. This will significantly improve the child’s condition and avoid serious complications. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Classification of rhinitis
Most often, the development of allergic rhinitis is due to the frequency of seasons. The seasonality of the annual exacerbation of allergies is determined by the climatic characteristics of the region and practically does not change from year to year. Thus, the peak of atopic reactions occurs in the spring, when pollen is intensively released during plant flowering.
This form of rhinitis is called seasonal. In this case, the symptoms disappear after flowering ends. If the manifestations of the disease persist throughout the year, this form is called year-round. A similar runny nose is provoked by household allergens, particles of the epidermis of pets, various chemicals, and household dust containing micromites. Forms of the disease depending on the severity of symptoms:
- mild, which is practically asymptomatic;
- average;
- heavy.
With moderate and severe manifestations of allergies, the patient may complain of deterioration in the quality of sleep, constant fatigue from lack of sleep, conjunctivitis, and other characteristic symptoms. At the same time, performance decreases noticeably. The duration of atopic runny nose is:
- intermittent: manifestations of allergies persist for 1 month or less than 4 days a week;
- persistent: allergy symptoms do not disappear within 1 month.
Sinuses hurt – how to treat?
The primary and most important recommendation is to visit a doctor.
You should not self-medicate, especially with chronic pain. In this situation, you simply cannot do without advanced diagnostics. The most comprehensive examination of the sinuses and paranasal area is carried out using nasal endoscopy and computed tomography. Therapeutic treatment , for example for sinusitis, consists of prescribing vasoconstrictor, mucolytic and antimicrobial drugs. The main goal is to suppress the inflammatory process and normalize the outflow of contents from the sinuses. Additionally, outside the stages of exacerbation, physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, UHF sinuses, can be prescribed. Salt rinses and inhalations also have a fairly good effect. For temporary pain relief, the use of painkillers, for example, NSAIDs (Nise, etc.) is allowed.
Of course, surgical treatment , especially for anatomical changes and chronic inflammatory conditions. Which depends on the root cause of sinus pain:
- For chronic sinusitis, various sinusotomies: maxillary sinusotomy, polysinusotomy, etc.
- For a deviated nasal septum – septoplasty.
- For adenoid hypertrophy - adenotomy.
Your counterpart specializes in endoscopic paranasal surgery. This is a more gentle effect, which allows you to minimize the time of both cure and recovery period. Discharge from the hospital usually occurs within 24 hours after surgery.
More detailed information about the surgical treatment of ENT organs is located on the corresponding page: Treatment of ENT diseases
Symptomatic picture
Characteristic symptoms of allergic rhinitis in adults:
- feeling of nasal congestion and thick mucous discharge;
- rhinorrhea, which is manifested by copious watery discharge;
- itching in the eyes, nose, ears;
- inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa;
- "sore throat;
- redness of the eyes;
- deterioration of taste and smell;
- bouts of sneezing;
- sometimes the body temperature is subfebrile and rises to 37;
- swelling of the eyelids and face;
- symptoms persist for more than 2 weeks.
In this case, rhinorrhea is more typical for seasonal rhinitis, and thick discharge with nasal congestion is more typical for year-round rhinitis. In 75% of patients, symptoms increase at night and early in the morning, as well as after direct contact with the allergen.
Important! If you notice such symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable!
Dry cough and runny nose in children. How to treat?
Babies and older children should be treated by a pediatrician. Only a doctor can prescribe medications to improve the drainage of nasal discharge and mucus from the bronchi. A bacterial infection is treated with antibiotics. If the runny nose and cough are allergic, drugs from the group of antihistamines are used.
Self-medication of a child, especially under the age of one year, is unacceptable!
Possible complications
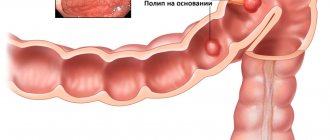
Year-round allergic rhinitis in adults can be complicated by the addition of a secondary infection, which is caused by constant blockage of the maxillary sinuses with thick contents. This condition can lead to sinusitis, otitis media, hearing loss, and enlarged tonsils. In chronic cases of runny nose, polyps may form in the nose.
These neoplasms clog the openings of the sinuses and make breathing difficult, which aggravates the course of associated pathologies. Hay fever is not a life-threatening disease. However, it greatly worsens the patient’s quality of life. Due to the lack of normal breathing, patients complain of increased irritability, constant fatigue, apathy, and a sharp decrease in performance.
Constant swelling and increase in the size of the nasal turbinates and tonsils provokes unremovable nasal congestion, headaches, apnea, and dental malocclusion. Research also shows that with constant contact with an allergen, a patient with allergic rhinitis develops inflammation of the bronchial tissue. In the absence of adequate therapy, bronchial asthma may occur. Seasonal rhinitis very rarely leads to complications.
What can hurt your nose?
The most common cause of nasal pain is inflammatory reactions . They occur in response to the penetration of pathogenic microflora or mechanical damage. Inflammation can begin in any area, but often spreads to adjacent areas and affects several structures simultaneously. It often begins on the mucous membrane, as this is where the immune system's initial fight against viruses and bacteria occurs. Then the process can spread to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, cartilage tissue, blood vessels and nerves, paranasal sinuses, and nasopharynx.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults begins with obtaining a detailed medical history. Close attention is paid to the seasonality of exacerbations of allergies, which is associated with the flowering periods of certain plants. Allergic rhinitis is diagnosed by an allergist. He orders the following studies:
- to confirm hay fever: a positive result of a subcutaneous prick test with a respiratory allergen. This is the most sensitive, fastest and cheapest test to confirm the disease. Also, the development of an allergic reaction is indicated by an increase in the concentration of specific immunoglobulins IgE in the blood serum. However, this test is not recommended for screening purposes.
- Sinus endoscopy and anterior rhinoscopy. During the examination, bilateral, often asymmetrical swelling of the mucous membrane with watery discharge (in chronic rhinitis - thick discharge) may be detected.
- Cytological analysis of a smear from the nasal cavity is a nonspecific analysis. Only during an exacerbation is it possible to detect an increased percentage of eosinophils (more than 2%), mast and goblet cells (more than 50%).
- A blood test detects an increased number of eosinophils. The detection of neutrophils indicates the addition of a secondary infection.
- In some cases, a CT scan of the nose and maxillary sinuses is prescribed, which makes it possible to identify concomitant inflammation of the mucous membranes.
With year-round allergic rhinitis, anamnesis is not of great importance. Regular interaction with the allergenic factor leads to the fact that manifestations of rhinitis are constantly observed. In this case, it is almost impossible to accurately determine the allergen.
The year-round form should be differentiated from vasomotor rhinitis. The clinical manifestations of the diseases are very similar, but vasomotor rhinitis is more often provoked by nonspecific irritants. Sometimes allergic rhinitis is “masked” as:
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract of infectious etiology;
- anatomical defects of the nasal septum.
Types of dry runny nose
Dry rhinitis comes in two main types.
| Definition | Cause of the disease | Signs |
| Anterior (most common form) | Common causes include injury and exposure to irritants. | Damage to the anterior nasal cavity |
| Atrophic (chronic form) | Consequence of advanced rhinitis | Reduction of mucous membrane Mucosal atrophy |
Treatment tactics
Treatment of allergic rhinitis, the symptoms of which manifest themselves in mild to moderate form, involves taking antihistamines. In severe cases, complex therapy with the use of intranasal glucocorticoids and leukotriene antagonists is recommended. General recommendations for the treatment of allergic rhinitis include:
- eliminating prolonged exposure to allergens that provoke symptoms. Limit exposure to the street during flowering plants, avoid pets.
- Rinse the nose with isotonic or hypertonic solutions.
- Consultation with an otolaryngologist.
In the treatment of allergic rhinitis, conventional vasoconstrictor drops are useless. In addition, long-term and uncontrolled use leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane and chronic respiratory failure in the form of drug-induced rhinitis. The main focus of therapy is to avoid contact with the allergen that provoked the development of a sensitizing reaction.
However, it is not always possible to accurately determine the irritating factor. In this case, drug therapy is prescribed. Treatment of allergic rhinitis in adults involves a course of taking antihistamines (Cetrin, Aleron, Erius) during an exacerbation of symptoms. However, when treating with 1st generation antiallergic drugs, their side effects should be taken into account. Such medications can cause arrhythmia, urinary retention, blurred vision, and their sedative effect is often noted.
Symptomatically, it is possible to prescribe local medications, including antiallergic eye drops (Olopatallerg, Allergodil), hormonal intranasal agents (Nasonex, Avamis, Budesonide). To eliminate severe manifestations of allergic rhinitis, leukotriene antagonists (Montelukast, Zafirlukast) are prescribed. If medications cannot be taken or their effectiveness is markedly reduced, specific immunotherapy may be recommended.
This technique involves repeated subcutaneous injections of very small doses of the allergen under the supervision of an allergist. The procedure is repeated once every 2 weeks. The first injections are given in late autumn to minimize the occurrence of an anaphylactic reaction. Specific immunotherapy lasts up to 5 years. Treatment is contraindicated in severe bronchial asthma and cardiovascular diseases.
For patients with some forms of allergic rhinitis, the doctor may recommend following a diet. For example, if you are allergic to hazel pollen, it is recommended to avoid eating hazelnuts and hazelnuts; a reaction to birch pollen forces you to exclude apples from your diet. These tips are due to the high risk of cross-allergic reactions.
Important! Treatment of allergic rhinitis should be regular and continue even after symptoms disappear. Otherwise, the risk of developing a serious complication in the form of bronchial asthma increases. If conservative therapy is ineffective, an allergist may recommend surgical treatment.
A vasotomy is performed through the nasal sinuses under local anesthesia. During surgery, excess mucous membrane and partially the vessels that obstruct the passage of air through the nose are removed. This operation also allows you to remove polyps.
If your sinuses hurt without a runny nose?
This in most cases indicates a chronic pathology, the most common of which is chronic sinusitis or sinusitis of the maxillary sinus. This condition is characterized by periodic pain in the maxillary sinuses. During the period of exacerbation, pain is accompanied by catarrhal symptoms: serous-purulent discharge, rhinorrhea, postnasal drip, etc.
Other ENT causes of pain without manifestations of rhinorrhea (runny nose) are the conditions described in the previous section: deviated nasal septum, neoplasms, adenoids, dental pathologies, etc.
It should be remembered that pain in the sinuses may not be of otolaryngological etiology, for example, in neurological conditions: neuritis of the cranial nerves, migraine, fibromyalgia, etc. Therefore, it is important to promptly assess the condition and exclude more serious pathologies. In this regard, diagnosis should be carried out in sufficient depth, especially in chronic pain.
Sign up for a consultation
Preventive actions
The only preventative measure that will be truly effective is the complete exclusion of contact with the allergen. If the symptoms of allergic rhinitis are provoked by the epidermal cells of the animal, the animal should be removed from the house.
If the allergy is pollen, then a change of residence or installation of air filters in the house may be recommended. It is advisable to ensure low air humidity in the room and cover pillows and mattresses with special plastic covers.
With proper treatment of allergic rhinitis, its manifestations practically do not bother the patient. However, when the first symptoms appear, you should consult your doctor. Timely consultation will help avoid possible complications.
Prevention
Preventive measures for dry rhinitis are almost the same as for any other type of runny nose. This includes timely and correct treatment of any diseases and preventing them from becoming chronic, wet cleaning of premises, hardening of the body, sports, taking immunomodulatory drugs (as prescribed by a doctor), vitamins and vitamin complexes, as well as the use of special preparations - nasal humidifiers or nasal products. based on sea water. Any necessary medicine at a favorable price can be selected/booked through the Stolichka social pharmacy network.