Sore throat is one of the most common infectious diseases that affects our tonsils (tonsils). In the medical literature you can find another name for this diagnosis: acute tonsillitis. Purulent sore throat in an adult is an infectious disease that is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms, namely hemolytic streptococci of groups A and B, and less commonly staphylococci.
The disease is extremely contagious. The disease is transmitted not only by airborne droplets. You can become infected through contact when sharing the same dishes or towels with a sick person. Both children and adults are susceptible to the disease.
This disease has a clearly defined seasonality and most often appears in the autumn-spring period.
Despite the fact that many people treat the diagnosis of “acute tonsillitis” as something natural and commonplace, nevertheless, this disease is not as simple as it seems. If there is a careless attitude towards it, when proper treatment of purulent sore throat in adults is not carried out, severe complications can develop, involving associated organs (kidneys, joints and myocardium - heart muscle) in the chronic inflammatory process.
Why does infection occur?
In the vast majority of cases (60-80%), the causative agent of the disease is streptococcus bacteria. Less commonly - staphylococci and pneumococci. There are always microorganisms throughout the human body and in the palatine tonsils in particular. When a person’s health is normal and his immunity is not weakened, they do not manifest themselves in any way. But as soon as the body’s defenses fail in the presence of factors predisposing to the disease, pathogens become more active. If a person shows the first signs of a sore throat, it means that pathogenic microorganisms have penetrated deep into the tonsils and triggered the inflammation mechanism.
The reasons that provoke the inflammatory process include:
- prolonged exposure to the cold, cold drinks or food (sometimes it is enough to eat ice cream or fall asleep with the air conditioner on);
- tonsil injuries;
- reduced immunity;
- lack of full breathing through the nose due to the anatomical features of a person (adenoids, polyps, cysts in the nose and nasopharynx);
- inflammation present in the body;
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- unfavorable working conditions.
Prevention of tonsillitis
Prevention of tonsillitis includes hygiene measures and health procedures. It is necessary to keep the room clean, carry out wet cleaning and disinfection, especially in the children's room. It is necessary to regularly visit the dentist to monitor the health of the teeth and oral cavity, where additional infection may accumulate. Rinse your mouth regularly after eating and use the right toothbrush. It is especially important to visit a dentist in childhood, since the development of tonsillitis in children can cause serious complications in all organs and systems.
Measures to prevent tonsillitis include hardening the child, which should begin from a very early age, gradually increasing the temperature and duration of the procedure. Children should walk longer in the fresh air and breathe sea air to clear their airways. It is recommended to regularly engage in gymnastics, swimming and other types of physical activity. Nutrition should be complete, contain nutrients and vitamins to strengthen the child’s immunity. Women during pregnancy should also pay attention to the completeness of their diet and take strengthening vitamins.
During the cold season and periods of flu outbreaks, you should avoid contact with sick people and avoid places where there are many people. You should get a flu vaccination before the cold season. In the autumn and winter, avoid hypothermia, which can cause a sore throat, and subsequently tonsillitis.
Types of purulent sore throat
In otorhinolaryngology, several forms of the disease are distinguished: catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, and phlegmous, ulcerative-necrotic, dental and latent (Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent). Immediately after diagnosis, qualified treatment of the disease should be started on the same day in adults and children, regardless of the form of the disease. In this article we will describe the most basic forms of sore throat.
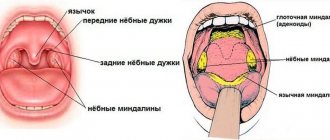
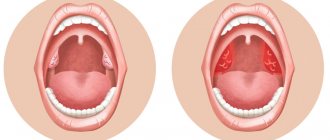
With follicular tonsillitis, the tonsils become greatly enlarged, and purulent spots appear on their surface. The disease begins rapidly with a sharp rise in temperature to 40°C. The lymph nodes become enlarged, and when pressed on them the patient experiences discomfort. The patient is overcome by headaches, “aches” throughout the body and general malaise.
With lacunar angina, purulent masses penetrate into the thickness of the entire tonsil, filling its lacunae. To the symptoms of follicular tonsillitis, a reaction from the gastrointestinal tract is added: vomiting, diarrhea, nausea. A characteristic yellowish coating is noticeable on the tonsils, upon removal of which the patient feels improvement and the body temperature drops.
Phlegmonous is the most severe form of the disease. It is characterized by the accumulation of purulent masses in the tonsil, the patient’s temperature reaches 40°C. In parallel, swelling of the neck and perimaxillary area occurs. Possible respiratory arrest. The patient experiences severe pain: it becomes impossible to speak or swallow. The patient must be immediately sent to hospital, since in the absence of prompt assistance there is a risk of death.
Such a division, of course, is quite arbitrary, since one type of disease can transform into another and cause serious health problems (provided that qualified treatment of the disease is not provided to adults).
Truths and myths regarding folk remedies
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Popular recipes for home therapy for certain diseases are common, which sometimes cause confusion: how can this remedy help you recover? But many “home” healers foam at the mouth to prove the high effectiveness of the promoted remedies, and even appeal to medical sources that supposedly prove the presence of such effectiveness.
In the case of acute tonsillitis, the most controversial remedies for home treatment today are kerosene, Coca-Cola and ice cream. It’s worth mentioning right away that evidence-based medicine does not recognize any of the above-mentioned remedies as a panacea against tonsillitis, and all those positive effects that the sources that promote them say, without the parallel use of drug therapy, can cause absolutely nothing but side effects.
Any therapy for sore throats, even carried out at home using traditional recipes, must be agreed upon with the attending physician, who will be able to correctly correct it. The use of dubious means for treatment can lead to a worsening of the condition and the occurrence of severe complications, so you should think several times before starting such experiments.
Symptoms
The first signs of the disease appear almost immediately (from ten hours to a day from the moment of infection!). Symptoms of purulent tonsillitis first appear similar to the symptoms of ordinary tonsillitis. The patient tries to cure a sore throat by gargling, but such measures have no effect. Then the following symptoms appear:
- high body temperature (up to 40°C);
- “lump” in the throat, increasing pain in the throat: ranging from a slight soreness to a “pain” when swallowing;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- enlarged lymph nodes, pain when pressing on them;
- tonsil hypertrophy;
- the appearance of purulent plaque or pustules on the surface of the tonsils;
- pronounced intoxication of the body - the patient loses appetite, feels weak and lethargic.
Patients need to remember the first and main rule: it is necessary to treat purulent sore throat immediately: the sooner you start treating the disease, the faster the recovery will come, and the risk of developing pathologies will be minimized.
What to drink
Drinking plenty of fluids for sore throat is the mainstay of home treatment. First of all, this is necessary to maintain water balance, which is important at high temperatures. Secondly, patients need a large amount of fluid to reduce the manifestations of intoxication. Thirdly, some drinks can disinfect the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tonsils, and have a mild analgesic effect.
For sore throats, it is recommended to drink a lot of ginger tea. This tea perfectly relieves pain and disinfects the throat. Ginger tea must be prepared from fresh ginger roots, which are peeled and grated or crushed in a blender. Having received 2 teaspoons of crushed root, pour it with a glass of water and boil over low heat for about 20 minutes. After removing from the heat, the broth is filtered and cooled. It is recommended to add 1 teaspoon of honey and lemon juice to the finished tea before drinking.
In order to reduce the temperature during fever, it is necessary to add one fifth of a large lemon to herbal or hot green tea without sweeteners.
Everyone has been familiar with the recipe for treating sore throat with honey and milk since childhood. This drink has a tonic, vitaminizing, calming, and analgesic effect on a sick person. Honey needs to be dissolved in hot milk, adding a little butter to soothe an irritated throat. At the same time, honey can be used only if you are completely sure that there is no allergy. Children can only be given milk and honey to drink after the age of 1 year.
Complications with purulent sore throat
The disease is dangerous due to its complications, which can affect not only the respiratory system, but also spread to other human organs.
One of the common pathologies is the transition from an acute form of the disease to a chronic form (chronic tonsillitis). In chronic tonsillitis, inflammation is constantly present in the tonsils, and exacerbations occur 2-3 times a year, and in severe cases, more often.
Delayed treatment of the disease can lead to inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis), joint diseases (rheumatoid arthritis) and kidneys (glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis). It is possible that a sore throat may develop into an abscess. This happens when the infectious pathogen has little space in the thickness of the palatine tonsil, and streptococcus begins to look for new sites for itself. Thus, inflammation can move to the paratonsillar and parapharyngeal tissue and provoke a paratonsillar or parapharyngeal abscess.
The pathologies listed above are powerful arguments for promptly starting treatment for purulent tonsillitis.
Surgical treatment of tonsillitis
If conventional treatment methods do not help and complications occur in other organs, the patient is prescribed surgery to remove the tonsils. First of all, for such complications as: rheumatism, nephritis, endocarditis and cholangiohepatitis. In most cases, removal of the affected tonsils significantly improves the patient's condition and reduces the extent of pathological complications in the affected organs. But the surgical method does not help in all cases.
It may happen that treatment of acute tonsillitis with standard methods does not bear fruit. The tonsils can swell so much that it will be extremely difficult for the patient to breathe any further. Then they are simply removed surgically. No one disputes that tonsils are an important part of the body's immune system throughout life and that everything should be done to avoid having them removed. But such a procedure is still better than the prospect of constantly suffocating from lack of oxygen. There are also nuances here. Most operations are performed using a scalpel. However, there are many alternatives to this traditional method. Many countries practice removal of tonsils using lasers, radio waves, ultrasound energy or electrocoagulation. These methods are much less painful than using a scalpel.
Like all surgical procedures, each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here you need to consult a doctor to choose the best option.
Diagnostics
In order to make a diagnosis, the doctor must examine the patient and study the complaints. One of the most important signs is a red, sore throat: from these external changes you can determine whether it is tonsillitis and what degree of tissue damage.
If the doctor has doubts, it may be necessary to conduct additional studies:
- standard urine test;
- throat smear analysis;
- a general blood test, in which the doctor will definitely look at the ESR and leukocyte levels.
Bacteriological culture will show what is the causative agent of sore throat. The analysis results will be ready in 3-5 days. Doctors do not wait for the result and prescribe antibiotics; this is done if there are signs of a characteristic streptococcal infection: enlarged lymph nodes, pain on palpation, temperature rises above 38 degrees, tonsils are swollen and red, no runny nose or cough.