Every person experiences a sore throat sooner or later. But this seemingly harmless symptom can cause serious problems.
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is an infectious disease that causes inflammation of the tonsils. Statistics show that about 15% of children suffer from an acute form of the disease. In the adult population, this figure is lower - 5-10%. But almost every person in large cities suffers from chronic tonsillitis. Why? Let's find out!
The acute form of tonsillitis, which goes away with an increase in body temperature and severe pain in the throat, is more familiar to us as a sore throat. In the chronic form, the patient may not even realize that he has this disease for a long time. A person may feel that periodic sore throats and frequent colds are simply the result of a weakened immune system. Such a careless attitude towards one’s health can cause serious complications and pathologies. To avoid them, it is necessary to diagnose the problem in time: know the first signs, symptoms and treatment.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Why are tonsils needed?
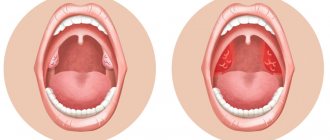
The tonsils are an integral part of our immune system. And their main purpose is to protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. In total, a person has six of them: palatine and tubal (paired), pharyngeal and lingual. By their names you can roughly understand in which part of the pharynx they are located. Their general arrangement resembles a ring. This ring acts as a kind of barrier for bacteria. When we talk about inflammation of the tonsils, we mean only the palatine tonsils (aka tonsils). Let's look at them in more detail.
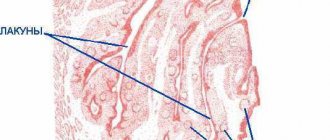
If you open your mouth wide, then in the mirror you can easily see two formations that look like almonds - tonsils, these are tonsils. Each tonsil consists of small openings (lacunae) and winding canals (crypts).
Bacteria that enter the air, in contact with the tonsils, are rebuffed and are immediately disposed of, without having time to cause an outbreak of a particular disease. Normally, a healthy person does not even suspect that real fighting is taking place inside him. Now you understand the importance of the mission of the palatine tonsils. Therefore, a good otolaryngologist will never rush to recommend their removal. Although to hear from a doctor, speaking about tonsils: “They need to be removed!” - a common phenomenon in our time. Unfortunately, today not all clinics can offer high-quality treatment for tonsillitis, and sometimes the turnaround rate is off the charts. That is why it is sometimes easier for a doctor to brush it off and refer the patient for surgery.
Types of tonsillitis.
The disease occurs in two forms - acute and chronic. Acute tonsillitis is an illness of an infectious nature and manifests itself in acute inflammation of the tonsil. The cause of exacerbation is staphylococci and streptococci. Acute sore throat in children and adults is also divided into catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, ulcerative-membranous and necrotic.
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term, persistent inflammatory process in the tonsils. It manifests itself as a consequence of past inflammation, acute respiratory viral infections, dental diseases, and reduced immunity. Chronic exacerbation of the disease in adults and children occurs in three forms: compensated, subcompensated and decompensated. In the compensated form, the disease “dormants”; exacerbation of tonsillitis symptoms occurs infrequently. In the case of a subcompensated form of the disease, exacerbations occur frequently, the disease is severe, and complications are common. The decompensated form is characterized by a long, sluggish course.
Antiviral drugs
Currently, the most popular antiviral drugs are:
- Kagocel;
- Ingavirin;
- Arbidol;
- Ergoferon.
For the viral etiology of acute tonsillitis, antiviral drugs are used, however, there is still intense debate in the scientific community about the effectiveness of such drugs. Opponents of antiviral therapy rightly argue that its effect is insignificant.
Symptoms of tonsillitis.
A symptom that combines both types is pain in the throat. The pain can be both severe and tolerable. The patient experiences severe discomfort while eating and swallowing.
Sore throat is much more severe than a chronic disease and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature (up to 40°C);
- very severe sore throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- accumulations of pus on the tonsils (plaque, pustules);
- enlarged tonsils;
- headache;
- weakness.
The symptoms and treatment of chronic tonsillitis are somewhat different from the manifestations of tonsillitis. With a chronic disease, the temperature remains at 37°C. A sore throat, cough, and bad breath are added. There is a white coating on the tonsils. The symptoms are less pronounced, since the course of the disease itself is characterized by remissions and exacerbations. A patient suffering from a chronic form of the disease loses his ability to work, gets tired quickly, and loses his appetite. Often a person suffers from insomnia.
What is angina: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Sore throat is an infectious disease that affects patients of all age groups. Most often it affects children under adolescence, as well as adults under 40 years of age. Cases of the disease in early childhood or old age are rare.
Effective treatment of sore throat at home can be difficult: the disease has many nuances that only a specialist can take into account. MedEx Clinic offers to make an appointment with a general practitioner. Our medical center employs doctors with many years of experience and high qualifications.
Causes of the disease
In fact, acute tonsillitis, or tonsillitis, is an inflammation of the tonsils. They are located on the side at the entrance to the pharynx and are clearly visible in the mirror. The tonsils are responsible for catching bacteria and viruses when inhaled and then destroying them. They contain antibodies and immune cells that can cope with many infections.
The causative agent of sore throat is pathogenic microorganisms:
- beta-hemolytic streptococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- Coxsackie A viruses;
- adenoviruses and others.
There are only two ways of infection - airborne or alimentary. You can get a sore throat if you come into contact with an infected person, drink an infected drink or eat food. In this case, a certain number of microorganisms may be in the throat before, but become more active in the presence of unfavorable changes in the temperature regime - human hypothermia or sudden climate change. It is important to understand that the cause of infectious sore throat is still a pathogen, and not a change in weather conditions.
Children can get a sore throat due to a short-term weakening of their immune defenses. Cold milk, ice cream, wet feet can become a factor provoking the development of the disease.
In adults, the risk factors are different:
- poor nutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- work in hazardous production;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse.
Sore throat in adults also develops as a complication of past or chronic purulent inflammatory diseases in the paranasal sinuses. It may be associated with sinusitis or caries. In addition, tonsillitis acts as a complication of some systemic diseases - tuberculosis, scarlet fever, diphtheria, infectious mononucleosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of sore throat are divided into local and general. The first group includes:
- a sore throat;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Common symptoms also include fever with sore throat, severe weakness, chills, and malaise. Sometimes the patient complains of heart pain, as well as muscle and joint pain. The temperature for sore throat in an adult is 39-40 degrees.
Children's tonsillitis, especially at an early age, has additional symptoms. The child refuses food, becomes capricious and whiny. In addition to redness of the throat, children who become ill often experience nausea, pain in the ears and stomach, indigestion, and convulsions. Problems with sleep may appear: insomnia, or vice versa – constant weakness. Often, childhood sore throat is accompanied by rhinitis and otitis media.
Forms of the disease
Symptoms of acute tonsillitis differ depending on the form of the disease. In this regard, the diagnosis of each of them also differs. Sore throat is classified depending on how affected the tonsils are, into the following forms:
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- lacunar;
- phlegmonous;
- fibrinous;
- ulcerative-necrotic.
Taking into account the pathogen, they distinguish between types of sore throat - streptococcal, staphylococcal, viral, fungal. In addition, there is a conditional classification that takes into account the severity of the disease. It distinguishes between mild sore throat, which occurs without serious complications, and severe one.
Catarrhal
The catarrhal form of sore throat is the most common, both in summer and winter. With this form of the disease, superficial damage is observed: inflammation is limited to the mucous membrane and the edges of the palatine arches. This form is characterized by a mild course and usually occurs against the background of a concomitant disease.
Symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis:
- lethargy;
- increased fatigue;
- temperature - 37.0-37.5 in adults, up to 38.0 - in children;
- pain while swallowing;
- coated dry tongue;
- soreness and feeling of dryness in the throat.
With catarrhal form, there is a slight enlargement of nearby lymph nodes. In rare cases, there is a sore throat without fever, but with redness and inflammation of the tonsils.
The duration of the disease is 3-5 days. After this, the symptoms gradually disappear, or a more severe form develops - lacunar or follicular tonsillitis.
Lacunarnaya
Purulent sore throat with acute onset and severe symptoms. The patient complains of high temperature (usually no higher than 39 degrees), severe weakness, and headache. Characteristic clinical symptoms of lacunar tonsillitis also include difficulty swallowing, enlarged regional lymph nodes, and joint pain.
The lacunar form of acute tonsillitis can also be called severe tonsillitis. With it, the inflammatory process is localized on the surface, and pus collects in the gaps. It also affects the ducts of the tonsils.
The lacunar form of tonsillitis poses a high risk for children. It often causes severe inflammation of the tonsils, which can lead to disruption of the respiratory system. In severe cases of the disease, as well as the specific structure of the upper respiratory tract, complete blockage of breathing is possible.
Lacunar tonsillitis in children can lead to seizures. It is characterized by symptoms of acute intoxication in combination with high fever, as well as an increase in ESR in the blood test and an increase in the level of leukocytes.
Follicular
Purulent, or follicular tonsillitis, usually begins quite acutely. The patient's temperature rises to 39 degrees. The lymph nodes are enlarged: they can be easily felt under the lower jaw and on the back of the head. Due to severe pain in the throat, it becomes difficult to swallow saliva, so there is increased salivation.
Other typical symptoms:
- fever;
- chills;
- aches in the lower back and joints.
Upon examination, reddened and swollen tonsils covered with follicles or plugs are visible. They rise above the surface in the form of yellowish or whitish dots, no more than 3 mm in diameter. The follicles are filled with gray-yellow pus and form a pattern reminiscent of a star map. As the disease progresses, they open, then the temperature drops, and the patient’s condition returns to normal. For some time after the disease, erosions remain at the site of the follicles.
In a child, follicular tonsillitis may be accompanied by fainting, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting. Stool disorder is common. In adults, tonsillitis leads to tachycardia, heart pain and stool retention. Symptoms of the disease last about a week.
Fungal
The fungal form of sore throat is typical for young children. It occurs most often in the autumn-winter period. The temperature in this form of the disease can remain at 37-38 degrees. The beginning is sharp. The throat with a fungal sore throat is red, with a whitish coating on the tonsils. The curdled discharge is easily removed, and the disease disappears on days 5-7. The fungal form of sore throat in children is diagnosed based on test results: they contain bacterial flora, thrush fungi, and yeast cells.
Viral
Viral sore throat develops as a complication of influenza, parainfluenza, coronavirus, adenovirus. It manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- cough;
- runny nose;
- redness of the throat and tonsils;
- the appearance of mucus at the back of the throat.
This form of the disease is also characterized by conjunctivitis. Small reddish blisters appear on the tongue, palate and palatine arches and other areas. They do not fill with pus, as in other forms of sore throat, but quickly burst, turning into erosions. The incubation period is typical for acute tonsillitis - 5-7 days.
For scarlet fever
According to medical statistics, there is a connection between scarlet fever and tonsillitis: during periods of increased incidence of one disease, the increase in cases of the other also increases. Scarlet fever develops as a result of infection with group A hemolytic streptococcus and is spread by airborne droplets. Most often it is recorded in children aged 2-7 years.
Symptoms of scarlet fever:
- heat;
- headache;
- sore throat, especially when swallowing;
- lethargy and weakness.
If the disease is accompanied by severe intoxication, nausea and vomiting are observed. Sore throat is a concomitant disease. It is manifested by severe swelling of the mucous membrane, swelling of the tonsils, and the appearance of a grayish-dirty coating.
Diagnostics
To diagnose a sore throat, the doctor studies the patient’s complaints and conducts an examination. The most characteristic symptom is a sore throat: it also allows you to determine the type of tonsillitis and the degree of tissue damage. To clarify the diagnosis, additional studies may be prescribed:
- clinical analysis of urine;
- bacteriological examination of a throat smear;
- a clinical blood test, in which the doctor analyzes the level of ESR, the presence of leukocytosis, and a moderate stab shift to the left side.
Bacterial culture helps to identify the causative agent of sore throat. The problem is that usually the results of this study need to wait at least 3-5 days. Therefore, the doctor can prescribe antibiotics for a sore throat in advance - if there are signs characteristic of a streptococcal infection: enlarged and painful regional lymph nodes, a temperature of more than 38 degrees, red and swollen tonsils, no runny nose and cough.
Treatment
Treatment of angina in adults is usually carried out on an outpatient basis: hospitalization is necessary only for severe forms of the disease. The choice of therapy depends on the form and type of acute tonsillitis. Mild catarrhal tonsillitis, for example, often goes away on its own.
To alleviate the patient’s condition with a mild form of the disease, you can:
- drink a lot of warm liquid - juice, fruit drink, weak tea;
- rinse with a solution of salt or furatsilin.
Purulent sore throat is treated with antibiotics. The doctor selects the medications, taking into account the condition of the individual patient and the characteristics of his body.
In the first days of the disease, the patient is recommended to rest in bed. In the future, he needs to limit physical activity and avoid overexertion in order to prevent the development of complications. It is useful to consult with a nutritionist - to choose food products that will not irritate a sore throat, but will provide the body with the necessary amount of nutrients.
Complications
Complications develop mainly after bacterial (streptococcal) sore throat. Their signs become noticeable on days 4-6 of the disease. Complications are divided into local and general.
Locals include:
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- cervical lymphadenitis.
Common complications include hemorrhagic vasculitis and acute glomerulonephritis, a kidney disease.
The severity of a sore throat does not determine the likelihood of complications developing. Sometimes they occur even with a mild form of catarrhal tonsillitis. If, after an illness, arrhythmia, pain in the heart, or shortness of breath appear, it is worth visiting a cardiologist: this may indicate myocarditis or rheumatism of the heart.
Diagnosis and treatment of sore throat in adults in Moscow
Sore throat is a common infectious disease that many are accustomed to carrying on their feet. Meanwhile, compliance with medical recommendations is extremely important: it has been established that violation of bed rest in the first days of illness increases the risk of complications. You shouldn’t get carried away with self-treatment when it comes to antibiotics.
MedEx Personal Medicine Clinic invites you to make an appointment. We work with an integrated approach and carefully select treatment for each specific case. Patients of the clinic can count on the help of a competent specialist, effective treatment and friendly service.
Price
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner (examination, consultation with a candidate of medical sciences) | 3500 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner (examination, consultation with a candidate of medical sciences) | 3000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the salivary glands | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pleural cavity | 1700 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone | 2400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of its contractility | 2000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pancreas | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2700 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys and adrenal glands | 3700 rub. |
| Ultrasound detection of fluid in the abdominal cavity | 1500 rub. |
All prices are inclusive of tax deduction.
Sign up
Contact our doctor
Make an appointment
Dzhgarkava Tea Gochaevna
Therapist-cardiologist
Experience: 5 years
Read more
Possible complications.
Both forms of the disease: chronic and acute, can cause serious complications. One of the most severe consequences of the disease is rheumatism. Practice shows that half of the patients suffering from rheumatism had to be treated for chronic tonsillitis or treated for acute conditions a month earlier. The disease itself begins with unbearable joint pain and increased body temperature.
There are frequent cases of heart disease caused by tonsillitis. Patients experience shortness of breath, interruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle, and tachycardia. Myocarditis may develop.
If inflammation spreads to tissues nearby the tonsil, paratonsillitis appears. The patient suffers from a sore throat and fever. If the infection from the tonsils spreads to the lymph nodes, lymphadenitis appears.
Untreated tonsillitis also leads to kidney disease.
Prevention
You can avoid acute tonsillitis in a child or adult if you follow some rules:
- Maintaining immunity through hardening, proper nutrition, normalization of work and rest;
- Avoiding hypothermia in the autumn-winter period;
- Avoiding sudden changes in temperature in summer (air conditioning, cold drinks, ice cream, etc.);
- Taking special immunostimulating agents that activate the body’s local defenses (Imudon®)4.
Secondary prevention, which involves preventing complications of angina, includes compliance with all treatment recommendations3. In addition, taking local immunomodulators that reduce the number of bacteria on the tonsils is encouraged.
Pregnancy and chronic tonsillitis.
The health of the expectant mother and baby requires close attention. Complications caused by the disease can lead to dangerous consequences, including miscarriage or provoke premature birth. Self-medication in this case is dangerous: it is necessary to undergo treatment with an ENT specialist in the clinic. The doctor will prescribe washing the tonsils, treating them with ultrasound and gargling with antiseptics that are safe for the expectant mother. Physiotherapy is contraindicated for pregnant women.
If you are just planning a pregnancy, it is worth carrying out planned therapy for prevention in order to reduce the negative impact of pathogens on the tonsils. At the planning stage of pregnancy, it is recommended that both parents undergo an examination to reduce the risk of this disease in the child.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Acute tonsillitis. Treatment.
Self-medication for this disease is unacceptable! To choose an effective method of treatment during exacerbation, it is necessary to treat tonsillitis in children and adults under the supervision of an ENT doctor. It should be remembered that the acute form of the disease is extremely contagious. When the first signs of the disease appear, a number of measures must be taken to promote a speedy recovery of the patient:
- the sick person must be isolated by placing in another room. He must have his own towel, linen and dishes, since the disease is very contagious;
- during the treatment period the patient is prescribed strict bed rest;
- take care of the patient’s nutrition: food should not be solid, so as not to cause unnecessary concern to the sore throat;
- do not forget about drinking plenty of fluids;
- a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed (Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, etc.). It is necessary to completely drink the entire course of antibiotics, even if the patient feels a noticeable improvement;
- For local treatment, drugs with an antibacterial effect are used;
- when treating a throat with tonsillitis, the drugs “Tantum-verde”, “Inhalipt”,
- rinsing with antiseptics (“Chlorgequidine”, “Furacilin”);
- lubricating the tonsils with Lugol's solution;
- to relieve swelling of the tonsils, you need to take allergy medications;
- If your body temperature is above 38°C, take antipyretics based on ibuprofen or paracetamol.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs must be taken for purulent (bacterial) forms of tonsillitis. Antibiotics are prescribed with a wide spectrum of antibacterial action:
- Penicillins (Amoxiclav, Flemoclav, Augmentin);
- Macrolides (Hemomycin, Azithromycin, Klacid);
- Cephalosporins (Cefixime, Zinnat, Ceftriaxone).
The dosage, frequency and duration of administration are determined only by the attending physician. Typically, the course of antibacterial treatment is about ten days, but not less than seven.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
When treating this disease, the rule applies: exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis should be treated in combination with the treatment of concomitant diseases of the nose and nasopharynx. Inflammation of the glands can be treated, but, for example, mucus constantly flowing down the wall of the pharynx due to constant inflammation of the inferior turbinates will provoke new inflammation.
Tonsillitis treatment clinics offer two treatment options: conservative and surgical. For compensated and subcompensated forms, conservative therapy is prescribed. In the decompensated form, when all conservative methods of therapy have been tried and they have not brought results, they resort to removing the tonsils. But by losing them, a person loses his natural protective barrier, so the surgical method should be considered as a last resort.
Drug therapy for the chronic form of the disease includes:
- treatment with antibiotics prescribed by an otolaryngologist;
- use of antiseptics (“Miramistin”, “Octenisept”);
- antihistamines to relieve swelling of the tonsils;
- immunomodulators to stimulate weakened immunity (for example, Imudon);
- homeopathic remedies (“Tonsilgon”, “Tonsillotren”)
- herbal decoctions: chamomile, sage, string;
- if necessary, prescribe painkillers;
- adherence to a diet (no solid food, very cold or hot, alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks are excluded).
Washing the tonsils.
The procedure for washing the tonsils has a great positive effect, as a result of which pus is released from the lacunae and the medicine is administered. There are several ways to carry out the procedure.
The oldest, so to speak, ancient method is sanitation with a syringe. It is used quite rarely due to its low efficiency and traumatic nature, compared to the advent of more modern methods. The syringe is used when the patient has a strong gag reflex or very loose tonsils.
In other cases, a more effective method is used - vacuum rinsing with a special attachment of the Tonzillor apparatus.
But it is not without its drawbacks:
- the container into which the purulent contents of the tonsils are “pumped out” is opaque, and the doctor cannot see whether the rinsing is complete;
- The design feature of the nozzle is such that when the pressure necessary for complete rinsing is reached, the nozzle can injure the tonsils.
Our clinic for the treatment of tonsillitis offers its patients an alternative painless option for washing the tonsils using the improved “Tonsillor” nozzle - this is the “know-how” of our clinic. There are no analogues of our nozzle in other medical institutions in Moscow. It eliminates the disadvantages of a conventional nozzle: the rinsing container, which is suctioned to the tonsil, has transparent walls, and the otorhinolaryngologist can see what “comes out” of the tonsils. This eliminates unnecessary manipulations. The nozzle itself is non-traumatic and can be used even by children of school age.
Complex therapy of chronic tonsillitis at the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev.
The method of complex treatment of the disease did not appear immediately. Our specialists have tried various methods of treating tonsillitis in practice. As a result of many years of experience in the study and treatment of chronic tonsillitis, this technique has taken root and is the most effective. It includes several stages.
The first stage is anesthesia of the tonsils. The tonsil is lubricated with lidocaine. The second stage is vacuum washing of the tonsils from caseous masses. The third stage is medicinal treatment of the tonsils using ultrasound. The fourth stage is irrigation of the tonsils with an antiseptic.
Stage five - lubricating the surface of the tonsils with Lugol's antiseptic solution. The sixth stage is physical therapy using a laser - this procedure relieves swelling and inflammation of the tonsils. The next stage is a vibroacoustic effect on the tonsils, due to which the blood flow rushes directly to the tonsils, and pathogenic substances are removed with it. The final stage of complex treatment is a session of ultraviolet irradiation, which heals the tonsils and fights pathogens.
The entire session takes about twenty minutes. To achieve a positive result, the patient usually needs five complex procedures.
Reasons for development
Acute sore throat is caused by exposure to bacteria called streptococci on the tonsils. They enter the body through contact with an already infected person, this can be a simple conversation, coughing or sneezing. The disease also occurs during a long stay in a room with high humidity and low temperature.
Bacteria can also enter the body as a result of eating poorly washed foods, because they can also be infected with streptococci.
Acute tonsillitis can develop due to the proliferation of bacteria that are present in the lacunae of the tonsils. This type of infection is caused by hypothermia, exposure to other diseases, stress and overwork. For example, when your feet get wet in the fall, or in the hot summer you drink cold juice.
Most often, children and young people under thirty-five years of age suffer from this disease. It is not observed only in infants, because their lymphoid tissue is still poorly developed. The possibility of infection should not be excluded for those who cannot tolerate temperature changes. Also, the cause of acute tonsillitis is impaired nasal breathing. Polluted air enters the respiratory tract, thereby causing inflammation. Poor nutrition is also considered to be a cause of tonsillitis.
Treatment of tonsillitis in Moscow
Chronic tonsillitis in Moscow, in fact, like the acute form of the disease, should be treated only by an otolaryngologist. The main thing is to choose the right medical institution where you will receive qualified assistance. Treating tonsillitis at the Doctor Zaitsev clinic means entrusting your health to professionals. Modern equipment and patented treatment methods allow us to provide the most effective care to patients. Our prices remain one of the best in Moscow, since our price list remained at the 2013 level. You can sign up for the clinic by calling the reception desk daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. or through the online registration form on the website. Come, we will be glad to help you!