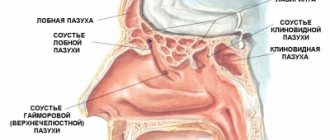
Every person experiences a sore throat sooner or later. But this seemingly harmless symptom can cause serious problems.
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is an infectious disease that causes inflammation of the tonsils. Statistics show that about 15% of children suffer from an acute form of the disease. In the adult population, this figure is lower - 5-10%. But almost every person in large cities suffers from chronic tonsillitis. Why? Let's find out!
The acute form of tonsillitis, which goes away with an increase in body temperature and severe pain in the throat, is more familiar to us as a sore throat. In the chronic form, the patient may not even realize that he has this disease for a long time. A person may feel that periodic sore throats and frequent colds are simply the result of a weakened immune system. Such a careless attitude towards one’s health can cause serious complications and pathologies. To avoid them, it is necessary to diagnose the problem in time: know the first signs, symptoms and treatment.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Why are tonsils needed?
The tonsils are an integral part of our immune system. And their main purpose is to protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. In total, a person has six of them: palatine and tubal (paired), pharyngeal and lingual. By their names you can roughly understand in which part of the pharynx they are located. Their general arrangement resembles a ring. This ring acts as a kind of barrier for bacteria. When we talk about inflammation of the tonsils, we mean only the palatine tonsils (aka tonsils). Let's look at them in more detail.
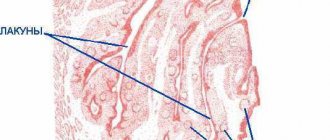
If you open your mouth wide, then in the mirror you can easily see two formations that look like almonds - tonsils, these are tonsils. Each tonsil consists of small openings (lacunae) and winding canals (crypts).
Bacteria that enter the air, in contact with the tonsils, are rebuffed and are immediately disposed of, without having time to cause an outbreak of a particular disease. Normally, a healthy person does not even suspect that real fighting is taking place inside him. Now you understand the importance of the mission of the palatine tonsils. Therefore, a good otolaryngologist will never rush to recommend their removal. Although to hear from a doctor, speaking about tonsils: “They need to be removed!” - a common phenomenon in our time. Unfortunately, today not all clinics can offer high-quality treatment for tonsillitis, and sometimes the turnaround rate is off the charts. That is why it is sometimes easier for a doctor to brush it off and refer the patient for surgery.
Types of tonsillitis.
The disease occurs in two forms - acute and chronic. Acute tonsillitis is an illness of an infectious nature and manifests itself in acute inflammation of the tonsil. The cause of exacerbation is staphylococci and streptococci. Acute sore throat in children and adults is also divided into catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, ulcerative-membranous and necrotic.
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term, persistent inflammatory process in the tonsils. It manifests itself as a consequence of past inflammation, acute respiratory viral infections, dental diseases, and reduced immunity. Chronic exacerbation of the disease in adults and children occurs in three forms: compensated, subcompensated and decompensated. In the compensated form, the disease “dormants”; exacerbation of tonsillitis symptoms occurs infrequently. In the case of a subcompensated form of the disease, exacerbations occur frequently, the disease is severe, and complications are common. The decompensated form is characterized by a long, sluggish course.
Why does tonsillitis occur?
Among the possible causative agents of bacterial infection, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS) is of primary importance. It is the cause of the vast majority of cases of tonsillitis and is one of the most dangerous pathogens 2. Therefore, it is customary to divide acute tonsillitis into streptococcal, non-streptococcal (viral) and fungal.
Acute bacterial tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. Typically, the disease develops after contact with sick people, but in some cases healthy people who are carriers of the bacteria can become infected.
Symptoms of tonsillitis.
A symptom that combines both types is pain in the throat. The pain can be both severe and tolerable. The patient experiences severe discomfort while eating and swallowing.
Sore throat is much more severe than a chronic disease and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature (up to 40°C);
- very severe sore throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- accumulations of pus on the tonsils (plaque, pustules);
- enlarged tonsils;
- headache;
- weakness.
The symptoms and treatment of chronic tonsillitis are somewhat different from the manifestations of tonsillitis. With a chronic disease, the temperature remains at 37°C. A sore throat, cough, and bad breath are added. There is a white coating on the tonsils. The symptoms are less pronounced, since the course of the disease itself is characterized by remissions and exacerbations. A patient suffering from a chronic form of the disease loses his ability to work, gets tired quickly, and loses his appetite. Often a person suffers from insomnia.
Specific features of bacterial sore throat
It is often difficult for parents to distinguish bacterial tonsillitis from other types of acute tonsillitis. Because of this, the patient’s condition often worsens.
- A sore throat caused by bacteria can be recognized by the following clinical picture:
- The lymph nodes in the neck and lower jaw become inflamed. On palpation they are sharply painful.
- There is no mucus or redness on the back of the throat.
- Pus accumulates on the tonsils in the form of white or gray-green dots, but it does not extend beyond them. With a viral sore throat, pus spreads over the entire surface of the throat and surface of the mouth.
Sore throat caused by bacteria differs from other types of acute tonsillitis in that the runny nose and cough are mild, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and indigestion are absent.
Possible complications.
Both forms of the disease: chronic and acute, can cause serious complications. One of the most severe consequences of the disease is rheumatism. Practice shows that half of the patients suffering from rheumatism had to be treated for chronic tonsillitis or treated for acute conditions a month earlier. The disease itself begins with unbearable joint pain and increased body temperature.
There are frequent cases of heart disease caused by tonsillitis. Patients experience shortness of breath, interruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle, and tachycardia. Myocarditis may develop.
If inflammation spreads to tissues nearby the tonsil, paratonsillitis appears. The patient suffers from a sore throat and fever. If the infection from the tonsils spreads to the lymph nodes, lymphadenitis appears.
Untreated tonsillitis also leads to kidney disease.
Complications of bacterial tonsillitis
Depending on what causative agent of sore throat is identified and how long the treatment is delayed, the risk of complications increases. Thus, staphylococcal tonsillitis is dangerous due to the development of a pharyngeal abscess due to the spread of inflammation inside. Streptococcal tonsillitis threatens to damage the heart, kidneys and liver and can provoke rheumatism or glomerulonephritis, lower back pain.
The likelihood of complications with bacterial tonsillitis is higher than with viral tonsillitis, so you need to seek medical help in a timely manner and not attempt treatment on your own.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, otorhinolaryngologists will quickly conduct an examination, identify the pathogen and prescribe treatment. Our specialists regularly undergo training and improve their skills; they use modern physiotherapeutic techniques and drug therapy regimens in treatment.
Pregnancy and chronic tonsillitis.
The health of the expectant mother and baby requires close attention. Complications caused by the disease can lead to dangerous consequences, including miscarriage or provoke premature birth. Self-medication in this case is dangerous: it is necessary to undergo treatment with an ENT specialist in the clinic. The doctor will prescribe washing the tonsils, treating them with ultrasound and gargling with antiseptics that are safe for the expectant mother. Physiotherapy is contraindicated for pregnant women.
If you are just planning a pregnancy, it is worth carrying out planned therapy for prevention in order to reduce the negative impact of pathogens on the tonsils. At the planning stage of pregnancy, it is recommended that both parents undergo an examination to reduce the risk of this disease in the child.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Treatment
Treatment for bacterial tonsillitis should begin immediately. Antibacterial drugs play a leading role in successful recovery (strictly as prescribed by the doctor). Taking them ensures the destruction of the infectious agent and successful recovery. Local immune activators will help speed up recovery and reduce the risk of complications and chronicity of tonsillitis2. These drugs include the local immunomodulator Imudon®. The drug contains fragments of bacteria, the presence of which makes it possible to strengthen immune protection against bacterial and viral pathogens, as well as fungus of the genus Candida5. Adding Imudon® to the main therapy helps eliminate the symptoms of tonsillitis 2 times faster6.
Additional agents used to treat bacterial sore throat:
- antipyretics;
- local antiseptics and agents with antibacterial activity;
- local anti-inflammatory, painkillers;
- vitamin complexes.
Gargling with a soda-salt solution or a solution with the addition of furatsilin will help speed up recovery. Drinking plenty of fluids will reduce intoxication. The drink should be warm, but not hot. A nutritious diet that is gentle on the mucous membrane of the throat is recommended.
Acute tonsillitis. Treatment.
Self-medication for this disease is unacceptable! To choose an effective method of treatment during exacerbation, it is necessary to treat tonsillitis in children and adults under the supervision of an ENT doctor. It should be remembered that the acute form of the disease is extremely contagious. When the first signs of the disease appear, a number of measures must be taken to promote a speedy recovery of the patient:
- the sick person must be isolated by placing in another room. He must have his own towel, linen and dishes, since the disease is very contagious;
- during the treatment period the patient is prescribed strict bed rest;
- take care of the patient’s nutrition: food should not be solid, so as not to cause unnecessary concern to the sore throat;
- do not forget about drinking plenty of fluids;
- a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed (Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, etc.). It is necessary to completely drink the entire course of antibiotics, even if the patient feels a noticeable improvement;
- For local treatment, drugs with an antibacterial effect are used;
- when treating a throat with tonsillitis, the drugs “Tantum-verde”, “Inhalipt”,
- rinsing with antiseptics (“Chlorgequidine”, “Furacilin”);
- lubricating the tonsils with Lugol's solution;
- to relieve swelling of the tonsils, you need to take allergy medications;
- If your body temperature is above 38°C, take antipyretics based on ibuprofen or paracetamol.
We care about your health
Tonsillitis is one of the most common diseases. Infections of a viral or bacterial nature enter the respiratory tract (often one of them is joined by another), causing an inflammatory process. A surge in tonsillitis is most often observed in the spring and winter, when many people have a weakened immune system. Also, this disease can develop against the background of existing foci of infections in the body, for example, with dental caries, periodontal disease, sinusitis and others.
Tonsillitis is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets, pathogens: staphylococci, streptococci, fungi, bacilli.
Tonsillitis can have both acute (called sore throat) and chronic forms. Acute tonsillitis most often occurs as a result of an exacerbation of the chronic form, when a person with reduced immunity could, for example, become hypothermic.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
Compared to chronic tonsillitis, acute tonsillitis occurs in a more severe form: the body temperature can rise to 40 degrees, the patient feels a very strong pain in the throat, and it is difficult for him to swallow. The tonsils are swollen and enlarged, with the presence of purulent plugs. Patients feel headache, weakness, and their lymph nodes are enlarged.
Depending on the type of sore throat, which can be lacunar, herpetic, catarrhal, follicular, etc., ulcers, follicles, and a film called plaque form on the palatine tonsils.
With chronic tonsillitis, the temperature can rise to 38. The patient has a light coating on the palatine tonsils, and the tonsils themselves look enlarged and reddened. A person feels weakness, muscle pain, and aching joints.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by stages of remission and exacerbation. During the period of remission, the focus of infection is passive, and the person is not bothered by unpleasant symptoms. But as soon as one becomes hypothermic (especially with reduced immunity), he immediately begins to feel an unpleasant sore throat, pain when swallowing, cough, fatigue, poor general health and lack of appetite. The patient's lymph nodes may become inflamed.
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammation of the pharynx and palate. Its simple form has only a local symptom: sore throat. But if the picture is complemented by persistent lymphadenitis of the neck, changes in the functioning of the heart and high temperature, then this is already a toxic-allergic form.
Chronic tonsillitis has several stages: compensated, when the source of infection is not active, and decompensated, when exacerbation occurs due to repeated sore throats, inflammation of the ear and nose.
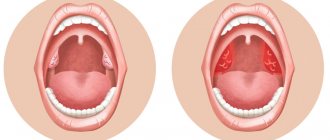
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis) - what inflammation looks like (photo of the disease)
Photograph of the throat with purulent sore throat
Photo - throat with follicular sore throat
Catarrhal sore throat - photo
Photo - lacunar tonsillitis
Possible complications of tonsillitis
Like many other diseases, tonsillitis is dangerous due to its complications . These include, first of all, rheumatism. After suffering from a sore throat, a person may feel severe aching in the joints and an increase in temperature.
In second place, as a rule, are cardiovascular diseases. Interruptions in heart function, shortness of breath, tachycardia are sure signs that a sore throat has caused complications.
Another unpleasant symptom after tonsillitis is swelling and tenderness of the lymph nodes, which have become infected from the tonsils. This is lymphadenitis.
The infection can also spread from the tonsils to the surrounding tissues of the upper respiratory tract, leading to pain when swallowing. And this disease is a complication of tonsillitis and is called paratonsillitis.
It should be noted that more than a hundred diseases are known that arise as a result of complications after acute tonsillitis. These include a variety of kidney, eye, skin and thyroid diseases.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
It begins, of course, with an examination by a doctor, who determines whether the tonsils and adjacent tissues are swollen and red, and whether the ear and cervical lymph nodes are inflamed. The patient is sent for a general blood test.
Before prescribing treatment to the patient, the ENT doctor determines the nature of the inflammatory process: in what form does tonsillitis occur - chronic or acute, the type of inflammation (purulent, catarrhal), is the sore throat primary or secondary, what is the causative agent (this is determined in the laboratory - a culture is done from the throat ).
Treatment of tonsillitis - specifics of therapy
In the treatment of tonsillitis, both conservative methods and surgical intervention can be used. Treatment methods depend on the specifics of the disease.
For chronic tonsillitis, if necessary, antibiotics are prescribed in tablets, and for sore throat they are often administered intramuscularly. Local treatment is also carried out: purulent plaque on the tonsils is removed, the lacunae are washed with antibacterial solutions, physiotherapy and a course of vitamins with immunomodulators are prescribed.
In case of acute tonsillitis, it is recommended to irrigate the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, rinse, treat the tonsils with iodine-containing preparations (if there are no allergic reactions to iodine), inhalations, and resorption of antibacterial tablets are useful. You should also drink a lot (weak teas, fruit drinks, juices, rosehip decoctions, etc.), take antipyretic and painkillers.
Acute tonsillitis is not recommended to be treated with antibiotics, because they reduce local immunity. But if the form of the disease is more severe, then the patient requires mandatory bed rest and antibiotic therapy. However, the prescription of antibiotics should be preceded by an analysis of the results of culture in the pharynx area, which will identify the causative agent of the infection. It is recommended to include in the course of treatment drugs that enhance immunity, as well as general strengthening and anti-inflammatory drugs. Physiotherapy will also be useful.
If a person suffers from tonsillitis more than twice a year, has complications from this disease, and conservative treatment does not bring the expected results, then removal of the tonsils may be recommended. There are many modern methods of performing this operation (infrared laser, ultrasound, biopolar, radiofrequency ablation and others), but many consider the cold plasma coblation method to be the most effective and gentle. However, it should be remembered that the tonsils are the first protective barrier that stops and disarms pathogenic bacteria . But in many cases (especially after frequent colds), the tonsils stop performing their functions and themselves become a source of infection, causing serious complications. In this case, it is better to remove them.
Treatment of tonsillitis (tonsillitis) at the Medkvadrat ENT center in Moscow, Kurkino and Khimki.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
When treating this disease, the rule applies: exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis should be treated in combination with the treatment of concomitant diseases of the nose and nasopharynx. Inflammation of the glands can be treated, but, for example, mucus constantly flowing down the wall of the pharynx due to constant inflammation of the inferior turbinates will provoke new inflammation.
Tonsillitis treatment clinics offer two treatment options: conservative and surgical. For compensated and subcompensated forms, conservative therapy is prescribed. In the decompensated form, when all conservative methods of therapy have been tried and they have not brought results, they resort to removing the tonsils. But by losing them, a person loses his natural protective barrier, so the surgical method should be considered as a last resort.
Drug therapy for the chronic form of the disease includes:
- treatment with antibiotics prescribed by an otolaryngologist;
- use of antiseptics (“Miramistin”, “Octenisept”);
- antihistamines to relieve swelling of the tonsils;
- immunomodulators to stimulate weakened immunity (for example, Imudon);
- homeopathic remedies (“Tonsilgon”, “Tonsillotren”)
- herbal decoctions: chamomile, sage, string;
- if necessary, prescribe painkillers;
- adherence to a diet (no solid food, very cold or hot, alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks are excluded).
Surgery in the treatment of bacterial tonsillitis
Often, due to a weakened immune system, tonsillitis worsens frequently (more than three times a year). The tonsils become covered with purulent contents, causing pain and discomfort.
To prevent relapse, some otolaryngologists recommend surgical treatment - tonsillectomy. Surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia and involves excision (removal) of the tonsils.
The operation is also prescribed for complications, when inflammation of the tonsils has caused a soft tissue abscess (peritonsillar abscess).
Washing the tonsils.
The procedure for washing the tonsils has a great positive effect, as a result of which pus is released from the lacunae and the medicine is administered. There are several ways to carry out the procedure.
The oldest, so to speak, ancient method is sanitation with a syringe. It is used quite rarely due to its low efficiency and traumatic nature, compared to the advent of more modern methods. The syringe is used when the patient has a strong gag reflex or very loose tonsils.
In other cases, a more effective method is used - vacuum rinsing with a special attachment of the Tonzillor apparatus.
But it is not without its drawbacks:
- the container into which the purulent contents of the tonsils are “pumped out” is opaque, and the doctor cannot see whether the rinsing is complete;
- The design feature of the nozzle is such that when the pressure necessary for complete rinsing is reached, the nozzle can injure the tonsils.
Our clinic for the treatment of tonsillitis offers its patients an alternative painless option for washing the tonsils using the improved “Tonsillor” nozzle - this is the “know-how” of our clinic. There are no analogues of our nozzle in other medical institutions in Moscow. It eliminates the disadvantages of a conventional nozzle: the rinsing container, which is suctioned to the tonsil, has transparent walls, and the otorhinolaryngologist can see what “comes out” of the tonsils. This eliminates unnecessary manipulations. The nozzle itself is non-traumatic and can be used even by children of school age.
Treatment for sore throat
The patient is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department only in complicated cases. Most often, angina can be treated on an outpatient basis. The treatment method consists not only in eliminating the general symptoms of angina, but also in influencing the causative agent of the disease. The patient is prescribed:
- Regular gargling with saline solution or special antibacterial agents. During treatment, the deep parts of the pharynx should be affected, so when rinsing, it is recommended to tilt your head back.
- Local preparations with antibacterial and analgesic effects: tablets, sprays, lozenges.
- Treatment with antipyretic drugs if necessary.
- Antibiotics, which are prescribed only after evaluating the results of laboratory tests of blood and smears. Antibacterial drugs may have varying degrees of sensitivity to a specific group of pathogenic microorganisms. When treating a bacterial infection, antibiotics of the penicillin group, macrolides or cephalosporins can be prescribed.
During treatment of angina, the patient should be kept in bed. It is recommended to eat gentle foods that do not irritate the throat, mainly vegetable and dairy products. Due to the high prevalence of sore throat, a sick person should use separate personal hygiene products and utensils, and limit contact with others.
It should be remembered that at the first signs of the disease you should consult a doctor. Ignoring the symptoms of sore throat or poorly treated disease can provoke complications and also contribute to the development of a chronic latent form, which will enter the acute phase when the immune system is weakened.
Preventive measures consist of increasing the body's defenses by taking vitamin complexes and a balanced diet, daily walks in the fresh air, eliminating irritating factors, quickly responding to characteristic symptoms, and limiting contact with infected people.
Complex therapy of chronic tonsillitis at the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev.
The method of complex treatment of the disease did not appear immediately. Our specialists have tried various methods of treating tonsillitis in practice. As a result of many years of experience in the study and treatment of chronic tonsillitis, this technique has taken root and is the most effective. It includes several stages.
The first stage is anesthesia of the tonsils. The tonsil is lubricated with lidocaine. The second stage is vacuum washing of the tonsils from caseous masses. The third stage is medicinal treatment of the tonsils using ultrasound. The fourth stage is irrigation of the tonsils with an antiseptic.
Stage five - lubricating the surface of the tonsils with Lugol's antiseptic solution. The sixth stage is physical therapy using a laser - this procedure relieves swelling and inflammation of the tonsils. The next stage is a vibroacoustic effect on the tonsils, due to which the blood flow rushes directly to the tonsils, and pathogenic substances are removed with it. The final stage of complex treatment is a session of ultraviolet irradiation, which heals the tonsils and fights pathogens.
The entire session takes about twenty minutes. To achieve a positive result, the patient usually needs five complex procedures.
Treatment of tonsillitis in Moscow
Chronic tonsillitis in Moscow, in fact, like the acute form of the disease, should be treated only by an otolaryngologist. The main thing is to choose the right medical institution where you will receive qualified assistance. Treating tonsillitis at the Doctor Zaitsev clinic means entrusting your health to professionals. Modern equipment and patented treatment methods allow us to provide the most effective care to patients. Our prices remain one of the best in Moscow, since our price list remained at the 2013 level. You can sign up for the clinic by calling the reception desk daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. or through the online registration form on the website. Come, we will be glad to help you!