Signs of lobar pneumonia in adults
With lobar pneumonia, symptoms appear acutely. Key ones:
- a sharp increase in temperature to 39 - 40 ° C;
- severe chills, weakness;
- chest pain when breathing;
- cough - at first dry, but quickly becomes wet, with rust-colored sputum;
- severe shortness of breath;
- wheezing that may be heard when breathing;
- rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure;
- pale skin, nausea, muscle weakness.
The general condition is serious, the patient needs the help of doctors in the hospital.
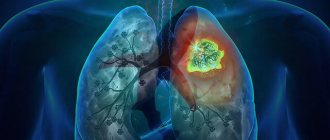
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia, popularly called “pneumonia,” is damage to the lung tissue. Depending on the stage of the disease, it can affect the lining of the lung and various parts, including the diaphragmatic pleura. Pneumonia is a very dangerous disease, often leading to death, so if there are signs of the disease, doctors prescribe an x-ray.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, pneumonia occurs due to harmful microorganisms entering the organ: viruses, bacteria, fungi. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Another type, eosinophilic pneumonia, is allergic in nature and requires urgent X-ray examination. Much less often, pneumonia is congestive, for example, when it occurs as a result of prolonged bed rest. It can also be a complication of other diseases. What pneumonia looks like on an X-ray largely depends on the nature and stage of the disease.
Signs of illness
Symptoms of pneumonia do not take long to appear, manifested by a dry or wet cough, with a temperature of up to 40 degrees. With a wet cough, the doctor pays attention to the nature of the sputum: “rusty”, bloody with pus, the presence or absence of odor. Other signs of pneumonia include pain in the chest, side, and even stomach—in this case, an x-ray is needed to confirm the location of the lesions in the lung.
Stages of lobar pneumonia in adults
Lobar pneumonia proceeds according to a special scenario, with a change of stages with typical changes in the lung tissue.
Stage one - high tide. A lot of blood flows to the lung tissue, which is why it turns red, and blood stagnates in small vessels. The stage lasts from 12 - 14 hours to 3 days.
Stage two – red liver. During this period, some of the fluid and red blood cells leak out of the small vessels of the lungs into the alveoli, which is why they work poorly. The affected part of the lung becomes dense, similar in appearance to liver tissue. Fibrin accumulates inside the lung sacs, a sticky substance that gives the tissue its density. This stage lasts up to 3 days.
Stage three – gray hepatization. Red blood cells stop entering the lung tissue, they are replaced by leukocytes and fibrin, epithelium. Therefore, the color of the lungs changes to gray and greenish. The stage lasts from 2 to 6 days.
Stage four – resolution. Gradually, fibrin dissolves, the alveoli are cleared, the lungs are restored and begin to breathe normally. This process is the longest, can last up to 2 - 3 weeks.
Differentiation of pneumonia from other lung pathologies
An important stage in making a diagnosis remains to distinguish it from other lung diseases, coronavirus. So, with bronchitis there will be no darkening in the image, but instead an increase in the pulmonary pattern.
Strengthening the pulmonary pattern
In the presence of a foreign body, a darkening with clear edges is observed, localized in the lower lobe of the lung. It is difficult to confuse it with inflammation of a typical nature.
With pleurisy, the picture shows an accumulation of exudate in the affected area. Pleurisy acts as a complication of untreated pneumonia.
In pneumothorax, a characteristic level of fluid is present. The image shows a clearing; the pulmonary pattern is not visible.
An X-ray is the main examination, and if necessary, a computed tomography scan is prescribed.
Modern methods of treatment
To treat lobar pneumonia, your doctor will prescribe two antibiotics.
One drug is administered intravenously, the second intramuscularly. Usually these are drugs from the group of penicillins and cephalosporins. Stronger medications are required less often. Additionally, complex therapy is required:
- immunocorrection (blood plasma and immunoglobulins are administered);
- correction of blood clotting disorders (intravenous blood thinning solutions, heparin);
- normalization of the protein composition of the blood (intravenous albumin, retabolil);
- oxygen (supplied through a nasal catheter or mask);
- hormonal drugs (for severe cases, prednisone is used for a short course);
- antioxidant therapy (ascorbic acid, rutin);
- bronchodilators (Berodual, Eufillin, Atrovent);
- expectorants (ACC, Bromhexine, Ambrobene, Lazolvan);
- antipyretic drugs (Nurofen, Paracetamol, Ibuklin);
- physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy.
As the patient’s condition improves, he undergoes a course of rehabilitation to completely eliminate foci of inflammation in the lungs.
Thin "slicing"
— The famous surgeon Nikolai Pirogov compiled the first atlas of topographic anatomy back in the century before last, cutting frozen corpses layer by layer. Thanks to CT, it is possible to “saw” a person transversely into thin layers intravitally and take pictures of each layer separately.
In one projection we see a person as if he is lying with his feet towards us, in another - frontal - as if he is facing us.
The tomograph step can be from centimeter to millimeter. The smaller the step, the clearer the tomogram. The obtained information can be converted into a three-dimensional image.
Interpreting an x-ray takes longer than the scanning procedure itself. Sometimes 10 minutes is enough to assess the patient’s condition and make a description, but in other cases you have to look in different projections and “rotate” the picture for an hour to give a clear conclusion.
Popular questions and answers
Pulmonologist Marina Samoilova told us why lobar pneumonia is so dangerous and how to treat it.
What complications can occur with lobar pneumonia?
If a person has a weakened immune system or treatment is started untimely or incorrectly, complications are possible in the form of:
- abscess (purulent melting of lung tissue); gangrene of the lung;
- purulent pericarditis (inflammation of the lining of the heart);
- purulent brain damage;
- blood poisoning;
- respiratory failure and even death.
Pneumococcal pneumonia, even in our time, is a fairly common cause of death, especially in older people, smokers, people suffering from alcoholism, with cancer and systemic diseases, and HIV-infected people.
How is an x-ray taken for pneumonia?
For pneumonia, an X-ray of the lungs is usually taken, regardless of the cause of the disease. Before the study, it is necessary to remove everything that could distort the results: metal objects, jewelry, long hair, etc. X-ray of the lungs
done in a vertical position, having first undressed to the waist and stood in front of the machine as the radiologist says. At the doctor’s command, the patient draws air into his lungs and holds his breath, while the device takes a picture.
Is it possible to treat lobar pneumonia with folk remedies?
As a rule, patients with lobar pneumonia should be hospitalized for constant monitoring by medical staff and emergency measures at the slightest sign of complications.
Often such patients experience nausea, vomiting, bowel movements, and confusion, so medications and solutions are administered intravenously. Thus, we cannot talk about treatment at home without the participation of qualified specialists. Fortunately, in our time, subject to a healthy lifestyle, such serious diseases as lobar pneumonia are becoming less and less common, and with modern treatment methods, in most cases it is possible to avoid serious complications and save the patient’s life.
Published on the portal kp.ru
Contraindications to X-rays
X-rays should not be taken for pregnant women at any stage, as well as for children under 15 years of age. In some cases, the patient's condition may be an obstacle to conducting the study. A patient in a supine position cannot undergo the study due to the inability to assume an upright position. In an inadequate condition, when the patient cannot stand still, signs of pneumonia on an x-ray cannot be recorded properly.
How often can an x-ray be taken for pneumonia?
A confirmed diagnosis is an indication for regular x-ray examinations to monitor the course of the disease. Whether the treatment prescribed by the doctor helps will show what pneumonia looks like on an x-ray. In this regard, many patients are concerned about how often this procedure can be performed without harm to health. After the start of treatment, depending on the type of disease, an x-ray for pneumonia must be done after 6-10 days. If positive dynamics are noticed, treatment continues as it was started. The patient, who is considered to be cured, is subsequently re-examined after 1, 3 and 6 months. With favorable treatment, the patient receives a small dose of radiation, far from acceptable levels. This is possible thanks to the development of medical technologies and protective measures during the procedure.
Fluorography, X-ray and CT
— Fluorography and radiography of the lungs are one and the same when it comes to digital devices. It’s just that in our country it has historically developed that an X-ray machine for examining the lungs is called a fluorograph. The quality of the images is the same.
And it is absolutely correct that patients with suspected Covid undergo a fluorogram. It is several times cheaper than CT and allows you to evaluate large lung lesions. In addition, every clinic has a fluorograph, and we only have about 30 tomographs in the entire region. If using a fluorogram we have identified a pathology, then there is no point in doing a CT scan.
Of course, CT is a more “sensitive” method if we are talking about Covid viral pneumonia. Sometimes it is visualized as very small and isolated areas with a barely noticeable dullness. If a patient has been sick for several days with a high fever, and the x-ray shows nothing, then he really needs a CT scan.
Thus, a kind of primary “sorting” of patients occurs. Already at the clinic, doctors see the extent of lung damage, can make a diagnosis and decide on hospitalization.
Lungs. CT scan.
Anna Zaikova.
Incidental finds
— In addition to the lungs, the tomogram shows the mediastinum with large vessels, lymph nodes, bronchial tree, trachea, ribs and shoulder blades, fatty tissue of the chest, spinal cord, spine, etc. Therefore, it happens that we find other pathologies in “Covid” images.
Yesterday, for example, we did about 90 studies. Three people were diagnosed with lung cancer, and another had tuberculosis. In general, about 3-5% of patients at the Diagnostic Center receive news about an inflammatory process in the lungs and other serious pathologies.
It requires detailed research, so data on patients who have signs of cancer is sent daily to the regional oncology clinic, and data on tuberculosis is sent to the corresponding regional medical institution. There the tomograms are examined again in more detail.
The clinic at the place of residence will also learn about such preliminary diagnoses in order to conduct additional examinations, confirm the diagnosis and begin treatment as quickly as possible. On CT scans, tumors can be seen at very early stages, so Covid studies secretly help patients prolong their lives.
Lungs. CT scan.
Anna Zaikova.
Shine, doctor, shine
— Conrad Roentgen discovered rays in 1895, and they almost immediately began to be used in medicine. He opened them by accident because he “photographed” his finger. How the devices were invented is a whole story. The main thing is that the X-ray tube has only 2% efficiency, all the rest of the energy is heat. Imagine how hot it was.
I didn’t catch this time, but old radiologists say that they tried to cool the tube with water, but it boiled and literally exploded with steam, burning the patient. Of course, this doesn't happen now. But this does not mean that modern devices are completely safe.
Radiation exposure with CT is several times greater than with classical X-ray examination. If a person often undergoes a tomogram, the radiation doses will subsequently affect his health. However, for older people this danger is minimal, and there is an explanation for this.
The cells of the body are defenseless to ionizing radiation during the period of division and growth. In old age, when degenerative processes begin, cells divide less frequently and, accordingly, become resistant to X-rays. At the age of 55-60, you can no longer be afraid of radiation exposure, and children and nursing women are most at risk.
If there are no indications for a CT scan from a therapist, then you should not prescribe this study yourself.
Lungs. CT scan.
Anna Zaikova.