Otolaryngologist for adults and children
Manevich
Igor Semenovich
Experience 26 years
Otorhinolaryngologist of the highest category, member of the European Rhinologic Society
Make an appointment
Acute sore throat or inflammation of the nasopharynx and mouth requires the most careful treatment. If it is not possible to completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease, chronic tonsillitis develops. It is “provoked” by pathogenic microorganisms covering the tonsils and mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. In case of hypothermia or traumatic tissue damage, the vital activity of microbes is activated, and acute tonsillitis develops. The infection quickly spreads throughout the body and can cause severe damage to internal organs and the respiratory tract. Therefore, at the first signs of tonsillitis, you should seek qualified medical help as soon as possible.
Causes of tonsillitis development
The main factors that trigger the pathological process are:
- infectious diseases that the patient tried to cure with home and folk methods;
- frequent pharyngitis, which reduces the body’s immunity and causes inflammation of the throat mucosa;
- allergic reactions that weaken the body;
- dental diseases, treatment of which has been postponed indefinitely;
- low immunity after suffering serious illnesses or prolonged stressful situations;
- congenital pathologies of the structure of the respiratory tract, curvature of the nasal septum.
All of the listed causes of tonsillitis are summarized by one main factor – weakening of the immune system and deterioration of the body’s condition. Having lost the ability to resist infections, it becomes vulnerable to pathogenic microorganisms that cause prolonged colds and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Surgical methods
Complex therapy for chronic tonsillitis is the most effective treatment method today. But unfortunately, there are cases when the tonsils do not respond to conservative treatment, and the infection concentrated in them affects other organs and systems of the patient. In such a situation, one has to resort to surgical removal of the tonsils.
Some thirty years ago, tonsils were removed if an adult or child was very often sick, so to speak, for prevention. Modern otorhinolaryngology has changed its view on the indications for tonsillectomy - this is the name of the operation to remove the tonsils.
At the very beginning of the article it was already mentioned that the tonsils are an important organ of the immune system, and if there are no direct indications for their removal, the tonsils can and should be fought for. Direct indications for their removal are:
- frequently recurring sore throats (more than four per year);
- peritonsillar abscess;
- poor performance of rheumatic tests;
- complications that appeared on the kidneys, heart and joints.
Today, there are several ways to remove tonsils: classic removal using a scalpel, laser removal, electrocoagulation, radiofrequency ablation, cryodestruction.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of removal method remains with the ENT doctor, since it is the doctor who is responsible for the result of the operation and its safety.
Risk factors
The risk of developing chronic tonsillitis of the throat increases if the patient has a hereditary predisposition to the disease. About 3% of all recorded cases are transmission of the inflammatory process from parents to children. Also, the protracted course of infectious diseases is caused by formations in the nasal cavity, polyps and sinusitis. The source of infection can be a carious tooth, gum disease, or periodontitis. Additionally, the body is weakened by poor nutrition, bad habits, constant stressful situations, and prolonged use of potent drugs.
Causes of inflammation
Most cases of chronic tonsillitis are associated with incomplete or poorly cured tonsillitis. With incorrect treatment tactics, angina becomes chronic, and under unfavorable conditions the disease manifests itself in a series of exacerbations.
Chronicity of the inflammatory process can also be provoked by:
- previous nasopharyngeal infections;
- chronic diseases of the ear, nose and throat;
- hypothermia;
- dental problems (caries, stomatitis, periodontal disease);
- hormonal disbalance;
- stress, nervous tension;
- reduced immunity.
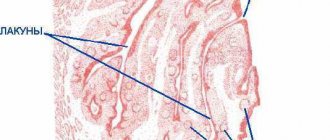
The patient’s immunity cannot cope with the streptococcal and staphylococcal flora, which is constantly present in the lacunae of the tonsils. And at the moment when the tonsils can no longer fight the ever-increasing number of bacteria, an exacerbation occurs.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis in adults
Signs of tonsillitis resemble symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections and inflammatory diseases. Most patients complain of the following problems:
- tickling sensation;
- sore throat while eating and in the morning after sleep, feeling of a foreign object in the respiratory tract;
- inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes, pain when touched;
- the presence of lumps in the throat, visible ulcers on the surface of the mucous membrane;
- frequent cases of colds, persistent cough;
- increased body temperature, especially in the evening;
- irritability, drowsiness and constant feeling of fatigue;
- bad breath caused by the activity and decomposition of bacteria.
Quickly spreading throughout the body, the infection causes a feeling of aching joints, pain in the lower abdomen, allergic manifestations and skin inflammation, shortness of breath and irregular heart rhythms. Often, during chronic tonsillitis in an adult patient, the symptoms of major diseases of the internal organs intensify: heart, liver, kidneys, etc.
Are you experiencing symptoms of tonsillitis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Symptoms of the disease and its course
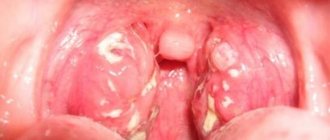
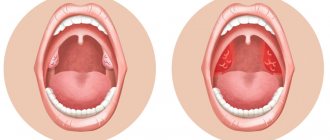
One of the characteristic symptoms of a chronic disease is the appearance on the surface of the tonsillitis plugs - purulent white or brown deposits in the lacunae of the tonsils. They are clearly visible upon visual inspection and emit a persistent, unpleasant, putrid odor from the oral cavity.
With an exacerbation of the disease, the patient notes pain in the throat, which increases during the process of swallowing. It happens that no pain is observed, but discomfort is felt in the throat, as if something is stuck in it. Patients compare this condition to the sensation of a lump in the throat.
Another symptom of chronic inflammation is increased body temperature, which stays at 37.1-37.5℃ for a long time. Of course, this condition provokes constant fatigue, irritability and malaise.
Against the background of the inflammatory process, symptoms such as pain in the joints, lower back, shortness of breath or rapid heartbeat may appear. The results of an electrocardiogram can reveal arrhythmia and tachycardia. Such symptoms are a good reason to contact an otolaryngologist, because they may indicate the development of complications in the heart, joints or kidneys.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
During an exacerbation of tonsillitis, the patient’s immunity malfunctions and begins to intensively produce antibodies, but not to the causative agents of the disease, but to the cells of their own organs. As a result, the body fights with itself, causing complications in other organs.
At the first signs of the disease, you must contact an ENT doctor to confirm the diagnosis and receive effective treatment.
When to see a doctor
Frequent cases of sore throat, prolonged recovery from respiratory infections, and persistent cough are reasons to immediately seek help from an otolaryngologist. The specialist will not only conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the body, but will also tell you how to quickly and without consequences cure chronic tonsillitis. For additional consultations and examinations, you can contact the doctors of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitber) in the central district of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10 (metro stations Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya) . Experienced ENT doctors will offer an effective course of treatment for tonsillitis, taking into account the age and characteristics of the patient’s body. The selection of antibiotic drugs and physical therapy will be made based on the results of the examination and a history of diseases.
Complications of tonsillitis
By ignoring the symptoms of tonsillitis and refusing to see a doctor in favor of home treatments, the patient is at serious risk. The spread of infection throughout the body and tissue inflammation can cause a peritonsillar abscess on the tonsils. This condition is dangerous due to its similarity to a sore throat, the symptoms of which can be ignored or you can try to cope with them using traditional methods. Without appropriate treatment, the tissues of the throat and tonsils swell during an exacerbation of tonsillitis, making breathing and swallowing difficult, and the pain becomes more severe. The problem can only be dealt with in a hospital setting.
Further development of the infectious process can affect the internal organs and tissues of the body. Diseases caused by chronic or acute tonsillitis include psoriasis and eczema, endocrinological problems, joint inflammation and the development of arthritis, tissue damage to the heart muscle and urinary tract.
Forms of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis (or sore throat) is an inflammation of the tonsils, often accompanies colds.
Types of sore throats
Sore throats are acute:
- Banal (vulgar or typical) tonsillitis: there are catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, mixed.
- Atypical tonsillitis: herpetic, Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent's tonsillitis, phlegmonous, fungal and mixed forms. Usually they are severe, as they appear against the background of decreased immunity.
- Sore throats associated with infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, sore throat due to HIV infection and others).
- Angina in blood diseases: monocytic, agranulocytic, tonsillitis in leukemia.
Tonsillitis can also be chronic (compensated and decompensated)1.
Interesting fact!
Our defense against infections is located in the pharynx - an anatomical structure consisting of lymphoid tissue. The lymphoid elements in the pharynx are located around the pharynx in the form of a ring, so it was called the “lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring” by Waldeyer-Pirogov. It is formed by two palatine tonsils (those that are sometimes called “tonsils”), one pharyngeal or nasopharyngeal (located on the back wall of the pharynx), one lingual (a collection of lymphoid follicles at the root of the tongue) and two tubal (located in the thickness of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx near the openings eustachian tubes). Tubal tonsils are most pronounced in children under 5-7 years of age, and later undergo reverse development. In adults, due to their small size, they are almost invisible.
The pharyngeal ring is an additional barrier for bacteria between the external and internal environment of the body. These structures also produce antibodies and lymphocytes - immune response cells.
Acute tonsillitis
This is an acute inflammatory disease of the palatine tonsils. Their mucous membrane becomes swollen, hyperemic, and purulent deposits may appear in the crypts of the tonsils. But depending on the factors that caused the disease and the patient’s condition, the process is not limited to damage to the tonsils alone. A severe infection can take over the entire body. The most dangerous complications are rheumatic heart defects, joint damage, kidney damage (glomerulonephritis). Therefore, self-medication can be dangerous. For correct diagnosis and effective treatment, you need to consult a specialist.
Purulent tonsillitis is one of the forms of tonsillitis and can be a complication of acute or chronic tonsillitis. It is characterized by the presence of purulent discharge in the crypts of the palatine tonsils. Most often accompanies a bacterial infection. Improper treatment can lead to chronicity of the process.
Chronic tonsillitis is a persistent chronic inflammation of the tonsils, characterized by recurrent exacerbations in the form of tonsillitis, a sluggish course, and a decrease in the body's resistance to infection. Slight hypothermia or draft causes exacerbation of tonsillitis. Many factors play a role in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory process in the tonsils. Most often the disease occurs after repeated sore throats. Chronic tonsillitis is of two types: compensated and decompensated. This is important for further treatment tactics.
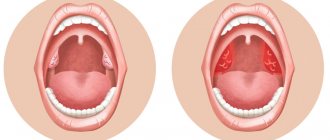
With compensated chronic tonsillitis, examination reveals some looseness of the tonsils, hyperemia, swelling, purulent plugs or plaque in the crypts of the tonsils, but this process is limited to the tonsils and does not spread beyond its boundaries. This precarious balance between local immunity and the body’s resistance on the one hand, and the presence of pathogenic organisms in the inflamed tonsils on the other, can shift towards decompensation if the course of the disease is unfavorable. With decompensated chronic damage to the lymphoid apparatus of the pharynx, local signs of chronic tonsillitis are usually clearly expressed. With this form, exacerbations often occur in the form of sore throats, peritonsillitis, peritonsillar abscesses, regional lymphadenitis, and in clinically advanced cases, disturbances in the functioning of other organs and systems (kidney pathology, formation of cardiac flow, articular syndrome, damage to the nervous system).
Up to contents
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis
A preliminary diagnosis can be established with a high degree of accuracy based on the patient’s complaints and study of his medical history. The lymph nodes are palpated and the pharynx is examined using special lighting. Redness of the tonsils, the presence of pus and grooves on their surface, thickening and inflamed areas, and cheesy discharge unmistakably indicate chronic purulent tonsillitis.
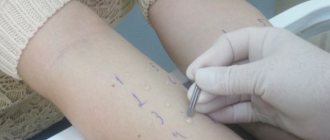
A set of laboratory tests will help confirm the specialist’s assumptions:
- general blood test and biochemistry to clarify the level of ESR and leukocytes;
- a throat smear, with which you can clarify the type of pathogens and the presence of a purulent process on the surface of the mucosal tissue;
- urine analysis to clarify ESR, protein and leukocytes.
In order for the above tests to give the most accurate result, you should avoid drinking alcohol three days before the test, and stop smoking two hours before the test.
The listed laboratory tests have an important goal - to clarify the nature of the infectious disease and the extent of its spread throughout the body. The test results will tell you which treatment tactics for purulent tonsillitis should be chosen to eliminate all dangerous symptoms.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Provided there are no complications, a patient with chronic tonsillitis is prescribed a conservative course of treatment.
Conservative treatment for adults
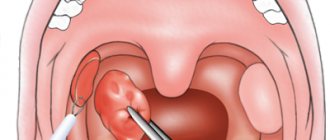
A course of antibiotics and rinsing using a syringe or special devices gives good results for tonsillitis. The affected tissues of the palatine tonsils are treated without affecting adjacent healthy tissues. The result is noticeable after the first session: there is an improvement in blood circulation, the process of restoration of the mucous membrane begins, the number of microbes sharply decreases, and their activity decreases. The formation of scars on the surface of the tonsils in areas of inflammation slows down, and the regeneration process becomes more pronounced.
Surgical treatment of chronic tonsillitis for adults
The decision on surgical intervention is made in cases where:
- It was not possible to cure chronic tonsillitis with conservative methods;
- the frequency of exacerbations of the disease remains unchanged or increases despite the completed course of treatment;
- the patient has complications of tonsillitis - arthritis, kidney problems, rheumatic diseases;
- purulent lesions involve not only the tonsils, but also adjacent tissues.
In the vast majority of cases, after surgery, the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis completely disappear. However, due to the removal of the tonsils, the body's protective properties are somewhat reduced.
Possible complications
Delayed diagnosis, improper treatment, non-compliance with otolaryngologist’s prescriptions - all this can cause an inflammatory process not only in the tonsils, but also cause complications in other human organs. The consequences of an exacerbation of the disease can be very severe and can trigger irreversible processes in the body:
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system - rheumatism, arthrosis, joint diseases;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system - high blood pressure, heart defects, ischemia, etc.;
- skin diseases - dermatitis, acne, acne;
- bronchopulmonary diseases - bronchitis, asthma;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, ulcers, etc.;
- vision problems;
- kidney diseases - for example, pyelonephritis;
- liver diseases;
- neurological disorders.
Separately, I would like to touch upon the topic of pregnancy and chronic tonsillitis. Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis during the first trimester is fraught with the threat of miscarriage, and in the later stages - with the risk of premature birth. The disease can provoke pathologies in the development of organs and systems of the fetus. You also need to remember about the hereditary factor. If the parents of the future baby suffer from chronic tonsillitis, then with a high degree of probability the baby will inherit this diagnosis. Therefore, during pregnancy planning, it is extremely important for both parents to undergo a course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis, to cleanse the body as much as possible of pathogenic microorganisms and eliminate the source of inflammation.