Chronic hepatitis is a very common disease: it affects at least 5% of the population of our planet. The concept of chronic hepatitis unites a whole group of liver diseases. They can be caused by different reasons and have different clinical signs, but they last for at least six months without any improvement.
Among the forms of chronic hepatitis are:
- persistent (this is a benign, inactive form);
- chronic active (close to acute hepatitis in its manifestations);
- chronic cholestatic.
Symptoms of chronic hepatitis
In the first case, chronic hepatitis manifests itself weakly, its symptoms are loss of appetite, heaviness and pressure in the right hypochondrium, caused by an increase in the size of the liver and its moderate hardening, and dyspepsia. Chronic active hepatitis is accompanied by a wider range of symptoms: weakness and fatigue; Some foods are not tolerated by patients (for example, fats); dyspepsia, the appearance of spider veins and nosebleeds, which are caused by deterioration of blood clotting; skin itching and increased body temperature, while not only the liver, but also the spleen enlarges. With lupoid hepatitis, as one of the forms of manifestation of chronic active hepatitis, there are furunculosis, lymphadenopathy, hormonal disorders, fever, abdominal pain, etc.
Skin itching, jaundice, lightening of stool and dark urine, soft nodular formations on the skin accompany chronic cholestatic hepatitis.
City hospital of the resort city of Gelendzhik
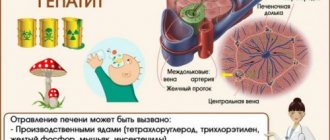
Chronic hepatitis is an inflammatory degenerative liver disease that lasts more than six months. In 50% of cases, acute viral hepatitis with improper treatment turns into chronic hepatitis (mainly hepatitis C). The cause of chronic hepatitis can also be the long-term influence of toxic substances on the body (alcohol, salts of heavy metals, benzene, etc.). Long-term use of medications (sedatives, tetracycline antibiotics, antihypertensive, cytostatic, anti-tuberculosis, narcotic drugs) can lead to the development of chronic hepatitis. In addition, chronic hepatitis may be associated with metabolic disorders and autoimmune processes.Symptoms of chronic hepatitis
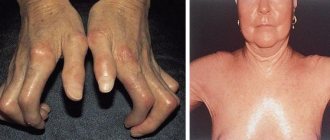
On palpation, the liver is enlarged in size, and a dull pain is felt. Due to the accumulation of bile acids in the blood and tissues, bradycardia occurs, and symptoms such as a depressed mental state, irritability, and insomnia may appear. Characterized by decreased appetite, nausea, belching, flatulence, intolerance to fatty foods, alcohol, unstable stools, increased fatigue, decreased performance. The skin and sclera acquire a yellowish tint (jaundice). “Liver signs” include dilated capillaries in the form of stars on the cheeks, back, redness of the inner surfaces of the hands (“liver palms”). The spleen may become enlarged. Blood clotting is impaired, which is manifested by nosebleeds and easy bruising. Joint pain is possible.
Exacerbation of chronic hepatitis develops, first of all, with violations of the diet, heavy physical activity, alcoholic excesses, and stress. Remission (improvement in general condition) occurs after active treatment and exclusion of provoking factors. The patient does not experience any particular discomfort. Depending on his compliance with safety rules, the period of remission can be long (up to several years).
Diagnostics
- Biochemical blood test: characterized by an increase in bilirubin and liver enzymes.
- Ultrasound examination of the liver: signs of inflammation.
- For a more accurate diagnosis, a liver biopsy is performed, which makes it possible to assess the severity of inflammation, determine the presence of fibrosis or cirrhosis, and sometimes makes it possible to find out the cause of hepatitis.
- Serological blood test: detection of antibodies to hepatitis B and C viruses.
- Virological research: identification of the corresponding virus.
- Immunological study: detection of antibodies to components of liver cells.
Basic principles of treatment of chronic hepatitis
First of all, for the treatment of chronic liver hepatitis, it is necessary to follow the rules of behavior prescribed by the doctor. The main thing is to ensure peace; bed rest is recommended. Due to the fact that with strict adherence to bed rest, metabolic processes in the liver improve, liver cells recover faster.
One of the main principles of treatment of chronic hepatitis is diet. Food should be rich in proteins, carbohydrates and vitamins, fats should be limited, and some should be excluded altogether. Meals should be frequent, fractional, small portions. Of course, alcohol is strictly prohibited!
Drug therapy must be agreed with the attending physician. In severe cases of chronic hepatitis, the patient is usually hospitalized in a specialized department of the hospital, where he is prescribed combination treatment.
Prevention of chronic hepatitis
Prevention of chronic hepatitis consists of preventing acute viral hepatitis, timely treatment of acute hepatitis of any etiology, combating alcohol abuse, limiting the amount of medications taken to the required minimum, and caution when contacting hepatotoxic substances.
To prevent chronic hepatitis, the working day must be organized, moderate physical activity must be alternated with periods of rest, and it is strictly forbidden to work with pesticides (herbicides, pesticides, aggressive technical fluids). Twice a year, patients with chronic hepatitis should undergo preventive examinations, blood and urine tests.
For the prevention of chronic hepatitis, a very important condition is timely consultation with a doctor regarding diseases of various organs and systems and their full treatment.
GBUZ "Center for Medical Prevention" of the Ministry of Health of the Krasnodar Territory.
Signs of chronic hepatitis
Chronic hepatitis is characterized by weakness and fatigue, and asthenic syndrome manifests itself. The patient's condition worsens significantly if liver cirrhosis develops. Then the signs of chronic hepatitis become jaundice (yellowness of the sclera, icteric skin tone, darkening of urine, discoloration of feces, etc.), the abdomen enlarges. Sometimes hepatic encephalopathy develops; when the brain is damaged, its activity is disrupted, and hallucinations may occur.
Signs of chronic hepatitis do not appear immediately in patients; the first stages of the disease can be asymptomatic, which makes it especially dangerous. Chronic hepatitis is often detected during examination in connection with other diseases.
Causes of chronic viral hepatitis
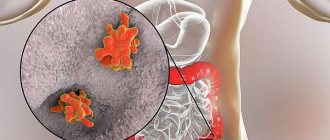
The disease is caused by hepatitis B, C and D (delta) viruses - the hepatitis A virus, as a rule, provokes an acute form of the disease. The most common cause of chronic hepatitis is the hepatitis C virus; it is found in 77.97% of cases of newly diagnosed chronic hepatitis in Russia. Every year, it infects about 50 thousand people throughout the country.3 The next most common is the hepatitis B virus. According to WHO, at least 257 million people worldwide are sick with it.4 In Russia, the incidence averages 10.78 people per 100 thousand ,5 but varies greatly by region. Hepatitis D can only accompany and aggravate hepatitis B, since it is not self-sufficient in terms of reproduction.
Invading liver cells, hepatitis B and C viruses leave particles of their antigens on the surface of the membranes. The immune system begins to view infected hepatocytes as foreign cells and attacks them. If the immune response is adequate, such an attack, although accompanied by symptoms of liver damage (clinical manifestations of acute viral hepatitis), quite quickly destroys infected cells. But the immune system cannot cope with the virus itself, and its activity is not enough to completely eliminate the infectious agent, as a result of which chronic hepatitis develops.
The liver has enormous regeneration capabilities, but since in chronic hepatitis the inflammatory process can last for years and decades, sooner or later the organ’s reserves may be depleted. In this case, connective (fibrous, scar) tissue is formed in place of the dead cells. It is not able to perform the functions of hepatocytes, and fibrotic degeneration of the liver can result in the development of liver failure. Another long-term, but very dangerous outcome of chronic hepatitis is the degeneration of hepatocytes and the formation of hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer).
If the infection occurs in adulthood, and the activity of the inflammatory process is low, chronic viral hepatitis can last for several decades. In this case, there is a possibility that the patient will die from causes unrelated to chronic hepatitis. If the infection entered the body in youth, and the inflammatory process is active, the likelihood of unfavorable developments is much higher. According to WHO, 720 thousand people die annually from liver cirrhosis due to viral hepatitis and 420 thousand die from hepatocellular carcinoma.4 Chronic hepatitis B with the delta agent (combined infection B and D) develops especially quickly and unfavorably.6
Classification of hepatitis
Chronic viral hepatitis is classified according to its causes and is divided into the following types:
- chronic viral hepatitis B;
- chronic viral hepatitis C;
- chronic viral hepatitis B with delta agent.
According to the degree of activity of the pathological process, the following types of chronic hepatitis are distinguished:
- with minimal activity;
- with moderate activity;
- with pronounced activity.
In addition, there are four stages of development of liver fibrosis - from mildly expressed to entailing a violation of the architectonics (characteristic structure of tissues) of the organ. The higher the stage of fibrosis, the more pronounced the pathological changes.
Diagnosis of hepatitis
Manifestations of hepatitis vary and depend directly on the cause of liver damage. There are cases when hepatitis does not have specific symptoms or is completely asymptomatic. Only a detailed survey and thorough examination of the patient allows a specialist to establish hepatitis in such cases. But in order for the diagnosis to be confirmed as final, additional research may be needed.
Laboratory diagnosis of hepatitis includes the following tests:
- Clinical blood test;
- Gamma-GT;
- Coagulogram;
- Direct and total bilirubin;
- AST;
- ALT;
- alkaline phosphatase;
- Albumin (code 79) and total protein in serum;
- Transferrin (code 28);
- Copper in the blood;
- Ceruloplasmin (code 110);
- Ferritin (code 30);
- Total cholesterol;
- HBsAg (code 833 or code 839);
- Anti-HCV, antibodies, ELISA;
- Cytological examination of punctates, as well as scrapings of other tissues and organs;
- A screening study to detect the presence of psychotropic, narcotic and potent substances.
Additional tests to diagnose hepatitis include an abdominal ultrasound.
Hepatitis treatment
To treat acute hepatitis, it is first necessary to stop the impact of the pathological factor on the liver, to avoid the disease becoming chronic. Most acute hepatitis can be cured completely.
Depending on the cause of its occurrence and the activity of the process, chronic hepatitis lasts from six months to several years. Its long course requires regular visits to a specialist for examinations, strict adherence to medical recommendations, as well as changes in the patient’s lifestyle. This is necessary to prevent liver failure, cancer and cirrhosis of the liver.
Causes of hepatitis
Non-infectious hepatitis occurs for various reasons:
- Alcoholic hepatitis occurs due to many years of alcohol abuse. Because of it, the metabolism in hepatocytes is disrupted, and they begin to collapse;
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis does not occur due to alcohol intake, but the changes in the liver with it are very similar to those that occur with alcohol;
- Drug-induced hepatitis is formed due to the use of various medications that have a toxic effect on the liver (oral contraceptives, antibiotics and anti-tuberculosis drugs);
- Toxic hepatitis is caused by alcohol substitutes, poisonous mushrooms, arsenic compounds, lead, benzene, toluene and other substances that destroy liver cells;
- Autoimmune hepatitis leads to disruption of the immune system, which begins to destroy normal liver cells;
- Metabolic hepatitis occurs due to various hereditary diseases associated with metabolism. These include Wilson's disease, in which copper metabolism is disrupted in the body, hemochromatosis, in which increased absorption of iron is observed in the intestines, etc.;
- Reactive hepatitis is formed due to exposure to toxins and metabolic products that enter the blood during diseases of other organs (pancreatitis, stomach ulcers, autoimmune and endocrine diseases);
- Primary biliary hepatitis occurs due to obstruction of bile flow and bile outflow, leading to damage to liver tissue.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of chronic viral hepatitis is based primarily on laboratory methods, since in the early stages the disease is often asymptomatic.
First of all, to confirm the cause of the disease, a blood test for specific markers of viral hepatitis is necessary. These are antigens of the hepatitis B or C virus (viral particles) and antibodies produced by the body in the fight against it. In addition to the qualitative determination (detection) of the antigen, it is also necessary to study the level of viral load (the amount of antigen in a certain volume of blood). This makes it possible to judge the activity of virus reproduction and determine indications for antiviral therapy.
To assess liver function, a biochemical blood test is recommended, which includes determining the level of liver enzymes, bilirubin, protein, protein fractions and other indicators. The doctor gives more specific recommendations based on the individual picture of the course of the disease.
To assess the size and structure of the organ, abdominal ultrasound is recommended: this is the simplest method of visualizing the liver.
To determine the degree of fibrosis, fibroelastography or liver biopsy can be performed - sampling a small amount of liver tissue under ultrasound guidance for further examination under a microscope.
Types of hepatitis
Currently, there are several types of viral hepatitis:
- hepatitis A. This is the most common type of virus, which has the most favorable picture of the course of the disease. Its symptoms and signs appear a week to two months after infection of the body. This form of hepatitis in rare cases becomes chronic, sometimes ending in complete self-healing of the body;
- hepatitis B. This is a dangerous form of hepatitis that is accompanied by severe symptoms. It requires mandatory treatment in a hospital setting using a full range of medications, adherence to a strict diet, and the cessation of bad habits. In 80% of cases, hepatitis B ends in a person being completely cured of the virus. It is possible to protect yourself from the disease through vaccination;
- hepatitis C. This is the most severe form of the disease, which is often accompanied by viral hepatitis of other groups. There is currently no effective vaccine against hepatitis C. The disease is difficult to treat and in every 7th infected person, it leads to chronic hepatitis with the subsequent occurrence of liver cirrhosis and cancer;
- hepatitis D. This is another form of viral hepatitis, which is similar in the course of the disease to group B hepatitis. The difference in viruses is the presence of a delta agent;
- hepatitis E. In terms of the totality of symptoms, this infection is similar to hepatitis form A. The disease can also be completely cured with timely consultation with specialists. If it develops into a chronic stage, it affects not only the liver, but also the kidneys. This form is dangerous for women in the last months of pregnancy.
Also, viral hepatitis differs in the form of the disease:
- acute hepatitis;
- chronic hepatitis.
Acute hepatitis most often manifests itself with obvious symptoms and signs of the disease; chronic disease is considered when the virus does not respond to treatment within 6 months.