Inflammation of the prostate gland is a common disease diagnosed in men over the age of 30. If the treatment of the pathology is incorrect or untimely, it develops into a chronic form that cannot be completely cured. Timely prevention of prostatitis, the rules of which are simple and accessible to everyone, will help prevent the development of the disease and its chronicity.
Risk factors for developing prostatitis
In most cases, prostatitis is bacterial in nature and occurs as a result of a decrease in the body's protective functions. Risk factors for developing inflammation of the prostate gland are:
- infectious diseases of the urinary system and their untimely treatment;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases occurring in the body;
- long-term sexual abstinence;
- promiscuous sex life, ignoring protective contraceptives;
- abuse of bad habits;
- inactive lifestyle;
- unbalanced diet, poor in vitamins, useful elements and substances;
- hypothermia;
- stress, overwork, lack of sleep.
Doctors have proven that obese men are more prone to developing prostatitis. Typically, such people lead a sedentary lifestyle, abuse bad habits, and eat improperly, which leads to a decrease in protective functions, the development of congestive processes in the pelvic organs, and the addition of a bacterial infection, which contributes to the progression of inflammatory complications in the prostate tissues. Therefore, in addition to generally accepted preventive procedures, it is important to normalize weight, improve nutrition, try to get enough sleep and get proper rest.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
The key to successful and timely treatment of prostatitis is an accurate and comprehensive diagnosis.
The low proportion of infectious prostatitis is explained in most cases by the fact that the pathogen was not detected. Chronic sexually transmitted infections can be asymptomatic, while their pathogens can penetrate the prostate tissue and cause inflammation. Therefore, laboratory research methods play a leading role in the diagnostic process. To determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, biological fluids are inoculated: urine, semen, prostate secretions. This method allows you to select a drug that is most effective for a specific pathogen strain, capable of penetrating directly to the site of inflammation [5].
The “classical” method of laboratory diagnosis of prostatitis is considered cultural (culture of urine, ejaculate, contents of urogenital smears). The method is very accurate, but takes time. To detect bacteria, a smear is Gram stained, but in this way it is unlikely to detect viruses, mycoplasma and ureaplasma [5]. To increase the accuracy of research, mass spectrometry and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) are used [4]. Mass spectrometry is the ion analysis of the structure of a substance and the determination of each of its components. The polymerase chain reaction allows you to detect fragments of DNA or RNA of the causative agent of an infectious disease, including viruses and plasma.
Currently, for a special examination of urological patients, the Androflor analysis is used - a comprehensive PCR study of the microflora of the genitourinary tract. The result of the study is ready in a day and reflects the complete picture of the microbial ratio in the body of the subject.
Tests for prostatitis include collection of urine and ejaculate and urological smears. The European Urological Association recommends the following set of laboratory tests:
- general urine analysis;
- bacterial culture of urine, semen and ejaculate;
- PCR diagnostics.
A general urine test allows you to determine signs of inflammation (the number of colony-forming units of microorganisms, the number of leukocytes, red blood cells, urine clarity) and the presence of calcifications (prostate stones).
General analysis is included in the methodology of several urological (glass or portion) samples. Glass or portion samples consist of sequential collection of urine or other biological fluids into different containers. In this way, the localization of the infectious process is determined. Prostatitis is indicated by the detection of infectious agents, blood cells (leukocytes and erythrocytes) in the final portion of urine during a three-glass sample or after urological massage of the prostate
Two-glass test - inoculation of the middle part of the urine stream before and after urological prostate massage.
Three-glass sample - the initial, middle and final portions of urine are taken during the same urination.
Four-glass test - culture and general analysis of the initial and middle parts of the urine stream, prostate secretion after urological prostate massage and a portion of urine after this procedure.
Cultural culture or PCR diagnostics of ejaculate [4, 5] and urogenital smear material are also performed.
To make a diagnosis of prostatitis, blood tests are also required. A general capillary blood test allows you to confirm or refute the presence of inflammation, as well as exclude other diagnoses that cause the same symptoms.
Diagnosis of non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome is more difficult, as it is based on the clinical picture and indirect laboratory indicators (including general analysis of urine and blood). The intensity of the pain syndrome is determined using a visual analog pain scale, and the severity of psychological changes is determined using scales for assessing anxiety and depression. At the same time, research is required to search for an infectious agent, since the range of pathogens can be very wide. Instrumental studies include urofluometry with determination of residual urine volume and transrectal ultrasound examination (TRUS) of the prostate gland [1, 5].
Asymptomatic prostatitis is detected by histological examination of a prostate biopsy specimen, prescribed for suspected cancer. A blood test for Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) is performed first. PSA in the blood serum appears with hypertrophy and inflammation of the prostate, and the normal criteria change with age. This study also helps to exclude suspicions of a malignant prostate tumor [1, 2, 3].
The role of physical activity in the prevention of prostatitis
An inactive lifestyle is one of the most common causes of inflammation of the prostate gland. In people who move little during the day and are predominantly in a sitting position, venous stagnation occurs in the pelvis, as a result of which blood circulation, oxygen supply and nutrition of prostate tissue are disrupted. This leads to a decrease in local immunity and activation of pathogenic microflora. Therefore, the prevention and treatment of prostatitis necessarily include moderate physical activity, which strengthens muscles, maintains the organs of the genitourinary system in the correct position, and ensures high-quality contraction of the prostate and its complete emptying.
If possible, it is advisable to enroll in a gym, where classes are conducted under the supervision of an experienced trainer. But not everyone has the time and opportunity to visit the gym, so the ideal solution in this situation is regular workouts at home. To prevent stagnation and always keep muscles toned, it is recommended to perform the following exercises daily:
- squats;
- circular movements and body tilts;
- pumping the press;
- running in place.
An excellent way to prevent prostatitis is daily walks in the fresh air, cycling, swimming, and brisk walking.
Chronic prostatitis: symptoms, causes of development, treatment and prevention
Category: Medical prevention.
- Exacerbation
- Causes
- Popular questions
- Prevention
Prostatitis is diagnosed exclusively in men. This is one of the most common diseases among diseases of the male reproductive system; 4 out of 5 men have experienced symptoms of prostatitis at least once in their lives.
Most often, men aged 20–40 years are susceptible to prostatitis at the peak of their sexual activity. Chronic prostatitis is diagnosed in every 10 men. It is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission and disguises itself as a number of other diseases.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis include the following:
- Discomfort and aching pain in the lower abdomen, with periodic cramps that do not go away for a quarter or longer. Pain may appear in the lower back, legs, scrotum, and anus. It becomes especially painful during urination and ejaculation.
- Penile erection worsens and sexual desire weakens. First, premature ejaculation develops, but over time, on the contrary, ejaculation practically does not occur; this becomes very difficult to achieve.
- Urination becomes painful and incomplete. There is always a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- A man’s quality of life deteriorates significantly.
There are 2 types of chronic prostatitis: bacterial and abacterial.
Bacterial (infectious) prostatitis occurs with a constant alternation of sharp exacerbations and remissions, while the prostate secretion contains infection and bacteria.
In this case, nearby organs, such as the urethra, bladder neck, and vas deferens, may also be affected, which is why the disease manifests itself in different ways. An accurate diagnosis can be made after a thorough examination.
Most often the disease manifests itself as follows:
- Frequent and painful urination.
- Burning in the urethra.
- Premature ejaculation.
- Small mucous discharge from the urethra.
- Serious sexual dysfunction.
All this greatly affects the performance and mental state of a man, which leads to long-term depression and neurasthenia.
Abacterial chronic prostatitis is a disease in which bacteria are not found in the prostate secretion. This form is very difficult to diagnose, as evidenced by numerous reviews from men on various forums. It is also very difficult to choose the right treatment regimen.
Important
Until now, doctors are faced with many unclear factors in the origin of this disease. This greatly complicates the treatment process.
Even ultrasound and laboratory tests of secretions may not show the presence of an inflammatory process. According to the recommendations of the European Association of Urological Specialists, the main signs of abacterial prostatitis are identified:
- It appears in middle-aged men.
- Prolonged pain in the pelvic area and groin.
- Impaired urinary function and frequent imperative urges.
- Erectile dysfunction and pain during ejaculation.
- Chronic congestive prostatitis: exacerbation and remission
- Chronic congestive prostatitis is characterized by several stages of development, which manifest themselves with different symptoms:
- Exudative - a man feels a cutting pain in the groin, scrotum and pubic area.
- There are problems with erection and accelerated ejaculation.
- Alternative - the patient complains of discomfort in the groin, scrotum and pubis.
- There is a frequent urge to urinate and rapid ejaculation during sexual intercourse.
- Proliferation - the patient notes frequent urination with a weak stream, a constant feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder. On the contrary, ejaculation becomes difficult and slow.
- Scar changes - at this stage, the prostate tissue begins to intensively thicken. The patient complains of discomfort in the pelvic and pubic area, frequent urge to urinate with a thin stream and incomplete emptying. The erection is very weak or absent altogether, ejaculation becomes almost impossible, and the orgasm is weak, without vivid impressions. Prostatitis passes into the stage of chronic prostatitis of unstable remission, in which constant pain is observed and remission occurs for only a few hours.
As for classification, it is customary to use the US NIH classification, which divides the disease into types: acute and chronic bacterial, chronic without signs of inflammation and congestive, as well as histological.
Factors and causes of chronic prostatitis in men
Despite the fact that some microbes of chronic prostatitis are present in the body of almost every person, only a few get sick. How can one explain the development of such a disease in a particular case?
Experts determine the occurrence of chronic prostatitis not only by the presence of infection in the body, but also by the conditions that influence the development of the disease.
The most common causes of chronic prostatitis in men include:
- stagnation of blood contained in the prostate, caused by a sedentary lifestyle;
- unstable sex life;
- uncomfortable and rather tight clothes;
- frequent hypothermia;
- injuries, as well as infections of various organs of the genitourinary system;
- poor nutrition;
- constant stressful state;
- frequent drinking and smoking.
Diagnosis begins with a conversation with the patient, who must accurately and completely tell what is bothering him. The doctor must find out why the patient developed chronic prostatitis, find out all the possible causes and symptoms, how they manifest themselves. The doctor should tell you everything down to the smallest detail; this will determine how correctly the diagnosis will be made and effective and comprehensive treatment prescribed.
Next, you need to palpate and submit the secretion for bacteriological analysis, through which you can determine the presence of infections and determine the resistance of the bacteria to antibiotics.
Attention
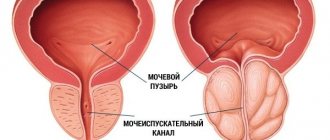
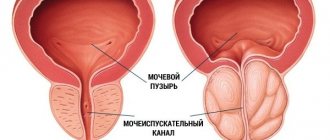
Palpation is carried out by a urologist through the rectum. This procedure makes it possible to find out the size and pain of the prostate. When palpated, hemorrhoids, adenoma or prostate cancer can also be detected. An ultrasound of the prostate will provide accurate data on the condition of the organ.
Determining the level of PSA in the blood makes it possible to exclude or confirm the presence of adenoma and prostate cancer.
If the urologist suspects the presence of a tumor, he will have to submit pieces of prostate tissue for a biopsy, which will show its presence or absence.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis is a complex and time-consuming process. Today, various methods are used to treat this disease.
Treatment with antibiotics. In this case, macrolide antibiotics and tetracycline are used.
Only the attending physician can correctly select the drug, its dosage and duration of treatment.
Usually the medications are taken for 10–15 days. After that, repeated tests are taken, based on the results of which the doctor will determine whether the patient has been cured or whether additional treatment is required.
Prostate massage is necessary so that prostate secretions do not stagnate and microcirculation occurs. This greatly contributes to a quick recovery.
However, massage is prohibited for acute prostatitis, hemorrhoids and rectal fissures.
Massage is usually prescribed as an additional therapy to antibiotic treatment.
Physiotherapy is prescribed to improve the condition of prostate tissue, thereby speeding up the healing process.
Laser therapy and ultraphoresis are used for treatment. The use of mud and enemas with mineral waters rich in hydrogen sulfide is also effective.
Herbal medicine is used as an additional stimulation for the patient’s recovery and is always used in combination with other methods. Pygeum africanum, peponen and other herbal remedies are used for treatment.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be indicated if the urethra is severely narrowed or the presence of abscesses or prostate adenoma is detected.
Important
Diagnosis and treatment must be carried out in a medical facility under the constant supervision of qualified doctors.
By consulting a doctor in time, you can achieve a quick cure. Once treatment is started, long-term remission will be observed. We can talk about complete recovery when all the symptoms of the disease disappear and laboratory tests show good results.
The most popular questions from patients about chronic prostatitis
How to cure chronic prostatitis with folk remedies quickly and effectively?
Treatment can be carried out using folk remedies. In folk medicine, the most popular is the use of infusions of chamomile, yarrow, and sage. These microenemas very well relieve inflammation that occurs in the prostate gland.
To prepare such a microenema, take two tablespoons of chamomile and pour 100 grams of the herb. boiling water You can also use horse chestnut peel for treatment, which is filled with alcohol and kept for 10 days in a dark place.
A decoction of the onion also helps. You need to finely chop two large onions and pour boiling water over them in a half-liter jar. Wrap the jar in a terry towel and let it brew for 2 hours. Then, every hour you need to drink 50 grams of the decoction.
How to cure impotence with chronic prostatitis?
Impotence can be cured at home if you follow a set of measures.
It is necessary to choose suitable drugs that will help fill the corpora cavernosa of the penis with blood. But before this, consultation with a urologist is required. Modern drugs to enhance potency - Levitra and Viagra.
You need to adjust your diet and go on a diet. You should not eat fatty foods or foods that reduce testosterone. You need to eat porridge and lean meat, drink juices and green tea.
Also, do not forget about physical activity. Walking and light running in the fresh air are very effective in this regard. You also need to swing your legs. This promotes contraction of the muscles of the anus and perineum.
How long does it take to treat chronic prostatitis and how to get rid of it forever?
Antibiotic therapy lasts 1–3 months, depending on the advanced stage of the disease. If necessary, additional treatment with small doses of antibiotics may be prescribed. Lipophilic antibiotics cope best with this task.
To forget about this problem forever, you need to change your lifestyle, eat right, avoid hypothermia and give your body rest.
Why is chronic prostatitis dangerous?
Chronic prostatitis is characterized by sharp exacerbations of the disease, which are replaced by remissions. When the pain subsides, it becomes easier and the man decides that he can cope with this problem on his own, instead of quickly turning to a urologist. However, delay will not help here, since with each exacerbation the inflammation will increase.
Inflammation can affect nearby organs, leading to cystitis, pyelonephritis and vesiculitis. As a result, a man may develop infertility.
What antibiotics should I take for chronic prostatitis?
A number of penicillins (Amoxilav, Amoxicillin) are often used. Tetracycline antibiotics are often prescribed for mycoplasmas and chlamydia.
Fluoroquinolones are very effective and penetrate well into prostate tissue (Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin). Macrolides accumulate well in the tissues of the prostate gland and quickly remove toxins.
Is it possible to have sex with chronic prostatitis?
If the disease is caused by an infection, then it is better to abstain from sex so as not to infect your partner. Although you can use a condom. It is simply necessary to have sex, because when aroused, blood rushes to the prostate gland, and it begins to contract. Also, during ejaculation, the pelvic muscles contract strongly, which is considered good self-massage.
Prevention of chronic prostatitis in men and its features
Prevention of chronic prostatitis in men involves a healthy lifestyle and daily exercise. You can constantly tense and relax your scrotum from time to time.
Each time you urinate, pause the stream a little, this way the bladder sphincter will be hardened. Such high-quality exercises will allow blood to circulate well through the veins of the prostate, as well as enhance metabolic processes in the body.
Print Email
Thermal procedures (sauna, ice hole)
Properly carried out thermal procedures have a beneficial effect on the prostate, as they activate blood circulation in the tissues and help increase local immunity. However, if relaxing in a bathhouse or sauna is accompanied by drinking alcohol and eating junk food, and the man suffers from chronic prostatitis, the risk of relapse of the disease in this case increases significantly.
When visiting a bathhouse or sauna, it is not recommended to alternate thermal procedures and exposure to low temperatures - diving into cold water or dousing. Sudden changes in temperature cause stress, which causes vasospasm and disruption of the genitourinary system, which can serve as a trigger for the development of prostatitis.
Prostate massage
You can resort to prostate massage after a preliminary examination and as prescribed by a doctor. The fact is that the gland may contain calcifications and other neoplasms that a man is not even aware of. Stimulation of the prostate gland in this case can provoke an exacerbation of the underlying pathology.
Massage manipulations must be entrusted to an experienced massage therapist, otherwise the risk of injury to the gland increases. This procedure is an excellent prevention of chronic prostatitis and frequent relapses.
Prevention of infectious prostatitis: sexual hygiene
One of the most common causes of infectious prostatitis is unprotected sex with a partner who is a carrier of pathogenic microflora. Men who practice anal sex without a condom are at risk. Microorganisms that live in the rectum, after penetration into the urethra, cause acute inflammation, which spreads to neighboring organs, including the prostate gland.
Oral sex can provoke prostatitis. The fact is that in the mouth there are potential sources of pathogenic microorganisms - tonsils, teeth affected by caries, tongue. To avoid infection, it is important to maintain sexual hygiene, and if the partner is not a permanent one, use protective contraception - condoms.
Signs of the disease
If a man discovers at least two of the following symptoms of prostatitis, he should immediately contact a qualified specialist:
- Disorder of urination with the occurrence of an intermittent, weak stream of urine, unusually short, causing splashing, difficulty and pain before urination. Frequent urge to empty the bladder occurs mainly at night.
- Soreness, which is localized in the lower abdomen, radiates to the scrotum, perineum, and rectum.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Problems with ejaculation, changes in sperm (consistency, quantity).
Nutrition
Diet and balanced nutrition play one of the most important roles in preventing the disease. To prevent the development of prostatitis, it is necessary to regularly empty the intestines and prevent constipation. The fact is that solid feces accumulated in the intestines put pressure on the prostate gland, disrupting normal blood circulation and fluid evacuation. Over time, stagnation leads to a decrease in local immunity and tissue inflammation.
To improve stool and bowel function, nutritionists advise diversifying your diet with fresh fruits, vegetables, and cereals. The menu must also include the following products:
- cottage cheese, kefir, sour cream;
- fish, seafood;
- lean meat;
- nuts, pumpkin seeds;
- dried fruits;
- vegetable soups;
- fresh salads with herbs and vegetable oil.
Patients suffering from chronic prostatitis will forever have to give up alcohol, salty, spicy, fatty, fried foods, which can cause exacerbation.
Pharmaceuticals
Medications for the prevention of prostatitis are aimed at normalizing the functioning of the gland. The main active components of such medicines are natural plant extracts, which gently eliminate the inflammatory process, normalize blood circulation, and eliminate congestion.
To prevent prostate inflammation, urologists prescribe the following pharmaceuticals:
- "Prostopin";
- "Vitaprost";
- "Longidaza";
- "Indigal";
- "Uroprost";
- "Hyperprost";
- "Fitoprostan";
- "ProstaNorm";
- "Peponen";
- "Cernilton."
An ideal remedy for the treatment and prevention of prostatitis!
For the treatment and prevention of prostatitis, urologists prescribe the drug “Prostamol Uno”, the main advantages of which are:
- anesthesia;
- normalization of urination;
- destruction of bacterial infection;
- antiandrogenic and antiexudative effects.
The drug has a positive therapeutic effect even in advanced cases. To stop the inflammatory process and pathological symptoms, one capsule per day is enough. The medicine has virtually no contraindications or side effects, so urologists readily prescribe it both for the treatment and prevention of inflammation of the prostate gland.
Preventive examinations
It is advisable for all men to undergo a preventive urological examination once a year. This is especially true for representatives of the stronger sex over 40 years of age. The fact is that in adulthood, the number of risk factors for the development of inflammation increases markedly: hormonal levels change, various chronic pathologies accumulate, and physical activity decreases. To identify diseases at the initial stage, it is advisable to visit a urologist at least once a year, undergo a preventive ultrasound, and undergo basic tests.
When to think about prostate health
With age, the amount of testosterone in the male body naturally decreases. This affects the activity of sexual life and increases the risk of stagnation. Upon reaching the 40th birthday, doctors recommend regular preventive examinations and monitoring the condition of the gland. According to statistics, by the age of 80, almost 90% of men suffer from some kind of disorder in this organ. At the same time, doctors urge young people to monitor their health. A sedentary lifestyle, infectious lesions, and chronic diseases contribute to the earlier development of pathology.