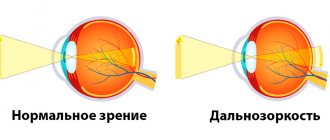
Farsightedness - a violation of the refractive power of the eye, in which the image of an object appears behind the retina. Normally, the light stream perceived by the eye should fall directly on the retina, which allows you to see well both near and far.
Another name for farsightedness, hypermetropia , is made up of three Greek words: hyper - upper, metron - measure and ops - eye. This name was given to the disease by the “father of ophthalmology”, the Dutch doctor Franz Donders. In the second half of the 19th century, he created a series of canonical works on eye diseases. In his 1864 book, Donders wrote that hypermetropia may have a shortened anteroposterior ocular axis or weak refractive power of the cornea. To correct farsightedness, Donders suggested using lenses.
1
Farsightedness (hypermyotropia)
2 Farsightedness (hypermyotropia)
3 Farsightedness (hypermyotropia)
What is farsightedness and why does it occur?
Farsightedness (in medicine - hyperopia) is a visual impairment in which a person has difficulty focusing on objects both far and near.
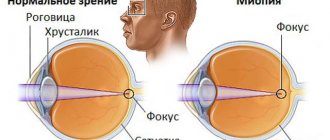
This is caused primarily by the incorrect - short - length of the eye, due to which light rays that are reflected from objects and pass through the optical system of the eyes are focused not on the retina, as it should be normally, but behind it. Another reason is insufficient refractive power of the cornea and lens. As a result, a person does not always clearly see the image far and near.
There is also age-related farsightedness, also known as presbyopia. The mechanism of age-related farsightedness is slightly different: due to the loss of elasticity of the lens, accommodation is impaired, that is, the ability to focus at any distance, especially near.
Farsightedness requires monitoring by a specialist.
Types of farsightedness
Congenital hypermetropia
manifests itself quite early. Decreased vision can be caused by both fetal developmental pathologies and hereditary factors. Important: in infants, due to the natural characteristics of the body, farsightedness is a sign of the norm. As the eye grows older, it acquires the correct shape and reaches normal length, and the disease goes away without medical intervention. This usually happens by 3-4 years.
Congenital farsightedness manifests itself quite early
Infant farsightedness is also called physiological farsightedness and is not considered a visual impairment. We can talk about the presence of farsightedness only if the problem does not go away as we grow older.
Parents should carefully monitor their children's vision, as the child often does not realize that there is a problem and cannot talk about it. Unnoticed farsightedness can lead to the development of strabismus, since in an attempt to focus on objects nearby, the child often squints his eyes towards his nose. Find out more about childhood farsightedness and how to identify it in our special material.
Age-related farsightedness (presbyopia)
in rare cases, it appears before the age of 40. On average, the first signs of the disorder are detected at the age of 45 years. At the initial stage, presbyopia affects only close distances, but as the disease progresses, it becomes difficult for a person to focus at medium distances.
Unfortunately, the causes of presbyopia cannot be treated. However, age-related farsightedness can be corrected with the help of optical products - glasses or lenses. Surgery is also possible to improve visual acuity.
Degree of farsightedness
Like other eye pathologies, farsightedness has three degrees:
- Weak degree – up to +2 diopters. At this degree, a person is able to examine nearby objects without moving them away, but this is accompanied by severe tension in the eye muscles and can cause headaches;
- Average degree – reaches +5 diopters. In this case, a person cannot focus on objects near and, most often, far away;
- High degree – from +5 diopters and above. A person perceives the image blurry at close and medium, and sometimes long distances.
Types of violation
There are three types of farsightedness:
- Hidden - develops with a weak degree of hypermetropia. This type is asymptomatic for a long time. A patient with latent farsightedness does not realize the presence of a problem for a long time, since the disorder is compensated by increased tension of the accommodative apparatus, namely the ciliary muscle. Symptoms include increased eye fatigue, headache, and visual discomfort when focusing on objects nearby. With such stress, the ability of accommodation deteriorates, which leads to the transition of the latent type of farsightedness to obvious;
- Explicit - prolonged tension of the ciliary body leads to the fact that it becomes difficult for a person to focus on objects nearby;
- True (complete) - in addition to accommodative disorders, refractive ones also occur, that is, it becomes difficult for a person to see objects near and far.
Norm and pathology for hypermetropia
Hypermetropia is normally present in young children (1-3 years old), does not cause concern and does not require treatment. During the period of development between infancy and school age (up to 6-7 years), active growth occurs, the child’s body weight increases, and internal organs and systems develop. Particularly active development occurs in the visual system - an exact ratio of the functionality of different parts of the eyeball is developed.
In children by the age of four, this defect in visual perception disappears. Experts believe that it is possible to detect the disease and distinguish it from the norm from the first months of life. If farsightedness is detected in children above the age-normal value, treatment is required.
It is very important to begin therapy immediately after diagnosis, as school-age children are subject to increased eye strain. In the future, in the absence of eye correction, the symptoms of hypermetropia intensify.
Symptoms of farsightedness
The main symptom of presbyopia is the inability to clearly see objects located at close range. If you have to move your hand farther away to read or use your cell phone, this may indicate farsightedness. With hypermetropia, there is also a problem with “distant” vision. In addition, hypermetropia and presbyopia are often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Reduced image contrast (typical of age-related farsightedness);
- Headache and increased fatigue during prolonged work at close distances, for example, when reading or writing;
- Painful sensations in the eyes, often manifesting themselves as a burning sensation;
- Increased intraocular pressure;
- A feeling of “blurry” of the image up close, regardless of the time of day and the degree of eye fatigue.
How does a farsighted person see?
Features of hypermetropia
In childhood farsightedness, a disorder of the visual analyzer is characterized by focusing of the image not on the visual part of the retina, but beyond it. Symptoms are manifested by the inability to distinguish between objects that are nearby, but which the child can clearly distinguish at a far distance. Thus, children with this defect cannot concentrate on a toy that is located next to them.
Clarity of vision and visibility of objects far and near are ensured by the accommodation apparatus. Focusing the image on the retina occurs due to a change in the curvature of the lens, for which the ciliary muscle (ciliary) is responsible. In order to clearly see objects at close range, the ciliary muscle tenses, and the lens becomes more convex and the refraction of light occurs more strongly. For distance vision, the lens becomes flat due to relaxation of the ciliary muscle. Thus, in order to view objects well at different distances, the curvature of the lens is constantly changing. The refractive index of the lens is measured in diopters.
In children from birth, the eye is characterized by hypermetropia, which gradually decreases with eye growth and disappears completely by the age of 7 years. This condition in infants is considered normal and is characterized by an incompletely formed visual analyzer.
Diagnosis of farsightedness
Even obvious symptoms do not always allow a person to correctly assess the state of his vision. To make a final diagnosis, you need to consult an ophthalmologist who will conduct a series of tests, including checking with an autorefractometer. This method allows you to automatically identify existing visual impairments, including hidden ones, which have developed against the background of underlying abnormalities.
Sign up for a free vision test
The doctor will conduct a full examination, based on the results of which you will be diagnosed and treated.
Prices for diagnostic services and consultation with an ophthalmologist
| Type of medical service | Service price in rubles |
| Complete ophthalmological examination | 1000 |
| Complete ophthalmological examination of children | 1100 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye disease in an adult | 500 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye diseases in children over 3 years of age | 700 |
| Selection of simple glasses with a prescription | 500 |
| Selection of glasses for astigmatism with a prescription | 700 |
| Selection of progressive, office glasses with prescription | 700 |
| Selection of contact lenses with training and prescription | 1000 |
| Training in the use of contact lenses | 400 |
Treatment methods
Complete ophthalmological examination
Has your visual acuity decreased or are you experiencing increased eye fatigue? Do you suffer from watery or dry eyes? Do you have chronic eye diseases? Our clinic specialists will conduct a full examination and identify the presence/absence of eye pathologies.
Hardware treatment of eyes in children
Treatment with ophthalmological devices makes it possible to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect in young patients. In some cases, it is possible to completely get rid of pathologies such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision, and false myopia.
Presbyopia or vision after 40
Presbyopia occurs after 40 years of age and is characterized by decreased vision at close distances. In order not to aggravate the situation, you should follow your doctor’s recommendations and use modern vision correction devices.
Selection of glasses
The selection of glasses is a necessary measure that will ensure the owner is able to see clearly. Experienced doctors select spectacle lenses taking into account many measured parameters and taking into account the slightest deviation from the norm.
Varilux progressive lenses
Varilux lenses are an excellent tool for correcting age-related changes that occur in the organs of vision after 40 years. They provide excellent, clear images regardless of the distance to the subject in question.
This is interesting
Blue light and optical coatings that reduce its transmission
What diseases can be diagnosed based on the condition of the eyes?
Preserving vision and eye health with Crizal Eyezen lenses
Protect your eyes from the sun with UV filter contact lenses
Which spectacle lenses should I choose? Choose your glasses with Crizal Corner
Treatment of farsightedness
The final treatment method is determined based on the causes of hypermetropia and the degree of impairment. There are conservative and surgical treatment options.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment as such is not aimed at eliminating farsightedness, but at alleviating the patient’s condition and eliminating asthenopic symptoms.
First of all, this includes effective vision correction. The patient is prescribed “plus” glasses or contact lenses. Depending on the degree of impairment, glasses/lenses may be prescribed for constant wear or for close-range work only.
If we are talking about moderate hyperopia or presbyopia, office or progressive lenses that have several optical zones, for example, near and far zones, can be prescribed for correction.
Hardware treatment
has proven itself in the fight against this violation. People with farsightedness may be prescribed electrical stimulation, physiotherapy, and ultrasound methods. Vitamin courses are often used to improve visual tone.
For farsightedness, a course of hardware treatment may be prescribed
These methods are unable to completely cure the disorder, but they can slow down or even stop the further development of the disease and alleviate the condition of a person with farsightedness, providing him with comfortable visual conditions.
Surgical methods for treating farsightedness
Laser correction is a common method; the procedure is fairly quick and is considered minimally invasive. The operation is performed using local anesthesia, and the patient is sent home the same day. However, this method has a number of limitations, for example, laser correction is not performed if the patient has a significant impairment of accommodation.
In severe cases, refractive lens replacement is possible. Phakic lens implantation is also used.
Causes
The causes depend on many factors, including age. For example, in older people, the elasticity of the lens weakens, which causes farsightedness to appear as a normal phenomenon. In children after birth, the manifestation of this disease is also not considered a pathology, as long as the indicators do not go beyond the normal range.
In addition to the normal physiological development of hypermetropia, it can occur due to:
- Flat shaped cornea.
- Shortened eyeball.
- Decreased accommodative capabilities of the lens.
The disease does not appear out of thin air. The causes of such pathologies are:
- Hereditary factors. If parents are diagnosed with farsightedness, then in more than half of the cases, this disease will be passed on to the child.
- Presence of pathologies. Some of the most common causes are secondary diseases: diabetes, cancer, astigmatism and others.
- Congenital form. Bad habits of the mother, poor nutrition and stress can affect the development of hypermetropia in the child even at the stage of fetal formation.
In other cases, farsightedness is an age-related phenomenon. At a young age, it is enough to do gymnastics and devote more time to physical development. This will help form a stronger eye system and get rid of mild hypermetropia.
Laser vision correction
For moderate or severe farsightedness, laser surgery can be done to eliminate the need for glasses and contact lenses. During the procedure, the doctor needs to change the shape of the cornea. The result is refractive changes in the visual system - the image is focused not in front of the retina, but on it, as is necessary. This operation can correct vision up to +6 diopters. Before the procedure, the patient must undergo a series of general tests and undergo a comprehensive examination of the visual system. If there are no restrictions, you can begin correction, which lasts no more than 30 minutes under local anesthesia. In this case, the person does not experience pain or other uncomfortable sensations. The accuracy of modern equipment allows you to avoid errors, and you can go home within a couple of hours.
There are several most popular methods of performing surgery to eliminate farsightedness with a laser, for example, Lasik, Epithelial Lasik, SuperLasik. The method is selected by a specialist based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Prevention
The principles of preventing further progression of farsightedness are as simple as they are effective. They do not require any special investment of time or financial expenses, but, at the same time, they really “work” to preserve vision. We are talking, first of all, about maintaining visual hygiene (lighting, distance, work-rest cycle), performing basic eye exercises and regular visits to an ophthalmologist, who will inform you in the most detailed manner about what measures are a priority in your particular case.