Doctor:
Pristalenko Olga Valentinovna
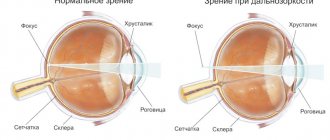
Farsightedness , or scientifically hypermetropia , is a defect in visual perception during which the visibility of objects located both near and far is reduced. Farsightedness is present in all newborn children, which is due to the physiological characteristics of the optical system of the eyes and is a normal variant.
But in some cases, the pathology persists in the future; additional symptoms arise in the form of burning and rapid eye fatigue, headaches, decreased vision, and strabismus.
Hypermetropia is a rather dangerous disease, because only very attentive parents can notice hidden symptoms, and only an ophthalmologist can make a final diagnosis. Timely treatment in children allows you to get rid of the pathology forever.
Norm and pathology for hypermetropia
Hypermetropia is normally present in young children (1-3 years old), does not cause concern and does not require treatment. During the period of development between infancy and school age (up to 6-7 years), active growth occurs, the child’s body weight increases, and internal organs and systems develop. Particularly active development occurs in the visual system - an exact ratio of the functionality of different parts of the eyeball is developed.
In children by the age of four, this defect in visual perception disappears. Experts believe that it is possible to detect the disease and distinguish it from the norm from the first months of life. If farsightedness is detected in children above the age-normal value, treatment is required.
It is very important to begin therapy immediately after diagnosis, as school-age children are subject to increased eye strain. In the future, in the absence of eye correction, the symptoms of hypermetropia intensify.
What causes farsightedness?
There are many reasons for the development of such health problems in children. The appearance of eye diseases can be influenced by various factors that affect the baby’s body during the period of intrauterine development. Lack of nutrients in the mother, unfavorable environmental and psychological conditions, hereditary predisposition - all this can play a key role.
If one or both parents have astigmatism or other visual impairments, a similar problem may arise in the child.
It is impossible to identify farsightedness in children independently at home. If you notice indirect signs of a disorder or your baby may have a genetic predisposition to eye diseases, you should make an appointment with a doctor. Only an ophthalmologist can diagnose the exact presence or absence of pathology. To make a diagnosis, they resort to dilating the pupil with the help of special medications. This leads to relaxation of the accommodative muscle, which makes it possible to determine the refractive characteristics of the eye.
The reserve of farsightedness, like the size of the eyeball, must correspond to the age norm. Otherwise, in the absence of timely treatment for farsightedness, complications may arise in older children and vision deterioration may progress.
An unfavorable sign is impaired growth of the eyeball. If it grows too quickly, you are more likely to develop myopia. If slow growth of the eyeball is diagnosed, pathological hypermetropia develops. If, during the first three years of a child’s life, abnormalities have been identified, prescribing competent treatment for farsightedness in children gives a high chance of completely eliminating the problem. With age, such patients may return to completely normal vision.
Features of hypermetropia
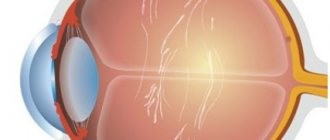
In childhood farsightedness, a disorder of the visual analyzer is characterized by focusing of the image not on the visual part of the retina, but beyond it. Symptoms are manifested by the inability to distinguish between objects that are nearby, but which the child can clearly distinguish at a far distance. Thus, children with this defect cannot concentrate on a toy that is located next to them.
Clarity of vision and visibility of objects far and near are ensured by the accommodation apparatus. Focusing the image on the retina occurs due to a change in the curvature of the lens, for which the ciliary muscle (ciliary) is responsible. In order to clearly see objects at close range, the ciliary muscle tenses, and the lens becomes more convex and the refraction of light occurs more strongly. For distance vision, the lens becomes flat due to relaxation of the ciliary muscle. Thus, in order to view objects well at different distances, the curvature of the lens is constantly changing. The refractive index of the lens is measured in diopters.
In children from birth, the eye is characterized by hypermetropia, which gradually decreases with eye growth and disappears completely by the age of 7 years. This condition in infants is considered normal and is characterized by an incompletely formed visual analyzer.
Treatment of farsightedness
Confirmation of the diagnosis of hypermetropia requires timely correction of this visual impairment.
- There is no drug therapy.
- Correction with contact lenses and glasses. The choice between contact lenses and glasses is up to the patient and depends on his personal preferences. The strength of the lenses is selected strictly individually. In some cases, it is possible to use nighttime orthokeratology lenses for a reversible correction effect during the day.
- Laser correction. A modern procedure that effectively restores vision by changing the shape of the cornea. Compared to a similar method for myopia, high efficiency applies only to hypermetropia up to +4.0 diopters. In all cases, before recommending surgery, it is necessary to conduct a specialized examination.
- In cases where laser correction is not indicated or is ineffective in the prognosis, surgical intervention inside the eye is recommended - implantation of an intraocular lens while preserving its own lens (phakic lens implantation) or implantation of a lens to replace the removed lens of the eye (phacoemulsification with implantation). The latter operation is performed when phakic implantation is contraindicated and/or in “aged” patients.
Classification of farsightedness
Severity of hypermetropia in children:
- The weak stage of farsightedness is characterized by indicators up to 2 diopters inclusive - children have no symptoms due to compensation for the accommodative abilities of the visual organ. The first stage of the disease is detected during preventive examinations and can be easily corrected with the help of special eye exercises.
- Average degree of pathology (from 2.25 to 5 diopters) - the child sees poorly near, but can clearly distinguish distant objects.
- High degree of impairment (5.25 diopters and above) – vision is significantly reduced, both near and far.
Preventive measures for farsightedness
It is important for parents to understand that farsightedness is a serious pathology that requires professional correction and treatment. If a child is born with a severe degree of this disease, it is necessary to ensure that he is monitored by an experienced specialist.
Preventive measures for hypermetropia consist of following simple rules:
- Regular scheduled examinations with a doctor;
- Active lifestyle, daily walks in the fresh air;
- Proper nutrition providing the body with all the necessary vitamins and microelements;
- Control over the time the child spends at the computer, near the TV or playing games on mobile gadgets;
- Proper organization of the workplace;
- Ensuring high-quality lighting while doing homework;
- Performing gymnastics for the eyes.
Etiological factors in the development of childhood farsightedness
The reasons for the development of farsightedness in childhood are:
- genetic factors; malformations of the visual system, incorrect formation of eye structures;
- disturbance of intrauterine growth of the fetus;
- traumatic eye damage from chemical compounds or physical factors;
- conditions after infectious processes;
- operations on the visual organ;
- increased stress, eye fatigue;
- incorrectly selected glasses or contact lenses.
Causes
Hyperopia in young children is a natural condition. At this age, the reasons may be physiological:
- short length of the anterior-posterior axis of the eye;
- weak refractive power of the cornea and lens.
But if the parents were diagnosed with farsightedness at one time, then we can assume that the child inherited this disease. You can also identify factors for the congenital development of farsightedness:
- improper nutrition of a woman during pregnancy and lactation;
- unfavorable environment;
- frequent stressful conditions, depression.
If parents observe symptoms of farsightedness in a 3-4 year old child, which can no longer be attributed to age-related physiological characteristics of vision, it is imperative to undergo a full diagnosis by an ophthalmologist and begin timely treatment.
Clinical picture of hypermetropia
With a weak degree of farsightedness, there are no symptoms of impaired visual function. Therefore, during this period, it is important for parents to monitor the child’s changed behavior. Signs of hypermetropia in the early stages of the disease appear:
- rapid blinking;
- moodiness and irritability;
- constant headaches, dizziness;
- inability to concentrate on toys and any other objects located close or in the hands;
- increased eye fatigue for no apparent reason;
- sleep disturbance;
- inflammation of the eyeball, hyperemia, dryness;
- increased lacrimation.
The middle stage of the disease is more often diagnosed in children during preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist at school age. The picture described above may manifest itself with more vivid symptoms. The main manifestations of moderate farsightedness are poor visibility of objects at close range and their blurriness. The child has difficulty reading and writing. Such patients are mistakenly diagnosed with dysgraphia, dyslexia, or developmental delay. With a high degree of hypermetropia, the child complains of poor visibility of near objects and distant objects. With hypermetropia, convergent strabismus often develops, and there are disturbances in binocular vision.
Treatment
Correction of farsightedness that exceeds the age norm in children can begin as early as possible. Early correction allows you to create conditions for the subsequent correct formation of the organ of vision and prevent the development of complications such as amblyopia (“lazy eye”) and strabismus. Correction of hypermetropia is performed using several methods; the choice depends on the degree of hypermetropia and the presence of complications.
- Wearing glasses - children's glasses are made with flexible frames and unbreakable lenses, which ensures convenience and safety.
- If amblyopia occurs, treatment is prescribed - wearing occluders - special device shields that cover the better-seeing eye, and eye training courses to make the “lazy” eye work better.
- If strabismus occurs, training courses and surgical treatment are prescribed according to indications.
- Wearing contact lenses is possible from the age of 6-7, during this period you can already teach your child how to care for them.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures - from any age to stimulate the functioning of the organ of vision.
- Laser correction is used exclusively from the age of 18. In some cases, drug therapy is prescribed.
Diagnostic measures
Get a complete vision examination at the Lege Artis Eye Clinic
It's time to correct your vision!
Make an appointment by phone:
8(804) 333-02-14 Free call
Diagnosis of hypermetropia in children is carried out by an ophthalmologist. Visual acuity testing is carried out using different methods, depending on the age of the child. Also, before the study begins, drops are instilled into the eye to dilate the pupil. This leads to relaxation of the ciliary muscle and allows you to correctly measure the light refractive ability of the eye. For timely detection of farsightedness, it is recommended to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist at least once a year.
Diagnosis consists of collecting an anamnesis, parents provide complete information about the child’s behavior and present complaints: a child with problems with visual perception quickly gets tired, becomes withdrawn, has a predominant bad mood, school-age children are characterized by slow reading, but bright pictures at a distance (billboards, posters) they look at with great interest.
To identify farsightedness, different diagnostic methods are used:
- visometry - tables with pictures are used for children, tables with letters are used for middle school children;
- determination of violations of the refractive power of the eye is carried out using autorefractometry, necessarily in conditions of cycloplegia: drug dilation of the pupil and switching off accommodation;
- skiascopy and retinoscopy.
Treatment of farsightedness in preschool and older children
If the diagnosis was detected in a child under one year of age, no special therapy is prescribed, only the dynamics of changes are monitored. The treatment of childhood farsightedness under the age of three should be approached very carefully. To improve vision, special gymnastics and sufficient intake of vitamin A are recommended. Physical exercise and physical activity are good for the eyes, as they increase metabolism in the tissues of the eyeball.
If, upon reaching three to four years of age, hypermetropia has not been compensated by the body’s reserves, the question of optical correction of the pathology is raised. An ophthalmologist selects glasses, and at high school age you can start using lenses.
Conservative therapy also includes hardware treatment, which provides training of the eye muscles and improves the optical abilities of the eyes. The most well-known techniques are color pulse stimulation, magnetic therapy, and electrical stimulation.
Treatment methods for hypermetropia in children
Farsightedness is treated conservatively in children under 18 years of age. If there is no positive effect after adulthood, microsurgery or laser vision correction is used.
Starting from a very early age - from several months of life - optical means for vision correction - glasses or contact lenses - are used. Spectacle correction is the most common due to its availability and low cost. Pleoptic hardware treatment is used to develop visual acuity. You can get high positive results and remove glasses in the future only if you choose the right lenses. To do this, a diagnosis is carried out, after which the doctor writes a prescription for the necessary glasses. Parents can choose the frame themselves; it is advisable to give preference to materials such as carbon or plastic. These frames are durable, reliable and light, and do not cause discomfort. To ensure that your child wears glasses without whims, it is better to choose frames in the child’s favorite color scheme.
Some parents and their doctor select contact lenses to correct farsightedness, as they have their advantages - first of all, the lenses do not slip or get dirty, and do not interfere with the child’s participation in active sports.
Where can hypermetropia be diagnosed and treated?
If you want to be sure that your baby will be in good hands and will receive all the necessary treatment, contact the Sfera clinic. We employ leading domestic specialists, who have everything necessary for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of farsightedness.
We pay special attention to diagnostics: for this we conduct comprehensive studies that allow us to accurately determine the pathology, its form, degree and characteristics. A treatment plan is drawn up on an individual basis, in accordance with the diagnostic results and the testimony of the little patient.
By contacting us in a timely manner, you can avoid the development of complications in your child and, together with our specialists, you will help him go through the complex process of physical development in the most gentle manner possible.
You can make an appointment with us by filling out the form on the website or by calling.
Degrees of hypermetropia and complications
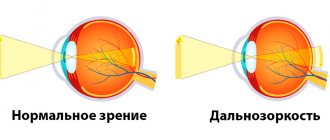
And those that are located in the distance, on the contrary, are clearly visible: this is explained by the fall of the image not on the retina, but behind it. Hypermetropia is a very common pathology - about 40% of the adult population and 90% of children under 3 years of age have it to one degree or another. But in the case of children, farsightedness is physiological in nature and does not require treatment.
According to the degree of visual impairment, hypermetropia is divided into weak, moderate and high.
Weak (up to +2 diopters)
Although the change in vision in this degree of farsightedness is small, it is considered very dangerous because its symptoms are usually ignored. Children and young people are most susceptible to such farsightedness, who often experience headaches due to visual strain and feel a burning sensation in their eyes. Near vision itself decreases insignificantly, so people rarely turn to an ophthalmologist.
However, mild hypermetropia can also occur after 40 years of age - people note that it becomes more difficult for them to find the right button on the computer, insert a thread into a needle, etc. Unfortunately, this process cannot be stopped; you can only slow down the development of other degrees of farsightedness by wearing glasses, doing special exercises, etc. At this age, symptoms of the problem also include lacrimation and blurred vision.
If a weak degree of hypermetropia is left unattended, this is fraught with the development of a number of complications - young people and children may experience inflammatory eye diseases (blepharitis or chalazion, etc.) or develop descending strabismus or strabismus. In older people, inflammatory processes can become chronic, and headaches and dizziness can also become constant. However, this degree of farsightedness does not require surgical treatment - wearing glasses, special vitamin preparations and a number of physiotherapeutic procedures is sufficient.
Medium (up to +5 diopters)
The second stage of development of hypermetropia, which occurs if the first degree is left without treatment or diagnosis. The causes of farsightedness in this case may be associated with age-related changes in the lens of the eyes or with the manifestation of congenital abnormalities of eye development that were not previously detected. At this degree of vision change, all objects located at a distance closer than an outstretched hand are seen dimly. At the same time, the eyes get tired quite quickly from reading and habitual work at the computer.
An average degree of farsightedness is fraught with serious complications: problems with the outflow of intraocular fluid (which can result in glaucoma), inflammatory eye diseases and additional development of myopia, which will significantly worsen the quality of life. If such a degree is detected in a child, it can lead to strabismus and the so-called lazy eye syndrome or amblyopia. Therefore, treatment is necessary.
The most effective method of treating moderate hypermetropia is considered to be laser correction, but this option is used only when conservative methods have not helped. Glasses, contacts and special eye exercises are required in such a situation.
High (after +5 diopters)
At this stage, the symptoms of hypermetropia are already pronounced - the clarity of vision disappears in principle, regardless of whether objects are located close or far away. Even if you bring them directly to the eye, the picture remains blurry. This is explained by the fact that the size of the image on the retina changes, and the ciliary muscle is in continuous hypertonicity. This almost non-stop tension causes headaches and dry eyes. And over time, the eye begins to change in appearance - the pupil narrows, etc.
A high degree of farsightedness can only be treated with laser correction, although this does not save a person from glasses. However, it is worth considering that the operation is not performed until the age of 20, so it is so important to catch the problem at its initial stage, because the third, most serious stage of hypermetropia occurs in stages, due to the constantly deteriorating condition of the eyes due to vision problems that have already begun. You should not refuse treatment for farsightedness, because it will definitely lead to glaucoma.
Diagnosis of hypermetropia begins with visometry (table with symbols), after which methods of perimetry, tonometry, fundus ophthalmoscopy, etc. are used. Timely diagnosis will allow maintaining visual acuity and quality of life without sudden deterioration. The same applies to preventive measures against farsightedness.
How does farsightedness occur?
Our eye has two light-refracting media - the lens and the cornea.
Rays of light passing through the visual path are refracted and hit the retina. There they are focused, transformed and transmitted through neurons to the brain in the form of signals. But with a short beam movement, weak accommodation of the lens or insufficient convexity of the cornea on the retina, an unclear image is obtained, and we get a blurry picture. Therefore, a person with farsightedness does not see small letters well when reading and is forced (to improve focus) to move the book as far as possible.
The main symptoms of hypermetropia:
- a person suffering from farsightedness usually sees well into the distance, but nearby objects blur before his eyes;
- at a young age, with slight farsightedness, there may be no problems with vision, but with prolonged tension of the accommodative muscle, a person experiences fatigue and headaches;
- there are frequent sensations of burning and stinging in the eyes;
- night vision deteriorates.
The prevalence of farsightedness among adults is 35-45%. In old age, the disease manifests itself in eight out of ten people.
If, when writing, reading or working with a computer, your letters become blurred, discomfort appears in your eyes and your head begins to hurt, you need to visit an ophthalmologist! Most likely, you have farsightedness. Left untreated for farsightedness can lead to complications such as strabismus, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma and even blindness.
Symptoms of farsightedness in children
The symptoms of farsightedness in a child will depend on its severity. For example, if it is weak, the eyes will quickly get tired, dizziness will appear, and headaches are possible. In moderate cases, the condition of a small child is hysterical, he sleeps poorly, and various inflammations of the visual organs, such as blepharitis and conjunctivitis, may bother him. Visual acuity at close range is low, but distant objects are clearly visible to him.
Severe farsightedness is characterized by poor vision of objects not only near, but also at long distances.
Since children from 1 to 6 years of age with hypermetropia cannot concentrate their vision on one object for a long time, and, accordingly, perform the same work for a long time, they become irritable and sometimes withdrawn. They are often tormented by a burning sensation and the sensation of a foreign object in the visual system. Inflammatory processes of the eyes with farsightedness in a small child 1-6 years old are very often associated with the fact that he rubs them due to fatigue, which increases the risk of infection.
Causes of farsightedness
Ophthalmologists identify the following causes of farsightedness:
- infancy - almost all newborns are born farsighted, but already in a three-month-old baby, vision returns to normal;
- weakening of the force of accommodation, up to the full ability of the lens to change curvature;
- “small eye” - a reduced eyeball along the posterior or anterior axis.
1 Diagnosis and treatment of farsightedness
2 Diagnosis and treatment of farsightedness
3 Diagnosis and treatment of farsightedness