Tongue cancer is a malignant tumor of the tongue, which originates from the cells and mucous membrane of the epithelium. This disease is characterized by diffuse or local compaction of tissue and the formation of ulcers and neoplasms on the surface of this organ. Such tumors of the tongue are characterized by rapid growth and metastasis to the lungs, bones, lymph nodes, liver and brain. Diagnosis of tongue oncology is carried out according to examination, smears, palpation, biopsy material, and radiography. To determine distant metastases, MRI of the brain, ultrasound of the liver, X-ray of the lungs, and scintigraphy of the skeleton are performed. Treatment for tongue cancer consists of a combination approach of chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery.
Causes of tongue cancer
In modern medicine, it is believed that the release of carcinogens during the combustion of tobacco is the main factor that influences the occurrence and development of tongue cancer. When combined with alcohol, carcinogens from tobacco smoke increase the likelihood of developing cancer among alcoholics and smokers.
Also, the development of tongue cancer can be influenced by components that are classified as occupational hazards, such as perchlorethylene, asbestos, heavy metal salts, and petroleum distillation products.
The formation of this tumor can be influenced by mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane. This type of injury can occur from sharp tooth edges, poorly fitting dentures, frequent tongue biting, poorly processed fillings, or a broken tooth.
According to research, a connection has been established between chronic persistent infection and tongue cancer, which is caused by the herpes simplex virus, HIV, or HPV. Patients who receive immunosuppressive drugs for a long time are also predisposed to tongue cancer.
If the carcinogenic factor continues to act on the organ, then changes in the mucosa will lead to oncology. Today, the following factors are classified as precancerous conditions of the tongue:
- papillomas;
- chronic tongue ulcer;
- hyperkeratic forms of lupus erythematosus;
- leukoplakia of the tongue;
- hairy leukoplakia of the tongue;
- Bowen's disease;
- lichen planus;
- systemic lupus erythematosus.
Long-term exposure to these trigger factors leads to changes in the DNA structure of tongue cells with the development of hyperplasia and dysplasia of the tongue mucosa. Most benign tumors of the tongue are susceptible to transformation into malignant tumors due to trauma to the oral cavity.
Causes
- Bad habits. Among which, smoking is of particular importance. The influence of carcinogenic substances in tobacco in the development of cancer has long been proven. The risk increases with duration and intensity of smoking. The risk increases further with alcohol consumption.
- Occupational hazards (contact with radiation, work in the oil industry).
- Constant traumatization of the mucous membrane (poor-quality dentures and damaged teeth, poor treatment of fillings, and constant biting of the tongue are important).
- Chewing mixtures (betel nut, non-smoking tobacco), consuming spices that have a carcinogenic effect.
- Oral infection.
- Pre-tumor conditions ( leukoplakia , Bowen's disease , ulcerative-erosive form of lupus erythematosus , papillomatosis , erythroplakia , leukokeratosis ).
- Action of oncogenic viruses. The connection of this pathology with chronic human papillomavirus infection and HIV . The oncogenic effect of viruses is associated with blocking or the influence of tumor suppressor genes.
- Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs.
Classification of tongue cancer
Tongue cancer, depending on location, is divided into the following types:
- cancer of the lower surface and cancer of the base of the tongue occurs in 10% of cases;
- tongue root cancer occurs in 20% of cases;
- Cancer of the body of the tongue occurs in 70% of cases and is most often localized on the middle of the lateral surface of the body of the tongue.
In modern medicine, there is a macroscopic classification of tongue cancer, which is characterized by an endophytic (infiltrative or infiltrative-ulcerative) and exophytic clinical form (ulcerative or papillary). According to this classification, 95% of tongue cancer is classified as squamous cell cancer of the tongue. Other histological forms, such as basal cell lymphoepithelioma or adenocarcinoma, are very rare.
Today, the clinical picture of tongue cancer is determined depending on the stage of its development. The following degrees of development of tongue cancer are distinguished according to ICD 10:
- For the first degree, it is typical that the size of the tumor under the tongue is about 1 cm and spreads inside the mucous membrane, but does not metastasize;
- The second degree is characterized by an increase in size of neoplasms on the tongue, germination and damage to soft tissues. In this case, the tumor does not extend below the midline of the tongue;
- The third stage of cancer development is characterized by the presence of single regional metastases. The tumor itself does not increase in size;
- The fourth stage of development of tongue cancer according to ICD 10 is characterized by the presence of an ulcer or tumor that spreads beyond the midline of the tongue and affects the bottom of the tongue cavity, resulting in the development of cancer under the tongue;
- At the fifth stage of development of tongue cancer according to the ICD, a large number of mobile regional metastases appear, the tumor spreads further throughout the body of the tongue;
- At the sixth stage of development of tongue cancer, the tumor affects almost the entire part of the tongue or covers the entire organ completely. There is distant metastasis, damage to the bones of the facial skeleton occurs.
General information
A malignant neoplasm in the tongue comes from the mucosal epithelium.
Despite the fact that tongue tumors are uncommon, they have an aggressive course, so early detection is important. Distinctive features of this disease are early metastasis (including distant), rapid growth, resistance to treatment, high recurrence rate and mortality. At the time of diagnosis, half of the patients had affected regional lymph nodes. Recurrence is observed in 30-50% of patients. If we consider the localization, then most often a tumor of the tongue occurs on the lateral surface, much less often there is cancer of the root of the tongue, the back and the tip. A neoplasm of the root of the tongue is classified as oropharyngeal cancer. The asymptomatic course of the disease makes early diagnosis difficult. Tumors are either not visible in the early stages or initial changes are regarded as a consequence of trauma to the tongue. Due to the lack of alertness of patients and doctors regarding malignant neoplasms, most cases are diagnosed with a full clinical picture or already in an advanced stage.
The highest incidence is observed after 50 years of age, but this disease also occurs in people under 30 years of age. In men, this pathology is diagnosed 5 times more often. In 95% of cases, tongue tumors are squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue is an aggressive tumor and insensitive to treatment ( chemotherapy ), but radiation treatment .
Symptoms at different stages
At an early stage, tongue cancer, like other malignant tumors, is treatable. The difficulty in identifying the disease at an early stage is that the signs and symptoms of tongue cancer at an early stage do not bother the patient and therefore go unnoticed. The main signs of tongue cancer are:
- Unpleasant smell. If you have healthy, unproblematic teeth and despite proper care, an unpleasant odor appears in the mouth at the initial stage of tongue cancer, which is one of the first warning signs of the presence of malignant tumors.
- Discomfort. With the onset of tumor development, discomfort begins in the affected area. A person may experience tingling, burning, or numbness in the tongue area.
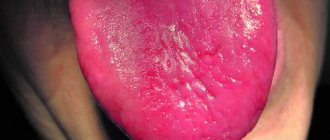
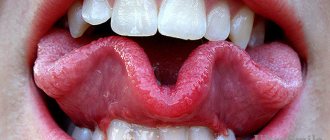
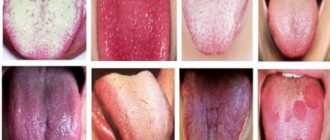
- Visual changes. At the initial stage of tongue cancer, symptoms include small neoplasms in the form of ulcers, papillomas, erosions and spots. When you press on them, you may feel a tightness.
- Migrating pain. At the initial stage of the disease, a person feels pain inconsistently, the pain can migrate and radiate to nearby locations, gums or cheeks.
In the later stages of the disease, the symptoms of tongue cancer are as follows:
- Increased salivation;
- Trouble swallowing;
- Bleeding of the tongue;
- The appearance of speech defects;
- Difficulty speaking;
- Loss of appetite;
- Severe pain;
- Loss of body weight;
- Significant increase in the volume of the tongue;
- Feeling chronically tired
- Enlargement of the postauricular and submandibular nodes.
For the third stage of development of tongue root cancer, the symptoms are as follows:
- There is a disturbance in the digestive system of the body, loss of sensitivity, immobility of the tongue, and difficulty in eating;
- I am worried about severe pain, it is localized in the frontal sinus and temporal area;
- Malignant tumors disintegrate, which causes an even greater increase in saliva production and a strong unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
In advanced situations, such as stage 4 tongue cancer, a very aggressive course of the disease occurs, rapid invasive tumor growth, metastases from tongue cancer spread to the lymph nodes, which are located nearby and gradually reach the bones, liver, brain and lungs.
Since there is difficulty in diagnosing tongue cancer at the initial stage, when the disease is detected in an advanced stage, patients wonder how long they can live at stage 4 of tongue cancer. Modern medicine gives a disappointing prognosis for patients with stage 4 tongue cancer and the chance of recovery is about 30%. Few people know what tongue cancer looks like, so at the first sign of discomfort you should seek advice from specialists.
Varieties
There are two main classifications of tongue tumors: according to the form of the disease and according to histological structure. Let's look at them.
The forms of tongue cancer are as follows:
- Ulcerative . With this form, an ulcerated, bleeding tumor is found on the tongue.
- Papillary . A dense growth forms on the tongue on the so-called “pedicle” or on a wide base.
- Infiltrative . The tumor is located deep within the organ.
Classification according to histological structure:
- adenocarcinoma;
- squamous cell carcinoma (the most common - 95% of cases);
- basal cell.
Diagnosis of tongue cancer
According to statistics, the success of treatment for tongue cancer depends on timely and high-quality diagnosis. If there are first symptoms of discomfort in the tongue area, the patient should consult a dentist. During the examination, the doctor examines the oral cavity using mirrors, palpates the affected area and, as a result, determines the medical history. If there is a suspicion of oncology, the dentist will refer you to an oncologist for further diagnosis.
In the process of diagnosing tongue cancer, the following methods are used:
- bacterioscopy. The method consists of examining a smear, which is necessary to identify pathogens that cause a number of diseases in the oral cavity;
- biopsy. The method consists of studying biomaterials that are taken from the affected area to determine the presence of metastases;
- computed tomography or MRI. Using this method, you can determine the presence of metastases in the brain;
- radiography. This method is used to determine whether there are changes in the bone structure.
- ultrasound diagnostics. Using this method, the size of the endophytic tumor is determined.
If there are primary signs of tongue cancer, you should consult a specialist, since diagnosing the disease in the early stages increases the chances of recovery. High-quality diagnostics using modern equipment can be performed at the Yusupov Hospital.
Tests and diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis, patients are prescribed:
- Biopsy of a tumor formation (or scraping and impression smears from the surface of erosions).
- CT and MRI of the affected area with intravenous contrast. This study makes it possible to assess the extent of the tumor and the depth of invasion into the tongue tissue.
- CT scan of the facial bones with contrast if there is a suspicion of tumor spread to the bones of the jaw and skull.
- Ultrasound of the lymph nodes of the neck.
- Puncture of the affected cervical nodes with cytological examination.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity to exclude distant metastatic process.
- Chest X-ray to exclude metastases.
- Osteoscintigraphy for metastatic lesions of skeletal bones.
Treatment of tongue cancer
A combination of methods is used to treat tongue cancer. The tongue is an important organ in the human body that is involved in speech and swallowing, therefore the choice of treatment method largely depends on the impact that the effect of this method can have on these processes. Also, when choosing a treatment method for tongue cancer, doctors take into account how it may affect the patient’s appearance.
Basic treatment methods for tongue cancer
In modern medicine, the following types of treatment for tongue cancer are distinguished:
- Surgery. Today, surgery is the most common treatment for tongue cancer in the early stages, leading to recovery in 80% of cases. However, there is a category of patients who, for certain reasons, cannot undergo surgery or the operation can negatively affect body functions, such as swallowing and speech. Surgical treatment of tongue cancer involves radical removal of the tumor, which includes complete glossectomy or partial hemiglossectomy of the tongue. If the cancer grows into the bone structures and soft tissues of the floor of the oral cavity, surgical intervention is accompanied by resection of the jaw bone and affected tissues. If necessary, doctors use an orthostomy and apply plastic surgery methods to restore lost structures of the maxillofacial part.
- Radiotherapy. Modern medicine has proven that the results of radiotherapy are similar to those of surgery. Clinical studies have shown that radiotherapy is effective as a single treatment or in combination with surgery, with less severe complications. Recovery is achieved in about 80% of patients.
- Radiotherapy in combination with surgery. This combination is usually prescribed in cases of large tumors. But it can also be used to treat patients with a small area of normal tissue that remains after surgery, as well as if cancer grows into the edge of the removed tissue. Also, for leukoplakia of the tongue, complex treatment is prescribed.
- Palliative radiation and chemotherapy are given to patients who have distant metastases of tongue cancer.
Removal of lymph nodes
When treating tongue root cancer in the early stages, doctors decide to perform surgery or radiotherapy on the lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are not treated, the cancer will spread to the neck through the lymphatic system. Untreated cancer leads to recurrence of the disease. It is very important to determine the presence of a tumor in the lymph nodes of the neck. Currently, this is effectively achieved through surgical removal of the lymph nodes.
For cancerous tumors in the neck, lymph nodes are removed, which is called radical dissection. If cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes, the patient is prescribed radiotherapy to the neck. Otherwise, no further therapy is carried out.
Diagnosis and treatment of various types of tumors are carried out by specialists from the Oncology Center of the Yusupov Hospital. For this purpose, the clinic has modern high-tech equipment, and also employs leading oncologists and chemotherapists with many years of experience.
Treatment options
Today, oncologists practice an integrated approach to the treatment of cancer of the oral cavity, in particular the tongue. Therapeutic tactics, volume of treatment and its duration depend on several factors, including :
- advanced stage of the oncological process;
- presence of metastases;
- degree of severity of pathological symptoms of the disease.
Types of treatment
Surgery
Surgery for tongue cancer is an important part of treatment, which allows you to remove malignant growth and prevent the progression of the pathological process. Currently, surgical correction is organ-preserving in nature. It is carried out using modern equipment, which is distinguished by its accuracy, efficiency and reliability.
Surgeries for tongue cancer do not lead to dysfunction of the organ and are not accompanied by complications such as loss of speech. After surgical correction, the tongue continues to perform its assigned functions. Therefore, patients very quickly return to their usual life.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy
These techniques, as a rule, are used simultaneously, as they perfectly complement each other and reduce the amount of surgical correction. With the help of radiation therapy and chemotherapy, it is possible to significantly suppress tumor growth, prevent the process of metastasis, reduce the size of the pathological formation and increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Research and forecasts
Thanks to the achievements of modern medical science, oncologist surgeons today have the opportunity to treat tongue cancer using high-tech equipment, which makes it possible to implement organ-saving operations in practice and reduce the duration of the recovery period, while simultaneously increasing the patients’ chances of recovery.
In our clinic, experienced specialists work only with proven techniques and offer their patients to take advantage of scientific advances that allow a sick person to return to a healthy life without cancer and its consequences.
The main criterion in assessing the chances of survival from tongue cancer is the degree of complexity of the pathological process. It has been proven that with effective and comprehensive treatment of initial forms of tongue cancer, patient survival is almost 80%.
Prevention and prognosis
The main goal of prevention against tongue cancer is to give up bad habits such as smoking and alcohol. Chronic injury to the mucous membrane of the tongue should also be avoided, including timely treatment of chipped teeth, high-quality treatment of fillings, and proper installation of dentures.
Be sure to visit your dentist regularly to have your mouth examined and look for any changes. With timely diagnosis, the prognosis for recovery is more expected. With timely treatment, life expectancy, according to research, ranges from 5 to 15 years.
Diagnostics
To accurately diagnose tongue cancer, laboratory and hardware tests are required. However, first of all, the patient should consult an ENT oncologist, who will give the necessary directions. Among the diagnostic methods:
- blood for tumor markers, other laboratory blood tests;
- biopsy of the affected area followed by histological examination;
- revision (revision) of the biopsy;
- MRI of soft tissues of the neck and face using contrast;
- CT scan of the neck and head with contrast;
- PET-CT.
Tongue cancer - treatment in Moscow
In the presence of tongue cancer, timely diagnosis of the disease and treatment started as early as possible are necessary, which will give the patient a chance for a full recovery. High-quality diagnosis and effective treatment of tongue cancer in Moscow at the oncology clinic will provide the patient with the opportunity to live a full life. The clinic has high-tech equipment and a staff of qualified specialists at its disposal. Rehabilitation is available to patients at the oncology clinic.
The price of treatment for tongue cancer at the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital in Moscow varies from 5 to 20 thousand rubles, depending on the complexity of the disease.
Symptoms
Often a person begins to notice symptoms of tongue cancer when a non-healing ulcer appears in his mouth or, conversely, some kind of lump (growth). If it is an ulcer, it does not heal and may bleed. When it comes to damage to the root of the tongue, there is pain when swallowing, a change in voice, and a feeling that something is blocking the throat.
If some kind of spot (white, red) or bump appears on the mucous membrane of the tongue, you should definitely go to the doctor. A sign may be a feeling of numbness, sometimes painful sensations radiate to the ear. The doctor must be chosen depending on the symptoms. If the symptoms of tongue cancer are localized to the tongue, you can start by visiting a dentist. When you experience a sore throat or a feeling of a lump, you should start a visit to the ENT specialist to rule out ENT diseases. A visit to a therapist is also possible. Any of these specialists, suspecting cancer, will redirect the patient to an oncologist.
Diagnosis of the disease
Often, patients first turn to the dentist. After an initial examination and detection of signs of pathology, they are referred to an oncologist. The examination begins with a visual examination and palpation of the muscle. The next stage is laboratory and computer research:
- Ultrasound - will show the size and shape of the tumor, the degree of damage to the tongue tissue;
- MRI/CT – allows to detect cancer metastases;
- biopsy - a sample of pathological tissue taken for research is tested for malignancy using a histological method.
Classification
Oral cancer is divided into three types:
- papillary. The nodule in the mucous membrane increases in size and hangs into the oral cavity. The neoplasm progresses slowly;
- infiltrative. The seal on the pinkish mucosa is distinguished by a whitish color, clear contours and shape, and thinning of the membrane around it. On palpation from the side of the cheek, a dense infiltrate is felt. The tumor tends to grow rapidly. The patient complains of unbearable pain;
- ulcerative The most common form of the disease. Ulcers on the mucous membrane do not heal, they grow, and the border around them turns red. The outline is torn and its edges are bleeding.
Tumor metastases appear quickly. Malignant cells grow into the mental, submandibular, and deep jugular lymph nodes. This process is influenced by the thickness and depth of the tumor. Thus, when the tumor deepens by 4-5 mm, metastases occur in 98% of cases. At the T1 stage of oncology, metastasis is detected in half of the cases, and when the T4 stage is reached, distant spread of cancer cells is observed in 85% of cases.
Dispensary observation
Since the tumor can recur and metastasize, after completing the course of treatment the patient is registered with the oncology clinic. The first year you should visit a doctor every month, the second year a preventive examination is carried out every 4-6 months, and then once a year or in case of any ailments. The examination involves an examination - ultrasound and contrast MRI of the soft tissues of the neck, PET, osteoscintigraphy. Consultation with an otolaryngologist, dentist and oncologist is required. The doctor may shorten the period of medical examination if there is a high risk of relapse.
List of references on the topic:
- Gantsev Sh.H. Oncology – M, 2012 – P.204-205.
- Golovin D.I. Errors and difficulties in diagnosing tumors, D.: Medicine. Leningr. department, 2015 305 pp.
- Selected lectures on clinical oncology/Ed. IN AND. Chissova, S.L. Daryalova. – M., 2010
- Matyakin E.G., Alferov V.S. Chemotherapy of head and neck tumors // Mat. 2nd Ros. oncol. conf. “Current trends in the development of drug therapy for tumors” December 8–10, 2021 – M., 256 p.
- Tumors of the head and neck: hands/ A.I. Paches. - 5th ed., add. And revised - M.: Practical Medicine, 2013. -478 p.
- Shine A.A. Oncology. M – 2014 365 pp.
- Encyclopedia of Clinical Oncology/Ed. M.I. Davydova. – M., 2014 –P.140-179.
- Bityutsky P.G., Kitsmanyuk Z.D., Trofimov E.I. Diagnosis and treatment of cancer of the oral mucosa // Medical consultations. - 2014. - No. 1. - P. 23-27.
- Byakhov M. Yu. Options for combined and complex treatment of locally advanced cancer of the oral mucosa and oropharynx: Dis. Dr. med. Sci. - M., 2013.
Methods of treating the disease
Treatments for this type of cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Let's consider these methods separately.
Surgery
The main method of treatment is resection (removal) of the tumor. The principle of the surgical technique is to remove a malignant tumor from the patient. Surgery is always performed, except in cases where the tumor is inoperable.
Operation options:
- Gentle resection, in which the tongue or most of it is preserved.
- Radical removal (the operation is called glossectomy, this is the total removal of the tongue).
- Together with glossectomy or after it, reconstruction of the tongue is often performed - one-stage plastic surgery with a skin flap. This intervention allows you to preserve the functions of the removed organ.
Radiation therapy
Radiation is designed to destroy cancer cells or slow their growth. For small tumors this is the main treatment method. Radiation can also be given before surgery (to reduce the tumor) and after it (to avoid relapse). In later stages, the technique is used as palliative therapy, that is, it alleviates symptoms.
Chemotherapy
This is a systemic therapy that aims to destroy malignant cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy is given before surgery (to shrink the tumor) or after it (to avoid relapse).
Reasons for appearance
There are a number of predisposing factors to the development of tongue cancer. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Tobacco and alcohol . When smoking, the risk of developing this disease is influenced by how much, often and for how long a person smokes. Those who have been diagnosed with this type of cancer need to completely stop smoking, since continued tobacco use increases the risk of developing cancer of another location. Of 10 patients with malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity, 7 are susceptible to alcohol dependence. The combination of alcohol and smoking increases the risk of oral cancer by 100 times compared to people who do not drink or smoke.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) . The incidence of oral cancers associated with HPV has increased in the last decade. According to research, cancer associated with HPV affects mainly young patients who do not have a long history of drinking alcohol and smoking. Now many doctors associate the prevalence of HPV in the last two decades with people's passion for oral sex.
- Floor . Men suffer from this type of cancer 2 times more often than women, which may be due to frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
- Age . Oral cancer is more often diagnosed in patients 55-60 years old. This is due to its slow development. However, the presence of HPV changes this situation.
- Poor nutrition . According to several studies, the risk of developing such cancer increases with a deficiency of vegetables and fruits in the diet.
- Weak immune system . The risk increases in people who have congenital or acquired immunodeficiency, as well as in those who take drugs to suppress the immune system (this is necessary after an organ transplant).
- Graft versus host disease (GVHD) . This reaction is typical for the condition after stem cell transplantation: this is how the body reacts to foreign donor cells. Oral cancer can develop within 2 years.
- Lichen planus. This disease most often affects the surface of the skin, but can also appear as white spots and lines on the oral mucosa. Increases the risk slightly.
- Bowen's disease. This is an obligate precancerous condition, the tumor is located inside the epithelial layer. Sooner or later it transforms into malignant.