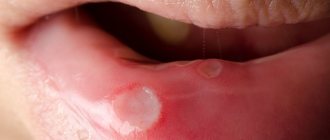
Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue caused by various etiological factors: viral, bacterial, fungal. Accompanied by swelling of the tissues of the tongue, transformation of their structure and color. The patient feels a specific burning sensation, loses taste, there is pain when swallowing and chewing, as well as difficulty speaking.
It develops separately or in combination with stomatitis and can cause a number of serious health consequences, therefore, if characteristic symptoms are detected, it is necessary to contact specialized specialists as quickly as possible, they will conduct an effective diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
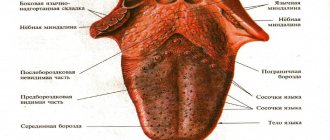
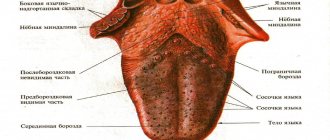
What does a healthy tongue look like?
First, let's remind parents what a healthy tongue looks like. The following signs indicate the state of normality:
- the size is not increased;
- humidity is moderate;
- the color of the tongue is pale pink, without spots or grooves;
- sensitivity is normal, papillae are not enlarged;
- allow for a light coating that is easy to clean;
- There is no bad breath.
If, upon examination of the child, the condition of his tongue corresponds to the signs described above, there is no reason to worry and see a doctor.
Characteristic symptoms of glossitis of the tongue
Symptoms are varied, as a rule, they depend on the type of disease: viral, bacterial, candida glossitis - photos can be found on the Internet or in consultation with a specialized specialist. Glossitis in adults and children develops in the same way and has no obvious symptomatic differences.
In the initial stages of development, a person experiences discomfort in the mouth, a burning sensation, and a sensation of a foreign body. After some time, the color of the mucous membrane of the tongue changes - it acquires a rich red, grayish or burgundy color.
Gradually increasing swelling provokes excessive salivation, taste sensations disappear, and in some cases taste is distorted. Eating food becomes difficult and quite painful, so patients, when eating, try not to use their tongue when chewing, which leads to crumbs and whole pieces of food falling out of the mouth.
Most patients do not know how to treat glossitis on the tongue in adults, some of them do not go to the doctor - this provokes the appearance of abscesses and phlegmon, as well as the transition of the acute form of the disease to a chronic one, with all the ensuing consequences.
Changes that should alert parents
In addition to changes in the color of the taste organ, parents should be wary of other accompanying symptoms, including:
- swelling, against which the imprints of teeth can be seen;
- insufficient moisture or obvious dryness of the surface of the tongue;
- enlarged papillae, especially pronounced in the root part;
- formation of persistent plaque on the surface of the tongue;
- burning sensation and impaired taste perception;
- the appearance of a specific odor from the mouth.
Parents can notice these changes during a visual inspection, which is best done in the morning in natural light. If the situation continues for a long time, the plaque thickens and the color of the tongue does not return to normal, there is every reason to consult a doctor to find out the reasons and identify hidden pathology.
Types of glossitis
In modern dentistry, there are six main types of tongue glossitis, differing in the form of their manifestation:
- Desquamative glossitis is accompanied by the appearance of a white coating on the tongue in the form of specific spots. As a rule, it is caused by a number of pathological changes in internal organs or as an allergy to various irritants;
- Catarrhal glossitis - has distinct symptoms in the form of redness and swelling of the tongue. Caused by mechanical injuries or thermal burns;
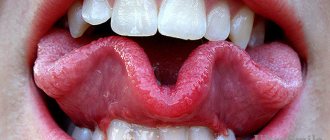
- Folded glossitis is characterized by the appearance of specific, fairly deep “grooves” on the tongue. It is often a congenital pathology, but can also be acquired;
- Ulcerative glossitis is accompanied by the appearance of ulcerations on the mucous membranes of the tongue, and can be combined with aphthous stomatitis. Treatment of glossitis in adults and children is quite complex and takes a long time;
- Rhomboid glossitis - accompanied by the formation of compaction of rhomboid epithelial tissue, is the cause of the development of various gastrointestinal pathologies and requires an integrated approach in the treatment process;
- Purulent-phlegmonous glossitis is the most severe form of the disease, which poses a danger not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient. Symptoms affect the oral cavity and other organs/systems of the body, and treatment may require surgery to amputate part of the tongue.
A red or pale tongue is not the norm!
Both options indicate pathological changes occurring in the child’s body:
- A crimson-red tongue always indicates the presence of an infection (viral, bacterial or fungal). Most often it is tonsillitis, scarlet fever, stomatitis or glossitis.
- A red and shiny tongue is a sign of anemia, exhaustion and severe stomach disease;
- A cherry tint is a sign of influenza and measles, as well as general intoxication or kidney dysfunction;
- A bluish color indicates a lack of oxygen; there is reason to suspect disorders in the cardiovascular system or lungs;
- Purple color may indicate blood and lung diseases, heart failure.
- A too pale tongue, being penetrated by blood vessels, a priori cannot be lighter than blood. In most cases, this sign indicates exhaustion, deficiency of folic acid or vitamin B 12.
Let us remind parents that very often there may be a coating on the surface of the tongue, the color of which also has its own characteristics.
Diagnosis of glossitis
Pronounced symptoms allow dentists and therapists (it is these doctors who treat glossitis) to judge the presence of one form or another of the disease. To assess the depth and nature of the lesion, as well as to diagnose the disease that provoked the development of glossitis, different methods are used:
- bacteriological;
- cytological;
- biochemical;
- histological;
- serological.
All these diagnostic methods are available in any modern dental clinic
. To exclude the presence of syphilis, microscopy of the scraping is performed for Treponema pallidum, and an anticardiolipin test (allows us to detect antibodies to the cardiolipin antigen present in the blood of patients with syphilis). If it is necessary to determine the causative agent of glossitis, the following is carried out:
- PCR diagnostics (detection of the pathogen by its DNA);
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). For analysis, blood is taken from a vein. The study is aimed at identifying specific antibodies produced by the patient’s body against the pathogen.
Causes of tongue redness
All existing causes of external changes in the language, including its color, can be divided into two groups. The first group of factors are easily solvable problems that do not signal internal disorders and are not a cause for concern on the part of parents. These include:
- consumption of coloring foods and drinks,
- eating too hot (cold) food;
- mechanical trauma from a brush, teeth, lollipop, etc.
The second one combines negative causes that are inextricably linked with pathological processes that are hidden or obvious in the child’s body:
- inflammation of the taste buds;
- any inflammatory processes caused by viruses or infection;
- intoxication of the body due to poisoning;
- taking medications (antibiotics);
- allergic reaction to food, medications.
- lack of vitamins and microelements.
Only a doctor can identify the true cause of changes in the color and texture of the tongue. Parents should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication; this will only mask the problem and complicate the doctor’s work.
Treatment of glossitis
Professional dentists do not recommend treating glossitis in adults and children at home - this can lead to a rapid worsening of the situation and the emergence of severe complications.
As a rule, doctors use conservative drug treatment with the correction of the underlying diseases that provoke glossitis of the tongue - photos can be seen on the Internet. To reduce pain, doctors recommend eating soft foods that do not cause mechanical irritation to the affected areas of the tongue.
In severe cases, the patient may require hospital treatment in a clinic and even surgery. However, such cases are extremely rare!
What diseases does a red tongue hide?
A red tongue can be a symptom of diseases of various etiologies, including:
- angina;
- flu;
- chickenpox,
- scarlet fever;
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
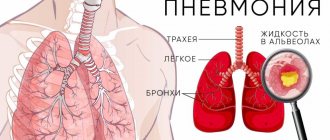
- pneumonia;
- Kawasaki disease;
- gastritis;
- severe poisoning;
- renal failure;
- vitamin deficiency (vitamin B deficiency).
As you can see, the list of diseases is quite wide and requires visiting not only an otolaryngologist, but also, if necessary, other specialized specialists: dentist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc.
How and with what to treat glossitis of the tongue in adults and children
Treatment of tongue glossitis requires elimination of the diseases that led to its appearance. This refers to anemia, gastrointestinal diseases, syphilis, etc. To minimize pain, you need to rinse your mouth with Furacilin, a solution of Chlorhexidine (0.05%) or potassium permanganate, and avoid eating rough food. In case of severe pain, local applications with anesthetics can be made:
- Trimecaine solution (2%);
- Lidocaine solution;
- Pyromecaine solution.
If the tongue is dry, it should be lubricated with a mixture of glycerin and Anestezin.
For a speedy recovery, the skin of the tongue must be cleaned of plaque using a cotton swab soaked in proteolytic enzymes (Chymotrypsin, Trypsin). If there are painful ulcers, these drugs for the treatment of tongue glossitis can be replaced with applications with Iruksol. After the hygiene procedure, it is important to treat the cleaned lesions with antiseptics. This helps prevent secondary infection and also prevents the development of serious complications.
To speed up regeneration processes, gel and jelly-like medicines with solcoseryl, as well as preparations containing vitamin A, can be used. The mixture formed by rosehip oil and vitamin A heals the affected skin well and relieves pain.
If excessive thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis (hyperkeratosis) is observed, surgical intervention is ordered. Antifungal, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are selected taking into account the severity of the disease and the dominant symptoms.
All patients with glossitis can take immunomodulators. Hormones are used extremely rarely - only for difficulty breathing. To avoid atrophy of taste organ cells, Hydrocortisone and Prednisolone ointments are prescribed in short courses.
How to treat tongue glossitis at home
Treatment of tongue glossitis at home can be carried out using traditional medicine recipes:
- decoction of chamomile flowers. 1 tbsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the flowers. Infuse, strain. Rinse your mouth after every meal;
- bedstraw decoction. 1 tbsp. pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes. Take 50 ml orally after meals and rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day. Similarly, you can use decoctions of sage and basil;
- soda solution. Add 2-3 drops of iodine and a teaspoon of baking soda to a glass of warm water. Rinse your mouth 3 times a day;
- natural honey Slowly dissolve a spoonful of honey;
- propolis. Lubricate the areas of inflammation 5 times a day. Instead of propolis, you can use raw carrot/potato juice or rosehip oil;
- tea tree oil. Dilute in equal proportions with olive, sunflower or sea buckthorn oil. Treat glossitis lesions 5 times a day or keep it in your mouth for several minutes.
Other reasons
- Avitaminosis.
A deficiency of microelements can cause sensitivity of the mucous membranes and the appearance of cracks in the tongue. - Allergy.
New dental care products and foods can cause increased sensitivity of the gums and tongue. - Worms.
The presence of parasites leads to the fact that the body does not absorb nutrients and beneficial microelements, which causes the condition of the mucous membrane to worsen. - Hormonal disbalance.
- Stress.
How to determine health status by language. Source: Yulianna Pliskina YouTube channel