The better humanity lives, the more it suffers from allergies - this is the paradox that emerged in the second half of the 20th century. The population of developed countries with a high standard of living already takes allergies for granted: a person who is not allergic to anything is becoming a rarity.
To understand why this happens, let's first look at what allergies are. An allergy is a chronic disease characterized by an unexpected and inadequate immune response to completely harmless things.
When the body comes into contact with certain foods, plant pollen, medications, etc. the human immune system sees them as a danger and produces a specific antibody - immunoglobulin E. And it, in turn, activates the production of substances (histamines, leukotrienes, cytokines) that form an allergic reaction.
At the same time, immunoglobulin E antibodies are specific depending on the type of allergen: they will be different in the case of an allergy to milk, cat hair, pollen, etc.
Causes of facial allergies
Atypical reactions of the immune system to foods, chemicals and biological substances can cause rashes, pimples, redness, swelling and itching. The person experiences physical and moral discomfort. The manifestations of allergic reactions are varied and depend on the individual characteristics of the body. Most often, localization is observed on the forehead, temples, cheeks, behind the ears, in the décolleté area and on the neck. The most common prerequisites for allergies are:
- heredity;
- consequences of long-term use of medications;
- unfavorable environment;
- constant stress;
- reduced immunity;
- too high a concentration of certain substances;
- insect bites;
- cold or direct sunlight.
There may be other reasons; you need to approach the problem individually.
Allergies to foods and medications
There is often cross-reaction to the protein in this group, making it difficult to find the source. The speed of onset of symptoms can vary from immediate to a period of 2-3 hours. In the case of medications, the prerequisite is overdose, long-term use, too many drugs taken during the day.
Sun or cold
The body’s response is characteristic not only of winter. This could be water or food at a certain temperature. The appearance of photodermatitis is promoted by internal and external causes. Within a day or a little later after exposure to the sun, soreness and itching of the skin begin to bother. When an allergic rash appears on the face of an adult, treatment should begin immediately, otherwise the situation will worsen with each passing hour. As part of complex therapy, immunostimulating cosmetics such as Laennec are effective. Before use, you should consult with specialists.
Reaction due to eczema
Skin diseases significantly reduce the body's resistance, and any violation provokes their exacerbation. Most often, the reaction appears externally in the form of small bubbles with liquid. The acute form can become chronic, which subsequently leads to relapses.
Errors in diet
Various dietary restrictions do not go out of fashion. There are programs based on the consumption of one or just a few products for a long time, which leads to an oversaturation of the body with certain elements, since in this case there can be no talk of balance. You should not be surprised at the deterioration in well-being, since such restrictions become the causes of severe allergies on the face of an adult, the treatment of which is carried out comprehensively and will take a lot of time.
We recommend
GHC Placental 3D Mask withQ10
Serum concentrate
Repairing cream with a moisturizing effect
Placental antioxidant lotion concentrate
Contact with animals, insect bites
A swollen nose and watery eyes when trying to pet a pet are a true classic of the genre. Mosquitoes, bedbugs and other blood-sucking creatures can also cause itching and redness on the skin. The toxins they inject in large quantities cause a rash, often accompanied by fever. In this case, external agents and antihistamines are recommended; dosages should be confirmed with a doctor.
Allergies due to stress
In addition to nervous tics, there are other reactions to emotional overload. Unconsciously, a person may scratch or clench their hands tightly. If such situations happen regularly, then health problems may begin. Itching, swelling of certain areas, redness, and difficulty breathing appear. The main direction of stabilizing the condition is the prescription of sedatives, breathing exercises aimed at calming the nervous system, ointments and gels to relieve external manifestations on the skin.
Allergy symptoms
As a rule, allergies develop gradually, intensifying over time. But sometimes it can immediately manifest itself clearly, creating a serious danger. If you begin to notice the first signs of an allergy in yourself or your loved ones, do not wait for it to develop - immediately consult a doctor.
- Sneezing. By sneezing, the body gets rid of foreign substances that have entered the upper respiratory tract. This simple physiological reaction in allergies becomes excessive - a person sneezes for a long time for no apparent reason.
- Nasal congestion, runny nose. Here it is necessary to distinguish an allergic runny nose from a cold: with an allergy, a large amount of watery mucus (“water”) is released from the nose, and with a cold, the discharge is thicker, yellow-green in color. Nasal congestion occurs due to inflammation and thickening of the mucous membrane, leading to disruption of the outflow of mucus. No matter how much a person blows his nose, he cannot get rid of a runny nose and stuffiness.
- Conjunctivitis, lacrimation. Redness of the eyes, causeless itching, and watery eyes are one of the characteristic signs of allergies. Typically, both eyes are affected at the same time, and discomfort can last for weeks.
- Cough. As with sneezing, coughing exists to remove irritating particles from the bronchi. This is a completely normal reaction to a cold and to foreign bodies entering the bronchi. But an allergic cough has a different nature: it occurs due to a narrowing of the airways due to allergic inflammation. It is characterized by prolonged attacks, the absence of sputum and the fact that it does not bring relief.
- Dyspnea. The feeling of shortness of breath is familiar to people from intense physical exercise. But if shortness of breath occurs at rest or after minor physical activity, and is accompanied by difficulty and whistling when exhaling, it is most likely an allergy.
- Attacks of suffocation. This is a much more serious condition than shortness of breath, often causing fear and confusion. Choking manifests itself as difficulty in exhaling and is often resolved by a coughing fit.
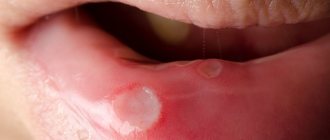
- Skin rashes and itching. Redness and rashes on the skin can have many causes. But allergies are always accompanied by itching: its skin manifestations are similar to a nettle burn or an insect bite. There are serious swelling of the face and other parts of the body, there are manifestations of dermatitis, which last a long time and, after healing, change the structure of the skin in the affected areas.
Types of allergies on the face
If in children the most vulnerable area is the buttocks, where signs appear that indicate certain foods or unfavorable conditions, then in adults this is the nasolabial triangle, eyelids, lips, tongue, neck and hands.
Atopic dermatitis
Chronic inflammatory skin disease. Most often begins in early childhood. The priority prerequisite is genetic predisposition. It can be a concomitant disorder with bronchial asthma and conjunctivitis. There are infant, child and adult forms of the disease.
Hives
Allergies and rashes in the form of pimples on the face, the photo of which most often appears on advertising posters of the newest antihistamines, occurs with a seasonal variant. It is characterized by lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids, obsessive itching, and redness of certain areas of the body.
Food reactions can occur instantly when certain foods enter the mouth and esophagus. Most often they are milk, eggs, red or yellow fruits, and nuts. Peanuts are the most dangerous in this regard.
Contact dermatitis
Recognizable by clear zones of irritation. The causes are hygiene and cosmetic products, chemicals that come into contact with unprotected skin, jewelry, piercings, latex products, extracts and juices of certain plants. It manifests itself in the form of weeping erosions, in place of which dry scales then appear. To understand how to remove facial allergies, you need to find and eliminate the substance that causes your health to worsen. Often a good result comes from moving to another region. This way, it is possible to cut off some of the options; for the rest, you will have to take special tests in the laboratory.
Toxicoderma
A distinctive point is inflammation not due to external factors, but due to the penetration of a provoking substance into the body. In some cases, it can cause secondary damage to internal organs and anaphylactic shock, since it develops rapidly from the ingestion of an allergen from the inside. One way to prevent inflammation is to take antibiotics, especially penicillin. At the same time, timely treatment gives good results.
The alimentary variety is included in a special group; the deterioration of the condition is provoked not by products, but by food additives in their composition. It is quite dangerous due to the fact that it can occur suddenly, since manufacturers do not indicate all the ingredients in the composition.
Quincke's edema
It poses a direct threat to life. In the question of what an allergy on the face and neck looks like in this case, what to do and how to treat it, time is of the essence. Choking occurs quickly, and the slightest delay can have fatal consequences. An acute inflammatory reaction of the body, which occurs locally in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, affects deep layers, including the muscles of the respiratory system, and in a third of cases is localized in the larynx. It is impossible to prevent the development of Quincke's edema. Women suffer from this disorder more often. The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture and requires medical attention. Signs may persist for several days and disappear gradually. Treatment includes the administration of potent antiallergic drugs. In severe cases, the patient requires urgent hospitalization in an intensive care unit or intensive care unit.
Rash caused by diseases of the blood and blood vessels
A rash due to diseases of the blood or blood vessels is caused by damage to the walls of the capillaries, as a result of which petechiae - small bright red dots - appear on the surface of the skin. Unlike ordinary hemorrhages, a rash due to blood diseases does not change color when pressed. Other signs indicate the disease:
- joint pain (knees, ankles);
- black stools, diarrhea, sharp pain in the abdomen as if poisoned;
- the rash covers the entire body.
Diseases that cause hemorrhagic rash include:
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof's disease) is a blood disease in which small arteries and capillaries are blocked by blood clots. Mainly found in children, especially newborns. The disease has autoimmune causes of unknown etymology. Those. Your own immune cells perceive platelets as a foreign body and attack them. The rash is painless, occurs as a reaction to the administration of any medication, and is localized at the injection site.
Hemoblastosis. This is a malignant tumor that occurs very often in childhood. The rash has several types:
- hemispheres of red-brown color, covered with a crust;
- blisters with serous fluid inside;
- rashes similar to bruises, both large in size and in the form of bloody dots that appear without any reason.
In all cases, the rash causes severe itching. Blood tests for hemoblastosis show a significant increase in the number of leukocytes due to decreased immunity. Hemoglobin drops, lymph nodes enlarge. Platelet counts drop and the child gets tired quickly. The main cause of rash in diseases of the blood or blood vessels is a decrease in the number of platelets and a disruption in the synthesis of proteins involved in blood clot formation. This rash also occurs when taking medications that thin the blood (Aspirin, Warfarin, Heparin).
Diabetic angiopathy. This is a violation of the vascular capacity of the lower extremities, provoked by type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to the disease, the walls of blood vessels become thinner and become fragile. This causes skin dystrophy. Ulcers and erosions appear on the skin.
What does an allergy look like on the face?
There are many manifestations of allergies, and they depend on the form, location and intensity. The main indicator of the disorder is sudden swelling of the eyes and lips, one or both. Changes also affect the structure of the skin. It becomes lumpy, swollen, with a small scattering of small dots. Red, uneven spots of varying sizes often appear. Cracks and a scaly structure may be observed. If you give in to temptation and start scratching the itchy areas, the condition will quickly worsen.
Depending on the type of disorder and the affected area, allergic rashes on the face are likely, the treatment of which requires an integrated approach. Along with pharmaceutical drugs, cosmetics have a fairly good effect. Plasma therapy with the Japanese drug CURACEN perfectly restores appearance, but only after the acute period ends and the condition stabilizes.
Infectious rash: characteristic features and difference from allergic rashes
The distinctive features of an allergic rash are vesicles (capsules with liquid inside), papules (grain-like compactions) and pustules (bubbles with pus). An infectious rash has these symptoms.
Various infections and viruses entering the body damage, first of all, the mucous membrane, as well as the skin. Unlike an allergic rash, an infectious rash is always accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Also characteristic signs of infection:
- body intoxication, vomiting, headache
- fast fatiguability
- phasing, spread of the rash to other parts of the body with each new day
- enlarged lymph nodes
- rashes look like papules, vesicles and pustules
- the skin dries out and flakes off.
The infection rash is not itchy, but touching it is painful. The causes of rashes are the following diseases:
- Herpes: depending on the type of virus, the skin of the face (lips) or the genitals (head of the penis, labia) are affected. The rash looks like blisters, which gradually open up and ulcers form in their place. Upon completion, a crust will form that should not be touched;
- Scabies: The causative agent is a microscopic mite that leaves tiny tunnels under the skin. Unbearable itching occurs;
- Chickenpox: The rash resembles a mosquito bite, filled with serous fluid. Vesicles spread throughout the body, including the scalp. The soles and palms remain intact;
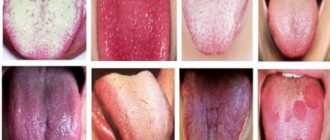
- Scarlet fever: the rash looks like roseola - pinpoint pink spots of various shapes. After a few days, the rash fades and turns brownish. After the temperature normalizes, the skin peels and flakes. A characteristic feature is redness of the tongue and enlargement of the papillae;
- Measles: the rash looks like papules, which are localized on the inside of the cheeks and gums. The rash spreads from the neck down the back, lastly moving to the limbs. The mucous membrane of the eyes becomes inflamed;
- Rubella: the skin becomes covered with red spots, localized in the thighs and buttocks, and malaise is observed;
- Infectious mononucleosis: lymph nodes enlarge, adenoids swell. The rash is observed throughout the body, including on the roof of the mouth;
- Meningococcal infection: This is an extremely dangerous infection that can lead to the death or disability of a child. It is by the appearance of the rash that one can notice the symptoms of the disease on the first day of infection. A rash with meningococcal infection is a consequence of exposure to toxins caused by the activity of meningococcus, which increase vascular permeability. The rash is hemorrhagic in nature, that is, it looks like small hemorrhages. Mainly localized on the buttocks and limbs.
There is an effective test to distinguish meningococcal rash from other rashes. You need to take a glass, turn it over, press on the area of the rash and twist it a little until the skin around it turns white. If the skin turns pale at the site of the rash, then it is not a meningococcal infection. If the rash remains the same color, you should immediately call an ambulance.
How to diagnose allergies
The main difficulty is to distinguish it from a skin disease. Rashes should not be a reason for panic, but a prerequisite for examination. To prevent exacerbation and speed up the process of identifying causes, it is necessary:
- try to independently identify the allergen by eliminating cosmetics or products from everyday use, doing this gradually in order to replace the changes in time;
- take an antihistamine that has already been used as prescribed by a doctor;
- Remove all alcohol-based external care products from use.
After such measures, it will be much easier to determine how to relieve an allergic reaction on the face and alleviate the general condition.
We recommend
GHC Placental 3D Mask withQ10
Serum concentrate
Repairing cream with a moisturizing effect
Placental antioxidant lotion concentrate
Treatment
It is not recommended to use drugs other than antihistamines on your own. In most cases, they are enough to eliminate the main symptoms and relieve swelling. It is necessary to take into account that the action must be comprehensive and must include creams, ointments and gels to relieve external signs of the disease.
Preparations for internal use
Medicines prescribed by a doctor are divided into corticosteroid and non-hormonal. The first are produced on a hormonal basis, have a powerful effect, but have a number of serious contraindications for long-term use. The second, milder ones, are prescribed to relieve mild forms of irritation. Several generations of antihistamines are available in pharmacies. If the former, such as Suprastin, influenced the level of attention, causing drowsiness and inhibition of reactions, then Cetrin, Telfast, Claritin, with high efficiency, do not give side effects that could become a limitation for work in areas where concentration is required.
Cosmeceuticals and their help in the fight against allergies
When the body reacts violently to a stimulus, skin lesions are sure to appear, and sometimes quite unpleasant ones. These are not only rashes and pimples, but also increased dryness and microcracks. Their danger lies in the possible entry of bacteria and the development of local inflammation. The main task, along with eliminating illness, is strengthening the immune system. Cosmetic products from the medical corporation "RHANA" are used in professional problem solving, provide a quick and lasting positive effect, allowing you to maintain beauty, health and prevent premature aging. And the skin is susceptible to it if an allergic reaction often appears on the face, a photo of which clearly demonstrates the degree of damage to the integument.
In order to give a fresh look and ensure cellular renewal, it is recommended to use placental preparations:
- Modeling mask with placenta hydrolyzate GHC Placental 3D Mask withQ10. It will prevent the risk of developing inflammation and give a healthy tone.
- Concentrate serum for intensive revitalization GHC Essence will instantly restore inner radiance, and also improve microcirculation and cell nutrition.
- LNC Repairing Cream with a moisturizing effect will preserve the beauty and freshness of the skin, and also protect it from moisture loss and eliminate the regeneration of ceramides (epidermal cells).
- Placental antioxidant lotion concentrate LNC Toning Lotion will protect cells, normalize melanin production and provide optimal hydration.
The dangers of self-medication
According to preliminary forecasts, the number of people reacting to certain stimuli will reach almost 90% by the end of the century. Allergists-immunologists mention the fault of allergy sufferers themselves, who, by self-medicating, expand the range of allergens and provoke the development of other diseases. In this case, the part is fixed and passed on by inheritance. By identifying the cause and drawing up an optimal treatment regimen, you can almost completely eliminate the likelihood of regular exacerbation of allergies.
Allergic contact dermatitis: basic approaches to diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Allergic contact dermatitis is a classic form of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction mediated by sensitized lymphocytes. According to a number of authors, this pathology affects 1% to 2% of the population in various regions. The prevalence of the disease is higher in industrialized countries. It is increasing as more and more new chemical substances are introduced into use in medicines, cosmetic products, medical implants, household chemicals, and industrial reagents.
Unlike simple contact dermatitis, in which an irritant causes inflammation in all people when exposed to the skin, allergic dermatitis occurs only in sensitized individuals, that is, in people who have immune cells specific to this substance - T-lymphocytes. Contact dermatitis is often caused by harmless chemicals that, under normal conditions, do not cause any clinical symptoms in healthy people. But allergic dermatitis is also known when in contact with aggressive agents - components of hair dyes, hair growth products, dyes for fabrics, fur and leather, detergents, medications, juice of poisonous plants.
A classic example of allergic contact dermatitis is dermatitis caused by plants of the genus sumac (in particular, poisonous sumac - Rhus toxicodendron), in which the rashes often have a linear shape and are located on exposed areas of the body.
The pathogenesis of allergic contact dermatitis is based on a tuberculin-like delayed (cellular) hypersensitivity reaction, the inductive phase of which begins with local exposure to the skin of low molecular weight chemicals of organic or inorganic nature. Their sensitizing (allergenic) properties depend on their ability to penetrate the skin and form stable covalent bonds with the proteins of the host organism. Thus, dinitrochlorobenzene forms complexes in the epidermis with proteins containing a lot of lysine and cysteine. Skin lipids can also serve as an adjuvant.
In the formation of hypersensitivity, the leading role is played by professional macrophages of the epidermis - multi-processed Langerhans cells. The resulting delayed hypersensitivity is directed not only to the chemical itself, but also to the carrier protein.
Typically, at least 10–14 days pass from the moment of skin contact with the allergen until the development of the first clinical manifestations. The duration of the sensitization period is usually shorter for aggressive chemicals. Thus, according to our observations, drug allergens when applied to the skin can cause manifestations of contact dermatitis as early as 7–8 days. The most common allergenic medications are local forms of antibacterial drugs; contact allergic reactions to local anesthetics, antiseptics and latex are less common.
The location and configuration of the lesion is determined by the causative factor. The most common form of the disease is eczematous dermatitis. The disease is easy to diagnose and, as a rule, is characterized by a favorable course. The rash disappears when exposure to the pathogenic factor ceases. To accelerate the regression of clinical manifestations, local anti-inflammatory drugs, mainly topical glucocorticosteroids, can be used.
Etiology
According to our observations, the most common cause of allergic contact dermatitis is stainless metal alloys from which household products are made - kitchen utensils, jewelry, watches, denim rivets, zippers, keys, as well as medical supplies - dental crowns, braces , devices for focal and extrafocal osteosynthesis. Thus, having analyzed 208 cases of allergic contact dermatitis that we encountered in practice in the period from 1999 to 2009, we came to the conclusion that the metals nickel, cobalt and chromium, which are part of stainless alloys, were the cause of inflammation in 184 (88.5% ) patients.
A list of the most common, according to our data, causes of allergic contact dermatitis is given in
.
Pathogenesis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a delayed-type allergic reaction. An allergen that gets on the skin binds to tissue proteins, forming a compound that can cause an allergy - an antigen. Langerhans cells absorb antigen in the membrane molecules of the major histocompatibility complex class 2 by T lymphocytes. Activated T lymphocytes and Langerhans cells produce gamma interferon, interleukins 1 and 2, which enhance the immune response and inflammatory response. Activated T lymphocytes migrate through the lymphatic vessels to the paracortical zone of the regional lymph nodes. In the lymph nodes they undergo antigen-dependent proliferation and differentiation. Some of the “specialized” T-lymphocytes take part in the immune response, while the rest turn into memory cells. They cause the appearance of a rapid, pronounced response after repeated contact with the allergen. After the first contact with the allergen, T-lymphocytes recognizing it accumulate, which usually lasts 10–14 days. After this, T-lymphocytes leave the regional lymph nodes into the blood and populate all peripheral organs of the immune system. Upon repeated contact with the allergen, memory cells are activated and rapid accumulation of delayed-type allergic reaction effector cells—macrophages and lymphocytes—occurs.
Histological picture
The histological picture of allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by infiltration of the dermis with mononuclear cells, primarily near blood vessels and sweat glands. The epidermis is hyperplastic and also infiltrated with mononuclear cells. Typically, the formation of vesicles in the epidermis combines with the formation of bullae. The serous fluid filling them contains granulocytes and mononuclear cells.
Clinical manifestations
The disease, according to our data, is more common in young and middle-aged people. However, exceptions are possible. Thus, of the people we examined, the youngest was a one-and-a-half-year-old girl with an allergy to cobalt, and the oldest patient was an eighty-year-old man, sensitized to chromium and nickel.
In the clinic, allergic contact dermatitis is distinguished into acute, subacute and chronic forms, as well as mild, moderate and severe.
The interval from the initial exposure to the allergen to the formation of skin hypersensitivity can vary: from relatively short (2–3 days when exposed to a strong sensitizer, for example, urushiol from the juice of plants of the genus sumac) to very long (several months or years in the case of a weak sensitizer, for example, chromic acid salts or chloromethylisothiazolinone). As a rule, in an already sensitized organism, the disease develops acutely 12–72 hours after exposure to the allergen and is manifested by itching, bright hyperemia and swelling of the skin at the site of contact, against which papules, small blisters or blisters are visible, opening and leaving weeping erosions (wetting) . Sometimes skin necrosis occurs.
The subsiding inflammation leaves crusts and scales. In a chronic course, peeling and lichenification appear.
Acute allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by the following stages of development of rashes: erythema => papules => vesicles => erosions => crusts => peeling. For a chronic course: papules => desquamation => lichenification => excoriation.
In severe allergic contact dermatitis (for example, caused by sumac poison), the patient may experience symptoms of intoxication - headache, chills, weakness and fever.
The localization of dermatitis can be any and depends on the place of contact with the allergen. Thus, occupational allergens more often form foci of inflammation on the palmar and lateral surfaces of the hands and fingers, forearms, and metal allergens sensitize the skin and mucous membranes at points of contact with rings, bracelets, zippers, and denim rivets (“jean rivet disease”). , metal dental crowns.
Different areas of the skin are characterized by varying susceptibility to allergic dermatitis. Inflamed and infected tissues become sensitized more often. Friction, squeezing, maceration and increased sweating contribute to the formation of allergies. In this regard, the skin of the eyelids, neck, perineum, and anterior abdominal wall in the area of contact with fasteners and buckles is often sensitized. Often patients do not realize that they suffer from allergies, believing that they simply “rubbed” the skin in the area of inflammation.
Allergic contact dermatitis always begins at the site of exposure to the allergen. Therefore, at the beginning of the disease, the lesion is clearly demarcated, although it often extends beyond the area of skin in contact with the allergen. In sensitized patients, the lesion may spread to other areas of the body or become generalized.
With a single contact, the disease lasts several days or weeks. With frequent and regular contacts - months and years.
Diagnostics
Based on the location of skin lesions, as a rule, possible causative allergens can be assumed. In the future, their role in the pathological process is determined when performing skin patch tests. To conduct a patch test, the test material is applied to the skin for 48–72 hours, and then the size of the reaction caused by the allergen is assessed.
Since allergies are always a systemic process, the skin and mucous membranes of the entire body are sensitized. Consequently, inflammation develops when an allergen is applied to any area of the skin. However, it is technically more convenient to carry out patch skin tests in the interscapular region, the outer surface of the shoulder and the inner surface of the forearm, when fixing the material on which the patient feels most comfortable during the study.
The test materials are applied to dry skin treated with alcohol, covered with pieces of gauze and then attached with adhesive tape (that’s why the test is called “plaster”). It is convenient to use a standard test system with standardized allergens already applied to the adhesive base. Thus, the Allertest system for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis to 24 reagents has been registered in Russia. It is sold in a pharmacy and allows you to diagnose contact allergies to nickel sulfate, lanolin, neomycin sulfate, potassium dichromate, a mixture of local anesthetics - caine derivatives, a mixture of flavoring substances, rosin, epoxy resin, a mixture of quinolines, Peruvian balsam, ethylenediamine dihydrochloride, cobalt chloride, p-tert-butylphenol formaldehyde, parabens, carbamate mixtures, black rubber mixtures, chloromethylisothiazolinone, quaternium 15, mercaptobenzothiazole, paraphenylenediamine, formaldehyde, mixtures of mercaptans, thiomersal and mixtures of thiuram derivatives. This is a simple and ready-to-use patch skin testing system. Allergens are included in a hydrophilic gel, from which the allergen is then released when soaked. "Allertest" contains two plates that are adhesive to the skin, each of which contains 12 allergens. All 24 antigens can be tested simultaneously, or the desired allergen can be cut from the plate with scissors and applied independently.
After 48–72 hours from the start of placement, the flaps are removed, wait 20–30 minutes for the nonspecific mechanical irritation to subside and take into account the severity of the reaction. Changes at the site of skin contact with the allergen are taken into account quantitatively. The gradation of a positive result is carried out as follows: (+) - erythema; (++) - erythema and papules; (+++) - erythema, papules, blisters; (++++) - erythema, papules, blisters and severe swelling.
A true allergic reaction lasts 3-7 days, while a reaction caused by skin irritation disappears within a few hours. Therefore, in doubtful cases, the severity of the reaction should be re-evaluated the next day.
H1 blockers do not affect the results of application tests. Topical use of corticosteroids on the skin area selected for testing should be discontinued at least one week before the test. Taking systemic corticosteroids in a daily dose exceeding 15 mg of prednisolone can suppress even sharply positive reactions, therefore skin patch tests are carried out no earlier than 7 days after the cessation of immunosuppressive therapy. In rare cases, skin tests are performed in patients chronically taking corticosteroids if the dose of prednisolone does not exceed 15 mg/day. However, it should be borne in mind that in this case there is a risk of obtaining false negative test results.
When performing a patch test, it should be remembered that the procedure itself may cause sensitization in the patient. Among the substances that have the ability to cause sensitization even at the first contact, it is worth noting plant resins, paraphenylenediamine, and methyl salicylate. Therefore, the application test must be justified. In addition, when conducting the test, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of nonspecific inflammation - primary irritation of the skin by the tested substances. To do this, the test materials, if they are not included in the standard test system, must be used in concentrations that do not cause irritation in the majority of healthy people (in the control group). The test should not be performed in cases of acute or extensive contact dermatitis, as increased skin reactivity may lead to a false positive result. In addition, testing with the causative allergen can cause a sharp exacerbation of the skin process. Therefore, before conducting the study, the patient must be instructed in detail, drawing his attention to the fact that if severe irritation occurs, he must remove the bandage with the allergen and contact the doctor.
When receiving a positive result from a skin patch test, it must be remembered that it only indicates sensitization to the test substance, but is not absolute proof that this particular allergen caused the dermatitis, because the possibility of long-term and polyvalent sensitization always remains. In other words, another antigen that you have not tested may also be the cause of your allergy. Therefore, when making a diagnosis, it is also necessary to take into account the history and physical examination.
Differential diagnosis
Allergic contact dermatitis must be differentiated from simple contact dermatitis, seborrheic and atopic dermatitis.
Simple contact dermatitis can develop due to damage to the epidermis by irritating chemicals (croton oil, kerosene, phenol, organic solvents, detergents, caustic soda, lime, acids, etc.) or physical impact (overheating, squeezing, compression). There is no primary sensitizing effect. Symptoms of inflammation occur immediately after exposure to the irritant, rather than 12 to 48 hours later, as with allergic contact dermatitis. The presence of papules in acute contact dermatitis indicates its allergic nature. Occupational simple contact dermatitis is similar in appearance to allergic dermatitis. The patch test allows you to differentiate these conditions.
The distinctive signs of seborrheic dermatitis include oily skin, as well as other signs of seborrhea and typical localization - the scalp and nasolabial folds. The affected areas are covered with greasy crusts and peel off profusely; Itching is usually not typical.
Atopic dermatitis usually begins in early childhood. The skin is dry. Itching is characteristic that appears before the rash, and not after it, as with allergic contact dermatitis. The flexor surfaces are most often symmetrically affected. The edges of the affected areas are indistinct; There is no consistent development of the elements of the rash: erythema => papule => vesicle.
In our practice, we encountered combined skin lesions when allergic contact dermatitis developed in response to ointments and other topical dosage forms for the treatment of dermatoses. Thus, in a 45-year-old woman suffering from microbial eczema, aggravated by the use of Zinerit (erythromycin, zinc acetate), we identified sensitization to erythromycin, an antibiotic from the macrolide group. 3 days after stopping this medication, the symptoms of exacerbation disappeared.
Three of the patients we examined, who received topical Celestoderm-B with garamycin for a long time, complained of the lack of therapeutic effect from the use of this medication. That is, despite the use of an anti-inflammatory drug, the itching and intensity of the rash not only did not decrease, but sometimes intensified some time after applying the medicine. During an allergological examination using the patch testing method, sensitization was established - a drug allergy to the antibiotic gentamicin (Garamycin), which is part of the drug. Replacing the drug with the topical glucocorticosteroid Elocom after a few days led to complete regression of dermatitis symptoms in all three patients.
When carrying out differential diagnosis, it is also necessary to remember about photocontact, phototoxic and true photoallergic dermatitis.
Photocontact dermatitis is caused by the interaction of a chemical and ultraviolet light in the skin. With it, rashes appear only on open, insolated areas of the body. The sensitizing agent is most often drugs (tetracyclines, sulfo compounds, griseofulfin, hormonal contraceptives) or locally applied resinous extracts. In phototoxic dermatitis, skin damage is caused by the action of substances (for example, hogweed juice) that acquire toxic local irritating properties under the influence of ultraviolet rays. In true photoallergic dermatitis, the sensitizing allergen undergoes chemical changes under the influence of ultraviolet rays. In the absence of insolation, it is harmless to the patient's body.
One of the rare variants of contact allergies is contact urticaria. Depending on the pathogenesis, allergic, non-immune and combined forms of this disease are distinguished. The non-immune form develops due to direct exposure of the skin or mucous membranes to an agent, most often nettle, leading to the release of mediators from mast cells. Allergic contact urticaria is caused by the production of specific IgE antibodies and, according to the mechanism of development, is classified as type 1 hypersensitivity. Most often it is caused by food products (fish, milk, peanuts, etc.), pet allergens (saliva, fur, epithelium) and penicillin antibiotics. Little is known about the combined form of contact urticaria, caused by the influence of both immune and nonspecific factors. It is believed that ammonium persulfate, an oxidizing substance found in hair bleach, often causes this type of reaction.
Treatment
The treatment of allergic contact dermatitis is based on eliminating contact of the body with the allergen that caused the disease. In the acute stage, with swelling and oozing, wet-dry dressings are indicated, followed by topical application of glucocorticoids. If the rashes are represented by large blisters, then they are punctured, allowing the liquid to drain; the bladder cover is not removed; every 2–3 hours, change bandages moistened with Burov's liquid. In severe cases, systemic corticosteroids are prescribed.
Prevention and treatment of staphylococcal and streptococcal skin infections play an important role.
Allergic contact dermatitis generally has a favorable prognosis. With timely identification of the causative allergen and elimination of contact with it, the symptoms of the disease completely regress within 1–3 weeks, and sufficient patient awareness of the nature and causative factors of the disease significantly reduces the possibility of chronicity and recurrence of dermatitis.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of allergic contact dermatitis, the local use of medications with a high sensitizing ability, primarily beta-lactam antibiotics, furatsilin, antihistamines, sulfonamides and local anesthetics, should be avoided.
In case of frequent and professional contact with low-molecular compounds, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment for the skin, mucous membranes and respiratory tract - special protective clothing, gloves, and protective creams.
Once the cause of allergic contact dermatitis has been identified, the patient must be carefully instructed and all possible sources of the allergen discussed with him, drawing his attention to the need to stop contact with this reagent and cross-reacting substances (the most common allergens, their sources and cross-reactive substances are listed in
). For example, patients with nickel allergies are not recommended to wear stainless steel jewelry or use nickel-plated cookware. For such patients, implants containing nickel are contraindicated, including dental crowns and white metal braces, and steel structures for osteosynthesis. It is also recommended that steel rivets and fasteners on jeans or other underwear be sealed on the inside with adhesive tape or cloth to prevent their contact with the skin.
If dermatitis is caused by rubber gloves, they can be replaced with vinyl ones. It is also necessary to remember that rubber drains and other medical supplies should not be used in such patients. The use of latex condoms is contraindicated for them.
If you are allergic to formaldehyde, the patient should not use certain medications and cosmetics containing this preservative. The patient should be explained that before using medications and cosmetics, it is necessary to familiarize themselves with their composition indicated on the packaging.
In the case of occupational dermatitis, it is necessary to recommend acceptable types of work to the person.
Literature
- Harrison T.R. Internal diseases. Ed. E. Fauci, J. Braunwald and others. In two volumes. Per. from English M., Practice - McGraw-Hill (joint ed.), 2002.
- Patterson R., Grammer L.K., Greenberger P.A. Allergic diseases: diagnosis and treatment. Per. from English edited by A. G. Chuchalina. M., GEOTAR MEDICINE, 2000.
- Popov N. N., Lavrov V. F., Soloshenko E. N. Clinical immunology and allergology. M., REINFOR, 2004.
- Luss L.V., Erokhina S.M., Uspenskaya K.S. New possibilities for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis // Russian Journal of Allergology. 2008. No. 2.
- Fitzpatrick T., Johnson R., Wolfe K. et al. Dermatology. Atlas-directory. Per. from English edited by E. R. Timofeeva. M., Praktika, 1999.
E. V. Stepanova , Candidate of Medical Sciences, Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums named after. I. I. Mechnikova RAMS, Moscow
Key words: allergic contact dermatitis, patch skin tests, preventive dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, drug allergens, occupational allergens, contact allergens, metal allergy, contact dermatitis, metal dermatitis, contact urticaria.
Preventive measures
In order not to look with disappointment at your reflection in the mirror and not to wonder how to get rid of allergies on your face once again, you should listen to the simple but effective advice of specialists.
- Adjust the daily menu by removing from the diet foods that provoke the appearance of characteristic symptoms of an immune disorder.
- Do not use cosmetics based on alcohol and other aggressive substances, giving preference to soft and neutral ones.
- Do not stay in the sun for a long time, and in winter, protect your skin from the cold as much as possible.
- During seasonal exacerbations of hay fever, use inhaled isotonic saline solutions to reduce the concentration of pollen in the nasopharynx.
- Always keep in your medicine cabinet an antihistamine recommended by an allergist-immunologist.
It is worth remembering that angioedema alone cannot be prevented. Other types of allergies are completely preventable, and this is much more effective than constantly treating exacerbations. Immunity support should take the leading place in the list of mandatory activities.
Why are allergies on the face dangerous?
A scattering of small specks or red spots not only look unsightly, but also pose a hidden threat. Acute inflammation, accompanied by swelling, can spread to the neck and make breathing difficult.
Violation of the structure of the skin, accompanied by a feeling of tightness, reduces the natural resistance to external influences. Weeping areas, as well as cracks in the upper layer of the epidermis, create a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which leads to the appearance of pimples and ulcers. When such a condition occurs and is not treated, there is a high probability of it becoming chronic. In addition, an unpresentable appearance can cause a sensitive blow to pride and cause problems in communication.
If an allergic rash appears on the face, a specialist from a clinic or health center will tell you how to treat it. It is better to contact him at the first signs in order to make a timely diagnosis and receive an effective treatment regimen to avoid complications.