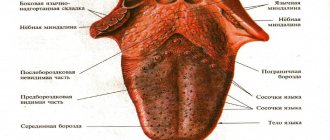
Anatomical structure of the tongue
The structure of human language corresponds to its multifunctionality, which lies in the fact that it participates in the processes:
- chewing;
- salivation;
- taste perception;
- speech.
The body of the tongue consists of striated muscle tissue, which is covered by a membrane of mucous tissue. Its surface, called the back, is conventionally divided into three parts:
- the last third, located near the pharynx, is called the root;
- the first two thirds are the body of the tongue.
A longitudinal groove runs in the middle, which is an external manifestation of the internal septum; it is, in fact, a reduced thyroglossal duct.
The mucous membrane, tightly adjacent to the muscle tissue, is covered on the outside with stratified squamous epithelium. It contains:
- salivary glands;
- taste buds;
- lymphatic ducts.
The mucous membrane of the posterior part forms three supraglottic folds, with the help of which the tongue is attached to the larynx:
- median;
- two lateral.
The tongue is abundantly covered with papillae, including:
- filamentous - act as organs of touch and, thanks to the rough surface, hold food on the tongue;
- cone-shaped – responsible for sensitivity to temperature and pain;
- mushroom-shaped - equipped with taste buds, thanks to them we distinguish many taste sensations;
- groove-shaped - located near the root, have serous glands and are also responsible for the sense of taste;
- leaf-shaped - equipped with lingual glands that secrete a mucous secretion.
The tongue is attached to the oral cavity by a fold of mucous membrane called the frenulum.
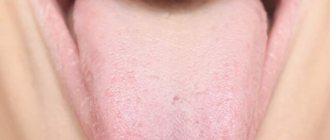
What does a healthy tongue look like?
A white-pink color of the tongue is considered normal. There are a number of other accompanying signs of his health:
- the longitudinal fold of the tongue is clearly visible;
- the papillae are clearly visible, but not hypertrophied;
- the edges are smooth.
The surface must be clean, although a slight coating on the tongue is acceptable.
For an adult, seasonal changes in the color of the tongue are possible:
- in winter, a slight yellowish coating on the tongue in adults can be considered normal if there are no other abnormalities - pain, increase in size, lack of taste;
- in summer, a light white coating, not localized, but over the entire surface, is also not considered a pathology.
A healthy child’s tongue is not much different from an adult’s tongue. One significant feature: it reacts to the slightest changes in the condition of the baby’s body - teething, the introduction of complementary foods, even a change in the brand of baby food. Therefore, plaque on a child’s tongue requires close attention.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a problem with your body, rush to see your local physician. It will help to find out the causes of the white deposits. Typically, primary diagnosis includes :
- examination of the tongue;
- general analysis of blood fluid;
- smear to check flora;
- Ultrasound of organs;
- urine check.
If a light coating has accumulated on your child's tongue, make an appointment with your pediatrician as soon as possible.
Differential diagnosis
In some cases, you will need to consult specialists working in the field of gastroenterology and endocrinology. In case of a fungal infection, an examination by a dermatologist will be required. In case of dental defects, the therapist will send the patient to the dentist.
The doctor must examine the patient and ask questions about his state of health and well-being , namely:
- Are there any changes in taste?
- Are there any bad habits?
- Does pain in your mouth bother you?
- What ailments worry you?
- When was the plaque first discovered?
- What drugs are currently in use?
A gastroenterologist may prescribe the following procedures :
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- gastroscopy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
To clarify the cause of the white plaque, you will need a test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis or gonorrhea, stool culture for dysbacteriosis and the presence of helminths.
The endocrinologist will check the thyroid gland and lymph nodes. Additionally, he may need the results of blood tests for hormones, ultrasound, CT or MRI of organs.
Reference! It is necessary to treat a specific disease, not a white coating.
What is plaque on the tongue?
The most numerous - filiform papillae - form a white coating on the tongue due to their structure:
- the lamina of the mucous membrane of the filiform papilla is covered with stratified squamous epithelium;
- this is a keratinizing epithelium that periodically exfoliates, covering the entire tongue with a light white coating;
- In case of any malfunctions in the human body, desquamation slows down and a layer of keratinized cells grows, which acquire different colors depending on what pathology led to the malfunction.
By the color of the plaque and where it is localized, diseases that have led to pathological changes in the tongue are judged.
Comments
Good afternoon There is a white coating on the tongue and a bad acetone smell from the mouth, could this be somehow related to the fact that I am now on a weight loss diet?
Yana (01/02/2020 at 17:51) Reply to comment
- Dear Yana! You are thinking in the right direction. If your diet is low-carbohydrate, then this phenomenon is quite possible. The fact is that while following a diet, your body, in the process of burning fat, releases specific ketone bodies, which also end up in saliva. Hence the white coating on the tongue and the bad acetone smell. To get rid of the problem, try drinking more water and eating greens. For example, parsley. If the alarming signs do not go away, then consult a doctor, because... the smell of acetone may indicate diabetes.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (01/07/2020 at 09:18) Reply to comment
Good afternoon. For 8 months I have been bothered by pain and burning in the right hypochondrium, sometimes on the side of the back, sometimes on the side of the abdomen, sometimes just below the hypochondrium. After 2 months, I went to see a therapist, they did an ultrasound of the abdomen and kidneys, they said that there were some salts in the kidneys, but otherwise everything was perfect, and they diagnosed osteochondrosis. After 6 months it got worse. A white coating appeared on the tongue, sometimes it hurts in the stomach and pancreas, the pain and burning remained, recently I had diarrhea with a high fever. Due to the pandemic, I can’t visit a doctor. What can you do to wait until the pandemic is over?
Maria (05/24/2020 at 09:57 pm) Reply to comment
Hello. According to the results of FGSD - chronic distal esophagitis, insufficiency of the cardia and pylorus, the mucous membrane is edematous, hyperemic, with foci of atrophy. According to ultrasound, ABP is diffusely heterogeneous changes in the liver and pancreas, pancreatic polyps. Worrying about thick coating on the tongue that is white, yellow, brown, pain behind the sternum, belching after eating. Treatment: dexilant, itomed, rebagit. The therapist canceled it and prescribed omeprazole and mezim. The infusion of aloe with honey helps noticeably) When I stopped taking it, the pain returned. What to do? Thank you.
Love (07/09/2021 at 16:44) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Why does plaque appear on the tongue?
The tongue is a muscular organ that can tell a lot about the state of the body. It is soft and easily mobile, and has a pale pink color if the person is healthy. From time to time, plaque may appear on the mucous membrane, the density of which is often seasonal. This is explained by the fact that at different times of the year the body needs certain vitamins. For example, in summer the deposits are thicker and more saturated. At this time they may acquire a yellow tint.
Bacteria constantly accumulate on the mucous membrane of the tongue. These microorganisms are the cause of plaque and bad breath.
The following factors contribute to their intensive reproduction:
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- infections and inflammatory processes;
- taking medications;
- chronic diseases;
- poor oral hygiene.
Since the tip of the tongue is mobile, it is cleaned more and, accordingly, there is less plaque here. At the root, its density is higher, since in this place there is contact only with the sky. Such manifestations are also possible with dysbacteriosis, vitamin deficiency, and improper hygiene.
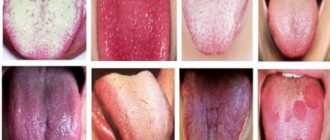
Types of plaque on the tongue
White plaque
A thin white coating is a common occurrence. You can especially notice it in the morning, when your teeth have not yet been brushed. Homogeneous white deposits occur in infants after feeding. This is also considered normal in older children.
The presence of other features may indicate certain ailments:
- an increase in plaque thickness is a symptom of prolonged constipation;
- elevated temperature and symptoms of intoxication - indicate infectious processes in the body;
- localization on the root of the tongue, its back – gastrointestinal diseases;
- placement on the sides of the tip of the tongue - pay attention to the kidneys.
A white coating with a cheesy structure, as well as dry mouth, indicate candidiasis (popularly called thrush). It often affects infants. The cause of the disease is weak immunity. To prevent thrush from spreading to the cheeks and gums, you should consult a doctor. He will prescribe antifungal medications. This disease is also possible in older children, but more often these are asthmatics or children with weakened immune systems. The disease may be accompanied by an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Gray, green and brown plaque
And if the deposits are not white, but of a different color - what is it? Each shade has its own characteristics:
- Grayish
is a common symptom of gastrointestinal diseases. This could be, for example, a stomach ulcer. But a grayish-white coating is not a deviation from the norm. - Brown
. Such deposits on the root of the tongue appear in chronic alcoholism. It also occurs in smokers and with lung diseases. - Green
is a rare occurrence. Occurs with different types of glossitis. The disease can develop as a result of taking antibiotics, steroids and other substances that reduce the body's immune strength.
Please note that the tongue often changes color after eating and drinking. For example, strong tea can turn it brown.
Yellow plaque
As already mentioned, a yellowish coating appears in the summer. You need to worry if its shade becomes saturated. You should pay attention to the following signs:
- Bright yellow color - the liver and bile ducts may be affected.
- Yellowness of the lower part of the tongue is a symptom of incipient jaundice.
- A thick yellow-green coating is a sign of improper functioning of the digestive organs and stagnation of bile. These disturbances in the body may be accompanied by the formation of a red plaque.
Sometimes yellow deposits indicate an increased amount of bile.
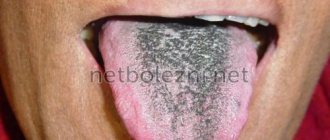
Black plaque
Black deposits on the tongue are very rare. More often this is one of the signs of a serious illness:
- serious disruption of the pancreas, gallbladder, and gastrointestinal tract;
- high blood acidity resulting from dehydration;
- cholera.
- There is such a thing as a “villous” tongue, when the papillae on it turn black and become hard. Such manifestations can be observed in smokers and people who abuse alcohol, as well as when exposed to certain organisms and medications.
Spotted plaque
Geographic tongue, when its mucous membrane is covered with uneven red spots, scares many. This condition occurs in people of all ages. There is no danger in it, and often it goes away on its own.
Today, science does not fully know what the appearance of such spots means. Each case is individual, so it is important to monitor your condition. For example, spots may occur due to an allergic reaction. But in most cases they are then present on the skin.
What does plaque formation mean?
The causes of plaque are related to the oral cavity, internal pathologies and some other factors. The main thing is to avoid staining the organ with food coloring.
Dental reasons
If the tongue is covered with a white coating, this indicates the onset of infection or inflammation in the oral cavity. The most common pathologies include:
- Thrush (candidiasis) . It is the spread of a fungus observed in people with weak immunity, hypovitaminosis, and dysbacteriosis. The proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms on the tongue is facilitated by mechanical trauma to tissues, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and disorders of the thyroid gland. With thrush, the coating on the tongue looks like a curd mass.
- Caries . Its appearance is associated with plaque on the enamel. The destruction of dentin is accelerated by the consumption of sweets and non-compliance with the rules of cleaning the mouth.
- Stomatitis . The inflammatory disease is characterized by the formation of painful ulcers. Its causes are an unbalanced diet, allergies, stress, bacteria, and an imbalance of substances produced by the endocrine glands. Externally, plaque with stomatitis looks like milk or cottage cheese.
- Gonorrhea . A sexually transmitted infection causes pain in the throat and purulent plaque. A white film is visible on the tongue and palate. You can become infected through kisses, towels or dishes.
The color of the tongue may vary depending on the specifics of the disease and its neglect.
Causes not related to the oral cavity
The human body reacts differently to pathologies. Ailments that cause the accumulation of bacteria on the tongue include the following diseases :
- Stomach ulcer . One of the most common gastrointestinal pathologies is characterized by the appearance of scars on the mucous membrane. Provoking factors are stress, increased stomach acidity, prolonged use of medications, and alcohol abuse. Plaque on the tongue appears on the root zone and cannot be removed.
- Pancreatitis . Pancreatic disease is inflammatory in nature and is often caused by drinking alcohol and eating fatty foods. The tongue is white with a yellow tint. Deposits can be densely located throughout the organ.
- Gastritis . Inflammation of the gastric mucosa can be caused by infection, chemicals, malnutrition, chronic stress, hormonal imbalance, and medications. The plaque is white and has a yellow tint.
- Cold . If it occurs with complications, the tongue may turn white. The higher the temperature, the thicker the coating.
- Oncology . In cancer, the immune system is weakened. Malignant tumors are accompanied by weight loss, pain, and lack of appetite. Due to the high number of leukocytes, a white coating of dense consistency appears.
- Diabetes . Disorders of material metabolism require constant monitoring by a doctor and competent treatment. Plaque occurs against a background of nausea, stress, and dry mouth.
- Pathologies of the genitourinary system . Milk spots are located near the root of the tongue and on the sides.
- Liver failure . With this disease, a whitish or yellowish coating is observed that completely covers the tongue. It emits a pungent odor of ammonia.
- Respiratory tract diseases (bronchitis) . Snow coating is visible on the tip and along the lateral surfaces of the organ. A person complains of cough, weakness and fever.
- Gastric carcinoma . The plaque is dense and evenly distributed.
In rare cases, the symptom is associated with genetic and systemic diseases :
- Leukoplakia . Dead cells form plaque and affect the mucous membrane of organs. The pathology often occurs in smokers aged 30-40 years.
- Follicular keratosis . The skin disease provokes inflammation and the appearance of plaques. If you try to wipe off the white coating, wounds may appear.
- Brunauer syndrome . The disease is characterized by palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and problems in the process of keratinization.
If plaque is associated with one of these pathologies, treatment will be required from a specialized specialist followed by consultation with a dentist.
What diseases can be diagnosed by the tongue:
Determining the disease by the color of plaque
The first diagnostician on the condition of the tongue was the Russian doctor M. A. Nechaev, who in 1833 published the book “Recognition of diseases by changes in the language” in the printing house of Kazan University. Several generations of Russian doctors were grateful to him for this unique work, which helped to carry out diagnostics without additional instruments.
Today, the technique is widely used not only among traditional healers, but also among practitioners of traditional medicine. However, the diagnosis must be confirmed after a comprehensive examination carried out in a laboratory, or using ultrasound, CT, MRI, fluoroscopy, etc.
What do you pay attention to during this diagnosis:
- plaque color;
- its consistency.
As for the color of plaque, it can be:
- white;
- grey;
- yellow;
- greenish;
- bluish;
- brown;
- even black.
And the consistency can be:
- almost transparent;
- flaky;
- viscous.
All signs are compared, and a certain diagnostic verdict is made.
Diseases of the oral cavity and plaque on the tongue
Most often, the condition of the tongue depends on the conditions in the oral cavity. The presence of plaque may be due to:
- caries;
- stomatitis with fungal and bacterial etiology;
- periodontal disease – systemic damage to periodontal tissue (gums, bone and tooth ligament);
- glossitis - inflammation of the tongue that occurs as a result of mechanical damage to the organ, or as a condition accompanying other diseases;
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums without damage to bone tissue.
The mucous membrane of the tongue reacts very sensitively to any problems in the oral cavity caused by inflammation, caused by bacterial or fungal infections.
They are diagnosed quite easily:
- A loose white coating indicates that a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida has settled in the mouth.
- The presence of periodontal disease and gingivitis is determined by the condition of the gums.
- The presence of caries is accompanied by an unpleasant odor and putrefactive damage to the bone tissue of the tooth.
- Glossitis is accompanied by a burning sensation, salivation, pain and inflammation.
If everything is more or less clear with these signs, then plaque caused by systemic diseases is not so easy to recognize without special knowledge.
Possible complications
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can prevent the development of complications. If you neglect the pathology, you can provoke the appearance of plaque and face the following consequences :
- gastritis of the stomach;
- ulcer;
- bowel cancer;
- liver cirrhosis.
Complications also depend on the cause of the white plaque:
- Caries . In the future, pulpitis may appear, which is an inflammation of the nerve of the tooth.
- Stomatitis . If this pathology is not treated, it will become chronic. An aphthous form of the disease may develop, affecting a large area of the mucosa.
- Candidiasis . The fungus can spread to organs and cause nephritis, meningitis, and endocarditis.
- Pancreatitis . The disease can cause swelling of the brain and disrupt kidney function.
- Gastritis . Pathology can lead to a decrease in the secretory function of the stomach and impaired absorption of nutrients.
- Cold . The most common complications are otitis media, tonsillitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis.
- Diabetes . The disease can cause damage to the kidneys, liver and even death of the patient.
- Hypovitaminosis . Lack of vitamins can lead to disability.
The prognosis is made individually and depends on the patient’s health status and the advanced stage of the disease. In the case of pathologies such as HIV, it is unfavorable. It is only possible to temporarily support the body and continue to follow body cleansing procedures.
In the absence of quality treatment, serious complications can occur. Therefore, do not risk your health and at the first alarming symptoms, consult a doctor.
What diseases does plaque on the tongue foreshadow?
It is believed that the nature of the disease and its location can be determined by the color of the plaque:
- White plaque is quite acceptable if it is easily removed after hygiene procedures. If it lies in a thick layer and has a cheesy consistency, then this is a sign of fungal infection, intoxication, the presence of foreign bodies in the oral cavity - implants or dentures - and the allergic reactions they cause.
- A gray coating may indicate that a course of antibiotic treatment has been carried out or there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Most often these are ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum. A decrease in general immunity can also be the cause of plaque of this color.
- A yellow coating indicates stagnation of bile or problems with the liver. It can also be observed with kidney damage, then its localization is at the edges of the tongue. Constipation also causes such plaque, in which case bad breath also appears.
- The green color of plaque occurs from excess bilirubin during hepatitis of various etiologies. This may also be a consequence of a viral infection.
- Brown plaque can be a consequence of gastronomic preferences - among lovers of brewed coffee and strong black tea. Heavy smokers also often have a brown coated tongue. Inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal mucosa can cause such plaque.
- A bluish coating is a consequence of problems with the cardiovascular system. This may be coronary heart disease or chronic hypotension.
- A dark, almost black coating should alert you. This is a consequence of a serious pathology in the body - oncology, severe dehydration, rare Crohn's disease or cholera infection.
For adults, a constant coating on the tongue may mean that the person is a heavy smoker. It is difficult to find among smokers those whose organs have not been damaged by nicotine tar. This means that they are no longer healthy.
The most common causes of problems in adults
If the tongue is white, what does it mean? Let's look at the most common causes of white deposits on the tongue.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
All doctors unanimously say that the most common reason for the appearance of a dense white coating on the tongue is pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, it is the white color that indicates the very initial stages of the disease; as they progress, it changes to yellow or gray.
With gastrointestinal disease, a white coating appears and changes to yellow
The most common gastrointestinal disease is gastritis. It is this that signals itself through a white coating appearing on the tongue. Pathology has many forms and varieties:
- chronic gastritis: this is the most common gastrointestinal disease among the world's population. According to statistics, it affects about 50% of adults of both sexes,
- autoimmune type: this is a rare disease accompanied by the appearance of a profuse white coating on the tongue, which turns yellow during periods of exacerbation,
- gastritis with low acidity: if you are a fan of fatty and spicy foods, as well as alcoholic drinks, then the likelihood of getting sick increases,
- hemorrhagic: one of the most dangerous types, because progresses rapidly, contributes to the appearance of erosions on the surface of the gastric mucosa and internal bleeding,
- atrophic: dangerous because it can degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
Less common gastrointestinal diseases are biliary dyskinesia, when dysfunction of the bile ducts leads to either excessive secretion of bile or stagnation. As well as inflammation of the duodenum or duodenitis, inflammation of the small intestine - with these pathologies, teeth marks are noted on the dense layer of plaque along the edges of the tongue.
Dental diseases
Several dental pathologies can signal themselves through a whitish coating on the tongue: glossitis, galvanic syndrome, candidiasis or thrush (manifest themselves as a white curdled coating), stomatitis, oral leukoplakia.
If hygiene does not help - if the alarming symptom does not disappear after this or appears after a short period of time, then consult a dentist-therapist first, and then a general practitioner, i.e. see a therapist. You may need to undergo a comprehensive examination of the body to identify internal diseases.
Infectious lesions
The pathology can be caused by AIDS, HIV infection, diphtheria, gonorrhea, syphilis, and urogenital infection in men. The latter, by the way, is called thrush or candidiasis, just like dental disease, which is less harmless in its consequences, because caused by the activity of Candida fungi.
Lack of saliva
This often occurs against the background of dehydration and dehydration of the body, stress, drinking alcohol and smoking, and physical activity. To get rid of the problem, try to drink more clean drinking water or eat vegetables/fruits with a high liquid content (for example, cucumber, zucchini). And remember that if this is not done, then the lack of salivary fluid, which also performs a protective function for the oral cavity, can lead to increased accumulation of bacterial plaque, the development of caries, gingivitis and other dental diseases.
Plaque in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract, or digestive system, includes:
- oral cavity;
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- liver;
- gallbladder;
- pancreas;
- duodenum;
- small and large intestines;
- rectum and anal sphincter.
Any malfunctions in the organs of the digestive system cause plaque on the tongue:
- if it is concentrated in the area of the root of the tongue and has a gray tint, this means that the large intestine and rectum are affected;
- a thin yellow coating in the middle of the tongue indicates the presence of gastritis or gastroduodenitis, and a thick layer localized in the middle indicates its exacerbation;
- with cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder - a yellow-brown coating appears, while the tongue itself is dry, bitterness and dryness in the mouth are felt;
- if there is a problem with the biliary tract, the plaque can take on a color from yellow to green; it is the greenish shade that indicates that not everything is in order with the biliary system;
- a bluish coating indicates an intestinal infection;
- a thick yellow coating in combination with heartburn, belching and a burning sensation indicates that pancreatitis has worsened - inflammation of the pancreas;
- a reddish-brown, and sometimes even black, coating may indicate oncological processes or abscess inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
In any case, plaque on the tongue is not the main sign of diseases of the digestive system. Only a doctor, having collected an anamnesis, can make the correct diagnosis.
Diseases as the cause of white plaque
If your tongue is always coated and your mouth smells bad, you should be wary. During an in-person examination, the doctor will examine the condition of the oral cavity and make a preliminary diagnosis. It is possible that the patient will have to undergo blood tests and undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, because the most likely cause of the problem described is diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver. They are always the first to be excluded.
Among the pathologies in which the muscular organ becomes covered with a white coating that is difficult to remove:
- Glossitis. Inflammation of soft tissues, leading to changes in the color and structure of the tongue. Has a viral or bacterial nature. The patient experiences swelling, burning, pain when chewing and swallowing food. His diction is also impaired. In advanced cases, the pathology causes phlegmon of the neck.
- Gastritis. Acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach. Manifested by epigastric pain, dyspepsia, nausea, decreased performance. A “telling” symptom of gastritis is plaque on the organ of taste. It is associated with the pathological activity of pathogenic microflora.
- Candidiasis. Mycotic infection of the mouth caused by opportunistic yeast-like fungi Candida albicans. The mucous membranes swell and swell. They bake and crack. The lips begin to peel, and pockets form in their corners. The tongue and throat with thrush are very coated. It gets to the point where the kefir-like slurry can be easily removed with a brush or a teaspoon. But this does not help improve the situation, as soon its volume increases. This happens until medications are taken that destroy candida.
- Chlamydia. The pathology is sexually transmitted and, it would seem, should have nothing to do with oral health. However, in practice everything turns out differently. The violation provokes a sharp decrease in immunity. When the number of chlamydia increases greatly, the oral cavity becomes affected - a sticky white coating appears on its walls.
- Pneumonia. Whitish folds on the sides of the muscular organ most often indicate pathologies of the upper respiratory tract. They can be removed with a brush and paste, but they quickly return as the main provoking factor (pneumonia) continues to act.
- Chronic alcoholism. Alcohol addicts are diagnosed with multiple diseases of internal organs. After binge drinking, they are faced with a white tongue and an unpleasant aftertaste. In this case, the plaque caused by ethanol intoxication never reaches the tip of the tongue and is always localized at its root.
- Lung oncology. Cancer patients with lung damage often have a coated tongue.
The described symptom also occurs among pregnant women. The reason for this is a sharp change in hormonal levels. After childbirth, the situation returns to normal on its own.
Plaque for bronchitis and pneumonia
The area of the tongue immediately following its tip is an indicator of the health or disease of the respiratory system (bronchi and lungs). Based on the condition of this area, one can judge the presence of bronchitis or pneumonia:
- Red spots indicate that pneumonia or bronchial asthma is possible.
- A light film on the front of the tongue indicates the presence of a respiratory allergy or congestion in the lungs.
Plaque on the tongue caused by inflammatory processes of the upper and lower respiratory tract is not decisive in the diagnosis of these diseases.
Plaque due to oral chlamydia and thrush
There are two types of infectious diseases that affect the urogenital organs and the oral cavity. These are chlamydia and thrush. For candidiasis caused by a fungus of the genus Candida:
- a dirty white cheesy coating forms on the walls of the mouth and on the tongue;
- when mechanically cleaning the tongue from plaque, bloody discharge appears;
- an unpleasant putrid odor and taste appear in the mouth;
- treatment with special antifungal drugs is necessary.
Oral chlamydia shows a slightly different picture:
- thick sticky mucus forms in the nasopharynx;
- then it migrates to the upper and lower palate;
- only after this does it appear on the tongue, first in the form of spots, and later covering the entire tongue with a white pasty coating;
- At the same time, it has the smell of rotten fish.
It is diagnosed both by visual examination and by laboratory analysis of scrapings from the tongue and palate.
What else can cause plaque on the tongue?
There are many other reasons that cause plaque on the tongue:
- Chronic alcoholism leads to the development of fatty hepatosis, and later cirrhosis of the liver. As you know, a dirty yellow or even greenish coating on the tongue is characteristic of people suffering from liver diseases. In addition, alcoholics are rarely concerned about body hygiene, much less oral hygiene. This further enhances the coating and odor on the tongue of a person suffering from alcoholism.
- Plaque can occur as a side effect of taking medications, mainly antibiotics. Taken orally, they kill the beneficial microflora of the small and large intestines, causing dysbiosis, accompanied by poor digestion and absorption of food. And this, in turn, leads to the formation of plaque on the tongue.
- Intoxication of any origin necessarily causes a coating on the tongue. Thus, cancer patients after a course of chemotherapy all suffer from a dirty-brown coating on the tongue, which is caused by toxic chemotherapy, as well as tissue breakdown products destroyed by cancer cells.
- Impaired immunity, especially if failures occur in that part of the immune system that is located in the intestines, also leads to the formation of plaque, because T-lymphocytes die, settling in the form of a yellowish coating on the tongue and intestinal walls.
In these cases, consultation with a specialized specialist is necessary.
Reasons: what do different colors mean and say?
| Plaque color | Reason for formation | Which doctor should I contact? |
| White | A thick, white, cheesy coating is a clear sign of a fungal infection. | Dentist, gastroenterologist, immunologist |
| Yellow | Viral infection, gastrointestinal dysfunction, liver dysfunction, slagging in the body. | Gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist |
| Green | Liver dysfunction due to abuse of fatty, fried and salty foods. | Therapist, Hepatologist |
| Orange | Gastritis | Therapist, Gastroenterologist |
| Brown | Malfunctions of the gallbladder, gastrointestinal disorders, alcoholism | Therapist, Gastroenterologist |
| Black | Liver dysfunction, lead poisoning, Crohn's disease. | Therapist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist |
| Blue | Lack of folic acid, heart failure, kidney disease, heavy metal poisoning. | Therapist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, hepatologist. |
| Grey | Complication of bacterial diseases, long-term use of antibiotic drugs. | Therapist, dentist, infectious disease specialist. |
If you are in doubt about choosing a doctor, contact your therapist or dentist first.
Stay up to date! The doctor will prescribe you treatment or give you a referral to a specialized specialist.
Plaque on the tongue in children
In children from birth to 5 years of age, the immune system is so imperfect that a slight coating on the tongue is considered normal. Moreover, a rare baby has avoided thrush, which affects the oral cavity and tongue from the first days of life. But you need to know and be able to differentiate plaque on a child’s tongue in order to recognize dangerous infectious and autoimmune diseases in time and seek medical help:
- Thrush is characterized by a loose, cheesy coating on the tongue and oral mucosa. Cleansing causes the baby to cry because the papillae are hypertrophied and react painfully to touch.
- A dirty gray coating on a child's tongue may be an indicator of scarlet fever. This is an infectious disease that must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. With scarlet fever, the tongue gradually turns from dirty gray to scarlet, similar to strawberries, with characteristic dots along the entire surface of the tongue.
- A filmy coating covering the root of a child’s tongue indicates that he has diphtheria. This sign requires urgent hospitalization, because the disease develops rapidly and leads to suffocation.
- Black or dark brown plaque in babies can be caused by a latent form of diabetes, bacterial sore throat, or taking strong antibiotics.
- There is also such a thing as “geographical language”. It is also typical for young children. These are red spots scattered across the entire surface of the tongue against the background of a light white coating, making the picture resemble a map of the world. In this case, benign migratory glossitis is diagnosed. It occurs against the background of helminthic infestation, vitamin deficiency, acute infectious diseases, and exudative diathesis. Only a doctor can identify the cause of the disease, so you should contact him immediately.
All other causes of plaque on the tongue in children are not much different from adults. These are the same dysbacteriosis, gastritis and even stomach ulcers, problems with the liver and gall bladder.
Should you see a doctor?
Having a general idea of what type of plaque may be associated with a serious illness, it is worthwhile to be guided by it. It should also be taken into account that all serious systemic diseases, in addition to plaque on the tongue, have a number of formidable symptoms that cannot be ignored. It can be:
- pain;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- skin rashes;
- increase in body temperature, etc.
Plaque on the tongue must be taken into account along with other signs and contact a specialist for diagnostic measures.
Liver diseases
The liver is the most important organ of the human body, related in its structure and functions to the endocrine glands. The liver performs a huge number of vital functions, the main one of which is cleansing the blood of toxic, poisonous substances and allergens, as well as removing from the body excess amounts of hormones and compounds hazardous to health: ammonia, ethanol, ketones and their acids, etc.
With any liver disease, a person develops a gray coating on the tongue, which may be accompanied by a change in the color of the skin, mucous membranes, deterioration in general well-being, and pain in the right hypochondrium. The danger of many diseases of the hepatobiliary system lies in their practically asymptomatic course in the early stages, so it is important to know the signs and symptoms of these pathologies and be able to identify them before irreversible changes in the functioning of the liver begin.
Liver cirrhosis disease
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease accompanied by structural changes in the liver with the formation of scar tissue, shrinkage of the organ and a decrease in its functionality. Early symptoms indicating cirrhosis include the following:
- A feeling of bitterness and dryness appears in the mouth, especially often in the morning;
- The patient loses some weight, becomes irritable, and gets tired faster;
- A person may be bothered by periodic stool disorders, increased flatulence;
- Periodically occurring pain localized in the right hypochondrium. They tend to increase after intense physical activity or after taking fatty and fried foods, alcoholic beverages;
- Some forms of the disease, for example, postnecrotic cirrhosis, manifest themselves in the form of jaundice already in the early stages of development.
- In some cases, the disease manifests itself acutely and there are no early signs.
General advice for patients with liver cirrhosis:
- Rest as soon as you feel tired.
- To improve digestion, patients are prescribed multienzyme drugs.
- Avoid heavy lifting (this may cause gastrointestinal bleeding)
- Measure your body weight and abdominal volume at the navel level daily (an increase in abdominal volume and body weight indicates fluid retention);
- If there is fluid retention in the body (edema, ascites), it is necessary to limit the intake of table salt to 0.5 g per day, liquid intake to 1000-1500 ml per day.
Following a diet for liver cirrhosis involves, first of all, avoiding foods that have a high protein content. After all, in patients with liver cirrhosis, the digestion of protein foods is disrupted, and as a result, the intensity of putrefaction processes in the intestines increases. The diet for liver cirrhosis involves periodic fasting days, during which the patient does not eat food containing protein at all.
Prevention and elimination of plaque
The main “commandment” for the prevention of this unpleasant phenomenon is compliance with hygiene rules and regular sanitation of the oral cavity. This concept includes:
- mandatory brushing of teeth in the morning and evening;
- using floss to clean the space between teeth;
- using a toothbrush with a grooved surface, which cleans the surface of the tongue in the presence of plaque;
- the use of mouth rinses, which help get rid of unfriendly bacterial microflora present in the mouth even in absolutely healthy people.
There are many more ways to sanitize the oral cavity in order to prevent unhealthy plaque on the tongue, which you should familiarize yourself with in more detail.
How to properly brush your teeth and tongue
At first glance, the simple procedure of brushing your teeth is so familiar that there is nothing to add. In fact, proper cleansing can protect you from a host of oral diseases and more. After all, the mouth is the “gate” for any viral and bacterial infection. Therefore, it would be useful to recall that:
- You must brush your teeth twice a day – morning and evening;
- Cleaning your teeth should be done from top to bottom for at least 3 minutes;
- Using the corrugated surface of the toothbrush, use careful movements without much pressure to clean the tongue in the direction from root to tip, after each movement the brush is rinsed with running water;
- the evening procedure includes cleaning the space between the teeth with a special dental floss;
- Finally, use an antibacterial rinse, rinsing your mouth thoroughly.
Ideally, you should brush your teeth after every meal.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are used for rinsing and oral administration.
Infusions for oral administration
Anti-inflammatory for the gastrointestinal tract
St. John's wort
For herbal infusion, take the ingredients :
- St. John's wort;
- oregano;
- mint;
- lemon balm;
- 500 ml boiling water.
Preparation:
- Mix dry herbs together.
- 1 tbsp. l. pour boiling water over the mixture.
- After 2 hours, filter the composition.
Take 1 glass twice a day half an hour before meals. The course of therapy is 10 days.
For gastritis
Watch
For gastritis, boil the medicine from the following ingredients :
- watches;
- mint;
- yarrow;
- 200 ml water.
Preparation:
- Mix the herbs together.
- Take 1 tsp. spoon of mixture.
- Fill with water and leave for 15 minutes.
Take 50 ml three times a day.
With flax seeds
Flax seeds
To improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and intestinal motility, try a medicinal decoction. It is prepared from the following components :
- 200 ml purified water;
- 3 tbsp. l. flax seeds.
Preparation:
- Fill the grains with water.
- Boil and simmer for 10 minutes.
- Wait until it cools down.
- After 20 minutes, drain into a container through a sieve.
Take half a glass of the decoction before meals.
Alcohol tincture with propolis
Propolis
Propolis tincture helps with stomach ulcers, gastritis, and liver diseases. It is prepared from the following ingredients :
- 10 g propolis;
- 90 ml of alcohol (70 degrees).
Preparation:
- Grate the chilled propolis and place it in a glass container.
- Fill with alcohol and cover with a lid.
- Place the tincture in a dark place for 2 weeks.
- Shake the contents periodically for better dissolution.
- After 14 days, filter the product.
Drink the tincture in the morning, 20-30 drops dissolved in 50 ml of water. The course of treatment is up to 1 month. It is permissible to buy a ready-made propolis-based product at the pharmacy.
To strengthen the immune system
aloe leaves
To strengthen your immune system, consume a decoction of the following ingredients :
- 150 g aloe leaves;
- 300 g liquid honey.
Preparation:
- Remove the thorns from the aloe.
- Mash the leaves of the plant thoroughly.
- Pour warmed honey over them.
- Leave the product to knock.
- Reheat and strain.
Take the medicine before meals, 1 tsp. spoon.
Antimicrobial infusions for rinsing
With salt and soda
Salt and soda
The simplest and most popular recipe involves the use of the following components :
- 1 tsp. soda;
- 1 tsp. salts (sea, iodized or table);
- 200 ml boiled water.
Preparation:
- Dissolve salt and soda in 200 ml of warm boiled water.
- Stir the grains.
- Cool the liquid.
Rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day. To enhance the effect, you can add 2-3 drops of iodine.
With oak bark
Oak bark
For the recipe you will need :
- 1 tbsp. l. oak bark;
- 300 ml boiling water.
Preparation:
- Pour boiling water over the oak bark.
- Cover with a lid and wait 2 hours.
- Strain the mixture and let it cool.
Rinse your mouth three times a day after each meal. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. Every day you need to prepare a fresh infusion.
With chamomile and sage
Chamomile and sage
An antiseptic decoction is prepared from the following ingredients :
- 1 tbsp. l. chamomile;
- 1 tbsp. l. sage;
- 400 ml water.
Preparation:
- Mix dry herbs and add water.
- Simmer the mixture over low heat for 15 minutes.
- Let the broth brew.
- Filter and let cool.
Use the decoction to gargle 3-4 times a day for 14-20 days. This is an excellent remedy against inflammatory processes.
Carefully! Herbal infusions can stain tooth enamel.
Oil rinse
The oil can eliminate food debris and bacteria.
Rinse your mouth with it for 10 minutes. After this, the surface of the tongue will become lighter. Olive, grape, and sunflower oil are suitable. You can rinse your mouth with rosehip extract, sea buckthorn extract, and aloe juice.
Professional cleaning at the dentist
Even such thorough self-cleaning of the oral cavity is not enough to be sure that you will be free from periodontal disease or caries. From time to time it is necessary to contact a dentist so that he can carry out professional sanitation. Typically it includes:
- preventive examination and assessment of the condition of gums and teeth;
- removal of tartar mechanically or using ultrasonic devices;
- treatment with a special powder mixture to get rid of food pigmentation of teeth, typical for smokers, lovers of strong coffee and tea;
- final flossing to remove tartar fragments from the most difficult to reach places;
- polishing using a special paste to create the most even surface relief of the teeth.
It is recommended to carry out such cleaning every six months, in case of predisposition to caries and periodontal disease - once every 3 months.
Cleaning your tongue with a home irrigator
As an alternative to going to the dentist for professional oral cleaning, you can consider a home irrigator. This is a special device equipped with replaceable nozzles and a reservoir that supplies liquid under pressure to clean the space between the teeth. When choosing an irrigator, you must be guided by the following requirements:
- the number of attachments should be a multiple of the number of family members who will use it, because this is a means of individual use;
- It is highly desirable that the kit include devices for cleaning the tongue and dentures of any configuration;
- it is necessary that the device be equipped with a pressure regulator when supplying liquid, because everyone has an individual level of tooth sensitivity;
- It is better to choose a larger tank volume, this will allow cleaning more efficiently;
- It would be great if it was also equipped with a water supply regulator, that is, it could be a stream of water or a spray.
This device will save you the time and money needed to visit the dentist's office.
Preventive measures
To prevent plaque formation, follow preventive measures , namely:
- clean your tongue and teeth regularly;
- if you have dentures, treat them with antiseptic;
- avoid close contact with people with candidiasis;
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with water;
- follow the vaccination schedule;
- drink drinks based on ginseng and lemongrass;
- carry out hardening under the supervision of a doctor;
- do not take antibiotics without a doctor's prescription;
- immune strength is constantly strengthened;
- do not get carried away with alcoholic drinks and smoking;
- promptly treat gastrointestinal pathologies;
- try to be less nervous;
- Visit your dentist 1-2 times a year for an oral examination.
Particular attention should be paid to your diet. It must be complete and balanced. Eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals, fats and proteins every day.
Include the following products in your menu:
- soups and broths;
- dairy products;
- whole wheat bread;
- fruits and vegetables;
- sauerkraut;
- river and sea fish;
- dried fruits;
- fiber;
- cereal porridge;
- jelly;
- natural juices;
- pasta.
Eliminate from your diet:
- soda;
- alcohol;
- spicy dishes;
- everything is fatty and fried;
- chocolate;
- candies:
- cakes;
- White bread;
- baked goods;
- smoked meats;
- canned food
The following rules for caring for dentures deserve special attention :
- Don't sleep with your dentures on at night. Handle devices with care.
- Clean their surface thoroughly before use.
- Store orthopedic structures in warm water or a special solution.
- Do not use powders for cleaning.
If you suspect problems with the oral cavity, contact your clinic immediately.
3 ways to clean your tongue:
Using rinse aids
You can use rinses to clean your tongue only in conjunction with all other hygiene procedures. The choice depends on the condition of the gums and teeth:
- For loose, bleeding gums, you need to choose a rinse with a high content of fluoride and oak bark extracts.
- Coniferous tree extracts included in the mouthwash thoroughly sanitize the oral cavity, destroying bacteria.
- Zinc chloride, which is part of the mouthwash, helps keep teeth white and prevent the formation of tartar.
Using mouthwash ensures fresh breath.
Colloidal silver is a natural antiseptic
It is advisable to have colloidal silver in your home medicine cabinet, which is an excellent antiseptic and antibiotic. It destroys bacteria, fungi, and viral infections.
It can be used to treat your hands, mouth, and even be taken orally. The product is a suspension of silver microparticles in distilled water. They treat wounds with it, and rinse the mouth with the solution for any problems with the oral cavity, including plaque on the tongue.
Propolis tincture to cleanse the tongue
Propolis tincture, which can be purchased at any pharmacy, does an excellent job of sanitizing the oral cavity. It is used:
- for rinsing - prepare a solution at the rate of 15 ml of tincture per 100 ml of water and rinse your mouth after each meal;
- to clean the tongue - use undiluted tincture, apply to a tampon and clean the tongue from root to tip, changing the tampon each time.
Before you start cleaning with propolis tincture, you should test for an allergic reaction. Use a cotton swab soaked in the solution to clean a very small area of your tongue. Wait at least 12 hours for the reaction. If no manifestations of allergies occur, then you can clean the surface of the entire tongue.
Herbal decoctions to get rid of plaque on the tongue
Using herbal decoctions to sanitize the oral cavity is a great idea. But it is unreasonable to expect that simply rinsing will get rid of plaque on the tongue. Decoctions of medicinal herbs should only be used in combination with other cleaning methods. Herbal decoctions are ideal for rinsing the mouth:
- from oak bark;
- calendula;
- sage;
- chamomile;
- peppermint;
- lemon balm.
It is not difficult to prepare such a decoction:
- Buy a herbal mixture or use a monocomposition at the rate of 1 teaspoon of herbs or herbal mixture per 100 ml of water.
- Pour boiling water over it and leave over low heat, avoiding boiling, for 10–15 minutes.
- Cool and strain.
The decoction can be used to rinse your mouth after mechanical sanitation.
Method of mechanical tongue cleaning
Mechanical methods of getting rid of plaque on the tongue include:
- cleaning with the grooved side of a toothbrush or a special brush;
- the same action using a special scraper in the form of a plastic ring;
- cleansing with a teaspoon or a special scraper that resembles one.
The method of application is simple - you need to scrape off the plaque from root to tip, each time rinsing the scraper under running water.
The main thing here is not to overdo it. Do not press too hard on the tongue to avoid damaging the papillae and causing bleeding. After mechanical cleaning, be sure to rinse your mouth with a decoction of herbs, mouthwash or colloidal silver solution.
Cleansing the mouth with vegetable oil
This method of cleansing the oral cavity from any infectious lesions was known to our forefathers. It will help not only get rid of plaque, but also solve problems with caries, periodontal disease, and gingivitis. There are no contraindications for it, and the benefits will be obvious after the first procedure. The essence of the method is as follows:
- In the morning on an empty stomach or in the evening, 3 hours after the last meal, take 1 tbsp into your mouth. a spoonful of unrefined vegetable oil.
- Next, for 10 minutes, you need to rinse your mouth with this oil through closed teeth, without swallowing it.
- Ideally, the oil should turn white or dirty gray depending on your health.
- The oil is spat out, and the mouth is rinsed with water or herbal decoctions.
This procedure brings tangible results - bad breath disappears, plaque disappears, gums become stronger, and teeth become healthy and shiny. General well-being improves.
How to use saline or soda solution
You can also use a saline or soda solution only in combination. This procedure alone will not bring the desired result. But this solution is quite suitable as a rinse.
It is enough to dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda or ½ teaspoon of salt in 200 ml of boiled water, cool to room temperature and rinse the mouth after mechanical cleansing of plaque.
You shouldn't self-diagnose. If you have any suspicious symptoms, consult a specialist.
Treatment
The stages of plaque treatment look like this:
- Eliminating the cause.
- Relieving symptoms.
- Strengthening the body and restoring immunity.
- Compliance with preventive measures.
To remove plaque from your tongue, use folk remedies and therapy prescribed by your doctor. Do these activities at home :
- beware of nervous tension;
- keep your mouth clean;
- practice aromatherapy.
First, you need to devote enough time to hygienic maintenance of the oral cavity. Clean the plaque from the hyoid bone to the tip, covering the entire surface of the organ. To do this, use a small spatula.
You can use a brush with a special pad that has a soft texture. Treat the enamel of the teeth, and then change the position of the brush and clean the mucous membrane.
The main thing is not to overdo it, so as not to accidentally induce vomiting. Sharp objects or iron spoons should not be used. After each meal, treat your mouth with disinfectants.
Important! A large number of bacteria are collected on the back of the tongue, because this part is little active. It needs to be processed more carefully.
When removing a light film from a baby’s tongue, it is necessary to take into account his age :
- For infants, remove plaque using a piece of clean gauze;
- For a baby over 1 year old, remove plaque with a toothbrush;
- For a child over 3 years old, prepare a rinse solution.
Do not try to cure the disease yourself, so as not to worsen the problem.
Video about getting rid of plaque:
Treatment options depending on the cause of the problem
Treatment methods for white plaque can be seen in the table:
| Reason for the raid | Treatment Options |
| Taking medications | Within 1-2 days after stopping the medications, the plaque will go away on its own |
| Worms | Eliminated using medications |
| Smoking and alcoholic drinks | Requires giving up bad habits |
| Diseases in the oral cavity | Local anti-putrefactive drugs are used, oral hygiene is maintained, and junk food is required. |
| Scarlet fever | A course of antibiotic drugs from the penicillin group and rinsing with antiseptics are indicated. |
| Hypovitaminosis | The introduction of the necessary vitamins into the body is prescribed. |
| Gastrointestinal pathologies | The gastroenterologist prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs, enterosorbents, a course of vitamins and prokinetics |
| Liver failure | Treatment involves eliminating stress, drug therapy, and a strict diet. |
Typically, plaque disappears from the surface of the organ when the primary factor is eliminated.