Pain under the shoulder blade
- a fairly typical localization of back pain, although it is much less common than, for example, lower back pain.
The scapula is a flat bone, approximately triangular in shape, adjacent to the back of the chest in the area from the 2nd to the 8th rib. The shoulder blades tend to protrude slightly, forming the relief of the back, so we all know where they are and describe pain in relation to the shoulder blade if we feel it in the upper back to the right or left of the spine. Pain under the shoulder blade
Pain in the shoulder blade area can be caused by various reasons. A simple indication of what hurts under the shoulder blade is not enough to determine what caused the pain, which means you cannot self-medicate without visiting a doctor and establishing the nature of the disease. At the same time, pain under the shoulder blade can be caused by very serious diseases, so if you experience severe or recurring pain under the shoulder blade, you should definitely consult a doctor. Don't expect the problem to go away on its own.
If you have pain under the shoulder blade, you need to pay attention to other symptoms, this will help the doctor make a diagnosis.
Causes of pain between the shoulder blades
In some cases, the patient complains that he has pain between the shoulder blades. Such localization is typical, first of all, for diseases of the thoracic spine - osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, spondyloarthrosis, intervertebral hernia, protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Also, pain between the shoulder blades can be observed with coronary heart disease, intercostal neuralgia, and gastrointestinal diseases.
The causes of pain that cause pain under the right or under the left shoulder blade are different.
Causes of pain under the left shoulder blade
Pain under the left shoulder blade can be due to the following reasons:
- incorrect position while sleeping. In this case, a person wakes up with pain under the left shoulder blade and in the left shoulder. This pain usually goes away quite quickly;
- stomach ulcer. Peptic ulcer is a fairly common cause of pain under the left shoulder blade. In this case, the pain, as a rule, is aching in nature, gradually increasing, accompanied by gagging, heartburn and belching. After vomiting there is usually relief. As a rule, with a peptic ulcer, the onset of pain is associated with food intake;
- stress, panic and other psychological reasons. Psychogenic pain is described as congestion, compression, heaviness; may be accompanied by fever or a tingling sensation. Sometimes dizziness or a feeling of a lump in the throat is added. In this case, the pain is localized in the chest, and radiates under the left shoulder blade (people say “gives away”). The pain can spread wider, involving the shoulder blade itself, the neck, turning into a headache;
- heart diseases such as myocarditis, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction. A heart problem is very likely if there is pain both under the left shoulder blade and behind the sternum;
- osteochondrosis. With osteochondrosis, pain often occurs in the morning, that is, a person wakes up with pain. Patients in this case often say that the pain under the shoulder blade radiates to the arm or head;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- inflammatory lung diseases, in particular pneumonia.
This list contains the most common causes; the full list of causes of pain under the left shoulder blade is much longer.
Therapeutic measures in a hospital setting
It is not recommended to treat yourself. It is better to seek the help of specialists and undergo complex treatment, which will be selected by the doctor according to an individual scheme.
Complex therapy involves the use of medications in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises.
If there is an inflammatory process, the doctor prescribes a course of NSAIDs (Movalisa, Dicloberla). To eliminate muscle spasms, muscle relaxants (Baralgin, Mydocalm, Sirdalud) are indicated. When the cause of pain in the interscapular area lies in problems with internal organs, the doctor selects medications from certain pharmacological groups. In this case, antibiotics, hepatoprotectors, diuretics, analgesics, etc. are indicated.
Along with medications, physiotherapeutic procedures may be recommended:
- laser therapy;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis using lidase and novocaine;
- massage;
- magnetic therapy.
The gymnastic complex is prescribed on an individual basis, taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, the nature of the pain, and the patient’s well-being.
Causes of pain under the right shoulder blade
The most common causes of pain under the right shoulder blade are:
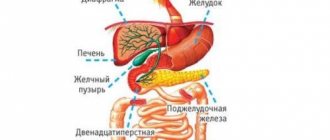
- problems of the biliary system. Acute pain under the right shoulder blade can be observed with acute cholecystitis or cholelithiasis. The usual localization of pain in this case is in the right hypochondrium. The pain may radiate to the scapula or right shoulder. Associated symptoms are a bitter taste in the mouth, heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- kidney diseases – nephritis, pyelonephritis. In this case, pain under the right shoulder blade is usually accompanied by pain in the lumbar region;
- liver diseases. The liver is located in close proximity to the right shoulder blade, and liver problems often lead to pain in this area;
- coronary heart disease (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction);
- osteochondrosis.
Also, pain under the right shoulder blade can be caused by other reasons, among which there are very dangerous diseases - aortic aneurysm, appendicitis and some others.
Diagnostics
The initial examination is carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist, who, after a physical examination, notices poor posture, curvature of the spinal column and other problems of the musculoskeletal system. If the pain between the shoulder blades is not associated with bone pathology, the patient is consulted by a cardiologist, neurologist, or gastroenterologist. To find out the etiological factors of back pain, instrumental studies are prescribed:
- X-ray of the spine.
Based on the results of the x-ray, the doctor determines the degree of scoliosis, the presence and severity of kyphosis or lordosis. The method is informative for diagnosing thoracic osteochondrosis and helps visualize post-traumatic bone changes. To detect intervertebral hernia, radiography or MRI of the spine is supplemented. - X-ray of the OGK.
The standard research method allows us to exclude pulmonary diseases as one of the causes of pain between the shoulder blades. X-ray imaging also shows widening of the mediastinal shadow and signs of subcutaneous emphysema, which gives the doctor the right to diagnose mediastinitis. - EFGDS.
To confirm the esophageal etiology of pain, an endoscopic examination of the esophagus is performed. During the examination, the gastroenterologist pays attention to the patency of the organ, the coherence of the sphincters, and studies the condition of the mucous membrane of the organ. Biopsies are taken from suspicious areas for histological analysis. - Ultrasound angioscanning.
Ultrasound scanning of the aorta is used as a screening method for detecting inflammatory changes and aneurysms. To assess the condition of the thoracic region, transesophageal echocardiography is performed. The diagnosis of dissecting aneurysm is confirmed by an x-ray method - aortography. - Laboratory methods.
They play a supporting role in the diagnostic search. Patients undergo a standard complex: hemogram, biochemical blood test, test for hepatitis and HIV infection. According to indications, a coagulogram is performed. In case of a possible acute inflammatory process, data on acute-phase indicators are informative. In patients with suspected ankylosing spondylitis, the HLA-B27 antigen is determined.
Given the variety of causes of interscapular pain, additional testing may be required. If there are disorders of the upper respiratory tract, consultation with an otolaryngologist and a complete ENT examination are necessary. If a malignant tumor of the mediastinum is suspected, oncologists are involved in the diagnosis.
Manual therapy for back pain
Causes of pain between the shoulder blades
In some cases, the patient complains that he has pain between the shoulder blades. Such localization is typical, first of all, for diseases of the thoracic spine - osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, spondyloarthrosis, intervertebral hernia, protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Also, pain between the shoulder blades can be observed with coronary heart disease, intercostal neuralgia, and gastrointestinal diseases.
When you need a doctor for pain under the shoulder blade
If the pain under the shoulder blade appeared for the first time and quickly passed, then it was probably associated with an accidental cause - for example, the body was in an uncomfortable position for a long time. If the pain persists, intensifies or causes discomfort (in case of severe pain), you should definitely consult a doctor.
In some cases, emergency medical attention is required. Call an ambulance if:
- pain under the shoulder blade is associated with injury. Especially in the presence of bleeding and signs of bone fracture;
- along with pain, deformation, swelling, edema or redness in this area is observed;
- pain is accompanied by increased heartbeat, difficulty breathing (shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air);
- the pain is accompanied by dizziness and faintness.
Pain under the shoulder blade: which doctor should I contact?
Treatment of pain under the shoulder blade
If you complain of pain under the shoulder blade, it is recommended to consult a general practitioner (general practitioner or family doctor). It is the general practitioner who must determine which specialists should be examined.
If the pain under the shoulder blade is associated with eating, accompanied by heartburn, belching, or a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, you will probably need to consult a gastroenterologist.
If there is reason to believe that the pain is related to the spine, for example, if the pain intensifies with movement of the torso or shoulder, then you will be referred to a neurologist, vertebroneurologist or chiropractor.
You must be prepared that you may need to consult a cardiologist or urologist.
Treatment of pain between the shoulder blades
In the vast majority of cases, conservative therapy is initially prescribed. It is especially effective when intervening during the pathological process in the early stages and allows you to completely eliminate the changes that have arisen. Only if severe complications develop, the patient is immediately referred for consultation to a neurosurgeon, since in case of sequestered intervertebral hernia, severe curvature of the spine or advanced spondylosis, the patient’s condition can only be improved through surgery. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible if pain occurs between the shoulder blades.
Conservative therapy is always comprehensive and involves taking measures to improve the patient’s well-being, as well as eliminating the cause of discomfort. Its main components are:
- drug therapy;
- osteopathy;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy (phonophoresis, carboxytherapy, ozone therapy, RF current pressure therapy);
- individual sessions with a rehabilitation doctor.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, neurologists recommend that patients reconsider their habits and lifestyle, in particular:
- normalize weight (but strict diets and excessive physical activity are unacceptable; a transition to a balanced diet and moderate physical activity is recommended);
- refuse to lift and carry heavy objects, grueling workouts in the gym;
- workers in “sedentary” professions should increase their level of physical activity, do a warm-up every hour, and walk more;
- buy an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- introduce into your daily diet foods rich in vitamins and minerals (fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, etc.).
Regular swimming has a very positive effect on the condition of the spine and the body as a whole. Usually visiting the pool 2-3 times a week is enough.
Drug therapy
The main goals of drug therapy are to eliminate pain between the shoulder blades, inflammation and activate the body's recovery processes. For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, widely used both to relieve various types of inflammatory processes and to eliminate pain;
- corticosteroids are drugs that have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and are prescribed to patients with severe inflammatory processes that cannot be eliminated with NSAIDs;
- muscle relaxants - medications that help eliminate muscle spasms caused by pain of vertebrogenic origin;
- chondroprotectors are drugs used in the initial stages of degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs and help restore their elasticity and strength. To prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system, we recommend to our patients the most effective drug Mermaids Marine Collagen;
- B vitamins – agents used to improve nerve conduction and improve the functioning of internal organs;
- vitamin D is a remedy responsible for the condition of bone tissue, as well as for higher brain functions, such as memory, attention, speech.
If the patient has detected pathologies of the heart, gastrointestinal tract and others, additional treatment is prescribed, which involves the use of antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, antihypertensives or other drugs.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy can be called the basis of the treatment of spinal diseases. It should not be confused with therapeutic massage. If the latter only allows you to improve the condition of soft tissues and activate blood circulation, then manual therapy involves the direct impact of a specialist’s hands on the spine.
Thanks to the use of certain techniques of manipulation, mobilization, post-isometric relaxation, osteopathy and especially the Gritsenko technique, it is possible not only to restore the correct position of the vertebrae and the straightness of the spinal column, but also to increase the distance between them to the optimal value. Due to this, the pressure on the intervertebral discs sharply decreases, which creates optimal conditions for their regeneration. Also, a chiropractor can eliminate the pressure of various anatomical structures on the spinal roots, due to which the radicular syndrome is overcome, i.e. pain in the hands, sensory disturbances, a feeling of numbness go away, and the functioning of the pelvic organs also normalizes. There are no general standards of treatment in our clinic; an individual approach is applied to each patient.
In addition, manual therapy allows you to eliminate functional blocks and muscle spasms, which has a beneficial effect on a person’s mobility and well-being. Since normalization of muscle tone reduces pain between the shoulder blades, improves tissue trophism and transmission of nerve impulses. The manual effect itself, as well as with therapeutic massage, has a beneficial effect on the quality of blood circulation. Thanks to this, all tissues receive the maximum of the substances they need, subject to the correct diet and taking medications prescribed by a doctor, which contributes to their speedy recovery.
An additional “bonus” of manual therapy carried out according to the Gritsenko method is strengthening the immune system and enhancing the body’s adaptive abilities. Patients may notice the first improvements in well-being after the first session. But to obtain the maximum possible, and most importantly, lasting result, you need to undergo a full course of treatment, the duration of which is selected individually.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed outside the acute period of the disease. With their help, you can potentiate the effect of other therapeutic measures, as well as achieve analgesic, anti-inflammatory, reparative, antispasmodic effects, as well as improve microcirculation in tissues.
Often, for spinal pathologies, courses are indicated:
- electrophoresis;
- traction therapy;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF, etc.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy is an essential component of the treatment of almost any disease. It involves daily performance of a set of exercises individually developed by a rehabilitation doctor that will help normalize muscle tone, activate blood circulation and increase the flexibility of the spine.
It is important not to use the complexes presented on the Internet, but to contact a specialist who will individually develop a training program for a specific patient. In this case, it will take into account not only the peculiarities of the condition of the spine, but also the age of the patient, any concomitant diseases he has, as well as the level of physical fitness, which will allow achieving the maximum effect from the exercises and eliminating the possibility of harm to the person.
The first classes are recommended to be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. This is necessary so that the patient can fully master the technique of performing each exercise and perform it correctly in the future at home. During exercise, it is important to avoid any sudden movements and overexertion, and if pain occurs, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Thus, pain between the shoulder blades may indicate the development of serious diseases. Therefore, when it appears, you should not hesitate to contact a specialist, otherwise the disease can lead to complications of various types, including disability. If you start treatment right away, you can almost always quickly achieve complete recovery of the body and eliminate the pain syndrome, along with the causes that cause it.
5 1 vote
Article rating