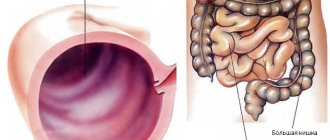
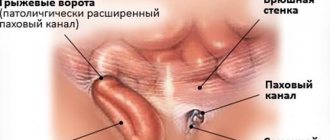
Anal fissure is one of the most common proctological problems associated with a violation of the integrity of the structure of the anal mucosa. The tissue rupture, which mainly forms on the back wall of the anus, can have different lengths and depths, but usually its length reaches 1-2 cm. Over time, the crack changes: granulation, “tubercles” form at the edges, which can later turn into a fibrous polyp . This pathology is encountered by people aged 20-60 years, but in females this disease is diagnosed much more often.
Causes
There are a number of factors that contribute to the appearance of anal fissures. These include:
- Constipation. Constant defecation of hard feces is fraught with the appearance of microcracks and damage to the anal tissues. When a person pushes, pressure increases in the anus, which can result in tissue rupture and cracks.
- Proctitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane). Inflammatory processes make the mucous membrane less durable and, therefore, more vulnerable to injury from feces.
- Childbirth. The mucous membrane can crack as a result of too active pushing, the use of vacuum and other manipulations.
- Poor nutrition. If food (nuts, seeds, etc.) is poorly chewed, then it may not be completely digested in the future. As a result, remaining sharp pieces of food can damage the mucous membrane during bowel movements.
- Increased power loads;
- Sedentary work;
- Examination of the intestines through the anus;
- Anal sex;
- An unbalanced diet - excessive consumption of spicy foods and alcohol.
Symptoms and clinical course of the disease
An acute anal fissure appears suddenly after exposure to one or more unfavorable factors (exacerbation of hemorrhoids, prolonged diarrhea or constipation, dietary errors, alcohol abuse). The disease makes itself felt by acute pain, which intensifies during bowel movements.
The pain is accompanied by the appearance of fresh blood on stool, toilet paper or underwear, but significant bleeding is rare.
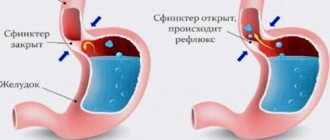
Acute pain causes a reflex spasm of the muscles of the internal anal sphincter, which disrupts the blood supply to the tissues and complicates the independent healing of the mucosal defect.
With a long course of the pathology (4 weeks or more), the edges of the crack thicken, so that healing becomes impossible even when the spasmodic internal sphincter relaxes. The disease takes a chronic course and can last for the rest of your life.
Complications
Every time you defecate, the wound comes into contact with feces, which contain a huge amount of bacteria. Pathogenic microorganisms settled on the crack aggravate inflammatory processes.
If left untreated, the consequences can be very different:
- Bleeding, which may cause anemia;
- The chronic form is a predisposing factor to the formation of tumors;
- Infection of the wound is fraught with the development of paraproctitis or sepsis;
- A prolonged inflammatory process is dangerous due to the formation of fistulas.
Surgical methods
The main goal of surgery for anal fissure is to create conditions for successful self-healing of the wound defect. In chronic pathology, healing is hampered by rough edges and deposits (granulation) at the bottom of the wound. Therefore, the edges of the crack are excised and granulations are removed, transforming the old wound into a fresh one.
In 30% of cases this is enough to get rid of the disease. The use of laser surgery allows operations to be performed on an outpatient basis, without placing the patient in a hospital.
However, most patients develop persistent spasm of the internal sphincter, which impairs blood supply to injured tissues and prevents wound healing. Therefore, the classic method of surgery for anal fissure is a combination of excision of the fissure with sphincterotomy (partial dissection of the internal sphincter).
Diagnostics
The presence of an anal fissure can be determined during a visual examination - the doctor can easily identify swelling and disorders of the mucous membrane. A finger examination allows you to determine the crack located inside by determining its size and feeling the edges.
Diagnostic methods
- Sigmoidoscopy - allows you to assess the condition of the rectum at a distance of 20-25 cm from the anus. During the procedure, tissue can be excised for histology, identified tumors can be removed, and medication can be administered;
- Anoscopy is an informative technique that allows you to examine the anal canal at a distance of 10-12 cm. Using an anoscope you can detect polyps, inflammatory processes, bleeding and other pathological changes;
- Laboratory tests - the patient is sent for a general clinical analysis of blood, feces and urine, culture for flora, etc.;
- Taking an anamnesis allows you to exclude other possible diseases.
Diagnosis and choice of treatment tactics
The diagnosis of anal fissure is established during the initial examination by a proctologist. For long and deep cracks, doctors prescribe anoscopy.
During the examination, indications for surgery are revealed: • rough edges of the crack; • symptoms of prolonged sustained spasm of the internal sphincter; • presence of hemorrhoids requiring surgical intervention.
If surgery is to be performed, the doctor will prescribe a standard list of diagnostic procedures (general blood test, coagulogram, ECG, laboratory tests for infectious diseases transmitted through blood (hepatitis, HIV, etc.), consultation with a therapist, fluorography of the chest organs, and for women also receive a report from a gynecologist).
Treatment
Treatment of acute anal fissure
In this case, conservative treatment methods are used, involving the use of special ointments, suppositories, and laxatives. Drug therapy is aimed at:
- Anesthesia;
- Relieving anal spasms;
- Normalization of stool;
- Healing of the wound (crack).
If conservative treatment does not achieve the desired effects, then minimally invasive methods can be used.
Treatment of chronic anal fissure
If the disease has become chronic, then most likely, surgical intervention will be required - removal of granulation and cutting off the tubercles. Further treatment continues using conservative methods.
Treatment methods:
- Radiosurgery – targeted removal of damaged tissue using the Surgitron radio wave apparatus;
- Pararectal blockade - injection of an anesthetic with a syringe and further divulsion - expansion of the anal sphincter to relieve spasms.
Branch
An anal fissure is a defect in the form of a tear or open wound (ulcer) in the lining of the anal canal.
The anal canal is the final part of the large intestine, located between the rectum (the reservoir of stool) and the anus, through which stool passes out.
Symptoms of anal fissure
The most common symptoms are:
- acute pain at the time of defecation, which is accompanied by burning pain and can last for several hours.
- bleeding after bowel movements, which most people characterize as a small amount of scarlet blood in the stool or traces of blood on toilet paper.
When to go to the doctor
Go to the doctor if you think you have an anal fissure. Put aside the embarrassment, the problem of anal fissure is the third most common problem in the structure of diseases of the colon.
In most cases, anal fissures do not require any specialized treatment. However, contacting a specialized specialist will help rule out other diseases that occur under the guise of an anal fissure.
The doctor will also provide recommendations for individual treatment that will help relieve your symptoms and reduce the risk of relapse of the disease.
How is an examination performed for anal fissure?
The doctor will ask you about your symptoms and find out the nature of your pain. He may ask you about the frequency and nature of bowel movements. And, for sure, the doctor will need to examine the crack itself, by carefully spreading the buttocks.
When diagnosing an anal fissure, digital examination of the rectum is not always performed, as it can be painful.
If, in the opinion of a coloproctologist, an anal fissure is a manifestation of any of your other diseases, he can expand the examination and involve other specialists in consultation.
An extended examination may include a more detailed examination of the anus using an anesthetic to reduce pain.
In some cases, with fissures that are not amenable to conventional treatment, it is necessary to assess the tone of the anal sphincter (the sphincter is a muscular ring that opens and closes the anus).
What causes anal fissure?
— Constipation is the most common cause. Hard or large-volume fragments of feces damage the lining of the anal canal.
Other possible causes of anal fissures include:
- prolonged diarrhea.
- inflammatory diseases of the colon such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
- pregnancy and childbirth.
- in some cases, sexually transmitted infections such as syphilis and herpes.
- a state of strong contraction (spasm) of the anal sphincter, leading to increased pressure in the anal canal, which contributes to its damage.
In many cases, the cause of an anal fissure is difficult to determine.
Who gets sick?
Every tenth person will develop anal fissure at one time or another in their lives.
Men and women of all age groups are equally prone to the formation of anal fissures. However, in most cases, cracks occur in children and young people aged 10 to 30 years.
Treatment and prevention of anal fissures.
Anal fissures usually heal within a few weeks or more without any treatment. However, the relapse rate is very high if the underlying cause of their occurrence, constipation, persists.
In some patients, symptoms of anal fissure may persist for 6 weeks or more (chronic form of the disease).
Measures taken independently by patients aimed at making stool easier can speed up the healing of existing cracks and reduce the risk of developing new cracks in the future.
To reduce pain, you can take regular painkillers (paracetamol or ibuprofen). Take warm baths for the perineum several times a day, preferably immediately after bowel movements during bowel movements.
Your doctor may recommend additional medications that will reduce the severity of your symptoms and help speed up the healing process.
The treatment regimen may also include pain-relieving ointments and laxatives, which make bowel movements easier.
Surgical treatment may be recommended for long-term non-healing cracks that are not amenable to conservative measures.
Surgery is an effective treatment for anal fissure in most cases. But, like any other operation, it can lead to complications, such as temporary or permanent loss of bowel control (incontinence of stool and gas).
Treatment of anal fissures.
Like any minor cuts or breaks in the skin, anal fissures often heal on their own within a few weeks.
However, if you have an anal fissure, it is better to consult a doctor who will prescribe you the necessary treatment, which will help you quickly get rid of the symptoms of the disease and make a full recovery.
Most anal fissures can easily recur after conservative treatment if you do not follow the recommendations below.
Independent activities.
There are several independent measures to relieve constipation, which in turn helps reduce pain with anal fissures.
Eliminating constipation allows you to heal an anal fissure and reduce the risk of its further development in the future.
Self-help measures to relieve constipation:
- Increase your daily dietary fiber intake by including high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Avoid dehydration, drink more fluids and just water.
- Get more exercise. For example, take a daily walk or jog.
- Choose a convenient place and time when you can comfortably go to the toilet to have a bowel movement.
- Don't put off going to the toilet if you feel the urge to defecate.
- If you use wet wipes, make sure they do not contain fragrances or alcohol, which may cause discomfort or itching. If you use toilet paper, choose a soft variety and avoid using too much pressure when wiping.
- Take warm perineal baths several times a day, especially after bowel movements. This helps relieve spasm of the anus muscles.
Drugs.
There are a number of different medications that can be recommended by your doctor to reduce the symptoms of an anal fissure and speed up its healing.
Laxatives
Laxatives are a group of medications that promote freer passage of stool.
Adult patients with anal fissure are prescribed drugs that increase the volume of intestinal contents and osmosis.
Children with anal fissure are prescribed liquid forms of osmotic laxatives.
As a rule, treatment begins with small doses of laxatives. If necessary, the dose of the drug is increased every few days until loose, soft stools are established with a frequency of 1 time per day or 1 time every 2 days.
Attention! Without dieting, laxatives only help for a limited period of time. Do not use them for more than 7-10 days.
Painkillers
If you have prolonged burning pain after bowel movements, your doctor may recommend regular over-the-counter pain relievers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
But remember that some painkillers can cause constipation. Read the instructions carefully.
Ointment with nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate)
If your symptoms do not go away within a week or two, you may be prescribed a topical ointment containing nitroglycerin. The ointment is applied directly to the crack area, usually 2 times a day.
Glycerin ointment promotes the expansion of blood vessels in the tissues surrounding the anus, which promotes better blood supply to the tissues in the fissure and, as a result, faster healing.
The use of these ointments leads to a decrease in pressure in the anal canal by relieving muscle spasms, which helps reduce pain.
Most acute anal fissures that last less than 6 weeks are cured with nitroglycerin ointment. In approximately seven cases of chronic anal fissure out of ten, with the correct use of nitroglycerin ointment, recovery occurs.
A common side effect of using nitroglycerin ointment is headache, occurring in 50% of patients.
Some patients experience dizziness or slight disturbances of consciousness after applying nitroglycerin ointment. Therefore, the ointment should be used with caution in children, pregnant and lactating women.
If you are bothered by headaches, you should reduce the amount of ointment applied. Using a small amount of ointment 5-6 times a day may be more effective than applying a large amount of ointment twice.
Apply the ointment only to the skin around the anus. Avoid getting the ointment into the anal canal.
As a rule, the duration of treatment with nitroglycerin ointment is approximately 6 weeks or continues until the crack is completely healed.
Local anesthetics
If you are experiencing severe pain, you may be advised to use a local anesthetic to reduce the sensitivity of the anus before bowel movements.
Local anesthetics are applied directly to the affected area. Their use does not have a direct therapeutic effect, but helps relieve pain.
The most commonly used anesthetic to treat anal fissure is lidocaine. Used as an ointment or gel. The duration of treatment is 1-2 weeks. As a rule, healing occurs within this time frame.
Calcium channel blockers
Calcium channel blockers, such as Diltiazem, are drugs commonly used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
At the same time, the effect of calcium channel blockers extends directly to the tissues around the anus, providing a proven positive effect in the healing of anal fissure in some patients.
Topical use of calcium channel blockers helps relax the anal sphincter muscles and improve blood flow in the tissues surrounding the anal fissure.
Side effects of calcium channel blockers include headache, dizziness, itching and burning at the site of application. All side effects of the drug disappear within a few days after use.
Topical calcium channel blockers are as effective as nitroglycerin ointments and are prescribed when other drugs do not help.
The duration of treatment with topical calcium channel blockers, as well as nitroglycerin ointment, lasts on average 6 weeks or until complete healing.
Botulinum toxin injections
The use of botulinum toxin in the treatment of anal fissure is a relatively new method of treatment. The method is used when other treatment methods are not effective. Botulinum toxin is a strong poison that is safe to use in small doses.
Botulinum toxin injections for anal fissure are performed in order to achieve paralysis of the anal sphincter muscles. This prevents muscle spasm, relieves pain and promotes healing of the crack. Currently, evaluation of the effectiveness of botulinum toxin in the treatment of anal fissure is ongoing.
The effect of botulinum toxin lasts for 2-3 months. This time is usually enough for the anal fissure to completely heal.
Observation
After several weeks of treatment, you should visit your doctor again. He will objectively assess the dynamics of the disease.
If the crack has completely healed, your doctor will schedule a follow-up examination in a few weeks.
If your anal fissure is a complex case and does not respond to treatment within 8 weeks, a consultation with a coloproctologist is necessary. He will assess the presence of indications for surgical treatment.
Operation
Surgical treatment is recommended if conservative treatment methods are ineffective.
Surgery is considered the most effective method for anal fissure, allowing to achieve good long-term results in 90% of cases. At the same time, there is a risk of complications.
There are a number of surgical operations used for anal fissure.
Lateral sphincterotomy
The lateral sphincterotomy technique involves making a small incision in the circular muscles of the anal sphincter, which reduces tension in the anal canal. Reducing stress promotes healing of the damage and reduces the chances of cracks reoccurring.
This is a relatively simple operation that is performed under general or epidural anesthesia. This means that you do not feel pain during the operation. Most often, the patient is in the hospital for the duration of the operation and a short period after the operation.
Lateral sphincterotomy is one of the most effective surgical methods for treating anal fissure with good long-term results. Most operated patients recover completely within 2-4 weeks.
Some patients (about 5%) who have undergone such an intervention are faced with the problem of incontinence of loose stools and gases as a result of damage to the muscular structures of the anal sphincter. Sphincter function recovers on its own within a few weeks.
Replacement of the defect with a skin flap
Skin flap surgery involves moving a piece of blood-supplied skin from another area of your body to the site of the anal defect to improve blood circulation in the tissues surrounding the crack.
This operation is recommended for the treatment of long-term anal fissures caused by pregnancy or trauma to the anal canal.
General recommendations
After defecation, you should treat the anus and the area around the anus with cold water - this will help reduce pain and prepare the anus for the use of topical medications.
To facilitate the act of defecation, it is recommended to use enemas. The procedure is performed when there is a urge to defecate.
- Oil enema. To prepare the solution, you need to measure 150 ml of water and add 50 ml of oil;
- Water enema. In this case, boiled water is used, preferably with the addition of disinfectants.
Preparing for surgery
3 days before surgery, you should avoid foods that stimulate gas formation in the intestines. The ban includes black bread, legumes, cabbage, fresh vegetables and fruits, juices, mineral water, and alcoholic drinks.
A day before excision of the anal fissure, they switch to easily digestible food (“chocolate” diet). 12 hours before surgery. If you smoke, it is advisable to also give up cigarettes on the day of surgery.
During preparation for surgery, a protective regime is followed. It is necessary to exclude physical and nervous stress, do not drink alcohol, as well as tonic drinks, including coffee.
The evening before surgery, the intestines are cleansed using enemas or laxatives.
How to avoid relapse: patient reviews and doctors’ recommendations
As an analysis of reviews published on the Internet shows, most patients tolerate anal fissure excision surgery relatively easily and are happy to be free of the disease.
However, in order to avoid such surgical interventions in the future, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of prevention: • timely treatment of diseases of the digestive system; • ensuring regular bowel movements; • combating physical inactivity (hiking, swimming, etc.).
The fact is that an anal fissure occurs as a result of the influence of causative factors (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, irregular bowel movements, a “sedentary” lifestyle leading to congestion of the pelvic organs, etc.). If the causes of the pathology are not eliminated, the disease may return at any time.
How is the operation performed?
Surgery for anal fissure takes 15-30 minutes. If intravenous anesthesia is used to control pain, the patient falls asleep before the operation and wakes up in the recovery room. If doctors prescribe epidural anesthesia or local anesthesia, the patient is conscious, but does not feel pain. When choosing an anesthesia method, both medical indications and the wishes of the patient are taken into account.
The surgery is performed using equipment that resembles a gynecological chair. Today in Moscow and other cities of Russia, surgeons prefer to replace the traditional scalpel with the latest methods: • electrocoagulation; • radio wave surgery (Surgitron device); • laser surgery.
These methods allow the operation to be performed bloodlessly, since the miracle knives simultaneously seal the vessels. In addition, when using modern technologies, tissue is less damaged, and the healing process is much faster. The choice of method is made by the doctor, taking into account medical indications (size and location of the crack, accompanying changes in tissue, etc.).
Early rehabilitation after surgery
Regardless of the chosen method of operation and anesthesia technique, after surgery, a tampon soaked in medicinal ointments is installed in the anus.
Then, throughout the early postoperative period (the first 2-3 days), dressings are performed daily. Gauze bandages soaked in levomekol ointment are applied to the anus.
Inpatients are advised to begin getting out of bed and walking the day after surgery. A slag-free diet is also prescribed (if there are no contraindications, a “chocolate” diet). The purpose of such a diet is to delay bowel movements for better wound healing.
From the third day, the diet expands, foods containing dietary fiber that stimulate bowel movements are prescribed. If on the third day it is not possible to achieve independent stool, a cleansing enema is used.
Symptoms of pathology
In the early stages of the disease, there are no symptoms. As the size of the cracks increases, bleeding, itching and burning in the anal area opens. After each act of defecation, the wound bleeds heavily, which causes pain. The affected area turns red, soft tissues become irritated.
There are the following types of proctological diseases:
- In the acute stage, soft tissues have a smooth surface and a dense bottom. The pain intensifies during defecation, and drip bleeding appears. A linear or slit appearance is diagnosed. Anal fissure is treated without surgery.
- Chronic stage - characterized by an oval or round shape. The soft tissues become denser and the edges become torn. Connective tissue grows rapidly. The bottom appears with plaque, scars and cracks that bleed heavily during bowel movements and even when moving.
Rules of conduct after surgery
After anal fissure surgery, patients are discharged from the hospital on the fifth day. It will take 2-3 weeks for the wound to heal completely. In order for surgery to result in successful restoration of health, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the rules. 1. Stool should be daily, preferably in the morning. 2. If it is not possible to achieve regular bowel movements with the help of a diet, mild laxatives are allowed - as prescribed by a doctor. 3. Toilet paper is replaced by washing. 4. Spicy, salty, smoked foods, fruits with small seeds, and alcohol are prohibited. 5. It is necessary to refrain from heavy physical exertion, as well as from prolonged sitting, visiting the bathhouse, sauna.
If the operation was performed on an outpatient basis, in the first days after surgery it is necessary to care for the wound (daily dressings and warm baths with potassium permanganate), relieve pain using recommended painkillers and strictly follow all the instructions of the attending physician.
What may be secondary changes in chronic anal fissure?
— sentinel tubercle (shown in the photo)
— skin fold (shown in the photo)
- fistula (shown in the photo)
Rice. 3. Anal fissure with the formation of a fibrous polyp similar to the hypertrophic anal papilla
Rice. 4. Progression of an anal fissure with the formation of a skin fold
Rice. 5. Anal fissure with the formation of a secondary fistula tract
If an anal fissure develops in a patient due to dense stools, frequent loose stools, anal sex or the use of sex toys, then it will be classified as a primary anal fissure. And if an anal fissure occurs in a patient who suffers from other diseases, such as anal cancer, cicatricial stricture of the anus, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, HIV, then we will classify it as a secondary anal fissure.
Based on location, cracks are divided into three types:
Rice. 6.