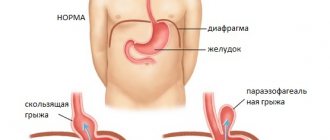
Types of umbilical hernias
Umbilical hernias can be congenital or acquired. Congenital ones arise due to impaired development of the tissues of the umbilical ring during the prenatal period. Such hernias are diagnosed immediately after the birth of a child or during the first month of the baby’s life. Acquired protrusions appear due to weakness of the abdominal muscles/ligaments and increased intra-abdominal pressure due to heavy lifting, loud laughter, loud crying or screaming, etc.
Umbilical hernias are divided into oblique and direct. An oblique hernia occurs when internal organs exit through the umbilical canal - it itself has an oblique direction. But with further progression, such a protrusion straightens out.
Also, umbilical hernias can be:
- Reducible. Such a hernia can be repaired by hand. Its contents easily move from the hernial sac back into the abdominal cavity.
- Irreversible. Hernias become like this when they are strangulated, the contents grow together with the hernial sac, or inflammation develops.
Classification
There are several classifications of the disease according to certain criteria. The main thing is to distinguish types based on origin. There are two types:
- congenital or embryonic defects that occur in a child even at the stage of intrauterine development, they are caused by disturbances in the formation of the abdominal wall;
- acquired or postnatal hernias that develop in infants during the first 1–4 months of life.
Additionally, direct and oblique hernias are distinguished depending on the direction of the protrusion, as well as reducible and irreducible.
Reasons for the development of umbilical hernias
The main reason for the appearance of umbilical protrusions is a combination of weakness of the abdominal wall and umbilical ring and increased intra-abdominal pressure. These factors contribute to the emergence of:
- genetic predisposition (hereditary weakness of the retroperitoneal fascia - connective membrane);
- pregnancy (especially after 30 years);
- obesity;
- increased physical activity;
- ascites (edema of the abdomen);
- fast-growing tumors in the abdominal cavity (both benign and malignant);
- presence of scars due to surgery;
- diastasis (divergence) of the rectus abdominis muscles;
- chronic constipation;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- sudden weight loss;
- complicated childbirth;
- abdominal injuries;
- strong laughter, hysterical cough.
The following factors increase the risk of developing an umbilical hernia in childhood:
- congenital hypothyroidism (overactive thyroid gland);
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- Down's disease;
- heredity (if the father or mother had an umbilical hernia in childhood, then there is a high probability of its development at the same age in the child);
- prematurity.
In young children (under 5 years old), the occurrence of acquired hernias is often caused by delayed closure of the umbilical ring. Usually the umbilical ring closes after the umbilical cord falls off. But in some cases this process is extended. Often, an umbilical hernia does not cause the baby any discomfort, and after the umbilical ring is strengthened (this happens by 2-5 years), it goes away on its own. But in any case, the child must be shown to a doctor, who will decide whether surgical treatment should be resorted to or whether observation tactics should be chosen.
Using an adhesive patch
This remedy can be used for newborns as soon as their umbilical wound has healed. The patch is glued so that a small fold is formed. The course of wearing the patch is 10 days. Typically, three courses are required with breaks in order to completely eliminate a hernia in an infant. The patch must be selected from a hypoallergenic material that allows air to pass through, so as not to irritate the baby’s sensitive skin. To ensure that the treatment of the disease is as effective as possible, it is recommended to combine the use of the patch with other methods. In this case, the result is more stable.
Complications of umbilical hernia
The most common complication is strangulated umbilical hernia. This is due to the fact that the contents of the hernial sac are almost always larger than the hernial orifice. Therefore, the risk of strangulation of internal organs is higher than with other types of hernias. Infringement can occur during physical activity, constipation, laughter, coughing. The consequences of this condition can be poor circulation and inflammatory processes in the strangulated organs. When the peritoneal tissue is pinched, peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) can develop. Even if a hernia does not cause any particular concern, there is no point in postponing its treatment until later. You should consult a doctor immediately if there are signs of infringement, which include:
- protrusion tension;
- increased temperature inside the hernia (the formation feels hot to the touch);
- disappearance of the possibility of hernia reduction;
- severe pain in the navel area;
- symptoms of body intoxication: high fever, headache, nausea and/or vomiting.
The following complications also occur:
- hernia inflammation;
- stagnation of feces in the intestines, intestinal obstruction.
Description of the disease
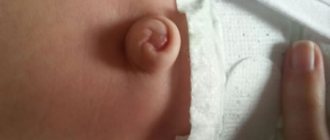
A hernia in a child’s navel is one of the most common surgical pathologies, which is more often observed in premature babies and underweight newborns, which is due to the immaturity of connective and muscle structures.
In itself, such a protrusion is completely harmless, although it frightens parents with its appearance. It does not cause pain, itching or other discomfort and in the vast majority of cases goes away on its own. The threat is posed by a condition called strangulation: it is compression of the hernial sac, which entails a disruption of the blood supply and the gradual death of surrounding tissues. Strangulation of an umbilical hernia in children is a direct indication for immediate surgical treatment.
Diagnosis of umbilical hernia
First, you will be examined by a surgeon. Then the following studies may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the protrusion and abdominal organs;
- X-ray examinations of the stomach and intestines;
- herniography (x-ray examination of the hernial sac using a contrast agent);
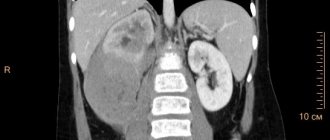
- CT scan;
- endoscopic examination of the intestine.
If the patient has digestive disorders or constipation, he may need to consult a gastroenterologist and/or nutritionist.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Recovery after surgery varies. Children recover the fastest after laparoscopy. Since this method is the most gentle of all, rehabilitation here takes 2-3 days maximum. Most often, babies are discharged within a day after such an operation.
Now we’ll tell you how a child feels after an umbilical hernia operation performed in other ways. If the surgical intervention was planned and timely, then the rehabilitation period takes no more than 14 days. This means that the child was operated on while still in preschool age. In this case, there should be no complications. The doctor will prescribe the wearing of a postoperative bandage, as well as the diet necessary for the little patient. You will not be able to eat foods that can cause gas in the intestines for some time. Physical activity will also need to be temporarily reduced.
The rehabilitation process takes the longest for those children who were urgently hospitalized. If the operation was unplanned, the hernia was strangulated or the hernia sac ruptured, then a longer recovery will be required. Usually, a course of medications and physical therapy are also prescribed.
Treatment of umbilical hernia
Treatment of umbilical hernia in adults and children over 5 years of age is carried out only by surgical methods. Exceptions are cases in which the operation cannot be performed due to the patient having contraindications (that is, such an intervention may significantly affect his health or even pose a danger to life). In such situations, conservative treatment is used, including:
- wearing a special bandage;
- abdominal massage;
- therapeutic exercises aimed at training the abdominal muscles and tightening the umbilical ring (in the absence of contraindications).
Surgical treatment of hernia
Hernioplasty (removal of hernias surgically) can be classical (an incision is made in the skin of the abdomen, through which further actions are carried out) and laparoscopic (the operation is performed through pinpoint punctures in the skin using the optical device of a laparoscope - this is a less traumatic method, after which the patient quickly recovers) . Classic surgery is performed under both general anesthesia and local or regional (spinal anesthesia) anesthesia; laparoscopic surgery is performed only under general anesthesia. The surgical intervention itself can be carried out using any of the following methods:
- With fabric tension. The umbilical ring is sutured in the transverse and vertical direction. If the patient has too much fatty tissue, the excess is removed during surgery. This method is suitable for small hernias.
- Using mesh implants. This is a kind of patch that is attached above or below the umbilical ring. This method can be used in the presence of hernias of any size, even large ones.
Surgeries are rarely performed on children under 5 years of age (they are mainly performed for strangulated hernias). As already mentioned, in such young patients the bulges often go away on their own. Therefore, conservative therapy is used, which consists of using bandages or adhesive tape, prescribing therapeutic massage and special gymnastics.
Surgical treatment of pediatric umbilical hernia at the Laser Medicine Center
or why you shouldn’t be afraid to go to a pediatric surgeon
If the time allotted by nature to your baby’s health for self-healing is coming to an end, if all your conscientious efforts to help your child cope with this harmless pathology have not yielded results, then you should not hesitate and gather your courage and make a decision on surgical treatment of the hernia.
Please note that the uniqueness of a child for parents does not apply to his illness for a doctor. If a pediatric surgeon has several dozen operations to repair an umbilical hernia, then his professional experience is a sufficient guarantee of the success of the operation. When you are dealing with a doctor who has performed hundreds of similar operations, the child’s parents have an objective reason to be completely confident in the successful surgical treatment of their child.
Dear Parents.
You can get qualified help regarding the treatment of an umbilical hernia, as well as hernial protrusions of other origins, in the pediatric surgery department of the multidisciplinary clinic “Laser Medicine Center”.
We widely use modern effective treatment methods to achieve positive results. The department is equipped to the most modern standards, so your stay in the hospital will be as comfortable as possible.
Prevention of umbilical hernias
Prevention of umbilical hernia is aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles and avoiding increased intra-abdominal pressure. In order to avoid accumulating extra pounds and avoid constipation, you should stick to a healthy diet. If you already have excess weight, you should gradually (not abruptly!) get rid of it. Regular moderate physical activity, including abdominal exercises, will help strengthen your abdominal muscles. Strenuous physical activity and heavy lifting should be avoided.
During pregnancy, it is recommended to wear a special bandage (only after consulting a doctor - this device is not recommended for all expectant mothers).
Physiotherapy
Often, umbilical hernia in newborn children can be well cured with the help of therapeutic exercises. In our clinic, experienced specialists will select the necessary set of exercises for the child.
You can also do some exercises on your own at home. For example:
- before feeding the baby, place the baby on his tummy (for a couple of minutes);
- turn the child onto the left and right side alternately for a couple of seconds;
- turn the child to face you and, holding his head, tilt him back slightly;
- when the baby is lying on his back, carefully lift him by the arms, while supporting his back (the head and legs hang freely);
- Also, while lying on your back, carefully turn the baby onto his tummy;
- Place the baby on a bulky ball and roll it around, holding it by the legs.
Children under 8 years old can visit a trainer and do exercises with him. Such services are also available in our clinic.
Reasons for appearance and development
The disease is most often congenital in nature and is diagnosed immediately after childbirth - when screaming, the contents protrude greatly and it is impossible not to notice it. The occurrence is primarily affected by the slow healing of the hole due to a lack of collagen. Much less often, but still acquired injuries occur, the causes of which are:
- frequent crying;
- digestive problems causing regular diarrhea or constipation;
- obesity;
- hereditary factor - weakness of connective tissues can be transmitted from the older generation to the younger;
- postoperative consequences;
- bronchitis and other problems with the respiratory system, provoking a hysterical cough and, as a result, severe tension in the walls of the abdominal cavity.
As a preventative measure, normalization of stool, weight control, and elimination of factors that cause anxiety and tears are used.
Types of abdominal hernias
Depending on the location, there are:
Inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernia in men
An inguinal hernia is the most common type of abdominal hernia. It is a pathological protrusion of the intestine or greater omentum into the cavity of the inguinal canal. In men, inguinal hernia occurs 5 times more often than in women, which is explained by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the groin area in both sexes. In men, the spermatic cord is located in the inguinal canal; in women, the round ligament of the uterus is located.
Inguinal hernia in women
An inguinal hernia, if it is not strangulated, usually does not cause pain. The only sign of such a hernia is a protrusion in the lower abdomen. If you cough and put your hands on the hernia, you can feel the shock.
Femoral hernia
Femoral hernia
A femoral hernia is a protrusion of internal organs through the femoral canal. Normally, the femoral canal does not exist, there is only a femoral ring filled with fatty tissue, loose enough to make this place vulnerable to protrusion of the hernial sac. Since women tend to have larger pelvises, femoral hernias are 4 times more common in them than in men.
A femoral hernia goes through several stages in its development - initial, canal (when the protrusion has already led to the creation of the femoral canal, but the hernia has not yet penetrated the skin and has not become noticeable), complete. In the first two stages, a symptom of hernia formation is pain in the groin and upper thigh, which intensifies with coughing, straining and long walking. At the last stage, a characteristic swelling the size of a walnut or larger appears in the area of the femoral-inguinal flexion.
Umbilical hernias
The navel is the place where the umbilical cord falls off, connecting the baby to the mother’s body. The muscles around the navel form an umbilical ring, which should contract fairly quickly. However, the umbilical ring remains a “weak” anatomical formation and protrusion of internal organs - the intestines or the greater omentum - can occur through it.
Umbilical hernia
In newborns, weakness of the abdominal wall muscles quite often leads to the formation of an umbilical hernia (detected in 20% of infants). Sometimes such a hernia is noticeable only when the baby is upright or when he strains or screams. In most cases, an umbilical hernia in newborns goes away on its own, as the muscles of the abdominal wall strengthen. However, observation by a surgeon is mandatory. The hernia should not increase or become strangulated. A massage may be prescribed.
In some cases, umbilical hernia occurs in adults. Causes: weakness of the abdominal wall, increased intra-abdominal pressure. Provoking factors are pregnancy, obesity, chronic constipation, etc. This hernia looks like a ball in the navel area. Sometimes it only appears when straining or coughing. If the hernia is large, pain may occur that intensifies after eating or during physical activity.
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen
The linea alba is a plate formed by intertwined tendons and separating the rectus abdominis muscles. It is called white because of the color of the tissue (it has few blood vessels). A white line runs down the middle of the abdomen - from the rib cage (xiphoid process of the sternum) through the navel to the pubis. Normally, its width is no more than 3 cm. But it can increase if the rectus muscles begin to diverge (for example, under the influence of high intra-abdominal pressure). This condition is called diastasis recti. In this case, hernias may form along the white line - above the navel (supra-umbilical hernia), in the area of the umbilical ring (peri-umbilical) or below the navel (sub-umbilical).
Methods for diagnosing hernia
Diagnosis of a hernia is carried out during examination of the patient. In this case, the doctor uses the methods of palpation (palpation), percussion (tapping) and auscultation (listening to the natural sounds of the body).
To obtain a more complete picture, instrumental studies are performed:
Radiography
Radiography of a hernia allows one to obtain additional information about the presence of adhesions, parietal strangulation of the hernia and partial intestinal obstruction.
More information about the diagnostic method
Ultrasound examinations
Ultrasound makes it possible to clarify the location of the hernia, the shape and size of the hernial orifice, assess the condition of the surrounding tissues (this allows you to choose the most effective technique for reducing the hernia), and determine the contents of the cavity of the hernial sac.
More information about the diagnostic method
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography for hernia is used if ultrasound data is insufficient.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
What danger might it pose?
If the pathology is not neglected, then it responds well to conservative treatment in childhood. Surgical intervention is necessary only when complications arise that are fraught with a very real threat to life:
- adhesive process, which subsequently threatens uncontrollability;
- intestinal obstruction, which appears as a result of the formation of the same adhesions;
- pinched umbilical hernia in a child is an acute and painful condition, which can only be eliminated through emergency surgery. Its main signs are loud sobs and the inability to straighten the intestines in a supine position. With such manifestations, it is important not to try to help the baby on your own - infringement poses a serious danger that requires prompt intervention from professionals.
If a child feels constant discomfort, cannot empty his bowels for a long time, screams, draws his legs in, does not calm down for a long time - all this should be the impetus for an urgent visit to the doctor.
Treatment methods
This pathology in children is treated both with and without surgery. Treatment tactics are chosen after a joint consultation of a small patient with a local pediatrician and a pediatric surgeon.
What methods will avoid surgery?
Monitoring a child and treating an umbilical hernia at home
Three methods for treating hernia at home:
Gymnastics and tummy massage
10 minutes before feeding, place the baby on his tummy on a hard surface covered with a warm diaper. He begins to actively move his torso, arms and legs, while intra-abdominal pressure decreases due to increased release of gases. The child's anterior abdominal wall will be strengthened by systematically repeating these actions 2-3 times every day.
It is better to start a tummy massage at the age of two months: first, with a massage instructor at a children's clinic, who will teach you the correct procedure technique, and then mom or dad performs this massage on their own.
Using an adhesive patch
The patch is applied for 10 days so that a fold forms in the navel area. Three courses of such sealing usually lead to the disappearance of the baby’s umbilical hernia.
The patch should be hypoallergenic and not irritate the baby's delicate skin.
Combining this method with therapeutic exercises and massage gives a more lasting result.
Instructions for use of the Porofix patch. To fix the patch you need to: 1) Clean and dry the skin around the navel well. 2) Fix the patch to the left and right of the navel. 3) Insert patch “a” into the eye of patch “b”. 4) Tighten the patch. 5) Fix this position.
Traditional methods
Many parents try to practice traditional methods of treatment: applying a copper coin, an oatmeal cake, a piece of gauze moistened with cabbage juice, etc. to the navel area. Reviews of such methods of dealing with an umbilical hernia are most often positive, but it is necessary to take into account a significant nuance : Any object placed on the hernia area requires fixation. And you can securely fix something on an infant only with the help of an adhesive plaster!
Operation
If the diameter of the umbilical ring does not exceed 1.5 cm, then surgical treatment can be avoided in 99% of cases. If parents actively use all the methods of conservative treatment recommended by the doctor, the hernia disappears on its own by 2–3, maximum 5 years.
If the diameter of the umbilical ring is 2 cm or more, surgery cannot be avoided. Children are usually operated on when they reach the age of three. In any case, the operation should be performed before the child goes to school.
There are two types of surgery.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| 1. Hernioplasty is performed for extensive hernias, as well as for their strangulation. | 2. The classic operation of suturing the umbilical ring is performed if the hernia is small, not strangulated and can be easily reduced. |
There are two types of hernioplasty:
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
| 1. With wire mesh installation | 2. Laparoscopy method |
| If the hernia is large, but can be easily reduced and is not strangulated, then during the operation after its reduction, a special “patch” made of synthetic material that is well compatible with the tissues of the human body is placed on the area of the hernial orifice. Outwardly, it resembles a tulle curtain. The hernial opening is securely closed; over time, the mesh grows into the child’s own tissues and becomes inseparable from them. This is a guarantee that the hernia will not occur again. | The least traumatic method of removing an umbilical hernia, in which the doctor makes only three small (5 mm) incisions using special ultra-thin surgical instruments. With this intervention, the rehabilitation period is minimal. Usually, on the second or third day, young patients return home. |
Sometimes an urgent operation is performed due to strangulation of the hernia and deterioration of the child’s condition (the baby is crying, he has severe bloating, non-reduction of the hernial sac and a change in its color and density, nausea and vomiting).
This operation takes longer, and the postoperative period is lengthened, since the intervention itself is more complex: it is necessary to eliminate the strangulation, restore blood circulation in the strangulated organ and cut through adhesions (connective tissue seals). And only after these steps they begin to correct the hernial opening. Usually, in this case, implants cannot be used, since simply suturing the hernial orifice will lead to the appearance of new adhesions and pain in the scar area.
Therefore, parents should not neglect the advice of a surgeon. It is better to perform the operation as planned, without creating a health risk for your baby.