Inguinal hernia: symptoms, causes and treatment options
An inguinal hernia in men is a disease in which the walls of the abdominal cavity weaken and cannot hold the internal organs in place. In this case, an inguinal-scrotal hernia appears due to weakening of the inguinal muscles. As a result, protrusion of the organ under the skin is visible. Hernia occurs quite often, especially in older men.
The main factor in its occurrence is serious and regular stress on the abdominal cavity. In order to recognize the disease in time and prevent the development of complications, you need to know its symptoms. And for clarity, you can see what an inguinal hernia in men is in the photo. They will help present the overall picture of the disease.
Causes
An inguinal hernia can occur for a variety of reasons. The following factors are identified that can contribute to the appearance of this disease in men:
- Frequent (chronic) cough, which will put a lot of strain and pressure on weakened areas of the abdomen, which in turn can give rise to the formation of an inguinal hernia.
- A person's hereditary predisposition to an inguinal hernia is revealed in the anatomical weakness of the abdominal muscle tissue.
- Some diseases of the intestinal system can increase intra-abdominal pressure, especially when they cause constant constipation in the sick person.
- Excessive physical activity, which puts strong pressure on the abdominal cavity (and increases intra-abdominal pressure itself). Lifting heavy objects, holding something suspended, and carrying heavy things in front of you is considered especially dangerous.
- Previously suffered injuries to the groin area, which caused a sharp weakening of ligaments and muscles.
- Sudden weight loss leads to the formation of empty volumes in the human peritoneum, which can push outward into the abdominal cavity.
- Excess weight can put excessive stress on internal organs, which increases a person’s tendency to develop an inguinal hernia.
As can be understood from the above, several factors can contribute to the development of an inguinal hernia in men, but the most common cause of this disease is lifting heavy objects. It is most quickly capable of leading to an acute condition in a person, in which he will require immediate treatment.
Why does pain occur?
The appearance of pain in the pelvic and groin areas may indicate the development of various pathologies. An experienced doctor can determine what exactly caused such symptoms after conducting a thorough examination.
Such symptoms can manifest themselves against the background of a heart attack in the hip joint, arthrosis of the hip joint, an inflammatory process in the femoral joint, or avascular necrosis.
In the human body, the hip joint (HJ) is the most powerful joint, the task of which is to provide motor activity and also maintain balance. As a result, disturbances in the functioning of this joint cause a decrease in the quality of life.
The articulation includes the acetabulum and the head of the femur, which makes movements inside this cavity. The head is covered with cartilage tissue, which ensures free gliding. There is still a significant part of the femoral neck in the joint cavity.
The most common cause of pain in the pelvic and groin area is joint injury. Not so common are factors of a non-traumatic nature, caused by various pathologies, due to which the joint, cartilage, periarticular tissues are destroyed, and the volume of synovial fluid decreases.
Diseases in different organs and systems can lead to the appearance of such signs. In some cases, pain is associated with inflammation in the area of the pubic, sacroiliac joint, gluteal muscle, and pelvic organs.
In addition, pain can develop against the background of neurological disorders - neuritis in the sciatic nerve, lumbar radiculitis, etc. Sometimes such symptoms are evidence of the development of diseases associated with articular and ligamentous tissue.
The occurrence of pain in the pelvic and groin area is associated with degenerative processes, inflammation, and injuries. Also, the reason may lie in the anatomical features of the articulation, the incorrect location of the femoral head in the acetabulum. The cause of the development of pain can be a dislocation, subluxation of the hip of a traumatic or congenital nature.
Classification
Depending on the origin of the hernial sac, hernias are:
- Acquired - occur mainly in adults who experience severe physical exertion. They are both straight and oblique.
- Congenital - occur when the vaginal process of the peritoneum does not grow, when the testicles descend into the scrotum before birth. They are only oblique.
According to the anatomical classification, hernias are of the following types:
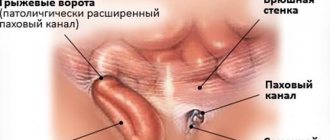
- Direct inguinal hernia is always acquired, never passes through the spermatic cord and does not descend into the scrotum; these are the signs that distinguish it from an indirect inguinal hernia. This hernia is very rarely strangulated. The sizes are usually not very large, on average 5-10 cm;
- Oblique PG - characterized by the passage of the hernial sac as part of the spermatic cord with the subsequent appearance of a protrusion under the skin of the groin area, and in advanced cases, in the scrotum. Has a tendency to infringe. Sizes vary from 4-5 cm to giant ones - 30-40 cm;
- Supravesical PG - occurs when there is weakness in the anatomical structures located immediately above the pubic bone. The protrusion is usually not very large;
- Sliding hernia – already from the name it can be assumed that this type of hernia is characterized by incomplete entry of the organ into the hernial sac, but only by one of its walls. Often, only part of the bladder and cecum ends up in the hernial sac. That is why, with this type of hernia, some difficulties arise when suturing the hernial sac during surgery;
- Combined inguinal hernia - with this type of hernia, the patient simultaneously experiences direct and oblique inguinal hernias, very rarely they are joined by a supravesical hernia.
Another important clinical classification on which the choice of treatment depends:
- Irreversible PG - occurs when there is a long-term presence of a hernia, when the hernial sac is connected by adhesions to the subcutaneous fatty tissue. In this case, it is not possible to reduce the hernia into the abdominal cavity, but its contents are not tense and may slightly decrease or increase;
- Reducible hernia - characterized by independent or manual reduction of the contents of the hernia into the abdominal cavity. Usually these are small hernias and at the initial stage of development, when adhesions between the tissues have not yet formed;
- Strangulated hernia - if it is strangulated, it is impossible, even with external help, to reduce the contents of the hernia into the abdominal cavity. In this case, the hernial sac is tense and painful.
You can determine whether an inguinal hernia is strangulated or not by performing a simple task - holding the hernia with your hand, you need to cough several times. If at the same time the hernial protrusion increases and decreases, then the hernia is reducible. Otherwise, if, when coughing, the protrusion does not change its size and continues to hurt, it is most likely that the hernia is strangulated!
The structure of the anatomical region in representatives of the stronger sex
The reproductive organs of the stronger sex are divided into those located inside and outside.
Organs that are located externally:
- reproductive organ;
- Scrotum.
Inside the reproductive system are:
- Testes and epididymis;
- Vas deferens;
- Prostate.
Purpose of the urinary and reproductive system in males:
- The genitals, which contain receptors, are considered an erogenous zone;
- The penis performs the act of intercourse.
Ejaculants
The paired male glands that are located inside the reproductive system are called testes.
The main task of the testicles is:
- Sperm production;
- Release of testosterone into the blood.
The testicles are oval-shaped, approximately 25 grams per testicle. The testes are located in the middle of the scrotum. The right testicle is higher than the left testicle. The testes are placed in a special shell and separated from each other by a crossbar.
The testicle is attached with the help of the spermatic cord; it consists of the following components:
- The duct through which sperm flows out;
- Nerve connections;
- Blood and lymph vessels;
- Muscles.
The testicular appendage consists of:
- Head;
- Body;
- Tail.
The peritoneal cavity surrounds the testes and creates a serous space that closes off. On the outside, the testes are covered with a tunica albuginea and under it is the testicular parenchyma. They divide the testicle into 2900 pyramidal particles.
In the middle of one of the lobules there are three tubules, which have a tortuous shape and a length of 90 mm. The seminiferous tubules are interconnected. 15 seminiferous tubules arise from here.
Duct for excreting seminal fluid
Near the prostate, the base of the vas deferens expands and a so-called ampulla is formed. It consistently narrows at the bottom and is directed into a narrow channel.
Spermatic cord
These bubbles are located in the middle of the pelvis, behind and to the side of the bottom of the bladder.
The seminal vesicles contain:
- The wide end, which is called the base;
- Body;
- The tapered end that moves into the duct to release seminal fluid.
The walls of the seminal vesicles contain many tortuous chambers containing protein fluid. It is part of the seminal fluid.
Prostate
The prostate gland has the following structure:
- Right and left lobes;
- Isthmus;
- The outer side of the gland is covered with a capsule; septa extend from it into the middle of the gland;
- The gland consists of glandular and smooth muscle tissue.
Bladder
There are two holes in the back wall of the bladder. The ureters enter through them. The continuation of the neck of the bladder is considered the urethra.
The bladder performs the following functions:
- Its capacity is approximately 350 ml;
- It can empty completely;
- The man has the urge to urinate and urine is released;
- With the help of the lower sphincter, a person has the ability to hold urine.
Rectum
The rectum is designed to collect stool. The intestine is approximately 16 cm long. 13 cm refers to the pelvic region and 3 cm in the anus. The wall of the rectum is covered with mucous and muscular membranes.
Functions of the rectum:
- Discharge of feces;
- Fecal masses collect in the rectum, where they are freed from liquid and formed into compressed feces;
- Approximately 4 liters of fluid enter the intestine per day;
- Water, alcohol, glucose and some medications are absorbed in the rectum;
- Serves as a reservoir;
- Gases and feces accumulate in it.
Penis
The penis consists of:
- Base or root;
- Trunk or middle part;
- Heads.
The appearance of the penis is unique for every man. Penis sizes are also individual. In a calm state, the length of the penis is about 5 cm, in the erection stage it is 16 cm.
Scrotum
The scrotum is a muscular organ covered with skin. In its middle are the testicles, epididymis, and the beginnings of the spermatic cord. All these organs are separated from each other by partitions inside and outside by the embryonic suture. The top of the scrotum is covered with hair, and her skin is darker than normal skin color.
The scrotum contains many sebaceous and sweat glands, which emit a specific odor. The temperature in the scrotum is 2 degrees lower , which creates optimal conditions for sperm production. If it's cold outside, the testicles are pressed closer to the body; in warm conditions, they drop back into the scrotum. The scrotum is also an erogenous zone in men. If you experience itching in the scrotum, read here.
Urine channel
The channel for the emission of urine is a thin tube that has increased elasticity. In representatives of the stronger sex, the size of the canal is about 22 cm. The urethra starts from the bladder and comes out at the head of the penis.
Symptoms
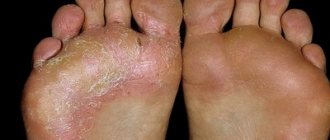
In men, the symptoms of an acquired inguinal hernia (see photo) are as follows:
- The formation can be straightened with regular pressure, and a characteristic rumbling sound can be heard.
- In a lying position, the protrusion usually either levels out or greatly decreases in size, and vice versa, in an upright position it increases and appears again.
- In the reduced state of the hernia, you can easily feel the enlarged inguinal ring through the skin.
- When the hernial sac descends into the scrotum, the corresponding half of the scrotum increases in size.
- With strong coughing, straining, or sneezing, the hernia increases in size and becomes tense; if you put your hand on it, you can easily feel it.
With a small inguinal hernia, there are no longer any symptoms that bother the patient. But with a significant increase in protrusion, the following ailments may appear:
- Pain in the lower back, lower abdomen - this occurs due to compression of other organs and intestines.
- Aching, prolonged pain in the area of the hernial formation.
- Other signs of indigestion, such as bloating, loud rumbling.
- Constipation, this is also caused by compression of the intestinal loops in the hernial sac.
- In rare cases, if part of the bladder gets into a hernial formation, problems with urination may occur.
The symptoms of an inguinal hernia are quite obvious upon visual examination; the formation has a dense elastic consistency and is easily palpable on its own. It can be round, and if the hernial sac descends into the scrotum, then the protrusion has an elongated shape. As a rule, with a genetic predisposition, the body’s tendency to develop a hernia, a hernial protrusion may occur after lifting weights and intense physical activity.
A hernia appeared in the groin. What to do?
You or your relative, father, husband, friend, colleague or just a loved one has an inguinal hernia. It always appears at the wrong time and unexpectedly for its new owner, sometimes on both sides at once (bilateral). The process of herniation begins. The scenario and first signs of the appearance of a hernia vary. Anything can happen against the background of complete well-being and good general condition. Unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower abdomen appear and disturb, or after strong physical activity (static tension, heavy lifting, repairs, sports) a sharp pain occurs in the groin. Unpleasant sensations and pain may subside and go away on their own, but then a characteristic tumor-like hernial formation (bulging, bulging) of an oval or round shape is discovered in the groin area.
Consultation with a surgeon, candidate of medical sciences
Make an initial appointment in Moscow by phone
An inguinal hernia comes in different sizes (from a pea or larger) and can enlarge with coughing, sneezing, straining and physical activity. Pain, discomfort and discomfort are usually periodic. The hernia is mobile, reducible, and over time, it can begin to descend into the scrotum, turning from just inguinal to inguinal-scrotal. In addition to pain and discomfort, there are often dysuric phenomena (impaired urination - frequent, difficult or involuntary, urinary retention, pain and discomfort in the urethra). Periodic chronic constipation and/or bloating may be a concern. If your close relatives (father, grandfather, great-grandfather and others) had a similar pathology, then the likelihood of it happening to you and your children is very high. The process, location and age at which the formation appears in the groin may be similar. The symptoms are often the same.
A hernia has appeared. It would seem that there is nothing wrong and you can continue to live with her. Especially if it is small in size and practically does not bother you. Yes, there is some discomfort, there are inconveniences, but it seems that you can put up with it. In this situation, some choose the “ostrich” tactic and try to avoid the problem and not pay attention to it. Others enter a mode of observation and watchful waiting. You know, indeed, you can live like this for some time, but you need to take into account that the hernia carrier’s quality of life will suffer and decrease. Taking this factor into account, you need to decide what to do next.
If nothing is done, the hernial protrusion, as a rule, gradually increases in size and becomes more and more disturbing. More and more new symptoms appear that make it difficult to live peacefully. The discomfort is growing. But most importantly, there is always a danger of complications (strangulation, coprostasis and others). An inguinal hernia is like a “bomb” in your pocket, which can suddenly explode at any moment (both day and night) (complicated - pinched). And then she will have to be operated on as an emergency, which means that the likelihood of postoperative complications increases many times over, even after a well-performed surgical intervention. Hernioplasty (surgery) in such a situation will be less reliable, and the likelihood of relapse is very high.
When an injury occurs, it will be a great success if there is a good hospital and a qualified surgeon nearby. And if not? What if you are far from home? Business trip? On a rest? Fishing? Abroad? In such a situation, everything is left to chance. You are taking a risk... The consequences can be unpredictable and sometimes disastrous. The hernia limits freedom of movement. You need to constantly remember it. Among other things, the condition of a person with a hernia negatively affects not only him, but also affects his family, relatives and friends. A man can quietly plunge into prolonged depression and frustration. It's no secret that behind the outer brutal shell, imperturbable character and iron will often hide fears that are not voiced even to oneself. The stronger sex can solve the most difficult problems, be a stone wall for their loved ones and friends, stand to death, but men also need help and support. Often, hernia carriers do not want to talk about their problems and show their weaknesses. Sometimes the mere mention of a visit to the doctor or the need for surgery puts you into a stupor. It seems that it is easier to die than to solve this problem.
No matter how difficult and scary it may be, it is necessary to face this problem head on. And here only really close people whom a man trusts can help. These are usually parents, wives, children or friends. We need to walk this path together, step by step. The path from the appearance of a hernia to surgery and successful rehabilitation. To make the right decisions, you need to find answers to the many questions that arise with your family and friends.
What is an inguinal hernia? How does she look? What are its reasons? Why did it appear specifically for me? What health risks does an inguinal hernia pose? Who is treating? Where to contact? How to cure a hernia? Is it possible not to contact a surgeon? Is it possible to do without surgical treatment (not undergo surgery)? Is it possible to cure a hernia with folk, home or alternative remedies? Is it dangerous not to have surgery? If I have surgery, where can I do it? Where is the best place to do this operation? How long does the operation take? Does it hurt? What anesthesia or anesthesia is used to perform the operation? What surgical procedures are used to remove an inguinal hernia? What is the best operation to do? Open cavity or laparoscopic? What are the differences between surgical interventions for inguinal hernia? Is it possible to cut out hernias from both sides at once? What is needed before surgery? What examinations are needed? How much does surgery to remove an inguinal hernia cost? Cost of surgery (hernia repair)? What are the complications? What to do if there is a complication? What kind of rehabilitation is necessary after surgery? For how long is sick leave issued? What to do? And many, many other very diverse questions...
No one prepares to answer these questions from childhood, and many will not even need it in life. But if you are faced with such a problem, then you cannot do without collecting information. You should not complain about fate, rely on miracles or traditional healers. You need to learn as much as possible and immediately and consistently act. If you go to any forum on inguinal hernias, to the questions and answers section or frequently asked questions (FAQ, Q&A), and type reviews in search engines, you will see a lot of different opinions and advice. Sometimes they can be contradictory or even mutually exclusive. In order to act, you need information and knowledge from different sources. Read, analyze, think, ask and make decisions, only for you. We will try to help you, tell you in detail about inguinal hernias in men and answer your questions...
Strangulated hernia
A strangulated inguinal hernia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness, tachycardia;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bloating, lack of stool;
- negative reaction to a cough impulse; when coughing, placing a finger on the inguinal ring, shocks are usually felt; if the hernia is strangulated, the impulse is not transmitted;
- the hernia stops being reduced;
- the hernial sac is very tense;
- sharp, acute pain in the hernia area and in the abdomen.
A strangulated inguinal hernia is a very dangerous complication, so medical care should be provided as soon as possible. The operation must be performed as quickly as possible, since serious complications may develop, such as:
- Necrosis is the necrosis of parts of the intestinal loops or omentum that have fallen into the hernial sac.
- Peritonitis - with prolonged strangulation of the groin hernia, inflammation of the abdominal cavity develops.
At the same time, irreducible and large hernias, even without complications, cause discomfort to patients: they limit their activity and are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms.
FAQ
- Do they take you into the army with an inguinal hernia? – The commission will pay attention to its size, location, and the likelihood of infringement. Category D (unfit) is assigned for large recurrent protrusions that have a negative impact on other organs. Category B (limited fitness, can be called up for training or military action) is assigned for moderate recurrent hernias, which manifest themselves during physical stress. In other cases, they will be drafted into the army. They may provide a deferment for the duration of surgical treatment.
- Is it possible to go to the bathhouse? - Can.
- Is it possible to ride a bicycle? – Moderately possible, if the hernia is not scrotal, otherwise it can be strangulated.
- Is it possible to have sex with an inguinal hernia? - Can.
- Is it possible to pump up the abs and play sports? – Abdominal stress provokes an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which will aggravate the pathology.
Doctors' opinion on physical activity and baths:
Treatment of inguinal hernia in men
The only treatment for inguinal hernia in men is surgery. During the operation, the doctor excises the hernial sac and performs plastic surgery of the hernial orifice, which prevents further relapses of the disease. Plastic surgery of the hernial orifice can be performed either using an aponeurosis (tension technique) or using a special mesh prosthesis (non-tension technique).
In most cases, removal of an inguinal hernia in men is performed with the subsequent use of a polypropylene mesh. It is installed in the hernial orifice and fixed. Subsequently, connective tissue fibers grow through its cells and form a reliable barrier for the abdominal organs on the way to the inguinal canal. Using this technique significantly reduces the likelihood of recurrence of the disease.
Surgeries for inguinal hernia in men can be performed either in the traditional open way with a skin incision, or laparoscopically - through a small puncture.
Afterword
There are many organs and structures in the groin area: for this reason, various diseases can cause pain, most of them have a strong impact on the female body, and therefore require prompt consultation with a doctor.
Read
Also:
- Anatomy of the uterus: location, structure and functions
- Causes and symptoms of inflamed lymph nodes in the groin, treatment tactics
- Ejaculation in women, what is squirting
- What healthy labia should look like
- Labia in women: anatomical structure, indications for labiaplasty
- What affects the duration of ovulatory pain
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia
Laparoscopic technology allows special manipulators to enter the patient's abdominal cavity through small punctures on the anterior abdominal wall. The advantage of the operation is that there are no scars left after it, and minor damage to the tissues is caused during the procedure.
- At the initial stage, the patient is given anesthesia. The intervention is performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia).
- Carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity, due to which the anterior abdominal wall is raised like a dome, and conditions are created for surgeons to work.
- The hernial sac with its contents returns back to the abdominal cavity.
- A mesh is sutured from the inside to the abdominal wall. As a result of this, it more effectively holds the abdominal organs and prevents them from extending beyond its limits. Gradually it grows and is securely fixed in its place.
Due to a number of advantages, laparoscopic hernia treatment methods are gradually gaining popularity. However, if the protrusion is large, then surgeons prefer to work using traditional methods, since it is technically easier to perform the intervention. Therefore, it is necessary to contact doctors for help as early as possible and receive treatment using the most modern methods.
How long do you need to stay in hospital? Usually, after laparoscopy, a man can go home within 1 day after the operation, if no complications arise.
Treatment
An inguinal hernia can only be cured surgically. There is a lot of information on the Internet about various conservative methods, but at best they are auxiliary. It is impossible to radically solve the problem with their help.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
You can do without surgery only if the hernia is in its early stages and does not cause any discomfort. It's quite possible to live with her. Preventive measures will help prevent development:
- Wearing a bandage.
- Special exercises to strengthen the abdominal wall.
- Prevention of constipation.
It is sometimes possible to straighten a protrusion without surgery, but this method only works in young children. In adult men, it will come out backwards, since the gate has already been created.
There are situations when surgeons are in no hurry to operate even on a large, unstrangulated hernia. For example, in the case of elderly patients, for whom anesthesia can cause more harm than the protrusion itself.
Treatment without surgery at home
If you experience nagging pain, you can take antispasmodics. The safest remedy is No-Spa. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are effective in relieving discomfort, but they cannot be taken long-term due to side effects. In addition, these drugs can dull the pain that is a sign of impingement, which can have serious consequences due to lost time.
In order not to provoke complications, it is important to monitor timely bowel movements. The diet must contain fiber: fruits, raw and stewed vegetables, cereals, herbs. Apples promote regular bowel cleansing. They should be eaten on an empty stomach 20-30 minutes before the main meal. It is better not to overuse cabbage and legumes to avoid flatulence. It is also undesirable to eat a lot of animal protein and baked goods - this can lead to constipation.
Surgeon, Doctor of Medical Sciences Viktor Nikolaevich Kosovan talks about the treatment of inguinal hernia without surgery using massage and gymnastics
To strengthen the abdominal wall, you can perform special exercises while lying on your back:
- Place a load weighing 1-2 kg on your stomach, breathe through the peritoneum without raising the sternum;
- Raise straight legs to an angle of 30˚;
- Place your hands behind your head, supporting the back of your head with your palms and lifting the shoulder girdle;
- Bend your knees, hold the ball between them and squeeze it.
For any load, you need to wear a support bandage. You don’t need to do it all the time, otherwise your abdominal muscles will weaken. Important note: a bandage is only permissible for reducible hernias and if there are contraindications to surgery. Otherwise, it may compress the protrusion, which will lead to complications.
Bandage
Cold should not be applied to the protrusion, so as not to provoke a spasm. It is also impossible to purposefully warm it up.
Traditional medicine offers local therapy as supportive measures, for example:
- Pour a tablespoon of crushed oak bark into 0.5 liters of water, boil for 15-20 minutes, leave until cool. In the resulting broth, moisten gauze folded in several layers and apply it as a compress to the protrusion. Keep for 2-3 hours.
- Compress with sauerkraut juice.
- Dilute 4 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar (natural) in 0.5 liters of water. Make lotions for half an hour.
- Ointment recipe: take onions, plantain leaves and golden mustache plants in equal proportions. Pass through a meat grinder, add pork fat as a binder.
With a large hernia, treatment with conservative methods is not only useless, but also dangerous.
Surgeries to remove inguinal hernia
There are more than 300 surgical techniques for removing an inguinal hernia. The general gist is this:
- First, the soft tissues are cut, the prolapsed organ is returned to its place (or, according to indications, its strangulated part is excised - a hernia repair is performed).
- Then the weak area of the abdominal wall, where the hernial orifice was, is strengthened using the patient’s own tissue (tension method) or a synthetic mesh (tension-free hernioplasty, or alloplasty).
- The mesh gradually fuses with the surrounding fiber and becomes part of the body.
Operations last on average from 30 to 60 minutes. In complicated cases, the process may take 3-4 hours.
Disadvantages of tension methods:
- Increased risk of suture divergence and improper scarring;
- Long and painful rehabilitation period;
- Relatively high relapse rate.
Currently, tension-free hernioplasty is predominantly used. Advantages: risk of relapse no more than 3%, accelerated rehabilitation period. The only negative is the high cost of the mesh.
Plastic surgery can be performed using open or laparoscopic access. Absolute indications are strangulated protrusion, recurrence or likelihood of rupture of the hernia, inflammation of the area around it, adhesions, and intestinal obstruction.
Strengthening the peritoneum with mesh
Incisions can be made either with a regular scalpel or with a laser. In the latter case, the operation proceeds without blood loss, and the risk of wound infection is significantly reduced. The procedure takes 20-30 minutes and does not require hospitalization. The postoperative scar completely disappears after 3-4 months. Relapses are excluded. Immediately after the operation, you can carry out your normal activities, with the exception of heavy physical activity for 2 weeks.
Laparoscopic surgery
The laparoscopic method of hernia removal (endoscopic hernioplasty) is considered the most gentle. Endotracheal anesthesia and complete muscle relaxation are required. The intervention is performed through small incisions in the abdominal cavity, into which instruments and a video camera are immersed. The cavity is filled with gas for better visualization.
Diagram of the arrangement of instruments for laparoscopic hernia removal
The laparoscopic method is used to treat small hernias. It is technically inconvenient to work with large protrusions using this approach. Some surgeons consider this method to be traumatic: the formation of urinary tract fistulas due to implant pressure sores, damage to large vessels, and the development of intestinal obstruction are possible.
Plastic surgery according to Liechtenstein
Hernioplasty according to Liechtenstein is considered the gold standard for the treatment of hernias. Suitable for all types of protrusions. Surgeons prefer to perform the operation under local anesthesia, but epidural or general anesthesia can be given if the patient wishes. Access is made through a small incision just above the inguinal fold.
Scheme of hernioplasty according to Lichtenstein (the spermatic cord going into the testicle is held at the top)
Mesh flap
Suturing the mesh to the inguinal ligament
Summing the mesh to the internal oblique muscle
End result: an internal inguinal ring is formed from the two ends of the mesh (reconstruction)
Video of hernioplasty (animation)
Operation video
Examples of tension methods
Tension methods are used for small hernias that have arisen for the first time. A classic example is Bassini's plastic surgery. Access is made through an inguinal incision up to 8 cm long. The peritoneum is not dissected. The surgeon cuts the inguinal cord, finds the hernia, pushes it back into the gate, then sutures the rectus abdominis muscle to the inguinal ligament.
Reduction of the hernial sac according to Bassini
The Postempsky technique involves eliminating the inguinal canal. The surrounding tissues are sutured in such a way as to move the spermatic cord and create a new inguinal canal for it.
Complications after surgery
The most common consequences after surgery are:
- Seams coming apart.
- Hematomas. To prevent them, ice is applied immediately after surgery.
- Infection and suppuration of the wound. To avoid this, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
- Dropsy of the testicles. Develops due to damage to the membranes of the testicle. A symptom of this complication is an enlargement of the scrotum on one or both sides. It can only be treated surgically.
- Damage to the spermatic cord. It occurs due to the fault of the doctor and is associated with the structural features of the inguinal canal. The spermatic cord passes close to the hernial sac, so if the doctor is insufficiently qualified, it can be damaged. This complication can lead to infertility.
- Damage to the hip joint. Occurs in case of rough sutures.
- Relapse. Recurrence of a hernia most often occurs due to patient non-compliance with the regimen.
- Damage to blood vessels. This is also a rather serious complication, as it leads to testicular atrophy.
Even an operation to remove an inguinal hernia in men that is considered easy and safe can be accompanied by complications. Most often, they arise through the fault of the patient himself, due to violation of restrictions during the rehabilitation period. Sometimes complications arise due to the fault of the surgeon, or arise as a result of the individual characteristics of the body.
Indications for training
Training for pelvic floor muscle dysfunction is prescribed by a doctor after eliminating contraindications. Considering the structure of the organs located in the female pelvis, symptoms of muscle weakness can be determined independently. Indications for starting intimate ligament training are factors such as:
- Childbirth planning. Due to the strengthened muscular corset, the uterus will receive the necessary support, and the risk of prolapse or prolapse of the organ will be reduced.
- The period during pregnancy and after childbirth. Due to trained muscles, the birth process is accelerated and facilitated, and the risk of perineal ruptures is reduced. After childbirth, the genitals will quickly recover to their previous state.
- Age over 30 years. Most women have weakened pelvic floor muscles with age if they are not trained. To avoid problems in the future, even in the absence of unpleasant symptoms, gymnastics of the intimate muscles is indicated.
- Injuries and surgeries in the female pelvic floor. In this case, the natural contraction of muscles is disrupted, and with it the transmission of nerve impulses. As a result, incontinence, anorgasmia and other problems develop.
- Hormonal disbalance. Poor blood circulation due to metabolic disorders leads to thinning of the vaginal walls and a decrease in its elasticity.
- Physical inactivity. A sedentary lifestyle leads to loss of elasticity and muscle tone. They contract worse, which affects the functioning of all pelvic organs.
Diet after hernia repair
A proper diet will speed up recovery. For the first few days, it is better to eat only liquid and pureed food in small portions. On day 4-5 you can go back to your normal diet.
You need to eat as many foods rich in protein and fiber as possible. The diet should include:
- lean boiled meat (chicken, beef);
- seasonal vegetables (raw or steamed);
- dairy products, especially cottage cheese;
- fruits and berries;
- various porridges (buckwheat, millet, oatmeal, pearl barley);
- Fish and seafood;
- nuts and dried fruits.
It is better to exclude alcohol and coffee from your diet, as well as smoking.
What are the options for treating an inguinal hernia without surgery?
Taking into account the pathogenesis of the disease, it is believed that treatment for inguinal hernias without surgery is impossible. It should be borne in mind that the bandage also does not cure, but only helps to keep a reducible inguinal hernia in men in the abdominal cavity.
According to some doctors, treating an inguinal hernia in men with physical exercise has no therapeutic effect. However, many experts advise using exercises to increase the strength of the abdominal muscles, but only while lying on your back or sitting.
For example, exercises such as:
- breathing with the stomach with a load (1-2 kg) on the abdominal wall;
- raising straight legs 30° relative to the horizontal position of the body;
- raising the shoulder girdle and shoulder blades from a horizontal position (with hands placed on head);
- squeezing a ball placed between the knees (lying on your back, with your knees bent), etc.
The most suitable yoga asanas for inguinal hernias are: uddiyana, pavanmuktasana, sarvangasana, etc. Uddiyana asana should be performed while sitting: exhale the air forcefully, “squeezing” it out of the lungs, drawing in the stomach as much as possible, hold for three seconds, and then take a deep breath through the nose. Repeat 5-6 times.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease is aimed at promptly identifying and recognizing an inguinal hernia. If symptoms appear, there is no need to try to independently determine the nature of the disease, since the symptoms of the disease are similar to other pathologies (for example, inguinal lymphadenitis, hydrocele, etc.).
The first thing you need to do when you notice a protrusion in the groin area is to contact a surgeon or urologist.
The doctor will conduct a full examination, collect the patient’s medical history, and prescribe the necessary set of diagnostic measures, if necessary.
The following methods are used for early diagnosis:
- palpation of the groin area and external genitalia;
- visual examination (the doctor may ask the patient to perform several simple exercises to assess the nature of the protrusion, its size and shape);
- Ultrasound of the scrotum (with its help you can determine what exactly fills the organ cavity;
- diaphanoscopy (examination of the scrotum using a lamp);
- urine and blood examination.
If the disease is confirmed, the doctor will recommend treatment methods and also assess the need for surgery.
Prevention
The disease can be prevented by avoiding excessive physical activity and lifting heavy weights. It is important to take care of the stable functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, because constipation provokes hernias. You need to lose excess weight and do physical therapy. You should strengthen your abdominal wall by performing abdominal exercises and “bicycle” exercises. Therapeutic gymnastics should be given at least 20-30 minutes a day.
It should be noted the importance of maintaining a competent diet. You need to eat often, but little by little, and no alcohol. Instead of fatty and spicy foods, flour and confectionery products, you need to eat vegetables, fish and meat, boiled or steamed.
Contraindications to strengthening the pelvic muscles
Physical exercise has contraindications, so you must first consult a gynecologist or other specialized specialist so as not to harm your health. You should not do exercises for the perineum in the following cases:
- damage to the mucous membranes of the vagina and uterus;
- chronic diseases at the time of exacerbation (cystitis, endometritis);
- recent surgeries on the pelvic organs;
- the presence of neoplasms of any type;
- erosion of the uterine wall;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
Other contraindications relate to increased uterine tone, the risk of miscarriage and premature birth.