Inguinal candidiasis is more often diagnosed in men than in women. The pathology belongs to the category of candidiasis of large folds and is characterized by severe symptoms, causing the patient discomfort and many unpleasant symptoms. The main cause of fungal disease is a decrease in the body’s protective functions under the influence of negative internal and external factors. Treatment of inguinal candidiasis should be carried out under the strict supervision of a physician. An important point is to identify the root cause that provoked the spread of fungal infection. Without its elimination, the risk of the disease progressing to the chronic stage, which is manifested by periodic relapses, increases. Medical specialists quickly diagnose the pathology and prescribe the most effective treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Our doctors pay enough attention to each client to achieve the most positive therapeutic results and prevent complications.
Symptomatic picture of mycosis
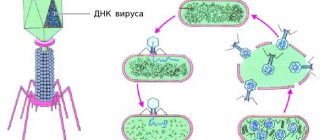
Candidiasis of the inguinal folds is caused by specific fungi, which are opportunistic microorganisms that live on the skin and mucous membranes of any healthy person. The immune system, functioning without failures, suppresses the active activity of pathogenic microflora, so they remain in a latent state in the human body. However, under the influence of pathological exogenous and endogenous factors, the immune system is weakened and ceases to fully perform its functions. This contributes to the activation of the infection and its unhindered reproduction.
The active activity of a fungal pathogen on the skin in the groin area is manifested by the following pathological symptoms:
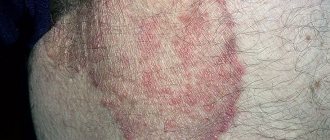
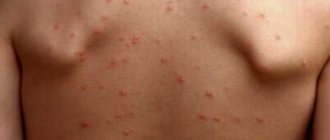
- Formation of spots in the groin. The lesions have clear boundaries and differ in color from healthy areas. The shade of the spots ranges from light pink to deep red.
- Peeling of the skin. In places where a fungal infection is localized, the skin becomes covered with a white coating and peels off. Peeling may spread to the perianal and pubic areas, as well as to the folds of skin between the groin and thigh.
- Uncomfortable sensations. In the groin area, the patient is bothered by severe, sometimes unbearable itching, which can cover the femoral part of the lower limb.
- Irritation. Swelling, redness, and irritation form at the site of active fungal activity.
On the skin of the groin area affected by the fungus, round, deformed areas are visualized, which differ from healthy skin in shade and the presence of peeling on the surface. Thanks to such visual signs, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis, which will be confirmed by the results of a comprehensive diagnostic examination.
How does it manifest?
At the moment, modern medicine has discovered several varieties of the described disease, which include: squamous, intertriginous, dyshidrotic and erased type. All types of illness have the ability to replace each other and be combined. The most common complaints encountered in medical practice include:
- The appearance of allergic rashes.
- The formation of red plaques with the additional effect of whitish peeling on the roof.
- Formation of yellow calluses with cracks on top.
- Irritating itching.
- The presence of edema and erosion.
- The presence of inflamed acne.
- Increased levels of nail brittleness and rejection.
- Bloody and purulent discharge.
Athlete's inguinal
The disease is caused by fungi of the genus Epidermophyton floccosum. The infection is transmitted through household contact and most often affects men. Factors that provoke the development of the disease include:
- wearing tight, constricting clothing that disrupts natural air exchange in the groin area;
- profuse sweating;
- increased environmental humidity;
- frequent injury to the skin in the groin;
- inactive lifestyle;
- excess weight.
In the initial stages of development, the infection is localized in the skin folds of the genital area, but as it progresses it spreads to the upper part of the inner thigh, affecting both limbs. Usually the fungus does not affect the skin of the scrotum.
The rash has a scaly, pinkish border. Inguinal athlete's foot is often accompanied by itching and pain symptoms. Lack of timely treatment leads to an increase in lesions and the spread of infection to healthy tissue.
To prevent the development of inguinal athlete's foot, it is advisable to follow simple rules of prevention:
- wear comfortable underwear made from natural fabric;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, especially in saunas and swimming pools;
- use personal hygiene items and do not give them to any strangers;
- normalize body weight;
- add moderate physical activity;
- If you have characteristic symptoms of a fungal infection, do not self-medicate, but make an appointment with a dermatologist as soon as possible.
Pathogen and routes of infection
The causative agent of athlete's foot is the parasitic fungus Epidermophyton floccosum. In the acute phase, the disease is contagious and is transmitted in the following ways:
- autoinoculation - transfer of the fungus from the source of inflammation on the arms or legs;
- indirect route - infection through household items on which there are scales of the epidermis with a pathogenic fungus: clothing, towel, sheet, seat;
- direct – transmission from a carrier during sexual intercourse.
Risk factors contribute to the active development of epidermophytosis of the inguinal folds:
- high humidity and local hyperthermia - the peak incidence is observed in residents of tropical and subtropical climates in the summer;
- tight, dense clothing that does not allow air to pass through - synthetic materials with thick thread;
- increased sweating;
- obesity, diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states;
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasmosis;
- trichomoniasis.
In men, such damage to skin folds occurs 3 times more often than in women, according to incidence statistics in the United States.
Candidiasis in the groin area
The causative agent of candidiasis in the groin area is a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida, which belongs to the opportunistic microflora and lives on the skin and mucous membranes of every healthy person. With natural balance and proper functioning of the immune system, the infection is in a latent state and does not provoke the development of pathological processes. But as soon as the immune defense fails, the fungi are activated and begin to multiply unhindered, causing the formation of deformable surface changes, accompanied by pathological symptoms.
Common causes of candidiasis in the groin area are:
- obesity, accompanied by the appearance of large folds on the skin;
- endocrine, hormonal disorders;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- uncontrolled use of certain groups of medications;
- unbalanced diet, predominance in the diet of foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates and sugar;
- infection through close contact with a carrier.
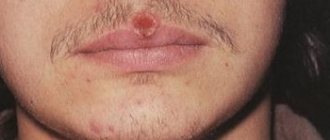
At the initial stage of development of inguinal candidiasis, the affected skin changes color to a darker one. Then the skin becomes covered with a small blistering rash. The spots have a clear outline. The areas where the blistering rash has formed begin to crack over time, forming erosions and ulcers. Injury is accompanied by unbearable itching and pain.
Fungi of the genus Candida produce a specific enzyme that accumulates in places of infection in the form of a thick, curdled mass. A whitish coating is a characteristic symptom of candidiasis and allows the dermatologist to differentiate the pathology. Treatment of candidiasis of the groin area must be carried out immediately, otherwise the disease will become chronic, accompanied by periodic exacerbations.
Possible complications
If athlete's foot in the groin area is not treated, cosmetic defects and complications are possible. The first includes hardening of the affected area of skin, like a callus. Complications include the addition of a secondary infection, which, depending on the pathogenesis, can affect the penis and urethra.
Differential diagnosis and treatment of athlete's foot in adults is carried out by specialists from the Dr.AkNer clinic in Moscow. Get professional help to prevent complications from a fungal infection. Effective painless techniques, proven by 40 years of experience.
Urologist, andrologist Akopyan Nerses Grigorievich.
Back to list of articles
Inguinal rubrophytosis
The infectious disease is caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton rubrum. This is a fairly common type of mycosis, which is diagnosed in a third of the population. You can become infected with inguinal rubrophytosis from a carrier through bodily contact, clothing, and household items.
Common reasons for increased growth of fungal colonies are:
- excessive sweating;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- regularly wearing tight, tight clothing, including underwear;
- hormonal and endocrine disorders;
- increased environmental humidity;
- uncontrolled use of certain groups of medications;
- obesity.
Inguinal rubrophytosis manifests itself in 2 forms:
- Erythematosquamous. It manifests itself in the formation of red spots on the skin that have an irregular shape with an intermittent border. On the surface of the affected skin, compactions and a blistering rash with liquid inside are noticeable.
- Follicular nodular. It develops when treatment of the erythematosquamous form is untimely. The follicular nodular form is characterized by the spread of infection to healthy areas of the body: buttocks, feet, forearm, hands, legs.
Inguinal rubrophytosis brings unbearable discomfort to the patient, causing severe itching, pain while walking and when in contact with clothing. If there is no therapy, the spots rapidly increase in size, spreading to healthy areas.
In terms of external signs, inguinal rubromycosis is similar to such common dermatological diseases as:
- eczema;
- psoriasis;
- candidiasis;
- erythrasmus.
To differentiate rubrotrophy, the doctor gives a referral for a comprehensive diagnosis, the results of which will help prescribe the correct and most effective treatment.
Diagnostic measures
With such problems, the patient should seek professional medical help from a mycologist. During the appointment, the doctor will conduct tests such as:
- Dermoscopic examination
- Scanning a surface using a special type of luminescent equipment.
- Skin pH assessment.
- Scraping test.
- Sowing to check the nutrient medium.
In addition, the expert can refer the patient for a consultation with colleagues in the orthopedic, phlebological, endocrinological and other departments.
What treatment therapy should I use?
Before prescribing treatment for inguinal candidiasis, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis and identify the pathogen. Therefore, after an initial examination and history taking, the doctor gives a referral for a comprehensive diagnostic examination, including the following procedures:
- microscopy;
- bacterial sowing;
- molecular biological analysis.
Treatment of candidiasis in the groin should be comprehensive and carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. Self-medicating with such a disease is dangerous and fraught with serious complications.
The treatment plan includes the following activities:
- Identification and elimination of factors that provoke immunodeficiency.
- Prescription of antifungal and symptomatic therapy.
- General strengthening therapy.
To combat a fungal infection localized in the groin, local antifungal drugs are prescribed in the form of creams and ointments, which contain an antimycotic component. In the fight against fungi, drugs such as:
- "Nystatin";
- "Natamycin";
- "Clotrimazole".
If the disease is advanced and accompanied by serious complications, in addition to topical medications, antifungal medications are prescribed for oral administration in the form of capsules and tablets:
"Fluconazole";
"Itraconazole"
In the most advanced cases, the doctor will recommend intravenous or intramuscular administration of antimycotics. As soon as the condition improves, you can switch to tablets.
In case of correct treatment, the disease completely disappears within 7–10 days. To confirm complete recovery, repeat tests must be taken after completing the main course. If the fungal infection is completely eradicated, the laboratory test results will be negative.
In addition to drug treatment, it is important to follow preventive measures that enhance the therapeutic effect and reduce the risk of relapse to zero. Therefore, together with drug therapy, it is advisable to follow the following rules of prevention:
- strengthen immunity;
- lead a healthy, active lifestyle;
- get rid of bad habits;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- normalize weight;
- use products that control sweat in large folds.
If there is no treatment for inguinal candidiasis, the fungal infection will gradually spread throughout the body, causing health and life-threatening complications. Therefore, if you have suspicious symptoms, you must make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist, take all tests and be treated under the supervision of a specialist.
Treatment options
Only based on the test results can it be stated that the inguinal fold is affected by epidermophytes. Treatment of inguinal athlete's foot in men consists of the following areas:
- etiotropic: fungicides, fungistatics to combat the cause of pathology;
- symptomatic: drugs to eliminate itching, discomfort, cosmetic defects;
- pathogenic: to eliminate risk factors.
The treatment regimen is prescribed only by a specialist. He will assess the presence of a secondary infection, the stage of the disease, and prevent its further spread.
Athlete's foot: diagnosis and treatment
- At the beginning of the appointment, the doctor should familiarize himself with the medical history and find out whether the patient has had contact with the patient or his things.
- Next, an external examination is carried out and scrapings are taken.
- The doctor prescribes treatment. Typically, your dermatologist recommends washing the affected areas with warm water and soap several times a day, and then lubricating them with an ointment containing clotrimazole.
It is important to remember that the ointment is usually applied at least 3-4 times a day, sometimes more often. Usually, the itching subsides already on the third day, and later the main symptoms disappear. But it is absolutely impossible to interrupt treatment: untreated epidermophytosis usually recurs quickly, and is more difficult to treat. A disease that is not completely cured is becoming less and less treatable each time. It can last for years, either gradually subsiding or exacerbating with renewed vigor.
Who is at risk: causes of the disease
The optimal conditions for the development of fungal infections are heat and humidity. Male professions (driver, military man) oblige a person to wear warm, unventilated clothes for long hours, day after day creating an optimal habitat for the causative agent of the disease.
A weakened body, the presence of mycosis on other areas of the skin, contact with people who are carriers of mycoses, metabolic disorders are factors that increase the risk of epidermophytosis.
Knowing the causes of the disease, we can identify the main categories of men who are at risk:
- elderly people;
- patients with diabetes and (or) obesity (treated and advised by an endocrinologist);
- men with hyperhidrosis (this means profuse, uncontrollable sweating);
- people with immunodeficiency;
- drivers, military, police, rescuers, etc.