Difficulty breathing and lack of nasal discharge are contradictory symptoms indicating that you are experiencing nasal congestion without a runny nose. As a rule, this uncomfortable condition is also accompanied by the following symptoms: lacrimation, pain in the facial area, sneezing and itching in the nasal cavity.
This problem significantly reduces the quality of life: the brain experiences oxygen starvation (respiratory hypoxia), increased fatigue is observed, endurance and performance decrease, and the quality of sleep also deteriorates, which negatively affects the nervous system.
After reading this article, you will learn the main causes of the problem, ways to diagnose the disease and understand how to treat nasal congestion without a runny nose.
Types of cold remedies
A runny nose is an extremely unpleasant condition, and you want to eliminate it immediately. Respiratory disease can occur in acute or chronic form, with difficulty in nasal breathing, moderate or heavy discharge. Frequent pathogens: bacterial, viral infections or allergens. A runny nose also occurs when blood vessels or the structure of the mucous membranes are damaged. The drugs are designed to eliminate painful symptoms and improve the outflow of secretions. Some contain hormonal, antibacterial or antiviral substances that help relieve irritation and reduce inflammation.
There are several types of medicine for the common cold:
- Vasoconstrictors: based on xylometazoline, naphazoline, oxymetazoline or phenylephrine. Upon contact with the membranes of the nasal sinuses, they cause a reflex microspasm of the capillary network. Thanks to this, swelling decreases, the lumen in the tissues expands, congestion goes away, and breathing becomes easier. Such drugs act almost instantly, restore physical comfort for a while, but do not have a therapeutic effect. These are emergency aids; they are allowed to be used in short courses: no more than 3–5 days in a row.
- Antiviral and antibacterial agents. They contain antiseptic components, interferons, help reduce inflammation, thin mucus clots, and moisturize the nasal membranes. To obtain a pronounced effect, they must be used in complex treatment. If there is severe congestion, they do not give quick results.
- Cameras. They contain extracts and essential oils of medicinal plants. Such nasal drops have a gentle effect, disinfect mucous membranes, help improve breathing and reduce secretions. The result of use is noticeable already on the first day. For a quick effect, such drugs are allowed to be used in combination with other drugs.
- Products with sea water. Designed for rinsing the sinuses from mucus clots. They are used as auxiliary drugs before diagnostic procedures and inhalations. Help relieve congestion, soften and moisturize.
Combined-action nasal preparations are also produced: the vasoconstrictor components in them are supplemented with essential oils and antiseptics. It is necessary to select drops and sprays by studying the composition, the list of indications and contraindications. During the treatment period, it is important to strictly follow the instructions to reduce the risk of side effects.
The list of effective drugs for the common cold includes diverse ones. Some are great for relieving congestion, while others are great for getting rid of allergies, infections, or eliminating all problems for a long time.
Symptoms
A condition in which the nose is stuffy, but there is no snot, is accompanied by the same symptoms as a regular runny nose:
- sensation of burning and itching in the nasal cavity;
- frequent episodes of sneezing;
- headache;
- discomfort or pain in the soft tissues of the face;
- increased lacrimation.
The only thing that distinguishes nasal congestion without snot is the absence of discharge, which is quite abundant with a normal runny nose.
Swelling of the nasal mucosa and impaired nasal breathing, in turn, can cause symptoms of a different nature: increased fatigue, problems sleeping, decreased concentration and ability to remember information. This is due to hypoxia - oxygen starvation of tissues, which is caused by insufficient ventilation of the lungs2.
Up to contents
Naphthyzin
A fast-acting vasoconstrictor for infectious rhinitis, hay fever, and sinusitis accompanied by debt. The drops almost instantly reduce the lumen of the capillaries; after just a minute of their use, breathing becomes freer. The effect lasts up to 6–8 hours. It is necessary to use Naphthyzin only when there is severe congestion, for example, at night. The course is no more than 5 days. Long-term use can cause addiction and decrease the sensitivity of blood vessels to the active substance. Naphthyzin should be used especially carefully in children. To eliminate a runny nose, it is allowed from 1 year.
Possible complications
The list of possible complications may include atrophic processes on the nasal mucosa, when it ceases to perform its functions. One of the functions of the mucous membrane is to humidify and purify the inhaled air, which reduces the likelihood of its infection and the penetration of pathogens into the middle respiratory tract. As a result of atrophic rhinitis, the nasopharynx remains defenseless in the face of infectious threats, which increases the frequency of colds and acute respiratory diseases.
The second most common complication is pathological changes in the nasal turbinates: the cavities expand over time, compensating for the increased load on the nasal passages. Most often, the only option to solve this problem is surgery.
Congestion not accompanied by nasal discharge that lasts more than 2 weeks requires immediate medical attention.
Up to contents
Accompanying illnesses
If the disease is not treated, very soon you may stop smelling, the mucous membrane atrophies, which means you have no protection against the penetration of microbes into the body. The nasal shells undergo a change in structure; they thicken and expand. To bring them back to normal, surgery will be required.
Pus accumulated in the sinuses infects the hearing organs, pharynx, bronchi and lungs. Frequent tonsillitis, sinusitis, laryngitis, headaches are constant companions of this disease. Sometimes the sinus contents break through the thin wall and enter the brain, causing meningitis. Once in the blood, the infection poisons the entire body.
Causes
Chronic rhinitis is often allergic in nature and is associated with diseases such as hay fever and bronchial asthma.
Non-allergic rhinitis occurs for a variety of reasons. We can speak of a chronic course if an exacerbation of the pathology is observed for at least a week annually. In this case, the symptoms are not associated with exposure to allergens and are more persistent.
Options for non-allergic rhinitis:
- idiopathic - does not have a clearly defined cause, usually associated with frequent colds;
- vasomotor - occurs due to circulatory disorders in the mucous membrane under the influence of cold or dry air, tobacco smoke, polluted environment, strong odors (cosmetics, household chemicals), changes in atmospheric pressure;
- hormonal - manifests itself during pregnancy, menopause, impaired activity of the thyroid gland;
- atrophic - can develop after surgery on the sinuses or with prolonged use of decongestants;
- nasal eosinophilia syndrome - an inflammation of a non-allergic nature, in which eosinophils - cells involved in hypersensitivity reactions - are found in the nasal discharge;
- professional – occurs during long-term work in conditions of ambient air pollution with dust and harmful gases;
- medicinal – develops as a complication when taking oral contraceptives, some antihypertensive drugs, antidepressants, anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs to eliminate erectile dysfunction.
Chronic rhinitis may be associated with structural abnormalities of the nose, such as a deviated septum, perforation, tumor, polyps, or foreign bodies.
In rare cases, chronic rhinitis accompanies conditions such as sarcoidosis, cystic fibrosis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and polyangiitis.
To successfully treat chronic rhinitis in adults, it is necessary to eliminate its causes.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis and treatment of the nose in adults is carried out by an otolaryngologist. During the consultation, the ENT doctor pays great attention to collecting complaints and the patient’s life history. During the consultation, the doctor asks the patient about when the symptoms appeared, whether they were preceded by injuries, whether he suffers from chronic diseases, whether he recently suffered from infectious diseases, etc.
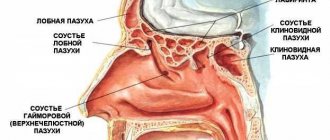
A direct examination of the nasal cavity begins with rhinoscopy, which allows you to determine whether there is swelling, whether there is a foreign body in the nasal passages, or helps to identify abnormalities in the structure of the nasal cavity.
Endoscopic examination allows you to see a complete picture of the nasopharynx.
Thanks to it, the doctor examines in detail those areas of the nasal cavity that cannot be seen during a classic examination. At this stage, neoplasms and adenoids can be identified.
If necessary, the patient is sent for an X-ray or MRI. You may also need to consult related specialists - an allergist, cardiologist, oncologist.
Correct diagnosis is possible only after all diagnostic measures have been carried out. After this, a treatment regimen is prescribed.
Prevention
The medical product for nasal congestion Aqualor is excellent for preventing sinusitis and rhinitis. Experts recommend using it during the flu and cold season to sanitize the nasal cavity. After being in crowded places, rinse your and your child’s nose. This way you will get rid of germs that have entered your mucous membrane. Strong immunity is a reliable barrier against harmful microorganisms. Make it a rule to do morning exercises, ventilate the room, and eat right. Get enough fiber and vitamins from food. Dress according to the weather, try not to get too cold. Only an ENT doctor can determine how to remove nasal congestion. At the first signs of illness, go to see an otolaryngologist. Do not self-medicate; you can make the situation worse by taking medications without knowing the cause of the disease.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Unpleasant symptoms can be reduced with non-drug treatment. It is recommended to increase the humidity in the room. For this, it is better to purchase a special humidifier. The patient must avoid strong odors and sudden changes in cold and warm air. You need to sleep on a high pillow so that your head is in an elevated position all the time - this reduces swelling of the mucous membrane. Persistent breathing problems through the nose are often a sign of illness, so to determine the cause of the disorder, you must seek qualified medical help.
Drug therapy
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the cause of the disease. Symptomatic therapy in the form of nasal drops with adrenergic agonists is recommended for short-term use during the period of greatest severity of discomfort, but it does not affect the causes of congestion. The basis of the treatment regimen for patients with impaired nasal breathing is usually medication. The following is used as etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy:
- Topical corticosteroids
. Inhaled forms of hormones are considered the most effective for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and vasomotor rhinitis. They also significantly slow down the growth of nasal polyps. Modern medications are not absorbed into the bloodstream and have no side effects. - Antiallergic drugs
. To eliminate swelling and congestion and prevent exacerbations of hay fever, antihistamines and mast cell membrane stabilizers are used. When taken long-term, these medications serve as basic therapy for allergic conditions. - Antibiotics
. For the treatment of rhinitis and sinusitis, various antibacterial agents are prescribed - penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins. Initially, the selection of drugs is carried out empirically. After receiving the results of bacteriological culture, the treatment regimen is adjusted.
Physiotherapy
Rinsing the nasal cavity with saline solutions helps eliminate dry mucous membranes. In patients with chronic diseases of the nasal cavity, along with medications, physiotherapeutic treatment methods are actively used - galvanotherapy, darsonvalization, microwave therapy, which stimulate blood circulation and improve immune defense processes. To enhance the effect of medications, they are injected directly into the affected area using electrophoresis.
Surgery
To eliminate nasal congestion caused by a deviated septum, surgical intervention - septoplasty - is indicated. Surgical methods are also used to treat polyposis: most often, endoscopic removal of a space-occupying lesion is performed, after which nasal breathing is restored. Advanced variants of hypertrophic rhinitis are subject to surgical correction: during the intervention, the specialist performs a conchotomy, removing part of the nasal concha to eliminate the mechanical obstruction to the passage of air.
Diagnostics
The correct diagnosis will be made by an otolaryngologist. Do not try to determine the cause yourself. Self-medication is fraught with even greater complications. The doctor examines the organs of the nasopharynx through:
- rhinoscopy (anterior and/or posterior);
- mesopharyngoscopy;
- otoscopy.
It may be necessary to take a smear from the mucous membrane to determine the etiology of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment for nasal congestion. If there are still questions in determining the location of the infection, you need to do an x-ray or ultrasound. Magnetic resonance imaging is also used in complex cases.