Vesiculitis is a urogenital disease of the genitourinary system, in which inflammation of the seminal vesicles occurs. As a rule, it has an infectious etiology. The second name for this pathology is spermatocystitis. It can develop as an independent disease, but is most often combined with pathologies such as epididymitis, prostatitis and various inflammatory diseases of the urethra.
In the absence of appropriate treatment, serious consequences can occur, including infertility in the patient. The acute form of the disease responds well to treatment without causing serious health consequences (in case of early detection and comprehensive treatment). With chronic vesiculitis, the prognosis is not so favorable: approximately 60% of patients suffering from the bacterial or cognitive form of this disease have serious problems with reproductive function and disorders in the intimate area.
Features of the anatomy of the seminal vesicles
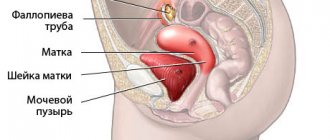
The seminal vesicles are paired glands that are part of the male reproductive system. Localized above the prostate gland (to the side of the vas deferens). Their back part is adjacent to the anterior wall of the rectum, and the front part is adjacent to the bottom of the bladder.
They perform extremely important functions in the male reproductive system:
- Providing seminal fluid with necessary substances and energy resources.
- Performing a protective function.
- Disposal of sperm residues.
Approximately 55-60% of the seminal fluid is the secretion of these vesicles. One of the most important substances in this secretion is fructose, which provides the necessary motor activity to sperm. It is by the level of this substance that experts assess the patient’s ability to reproduce.
In order for a sperm to reach the egg, it must have not only great motor activity, but also survival. It is the secretion of the seminal vesicles (combined with the secretion of the testicles) that provides the necessary protection, resulting in an increased chance of fertilization.
2. Reasons
In all organs and systems designed by nature to reserve biological fluids, one of the main etiopathogenetic factors is stagnation. Wherever stagnation occurs, they always sharply increase the likelihood of infection (hematogenous, lymphogenous, ascending), the formation of various kinds of distensions and bulges, the launch of degenerative processes, the accumulation of certain deposits, etc. Seminal vesicles are no exception in this regard . Stagnation of prostate secretion, for example, due to prolonged abstinence or more general difficulties with venous outflow in the pelvis, creates favorable conditions for the development of vesiculitis.
The direct cause of inflammation is one or more pathogenic organisms from a wide range of pathogens that are generally capable of causing infectious and inflammatory processes in the male urogenital area: strepto-, staphylo-, gonococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and tuberculosis bacilli, Trichomonas, chlamydia, fungi of the genus Candida, herpes virus, myco- and ureaplasma, gardnerella and many others.
Risk factors for vesiculitis, therefore, include all conditions that create the prerequisites for stagnation and infection of the seminal vesicles, as well as for weakened immunity, namely:
- irregular sex life with periods of prolonged abstinence;
- promiscuous sex life with frequent changes of partners;
- the interrupted coitus technique practiced as contraception;
- alcohol;
- injuries;
- hypothermia;
- physical inactivity.
The provoking role of allergic reactions, taking certain groups of medications, metabolic disorders, and immune disorders is also being studied.
Visit our Urology page
What are the causes of inflammation?
Inflammation of the seminal vesicles (vesiculitis) in most cases does not occur as a separate nosological entity. As a rule, it is a consequence of infectious diseases in the male reproductive system.
The causes of vesiculitis are usually divided into two groups – infectious and congestive (cognitive). Infectious causes are divided into specific and nonspecific. Specific: tuberculosis, gonorrheal, trichomonas and mixed type. Nonspecific: viral, bacterial, mycoplasma, chlamydia, candidiasis and ureaplasma.
Stagnant (cognitive) reasons mean:
- Stagnation of secretion in the prostate gland, seminal vesicles.
- Various congestive processes in the scrotum and pelvic organs.
- Mixed reasons.
The main factors that provoke the development of this pathology include:
- long-term abstinence from sexual intercourse;
- too frequent masturbation;
- interrupted sexual intercourse;
- abuse of bad habits (smoking, alcoholic drinks);
- irregular sex life;
- prostatic hypertrophy;
- hemorrhoids, anal fissures (especially in the chronic form);
- various microtraumas of the perineum that arose due to non-compliance with safety rules when riding or cycling;
- sedentary lifestyle (the problem is especially acute for representatives of sedentary professions);
- hypothermia of the body.
In addition, this pathology may be a congenital anomaly. In this case, the infection penetrates the seminal vesicles along with the urine.
Routes of infection
Penetration of microorganisms into the seminal vesicles can occur in the following ways:
1. By hematogenous route. If there is an infectious focus in the body, bacteria are introduced into the seminal vesicles through the bloodstream. This happens with tonsillitis, caries, sinusitis, pneumonia. In such a situation, the provoking factor of vesiculitis is streptococcus, staphylococcus, mycobacterium tuberculosis and others.
2. Lymphogenous route. Penetration of infection occurs through the lymph flow from a nearby organ. Pathogens include Proteus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
3. Ascending way. The inflammatory process moves along the mucous membranes of the urinary tract. In this way, sexually transmitted infections, as well as E. coli, spread.
Classification of the disease
According to the duration of the course, the pathology is divided into acute and chronic vesiculitis. The second form is a logical continuation of the first, i.e. In the absence of competent therapy, inflammation flows from the acute stage to the chronic stage.
Regarding the reasons that cause this pathology, vesiculitis is divided into:
- Primary. It occurs suddenly, for no apparent reason.
- Secondary. In this case, inflammation is a consequence of other pathologies (for example, prostatitis).
According to the changes observed as a result of inflammation, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Catarrhal. In this case, the seminal vesicles contain serous exudate. The glands themselves become larger in size, and there are traces of swelling.
- Deep. Inflammation even affects the muscle layer. The glands are compacted and there is severe swelling. The exudate contains admixtures of blood and pus.
- Paravesiculitis. The inflammatory process affects the fiber that surrounds the paired glands. It is considered the most dangerous form of the disease, so the risks of erectile dysfunction and loss of reproductive function are high.
- Empyema. The glands fill with pus, their walls begin to collapse.
Mechanism of disease development
With infectious vesiculitis, an inflammatory process develops due to bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The outflow of urine becomes difficult and the vesicles swell. Due to constant urinary retention, urethral-seminal reflux appears and the infectious process worsens.
In addition, the ejaculate produced decreases in quantity. The cause is impaired contractile function of the vesicles. There is an abundant blood supply to the vesicles, the inflamed vessels become less elastic and can rupture during ejaculation, when pressure increases in the pelvic cavity.
Aseptic vesiculitis is characterized by narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, venous congestion, and increased vascular permeability. Due to such processes, ischemia of the pelvic organs and vesicles develops. It is a proven fact that the inflammatory process provokes a decrease in testosterone levels and an increase in prolactin levels. As a result, the secretory activity of the vesicles deteriorates.
Aseptic inflammation causes disruption of the contractile function of the seminal vesicles, which is the cause of early ejaculation, spontaneous erection, and nocturnal emission. Any type of inflammatory process causes disturbances in spermatodynamics and the formation of infertility.
Main symptoms
In order to start treatment on time, the patient must be more attentive to the signals that his body gives him. Vesiculitis has characteristic signs, the presence of which is important to immediately consult a doctor.
The acute form is manifested by the following symptoms:
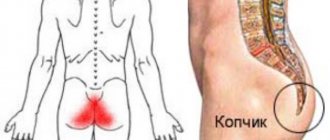
- Painful sensations in the pelvic area that radiate to the sacrum. Typically, men only feel pain on one side.
- Impurities of blood in seminal fluid.
- Pain during ejaculation.
- Often the pain intensifies during bowel movements or when the bladder is full.
- Symptoms characteristic of inflammation: headache, general weakness, increased body temperature.
As a rule, the acute stage lasts for a week. If during this period the patient does not see a doctor, the disease progresses to the chronic stage. In this case, the risk of erectile dysfunction and infertility increases.
The chronic form can occur without any symptoms at all, which leads to a worsening of the situation. In some cases, patients begin to suspect a problem only after they notice blood clots in the seminal fluid.
In addition, in the chronic form the following manifestations are possible:
- Pain during ejaculation, as well as when the penis is in an erect state.
- Pain after sexual intercourse (can last up to several hours).
- Involuntary ejaculation during the day.
- Aching pain that is localized in the sacral area.
- Problems with experiencing orgasm.
- Various problems with emptying the bladder (frequent urge, pain when urinating, or the patient has difficulty emptying the bladder).
Features of disease therapy and prevention
If the patient has acute vesiculitis, treatment is organized in a hospital. The specificity of conservative therapy depends on the causative agent of the disease:
- bacterial infection is treated with antibiotics;
- urogenital infection and rare provocateurs (Klebsiella) - a reason to take Biseptol, Lincomycin, Miranem;
- for specific infections (syphilis, etc.), antibiotics of the penicillin group are prescribed;
- if the cause of the pathology is a stagnant process, the patient will have to be treated with angioprotectors, undergo physical therapy, and prostate massage.
Treatment of vesiculitis in men is not complete without anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, acupuncture, and exercise therapy.
If there is severe inflammation of the seminal vesicles, treatment involves surgery. During the operation, the cavity of the anatomical structures is opened and drainage is performed.
Prevention of the disease consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding hypothermia, and regular visits to the urologist.
To make an appointment with a urologist at the Harmony clinic, just call us or make an appointment on the website.
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
Diagnosis of vesiculitis
The diagnosis is made by a professional urologist or andrologist. The first stage of diagnosis includes collecting anamnesis: finding out the patient’s complaints, details of his personal, including sexual, life. The doctor must find out what exactly preceded the onset of the first symptoms. An examination is carried out during which the specialist palpates the area of the seminal vesicles and prostate gland.
Next, standard laboratory tests are prescribed (general analysis of urine, blood and biochemistry). They allow you to detect the presence of an inflammatory process. The condition of the sperm must be examined. Not only fertility is assessed, but also various changes that are a deviation from the norm.
Cultural examination of seminal fluid allows one to determine the specific causative agent of this disease. Among the instrumental diagnostic methods, the following methods are used:
- TRUSY. Ultrasound examination can detect swelling of the vesicles, an increase in size, as well as other pathological signs. This procedure involves preliminary preparation so that the results of the study are as informative as possible.
- Computed tomography and MRI. A pelvic examination is prescribed if there is a suspicion of neoplasms.
How to cure chronic vesiculitis
It is impossible to determine inflammation externally during examination, so a spermogram, pelvic ultrasound, and rectal examination are prescribed. The doctor also collects and studies the patient’s medical history. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Drug therapy
Since the main cause of the disease is pathogenic bacteria, the basis of treatment is antibacterial drugs. A combined approach is often used, that is, the doctor prescribes 2 or 3 medications from different groups. To relieve pain, take analgesics with anti-inflammatory effects. If necessary, antimicrobial therapy is added.
If congestive vesiculitis is detected, treatment includes taking angioprotectors. They are aimed at improving blood circulation and strengthening the walls of blood vessels. After the acute period is over, physiotherapy is prescribed - UHF, electrotherapy, as well as physical therapy.
To improve health and prevent relapse, it is recommended to take vitamins and immunomodulators.
Other conservative treatments
These include:
- Heat therapy - using a heating pad, sitz hot baths. Heat compresses can be used independently during the lull of the disease. Sea salt is added to the bath, as well as herbal infusions of chamomile, calendula or sage.
- Microenemas with novocaine - for pain relief, with herbal extracts - for quick relief of inflammation.
- Mud therapy.
- Mineral baths (balneotherapy).
- Prostate massage. It is carried out only by a doctor in a clinical setting.
It is important during the treatment period to follow a certain diet. All spicy dishes, spices, pickles, and vinegar are excluded from the menu. All these products only intensify inflammatory processes. All drinks containing alcohol are strictly prohibited. Dairy and vegetable products, cereals are allowed. Meat and fish can be eaten, but preferably boiled or steamed.
Surgery
In case of complicated vesiculitis, as well as in the event of ulcers or accumulation of pus, surgical intervention is performed. The abscess is opened and cleared of purulent contents. In rare cases, vesiculectomy is performed, that is, partial or complete removal of the seminal vesicles.
Surgery may also be recommended if several courses of drug therapy are ineffective. Rehabilitation after surgery takes several weeks.
Treatment methods
Treatment of this pathology depends on the specific cause that caused the inflammation. If the pathology is infectious in nature, then antibacterial therapy is prescribed. In case of stagnation, the doctor prescribes drugs that eliminate these stagnation.
As a rule, in case of an infectious factor, the following are prescribed:
- Antibiotics to which microflora is sensitive
- Sulfonamides
- Nitrofurans
If the cause is stagnation, then the following are prescribed:
- Angioprotectors
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
- UHF therapy
- Massage the area of inflammation
Vesiculitis is accompanied by pain of varying degrees of intensity, so it is important not only to treat the root cause of the disease, but also to eliminate the accompanying symptoms. As a rule, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, which not only relieve pain, but also reduce the inflammatory process.
The administration of immunomodulators allows you to strengthen the body’s general defense mechanisms, which will help you cope with the infection faster. In addition, they reduce the risk of relapse.
List of sources
- Svetlova L.N. Mechanisms of persistence of pathogenic microflora in chronic prostate-vesiculitis in infertile men / L.N. Svetlova, Yu.V. Vasiliev, NH Martynovich // Bulletin. VSSC SB RAMS. - 2009. - No. 2. - P. 64-66.
- Borodina N.M., Merkulov V.I., Zakharova E.B., Tyutyunnik I.V., Kukurekin Yu.V. Features of the treatment of chronic prostate vesiculitis // Collection of scientific works. Issue 6 (102): Kiev-Lugansk. — 2010 r. - pp. 271-280.
- Inflammatory diseases of the accessory sex glands in men, caused by latent urogenital infection and complicated by infertility. Abstract of the dissertation/ Kalinina S.N. – 2003.
- Pathogenetic mechanisms of development of chronic prostate-vesiculitis in infertile men. Abstract of the dissertation/ Svetlova L.N. – 2009.
- Vasiliev Yu.V. A method for increasing the effectiveness of eradication of urogenital flora / Yu.V. Vasiliev, L.N. Svetlova // Men's health: materials of the 3rd All-Russian. conf.: Sat. abstract - M., 2006. - P. 180-182.
Prevention methods
The occurrence of this pathology can be prevented if basic preventive measures are followed. First of all, we are talking about timely detection and treatment of sexually transmitted infections.
In addition, it is important to eliminate provoking factors from your life, as well as make certain adjustments:
- Try to have a regular intimate life. It is important to always use contraception.
- When working sedentarily, you need to take breaks more often. During them, you can do simple exercises, or just walk around. Remember that your vacation should be active, and not sitting at the computer. In this case, even regular walking around the city will be useful.
- Eliminate fast food, too fatty and salty foods from your diet. It is better to eat more vegetables, fruits, and drink enough liquid.
- Eliminate or limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages. It is better to quit smoking altogether.
- You need to avoid too frequent masturbation, stress, etc.
Detection of the disease at an early stage is an important condition for successful treatment. If you allow the disease to enter the chronic stage, then there is a high probability of developing infertility and problems in the intimate sphere.
Diet
Diet for prostatitis
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21 days
- Time frame: 3 months
- Cost of food: 1380-1450 rubles per week
There is no diet directly for vesiculitis, however, given that in the vast majority of cases, vesiculitis occurs in the form of prostate-vesiculitis, patients can be prescribed a diet for prostatitis , which is an important component of complex treatment. The diet is based on the general principles of rational nutrition.
In the acute period, preference in the diet should be given to a dairy-vegetable diet (cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk, soft cheese, cereals, vegetables and fruits), limiting (excluding) from the diet foods that irritate the prostate gland - sausages, strong meat broths , hot spices, sauces (ketchup, mayonnaise), eggs, hard cheese, smoked meats, strong coffee/tea, all fried/fatty foods, spicy vegetables (horseradish root, radish, daikon, radish, onion, garlic, ginger), pickles/ marinades, alcohol-containing drinks (especially beer), fast food, carbonated drinks, limit salt and sugar intake to 8-10 g/day. The diet should include low-fat boiled/baked fish, poultry and rabbit meat, beef, potatoes, cereals, baked apples, vegetable/fruit purees, fruit/vegetable juices.
Of the fats in the diet, preference should be given to fats of vegetable origin (sunflower, olive, flaxseed, corn oil), excluding any refractory animal fats. To normalize bowel movements/prevent constipation , the diet should include foods rich in fiber (bran, grain bread, whole grain porridge, fresh vegetables/fruits, wholemeal products). Plums/prunes, beets, and fresh apricots contribute to normalization.
It is useful to include natural biostimulants in the diet (bee products - honey, propolis, pollen, beebread, royal jelly), Manchurian aralia, aloe extract, Schisandra chinensis, echinacea, eleutherococcus, mumiyo, elecampane, as well as products containing zinc - oysters, seafood, lean red meat, dry yeast, herring, wheat bran, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds; selenium (lard, seaweed, brewer's yeast, offal, wholemeal flour, rice, buckwheat, bran) and vitamin E (sprouted wheat oil, green peas, corn oil, chicken eggs, parsley).
Compliance with the drinking regime is also important. Non-carbonated mineral waters, freshly prepared fruit drinks, herbal teas, juices, compotes are recommended, however, in the presence of dysuric disorders, fluid consumption in the second half of the day must be limited.