Cystitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. By the nature of its occurrence, it can be infectious or non-infectious, that is, resulting from diseases of the bladder. In urology, this disease is one of the most common and affects 25% of women worldwide, and in 10% of them it occurs in a chronic form.
In men, cystitis occurs 8 times less frequently, which is due to the anatomy of the male genitourinary system. Since women have a much shorter and wider urethra, it is easier for ascending infections to enter the body, so this disease is most often considered to be a female disease.
Lack of treatment or the wrong approach to it can lead to very serious complications, therefore, if you suspect cystitis, the symptoms of which interfere with your normal lifestyle, you should immediately seek medical help at the private clinic “Doctor Anna”.
Cystitis in women - symptoms and treatment
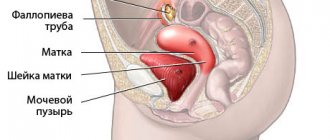
Due to the specific anatomical structure of the genitourinary system - a short and wide urethra and the proximity of the rectum and vagina - cystitis can most often be found in women.
The main signs of cystitis in women are:
- frequent, painful urination;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- cloudy urine, often mixed with blood;
- pain in the lower abdomen, in the projection area of the bladder;
- low-grade fever with cystitis (up to 37.5℃).
If you have at least two of the listed signs of cystitis, it is recommended to consult a urologist as soon as possible.
Diagnosis is carried out, first of all, on the basis of the patient’s complaints and tests for cystitis - a general urine test. Also, for better information, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys, and microbiological culture to determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
As an auxiliary diagnostic study, if the doctor has doubts when making a diagnosis, it is possible to perform a cystoscopy, in which the bladder area is viewed through a thin tube at the end of which there is a camera. If necessary, the patient is sent for computed tomography, MRI, and determination of general and biochemical urine analysis.
The following approaches are used in the treatment of cystitis in women:
- Medication. Depending on the specific causes of cystitis in women and based on test results, uroseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and antispasmodics, and herbal uroseptics may be prescribed.
- Physiotherapy. Physiotherapy speeds up the healing process, provides longer remission, and improves the delivery of medications to the affected area.
- Iontophoresis and instillation - intravesical administration of drugs. The use of instillation is recommended only during remission.
- Treatment of concomitant gynecological pathologies.
It is highly not recommended to prescribe any type of treatment for yourself. This can lead to irreparable consequences. Any type of therapy can be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
It is worth understanding that having discovered cystitis, treatment is not carried out according to a specific, universal scheme for each patient. Correct treatment depends on what medications the patient took and for how long before seeing a doctor, what effect these medications had, what are the causes of the disease and how long it has been present.
Having examined the visitor and carried out all the necessary tests for cystitis, the doctor, using all the presented methods of therapy, develops an individual approach in each individual case.
Often people, in an attempt to eliminate cystitis on their own, use traditional medicine methods. Preparations based only on herbal components can help get rid of the problem, but only for the recovery period, that is, they do not replace the main treatment, but only complement it.
The use of herbal preparations alone is not capable of destroying the causative agent of the disease, which means that the situation can become chronic or aggravate the course of the disease by moving the ascending infection to the kidney area.
It is important to remember that heating the bladder area during an exacerbation is strictly prohibited. Bacteria multiply at a faster rate as body temperature rises, thus making the problem worse.
Diagnosis of pathology
A urologist diagnoses and treats cystitis. Only a specialist knows how to properly treat this disease in order to avoid chronicity of the inflammatory process and not cause harm to health.
You can get examined and diagnosed at the nearest clinic. However, this takes time, since you need to wait 2-3 weeks for an appointment with a doctor. But in the presence of acute or subacute cystitis, time is the most valuable resource. Therefore, the best option is to contact the Medunion private medical clinic. Here you can sign up for an examination today and see a doctor tomorrow.
The urologist will determine your general health, ask about previous diseases, frequency of urination, and medications taken. Next, the specialist palpates the abdomen, kidney area, and lower back.
Cystitis in men - looks and feels the genitals. Examines the prostate gland - rectally.
Cystitis in women - assesses the condition of the mucous membrane, female genital organs, palpates the bladder and ureters.
The following tests may be needed for diagnosis:
- general urine analysis
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
- bacteriological examination of urine
- cystoscopy
- Ultrasound of the bladder and abdominal organs, including the kidneys
Signs of cystitis in women
Signs of cystitis vary and depend on many factors - from the age of the patient, to lifestyle and the type of pathogen.
Symptoms of cystitis are clearly distinguished, which cannot be ignored due to their intensity - severe pain during and at the end of urination, and frequent painful urges.
The appearance of bloody discharge may indicate the presence of an acute inflammatory process.
Cystitis with constant exacerbations leads to problems with sexual life. If cystitis is not treated in time, problems with urine leakage may occur, which significantly worsens a woman’s quality of life.
Therapy
The treatment regimen for chronic cystitis will vary depending on the pathogen. In addition to taking medications, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and diet. For a speedy recovery, rest and light food are desirable. The drinking regime is plentiful; the use of diuretics is recommended to remove pathogenic microorganisms.
Prescriptions may consist of the following medications:
- antibacterial (when pathogens are detected on crops);
- antispasmodic (eliminate muscle spasms, relieve pain, promote urine evacuation);
- anti-inflammatory (improves the condition of the mucous membrane, promotes epithelial regeneration).
Herbal medicine is effective as part of complex treatment. It is important to understand that the course prescribed by the doctor must be completed in full. Taking medications should not be stopped after the first improvement, because the disappearance of symptoms does not indicate complete recovery.
After a course of antibiotics, if necessary, the doctor may prescribe restorative therapy, which will be aimed at normalizing the microflora of the vagina and gastrointestinal tract.
Causes
The causes of cystitis can be divided into two groups - anatomical and concomitant. Anatomical reasons are associated with the proximity of the vagina and anus, and, as a consequence, the microflora of the rectum enters the urethral area. There is also no obstacle to the entry of microorganisms from the anal area due to the fact that the urethra of women is short and wide, unlike men.
Among the associated reasons are the following:
- Intense sex life. The number of sexual partners directly depends on the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms into the urethra.
- Features of sexual activity (combination of oral, anal and vaginal sex). If vaginal sexual intercourse occurs after oral or anal intercourse, this provokes the reflux of abnormal flora into the urethral area.
- Hypothermia;
- Concomitant surgical or gynecological pathology. Vaginal infections, infections in the pelvic organs, in the cervix, urolithiasis.
- Decreased immunity;
- Changes in hormonal levels during menopause. Female sex hormones estrogens have immunomodulatory and protective properties. That is why, when the concentration of estrogen in the body decreases during menopause, a woman becomes more vulnerable due to changes in her hormonal profile.
- Disturbance of urine outflow. A situation when a person puts off going to the toilet and endures without emptying the bladder on time.
- Violation of intimate hygiene.
It is extremely rare for patients to have only one cause, most often several are combined at once.
Preventive actions
Treatment of exacerbations of chronic cystitis involves the development of recommendations for preventing relapses. A comprehensive diagnosis helps with this. After establishing the cause of the pathology, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulants and drugs to support hormonal levels. Adjusting the drinking regime and diet help. Physiotherapeutic procedures and gymnastics have proven themselves to be effective preventive measures.
Treatment and recovery services for chronic cystitis are offered by the Dr.AkNer clinic. We employ urologists and gynecologists with extensive experience in successfully treating even the most complex cases. Specialists accept appointments by appointment, so you don’t have to spend time in queues.
What can cystitis be confused with?
It is difficult to give a definite answer to the question of what cystitis can be confused with, because similar symptoms of cystitis in women can be characteristic of a large number of pathologies. But we can highlight the main, most common diseases:
- Urinary dysfunction. Improper functioning of the kidneys leads to impaired blood filtration and urine excretion in small quantities.
- Mechanical damage to the ureter;
- Inflammation of the appendix. In the initial stages, cystitis and appendicitis have similar symptoms. Inflammation causes nagging pain in the lower abdomen, hyperthermia and deterioration in general well-being.
- Urolithiasis disease. Such pain can be caused by crystals located in the kidneys. Over time, small crystals form stones that can begin to move along the ureter and cause severe pain radiating to the perineum.
- Glomerulonephritis. Inflammation of the glomeruli and small blood vessels of the kidneys.
- Pyelonephritis. An infectious and inflammatory disease that affects the pyelocaliceal system and renal parenchyma. The signs of cystitis and pyelonephritis are similar, so a specific disease can be differentiated by a blood test.
- Gynecological pathology. Cystitis is often confused with gynecological diseases. These two conditions of discharge are distinguished - with inflammation of the bladder, white discharge from the urethra may be present, and if a woman finds unhealthy discharge from the vagina, this may be a sign of the presence of pathology of the genital organs.
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Hemorrhagic cystitis or hematuria is characterized by the presence of blood in the urine. Normal urine is straw-yellow in color, which can vary in shades from light to dark depending on the quantity and quality of fluid and food taken.
If the urine is colored red, then most often the reason for this is the presence of blood, that is, hemorrhagic cystitis.
There are many reasons for this disease. Blood can be a consequence of urolithiasis, neoplasms, infections, injuries, anomalies in the development of the genitourinary system, kidney prolapse, kidney cysts, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, taking certain medications, intense physical activity.
Postcoital cystitis
Postcoital cystitis is cystitis that occurs after sexual intercourse due to the low location of the urethra in a woman.
During frictional movements during sexual intercourse, the opening of the urethra is screwed into the vagina and aggressive external microflora enters the urethra, and then into the bladder, causing its inflammation.
The incubation period in this case is short - from several hours to 2-3 days. The woman experiences painful, scanty urination, and a constant feeling of a full bladder.
Treatment of cystitis in women is carried out surgically and non-surgically. During surgery, the urologist increases the distance between the urethra and the entrance to the vagina.
Non-surgical treatment of cystitis in women is based on intimate filling. In this case, in order to change the anatomy of the urethral opening, the doctor uses a dense gel filler based on hyaluronic acid. It is inserted under the urethra, raising the opening above the vaginal opening.
How does cystitis manifest during pregnancy?
During the period of bearing a child, a woman’s protective functions of the immune system decrease. Therefore, when a pathological organism enters the body, it causes an inflammatory process much faster.
The development of cystitis is facilitated by features of female physiology. The shorter and wider shape of the urethra, its proximity to the vagina and intestines, contributes to the rapid transmission of infections from neighboring organs.
With this disease, the walls of the bladder become inflamed, which leads to disruption of its functions. The symptoms of cystitis are quite specific - they are difficult to confuse with other pathologies. A woman may experience frequent, painful urination, blood in the urine, and fever.
First of all, a woman should visit a urologist. He will prescribe the necessary tests, examinations and advise you to undergo additional consultation with a gynecologist. This allows you to exclude the presence of genital infections, which can lead to bacterial vaginosis, colpitis, and thrush.
How to treat cystitis in pregnant women? The diet, immunity and hormonal status are corrected, and blood circulation is improved. Then it is necessary to begin the fight against pathogens (Escherichia coli, Candida fungi, STIs, viruses), and restore the damaged structure of the bladder.
Complications
One of the most common complications is vesicoureteral reflux - urine from the bladder enters the ureter and then into the kidneys, that is, it flows in the opposite direction.
If this process is not stopped, inflammation of the ureter and kidneys occurs, which can lead to inflammation of the uterus and appendages. In advanced conditions, urine accumulates in the kidneys, which provokes peritonitis and inflammation of the peritoneum.
Also, scars and abscesses can often form in the bladder, as a result of which the volume of the bladder decreases, frequent urination appears, and ulcers form.
Another complication is cystalgia, which is associated with inflammation of the nerve endings that innervate the bladder. Trigonitis often occurs - inflammation of the triangle located between the ureter and the urethra.
Other complications include reproductive dysfunction, since prolonged, protracted cystitis, especially in the acute stage, can lead to spontaneous abortion.
Cystitis in men can lead to inflammation of the prostate gland or prostatitis, since the outflow of urine is disrupted and it flows into the prostate gland. The presence of an infection in the bladder also infects the prostate gland, which leads to inflammation of the prostate, and in some cases epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis).
In advanced cases, paracystitis or inflammation may spread to the pelvic organs. With ulcerative cystitis, deep ulcers form on the mucous membranes; they do not heal for a long time and cause a number of symptoms characteristic of the acute form of this disease.
Before and after tests
According to standards, treatment of cystitis with antibiotics is prescribed immediately. Before treatment, only a general urine test is required to detect signs of inflammation. And if it is not possible to take it to the laboratory, you can use an express test strip. Next, antibiotics are prescribed. In more than 80% of cases, cystitis is caused by the bacterium E. coli, or Escherichia coli. But opportunistic bacteria (Klebsiella, ureoplasma, streptococcus, staphylococcus) can also be causative agents. They themselves do not cause the disease, but weaken the body’s immune defense, and against this background pathological flora - fungi, bacteria - joins.
And after a course of antibacterial therapy, it is recommended to do a bacterial culture of the urine to make sure that there is no causative agent of the disease, which means that the infection has been cured.
Treating cystitis with folk remedies is less effective than antibiotics. Therefore, warm heating pads, herbs and cranberry juice are best used only in addition to treatment. And also only with the permission of a doctor, because any drugs, even herbal ones, can cause allergies or have individual intolerance. However, medicine knows cases of spontaneous healing of cystitis, when a strong immune system managed to cope with the inflammation on its own. However, playing “roulette” with a disease is quite dangerous, especially if there are effective medications.
Which doctor should I contact?
Acute cystitis is usually treated on an outpatient basis, but before that you need to make an appointment with a urologist for examination and quality treatment.
The patient needs bed rest and limited physical activity. Treatment lasts on average from 5 to 7 days. As a medicinal treatment, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory, antibacterial therapy, and for painful urination, antispasmodic therapy.
It is recommended to exclude spicy and salty foods and alcohol. You should drink a lot of liquid, cranberry juices, compotes. If necessary, medications are instilled into the bladder.
Types of cystitis
There are several classifications of pathology: by course, type of inflammation, causes. We will dwell in more detail on the classification according to the course of the disease.
- Acute cystitis appears several hours after exposure to a harmful factor. It has pronounced symptoms of the inflammatory process with a tendency to progress. If acute cystitis is not treated or the wrong therapy is used, there is a high probability of developing a chronic form.
- Subacute cystitis has a blurred clinical picture. Symptoms are mild or not present. It may be accompanied only by pain and urination problems, but there are no symptoms of intoxication of the body (fever, aches, chills).
- Chronic cystitis occurs due to untreated acute cystitis. It is characterized by a sluggish course, the symptoms are not expressed, and sometimes it is completely asymptomatic. That is, the factor that provokes inflammation in the bladder remains, without revealing itself in any way, but at some point a sharp exacerbation occurs with all the ensuing consequences: frequent and painful urination, burning, itching, cloudy urine, ailments, etc.
Prevention
It is better not to get sick than to be treated. Of course, often the development of cystitis does not depend on the implementation of any recommendations - for example, during pregnancy or surgery. But in everyday life you should adhere to these rules:
- compliance with hygiene rules - do not introduce infection from the rectum, wash yourself in a timely manner, do not use aggressive detergents for washing;
- avoid hypothermia;
- change pads and tampons regularly so as not to provoke the growth of bacteria;
- Closely monitor the health of the genitourinary system, treat any problems so that they do not get worse.
Following these simple rules will allow you to never find out what cystitis is, or prevent a recurrence of the disease if you have already had such a sad experience.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Question answer:
What to do after treatment of acute cystitis?
At the end of the course of therapy, the patient must follow the doctor’s recommendations to prevent exacerbation of chronic cystitis. After an illness, the patient is recommended the following:
- Avoid hypothermia. Avoid sitting on cold surfaces. Do not swim in cold waters. Dress appropriately for the weather.
- Don't wear tight underwear. Avoid synthetic clothing.
- Maintain strict personal hygiene.
- Don't use tampons.
- When working in a sedentary position, do a five-minute warm-up every hour.
- Avoid stress and physical fatigue.
- Treat colds promptly.
- Review your diet. Avoid spicy, fried, fatty foods. Limit your salt intake. Reduce the use of spices.
- Eat fresh vegetables, non-acidic fruits, berries and herbs. Avoid alcohol.
- Drink at least 2 liters of liquid during the day.
- Get regular medical check-ups.
- Use infusions and decoctions of herbs with a diuretic effect.
Following the recommendations will significantly reduce the likelihood of recurrent cystitis and the disease becoming chronic.
What complications can occur with cystitis?
The main complication of the disease is the spread of inflammation to the kidneys and the development of pyelonephritis. Sometimes the infection spreads to the fibrous tissue around the bladder. Paracystitis forms.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of cystitis depend on the form of the disease. In the case of a chronic type of pathology, it shows almost nothing. The patient feels slight discomfort during urination. With an exacerbation, bright symptoms of the disease appear. They cause significant discomfort to the patient. The following symptoms of cystitis are distinguished:
- pain after urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- burning sensation in the urethra;
- frequent urination (every fifteen minutes);
- aching pain in the lower abdomen that radiates to the lower back;
- false urge with separation of a small amount of urine;
- temperature increase;
- general deterioration of health (vomiting, general weakness, nausea);
- cloudiness and darkening of urine with the appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- feeling of incomplete emptying;
- impurities in the urine (mucus, pus, blood).
The temperature reaction in acute cystitis often rises to low-grade levels. When it reaches high numbers, this serves as an indicator of the spread of inflammation into the kidney tissue or the penetration of infection into the deep layers of the bladder.
How to relieve the symptoms of cystitis before consulting a gynecologist
Rules that you can begin to follow even before going to the doctor and together with the recommended therapy:
- Bed rest. This will support the body in the fight against the disease.
- As mentioned above, drinking plenty of fluids will speed up recovery.
- Food should not be spicy or salty. It is best to eat foods high in calcium - dairy products, some vegetables.
- You can and should use herbal decoctions and special mixtures. Also in pharmacies there are tablets with extracts of the same herbs. If the disease is not very severe, such treatment may be sufficient. But it is better for a specialist to give recommendations regarding herbal treatment.