This information explains how to relieve shortness of breath.
Sometimes you may find it difficult to breathe and feel like you are out of breath. This condition is called shortness of breath or dyspnea. Shortness of breath may be caused by:
- damage to the lungs due to cancer or its treatment;
- blood clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism);
- fluid around the heart or lungs;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- asthma or emphysema;
- heart damage (chronic heart failure);
- anemia (low levels of red blood cells in the body).
Depending on the cause, shortness of breath may be transient or permanent.
to come back to the beginning
Causes of shortness of breath.
In order for the doctor to determine the cause of shortness of breath, it is very important to know how quickly it appeared. It can occur acutely (within minutes, hours, several days) or gradually (several weeks, months, years).
The most common causes of shortness of breath that occurs acutely (suddenly):
- Lung diseases such as pneumonia, bronchial asthma, pulmonary embolism. For example, bronchial asthma is characterized by an attack of shortness of breath or suffocation. Pneumonia most often causes a high fever and difficulty breathing.
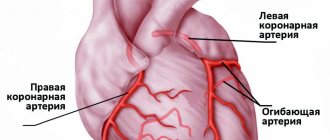
- Heart diseases: myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, heart defects, etc. Shortness of breath due to heart disease is colloquially called cardiac shortness of breath. For example, with myocardial infarction, pain in the heart and shortness of breath, palpitations and general weakness are disturbing, symptoms appear suddenly.
- Severe allergic reactions - Quincke's edema (angioedema) and anaphylactic shock. In these diseases, shortness of breath is associated with rapid swelling and narrowing of the larynx and/or bronchi, as a result of which air cannot enter the lungs.
The most common causes of shortness of breath, which progresses gradually:
- Lung diseases: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchial asthma (in the absence of treatment or severe disease), lung cancer, cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, emphysema, diffuse parenchymal lung diseases (sarcoidosis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, histiocytosis X and etc.), consequences of pulmonary tuberculosis, etc. In case of lung diseases, a feeling of lack of air is, in common parlance, called pulmonary shortness of breath. For example, with COPD, the lack of air is first a concern during exercise, and then at rest or with light exertion.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels that lead to the development of chronic heart failure: consequences of myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, hypertension (high blood pressure), heart defects, cardiomyopathy, etc. With chronic heart failure, dyspnea, edema, and palpitations appear. Symptoms initially occur with physical exertion, and as the disease progresses, severe shortness of breath occurs even at rest.
- Overweight, obesity. Difficulty breathing in obesity is a very common occurrence and in most cases is caused by developing pathologies. Shortness of breath during pregnancy is considered separately - this is a normal condition. It is most often minor and appears around the 26th week of pregnancy. Occurs during physical activity or in a lying position. It is due to the fact that an enlarged uterus increases intra-abdominal pressure, the diaphragm rises, and this leads to a decrease in lung volume.
In fact, there are many more reasons for shortness of breath. The diseases and conditions listed above are the most common. If you experience shortness of breath, it is best to consult a doctor to determine the specific cause of the feeling of shortness of breath. It is very important to see a doctor or call an ambulance immediately if you suddenly experience shortness of breath, especially if it is accompanied by chest pain, nausea, vomiting or fever. These signs may indicate a very serious illness. In any situation, the doctor will be able to determine an individual examination plan to determine the cause.
Relief from anxiety
Shortness of breath can cause feelings of fear. Some people say they feel anxious when they start to feel short of breath. However, anxiety can make breathing even more difficult.
Breathing exercises from this material can help you relax. You may also want to know other ways to help relieve anxiety. Talk to your doctor about any anxiety you have. He may prescribe anti-anxiety medications such as alprazolam (Xanax®) or lorazepam (Ativan®) to help you.
Our Integrative Medicine Service also offers relaxation programs that may be beneficial for you.
to come back to the beginning
The mechanism of shortness of breath.
In most cases, shortness of breath is due to hypoxia (low oxygen in the body) or hypoxemia (low oxygen in the blood). Low oxygen levels cause irritation of the respiratory center in the brain, resulting in a feeling of lack of air and breathing involuntarily quickens. The causes of hypoxia can be diseases of the lungs, heart or extrapulmonary diseases that limit the mobility of the chest and lungs (pregnancy, obesity, etc.).
Breathing exercises
Your nurse can show you how to take slow, deep breaths to help relieve shortness of breath. You can do them with the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity (see Figure 1). This type of breathing is called diaphragmatic breathing.
Figure 1. Aperture
Try to relax while doing breathing exercises. Relieve muscle tension. This will allow the abdominal cavity (belly), chest, and lungs to expand.
Here are some breathing exercises that can help relieve shortness of breath.
Deep breathing 4-8-8
This exercise improves the movement of air in the lungs. This helps increase oxygen levels throughout the body.
- Inhale through your nose, counting to 4.
- Hold your breath and count to 8.
- Exhale through pursed lips (as if you were whistling) for a count of 8.
- Repeat 4 times.
Chest wall stretch
This exercise will help the chest muscles become more elastic.
- Inhale through your nose, counting to 4. As you inhale, extend your arms in front of you and raise them above your head.
- Exhale through pursed lips. As you exhale, open your palms and lower your arms down to your sides.
- Repeat 4 times.
Rapid breathing through the nose
This exercise can help strengthen your diaphragm.
- Shut your mouth.
- Inhale and exhale quickly through your nose for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Practice this exercise several times until you can do it for 60 seconds.
Walking and breathing
These tips will help you breathe easier when walking.
- When walking on a level surface, inhale and exhale through your nose without opening your mouth.
- On inclined surfaces (slopes), inhale through your nose and exhale through pursed lips.
- When climbing stairs, exhale at each step through pursed lips.
Recovery from an attack of shortness of breath (from coughing or exercise)
- Tuck your chin to your chest.
- Take 10 short and sharp exhalations through your mouth. If necessary, take short breaths between them.
- When your neck muscles relax a little, inhale through your nose.
- Exhale 3 times through pursed lips. Inhale between exhalations.
- Inhale through your nose, counting to 4.
- Exhale through your open mouth, counting to 8 and making the sound “ah”.
- Repeat 3 times.
to come back to the beginning
How to treat shortness of breath? Is there a cure for shortness of breath?
The most important method of combating dyspnea is to treat the disease that caused it. As soon as the doctor finds out the cause, an effective treatment plan will be immediately determined. For example, for coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction - treatment with tablets. For COPD and bronchial asthma - regular treatment with inhalers. Since the main cause of shortness of breath in many cases is hypoxia and hypoxemia (low oxygen levels in the body), one of the effective ways to reduce shortness of breath is oxygen therapy. Currently, devices have been developed - oxygen concentrators, which allow you to “extract” oxygen from the air around the clock. Inhalation of oxygen in high concentrations eliminates hypoxia and hypoxemia.
With progressive diseases such as COPD, lung cancer, cystic fibrosis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, chronic heart failure, there comes a time during the course of the disease when medications no longer help as well as before. Shortness of breath increases and causes a lot of trouble: it is difficult to get dressed, wash, and eat. In this situation, there is a way out - oxygen therapy. This method of treatment, when added to the main therapy, helps:
- prolong life (for COPD - by 5-10 years);
- reduce the painful feeling of shortness of breath;
- improve sleep and mood;
- reduce the feeling of heartbeat during exercise and at rest;
- will help increase physical activity.
Many clinical studies have proven the effect of oxygen therapy on reducing shortness of breath, improving the quality of life and its duration.
Symptoms of shortness of breath
Dyspnea can be characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations due to the large number of possible causes. However, the most common symptoms are coughing and changes in breathing patterns. Signs may appear when a person is at rest and during intense exercise.
Symptoms that accompany shortness of breath:
- fatigue, weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- sudden lack of air;
- difficulty breathing in and out;
- signs of dizziness;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- fast, irregular heartbeat;
- decreased physical activity;
- cough or wheezing when breathing;
- hemoptysis (coughing up blood);
- blueness of nails and lips due to poor circulation;
- pain, tightness in the chest (if shortness of breath occurs as a result of a heart attack).
The patient feels as if after intense physical activity or hard physical work. Respiratory dysfunction prevents a person from speaking normally and pronouncing long words and phrases. Speech becomes short and abrupt.
All breathing problems, whether sudden or long-term, regardless of symptoms, should be taken seriously. Although many of the possible causes are harmless and easily treatable, you should still see a doctor for a thorough medical examination.
FAQ
Which doctor should you contact if you notice signs of shortness of breath?
First of all, you need to make an appointment with a therapist. He will issue directions for primary tests and diagnostic studies. Based on the results obtained, it will become clear which specialist to refer the patient to. Most often, further treatment is carried out by cardiologists, pulmonologists and neurologists.
Can pregnant women experience shortness of breath? Is it dangerous for the fetus and mother?
Shortness of breath during pregnancy is observed quite often. This is due to constriction of the lungs by the diaphragm. The fetus is constantly growing, the load on the heart and lungs increases. Therefore, shortness of breath should not be considered a danger in this case. The normal respiratory rate in pregnant women is 22-24.
How to deal with systematic shortness of breath?
Of course, you need to understand the reasons for its appearance in the first place. If shortness of breath is not associated with serious illnesses, but is only a consequence of physical weakness of the body (perhaps after an injury or a long-term serious illness), then evening walks in the fresh air will help. You can get a dog, which will become an additional incentive for physical activity and walks.
Treatment of shortness of breath
Treatment of shortness of breath is carried out in accordance with the cause and individually for each patient.
For bronchitis with difficulty in sputum discharge, the therapist may prescribe sputum thinners and expectorants; for bronchial obstruction, bronchodilators.
Treatment of shortness of breath in heart failure is complex and prescribed by a cardiologist.
For hematogenous dyspnea, treatment is aimed at combating anemia.
The psychogenically caused feeling of lack of air, characteristic of panic attacks and other forms of neurotic disorders, is treated in a course of psychotherapy.
In case of massive pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity and compression of the lung), puncture of the pleural cavity (removal of fluid) may be necessary, performed by a surgeon.
In acute conditions with severe life-threatening respiratory disorders, urgent hospitalization of the patient in the intensive care unit for mechanical ventilation is required.
If you are concerned about shortness of breath, you should consult a doctor. The multidisciplinary team of doctors at the Yauza Clinical Hospital will help you correctly prescribe and conduct an examination, establish the cause, and prescribe effective treatment.
Diagnostics
Patients with complaints of shortness of breath or difficulty in exhaling seek help from a pulmonologist or local physician. The diagnostic search involves conducting laboratory and instrumental studies of the respiratory system and functional tests. The most informative ways to clarify the cause of shortness of breath are:
- Assessment of external respiration
. Spirometry is a non-invasive and accessible method of research, during which the main parameters of the respiratory system are recorded - vital capacity of the lungs, forced expiratory volume in the first second. A bronchodilation test is indicated to differentiate between COPD and asthma. - X-ray examination
. Performing an X-ray of the chest organs in 2 projections allows us to detect typical pathological changes (diffuse sclerosis, emphysema, space-occupying formations), which usually cause shortness of breath. Further examination involves the use of computed tomography and MRI. - Laryngoscopy
. To identify narrowing of the lumen of the larynx and visualize foreign bodies, the mucous membranes are examined using a special laryngoscope. In the absence of signs of damage, laryngoscopy is complemented by tracheobronchoscopy for a detailed study of the structure of the bronchial tree with the collection of material for cytomorphological examination. - Electrocardiography.
An ECG is performed to exclude cardiac causes of shortness of breath. If the results are questionable, the cardiovascular system is examined in an expanded format: phonocardiography and cardiac ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound are prescribed. In case of possible periodic disturbances, Holter monitoring is used. - Lab tests
. Assessing blood oxygen saturation and carbon dioxide levels is necessary to determine the degree of respiratory distress. A general blood test may show signs of inflammatory processes (increased ESR, leukocytosis). A biochemical blood test is also recommended.
To identify the etiological factor of shortness of breath, allergy tests are performed; the results of an extended immunogram are informative. If suspicious formations are detected on radiographs, a transbronchial lung biopsy is performed. To diagnose rare congenital defects as a possible cause of dyspnea, specialized specialists are involved.
Inhaled bronchodilators are used to quickly relieve shortness of breath
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If an attack of shortness of breath suddenly begins, the patient must be calmed down, seated on a chair or bed so that the torso is in an elevated position. To make breathing easier, it is advisable to remove tight clothes, a belt, and unbutton your shirt collar. It is necessary to ensure the flow of fresh air into the room - open a window or door. The use of herbal sedatives is allowed. Frequent occurrence of breathing difficulties indicates the development of a disease or the progression of existing diseases. In such a situation, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Conservative therapy
The treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account the cause of dyspnea. An important place in the treatment of chronic conditions accompanied by shortness of breath is occupied by lifestyle correction: quitting smoking, regularly performing a special set of physical exercises. In case of hypoxemia, oxygen therapy sessions are performed. Etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic drug therapy with drugs from the following groups is indicated:
- Bronchodilators
. Short-acting beta-agonists in the form of inhalers are used to quickly relieve attacks of shortness of breath. Long-term β2-agonists, methylxanthines, are used as basic therapy. - Expectorants
. Medicines are effective for chronic bronchitis and COPD. They stimulate the discharge of sputum and improve the permeability of the bronchial tree. In some cases, expectorant drugs are combined with mucolytics. - Antibiotics.
Antimicrobial agents are prescribed for acute and chronic inflammatory damage to the respiratory tract caused by bacterial microflora. When choosing an antibacterial drug, the results of sputum culture are taken into account. - Cardiotonics
. To reduce shortness of breath in patients suffering from heart disease, cardiac glycosides are used. Pre- and afterload on the myocardium is reduced with the help of peripheral vasodilators and diuretics. - Corticosteroids
. In case of severe respiratory disorders, taking hormonal medications on an ongoing basis is indicated. In patients with bronchial asthma, inhaled forms of glucocorticoid hormones are effective. - Cytostatics
. Courses of chemotherapy with antitumor drugs are recommended for patients with malignant neoplasms of the lungs and bronchi. To enhance the effect, drug treatment is supplemented with radiation therapy.
Preventing shortness of breath
Since shortness of breath is not an independent disease, but only a symptom, you must first take care of your heart and lungs. For this purpose, the following are recommended as preventive measures:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- monitor the daily routine (ensure a balance of work and rest, sound, standardized sleep);
- exclude heavy, fatty foods, fast food, carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- reduce excessive physical activity;
- protect your nervous system from stress and anxiety.