Read about the diagnosis and treatment of cholelithiasis at the link.
Get help right away if you develop signs and symptoms of a serious complication related to gallstones, such as:
- Abdominal pain is so severe that you cannot sit still or find a comfortable position
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- High temperature with chills
Number to call an ambulance in Moscow – 103
Prevalence of the disease
Every decade, the number of patients with cholelithiasis is steadily growing. Since the middle of the last century, the number has doubled every ten years. Currently, more than 10% of the world's population suffers from this pathology. In our country, the disease has been diagnosed in 15 million patients; in the United States, more than 30 million patients are registered. Most often, residents of developed countries are susceptible to the disease, and the risk of the disease increases with age. Among people over 45 years of age, every third person develops the disease. The number of operations performed for cholelithiasis in America in the 70s of the last century exceeded 250 thousand; in the 80s, over 400 thousand were performed. By the end of the century, the number of operated patients had already reached 500 thousand. As you can see, the incidence rate is steadily increasing and today in America the number of surgical interventions on the biliary tract and cholecystectomies reaches 1.5 million cases annually; this figure exceeds data for all other abdominal operations, including appendectomy.
Causes of the disease
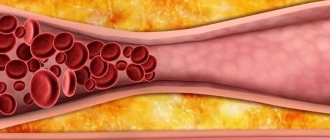
There are three main reasons for the formation of stones: metabolic disorders, bile stagnation and inflammatory changes in the wall of the gallbladder. Recently, there has been an increase in the prevalence of gallstone disease, which is associated with changes in the diet and lifestyle of the modern population. Abuse of fatty and fried foods leads to changes in the composition of bile, changes in the ratio of cholesterol and bile acids. Bile becomes lithogenic, i.e. prone to stone formation. The components of bile precipitate and form a substrate for further precipitation of cholesterol, bilirubin and calcium crystals on their surface. Lithogenic bile can be compared to sticky snow during the thaw period, when snow masses easily stick to a snowball. It is known that gallstone disease often develops in patients with metabolic diseases such as diabetes, obesity and hemolytic anemia.
Damage to the gallbladder wall is also important in the formation of stones. Most patients have bacteria in their bile that leads to the destruction of the inner layer (epithelium) of the gallbladder. The desquamated particles serve as the basis for the precipitation of bile components, which were previously in dissolved form, into a crystalline state - stones are formed.
Prolonged stagnation of bile leads to its thickening and also contributes to the precipitation of bilirubin, cholesterol and calcium into crystals.
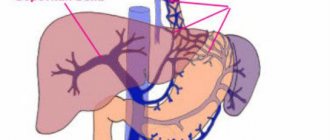
The most common site for stone formation is the gallbladder.
Causes
Rice. 1. Pathological anatomy of the biliary tract in cholelithiasis - stones in the gallbladder and obstruction of the cystic duct by one of them (diagram).
Rice. 2. Stages of laparoscopic cholecystectomy - clipping of the cystic duct and artery.
Rice. 3. Stage of laparoscopic cholecystectomy - intersection of the artery and duct and isolation of the gallbladder from the liver bed.
Rice. 4. View of the anterior abdominal wall during open cholecystectomy - suture after laparotomy.
Rice. 5. View of the anterior abdominal wall during laparoscopic cholecystectomy - 4 punctures.
Unfavorable factors that can provoke the appearance of gallstone disease include:
- age;
- overweight;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- abuse of low-calorie diets, hunger, parenteral nutrition;
- use of certain medications (postmenopausal estrogens, contraceptive steroids, ceftriaxone, fibrate derivatives, octreotide and analogues, etc.)
- heredity (predominance of lithogenic genes, enzymatic defect in the synthesis of solubilizers, cholesterol excretion)
- Crohn's disease, diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, duodenal, choledochal diverticula, infectious diseases of the biliary system, etc.
It should be noted that women are much more common among patients. In addition, there are so-called controllable factors: excess weight, the use of various low-calorie diets in order to reduce weight. For example, in obese individuals, the disease occurs in 33%. Studies conducted in the USA have confirmed that women whose body mass index (BMI) is 25-29 are more likely to get sick. The situation is aggravated by the presence of various diseases (diabetes, coronary heart disease, hypertension). As BMI increases, the likelihood of developing gallstone disease increases. So in women with a BMI above 35, the risk of developing cholelithiasis increases 20 times. It should be noted that low-calorie diets, as well as sudden weight loss (loss of body weight by 1.5 kg per week), weight loss of more than 24% of the initial weight, increase the risk of developing cholelithiasis.
In addition, the biochemical composition of bile is of great importance. Oversaturation with cholesterol, the state of the pronucleating and antinucleating systems, the formation of a crystallization nucleus, and other indicators are very important in the process of stone formation. In addition, a decrease in evacuation function and dysfunction of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acid should be taken into account. The formation of cholesterol stones is based on the hepatic secretion of vesicles that are enriched with cholesterol. However, neither the mechanism of vesicle development itself nor the factors that influence this process are currently not well understood.
Causes
Currently, there are several most likely causes of the formation of gallstones. It is expected that this could be:
- stagnation of bile of a mechanical or functional nature; with mechanical - the outflow of bile is obstructed due to obstacles (adhesions, kinks, tumors, etc.), with functional - disturbances arise due to impaired motility of the gallbladder.
- disturbance of bilirubin or lipid metabolism, which affects the circulation and synthesis of bile; cholesterol, bile pigments, salts are precipitated, the quantitative ratio of bile components is also disrupted, and solid formations appear.
The presence of unfavorable factors may be decisive in the development of the disease. The largest number of patients are in developed countries, with older people predominating; perhaps the reason lies in lack of exercise, poor diet, and stress. Also, the risk of this disease is higher in women. In addition, the likelihood of stone formation increases:
- obesity: in people with a body mass index of more than 35, cholelithiasis is diagnosed 20 times more often;
- dietary features: predominance in the diet of foods containing large amounts of cholesterol, abuse of low-calorie foods, sudden weight loss (more than 1.5 kg per week);
- various diseases: metabolic disorders, Crohn's disease, diverticula, infections, etc.;
- burdened heredity: among relatives there are already patients with the same diagnosis;
- long-term use of drugs that affect metabolic processes.
Clinical picture and symptoms of the disease
Most often, the first sign that forces the patient to see a doctor is pain in the right hypochondrium, of varying intensity. Cutting or stabbing in nature, the pain is most often constant, often radiating to the right shoulder blade, lower back, and forearm. In some cases (with cholecystocoronary Botkin's symptom), it can radiate beyond the sternum, resembling an attack of angina. It should be borne in mind that the intensity of pain is in no way an indicator of the severity of the process. For example, in some cases, severe pain may disappear, but mild pain does not mean a mild form of the disease.
Often the patient’s condition worsens after eating spicy or fatty foods; their consumption increases the need for bile to process food, which leads to contraction of the gallbladder. In any form of the disease, there is an increase in body temperature. In the form of short rises, the temperature rises to 37-38°C, and the patient often experiences pain. However, during an acute attack accompanied by chills, the temperature can rise to 38-40°C.
Symptoms
Manifestations depend on the location and size of gallstones; symptoms characteristic of this pathology:
- The pain is dull, constant, localized on the right hypochondrium, and can radiate to the shoulder, arm, neck, shoulder blade, and lower back. In some cases, the pain radiates beyond the sternum, resembling the pain of angina pectoris. Pain can occur after errors in diet or excessive exercise. But its intensity is not an indicator of the severity of the disease; some patients experience only mild pain and the presence of several stones of impressive size.
- Biliary colic, in which intense pain forces the patient to unsuccessfully search for a position that can relieve suffering. As the disease progresses, pain occurs more often, its intensity and duration increase.
- Temperature - periodic increases to 37-38°C, accompanied by pain; also during an attack, an increase to 38-40°C is possible, and the patient often experiences chills.
- Yellowness of the skin is characteristic of obstruction of the sphincter of Oddi or obstruction of the ducts.
Signs such as nausea, vomiting, and bloating, although they may occur in the presence of stones, are not specific; these symptoms often appear with other diseases of the digestive system.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is based on the results of instrumental studies and anamnesis data.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the upper abdominal cavity is performed to diagnose cholelithiasis and calculous cholecystitis. During the study, in addition to stones in the gall bladder or ducts, the size of the gallbladder, the condition of its walls, and pathology of the liver or pancreas are determined.
- gastroduodenoscopy - allows you to determine diseases of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum.
- retrograde cholangiography (x-ray examination using a contrast agent) is performed in the presence of complications.
- transgastric ultrasound of the ducts is necessary when diagnosing choledocholithiasis.
Gallstone disease: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Did you know that being a woman (or a man) is already enough to have an increased risk of a particular disease? And we are not necessarily talking about the intimate sphere.
Today we will talk about a disease, one of the risk factors for the development of which is female gender. This is gallstone disease. With questions about her, we attended an appointment with our regular consultant, gastroenterologist at the Expert Kursk Clinic, Vasilisa Vladimirovna Ishchenko.
— Vasilisa Vladimirovna, what is gallstone disease?
This is a multifactorial, multi-stage disease of the hepatobiliary system resulting in the formation of gallstones in the gallbladder and/or bile ducts.
— Archival materials indicate that gallstones bothered even the ancient Egyptians, which is confirmed by the study of mummies. How common is cholelithiasis among modern people?
According to statistics, gallstone disease is a common disease. On a planetary scale, it occurs in approximately 10% of the population, and the number of such patients only increases with every decade.
In developed countries, the prevalence of this pathology is higher and amounts to up to 40% among adults.
In our country - from 5 to 20%. This “scatter” is associated, in particular, with the heterogeneity of disease detection. Patients do not always seek medical help.
— Is cholelithiasis reflected in ICD-10?
Yes, its classification code is K80.
— Is gallstone disease a disease of adults or do gallstones also occur in children?
Stones also occur in childhood. Until the age of 7, boys predominate; from 7 years of age until adolescence, the ratio between boys and girls is approximately the same, and then the “primacy” goes to girls (3 times more than for boys).
For what reasons can a child have a stomach ache? Deputy Chief Physician for Pediatrics says
"Clinic Expert Smolensk" Zakharov Alexey Alexandrovich
—Who is more likely to develop gallstones: men or women?
Among women.
— Why do gallstones form?
The leading factor is an increase in the lithogenicity of bile (lithogenicity is the tendency to form stones). Also, the reasons for the formation of stones include a decrease in the contractility of the gallbladder, “biliary hypertension” (increased pressure in it) and its infection.
— Can gallstones form suddenly? Or do they take time to form?
The process of stone formation is quite long, a multi-year process. However, modern diagnostics makes it possible to identify disorders even before the formation of stones, at the stage of changes in the properties of bile.
— What are the risk factors for the development of gallstone disease?
These are female gender, family history, overweight and obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, liver pathologies, Crohn's disease, long-term intravenous nutrition; pregnancy; old age; some medications that disrupt the metabolism of cholesterol and bilirubin.
How to distinguish good and bad cholesterol? Cardiologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences says:
Ovsyannikov Alexander Georgievich
— What role does genetic predisposition play in the occurrence of this disease?
This is one of the leading factors. There is a connection between certain regions of the genome and an increased risk of developing this pathology. If one of them is inherited, the risk increases to 30%, and if two of them are inherited, the risk increases to 70%. Often, hereditary burden can be established already during a survey, when, in particular, it turns out that the patient’s mother also had or has cholelithiasis.
— What signs do patients have when they have gallstones?
Most often, no manifestations are noted. This kind of latent stone carriage is a stage of this disease.
A dyspeptic form is also isolated (it is rarely found in isolation). It is characterized by a disorder of the digestive system with periodic pain, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, bloating, unstable stools, heartburn, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, i.e. nonspecific symptoms.
The most striking picture is of biliary colic - another type of this pathology (currently the term has been changed and is called “biliary pain”). There is a pronounced pain syndrome with characteristic irradiation to the right shoulder, the interscapular space and the area of the right scapula, neck, and lower jaw. A connection between biliary pain and errors in diet has been noted. During an attack, laboratory tests may change (the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases, the number of leukocytes increases).
The painful torpid form is characterized by a long, persistent, constant pain syndrome that does not have typical manifestations in laboratory tests. However, you can suspect it already at the stage of examination by a doctor.
— Can gallstone disease be asymptomatic or put on “masks” of other diseases?
Yes, it may not manifest itself for a long time, leading in some cases to the development of serious complications.
Also, cholelithiasis can “masquerade” as many diseases of the organs of the upper half of the abdominal cavity. These are pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis and duodenitis, etc.
How should and how NOT should gastritis be treated? Read here
— Vasilisa Vladimirovna, how is gallstone disease diagnosed?
If there are complaints, suspicion of its presence may arise already at the stage of examination by a doctor. However, the leading method for making this diagnosis is ultrasound, and gallstone disease is often an accidental finding - for example, during a preventive study. According to indications, retrograde cholangiopancreatography and percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography are used - for example, when ultrasound does not reveal stones in the bile ducts.
How to prepare for an abdominal ultrasound? Find out here
To clarify the question of the nature and density of the stone, a CT scan of the abdominal cavity can be used.
— How is a patient treated when gallstones are detected?
It is important to adhere to a diet: fatty, spicy, salty, smoked, sweet, and sour foods are excluded. Ursodeoxycholic acid preparations are used to dissolve some stones (not all types are soluble, and for some stones these medications are contraindicated). To prescribe such treatment, stones must have very specific characteristics, and the bile ducts must be passable, etc.
Choleretic drugs and herbs are contraindicated.
Is it possible to cleanse the liver? Read here
— Are stones in the gall bladder always an indication for surgery?
It depends on at what stage the diagnosis is made, what type of stones are and how they “respond” to drug treatment. If they are small and gradually decrease when therapy is prescribed, then the patient is treated and observed by the doctor’s decision and after mandatory consultation with a surgeon. If there is no effect from the drugs or the presence of symptoms, the question of surgery is raised. In case of complications - removal of the gallbladder for health reasons.
— How do gallstones threaten a person’s health and life? What happens if gallstone disease is not treated?
It is dangerous due to its complications. Among them are cholecystitis; blockage of the gallbladder duct; obstructive jaundice; formation of fistulas (including between the gallbladder and intestine); dropsy or suppuration of the gallbladder; pancreatitis; intestinal obstruction caused by gallstones, etc.
There are also studies showing that patients with gallstones have an increased risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
— What needs to be done to keep the gallbladder healthy?
Primary prevention consists of developing a healthy lifestyle, following the principles of a balanced diet (it is necessary to exclude smoked foods, refractory fats, irritating seasonings, and sweets. The diet should include a large amount of plant fiber, which normalizes intestinal motility and reduces the lithogenicity of bile).
Once a year, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder and, if there are changes, immediately consult a doctor.
You can sign up for an ultrasound scan of the liver and gallbladder here
Please note: diagnostics are not available in all cities
For reference
Ishchenko Vasilisa Vladimirovna
In 2015, she graduated from Kursk State Medical University with a degree in General Medicine.
In 2021, she completed an internship in the specialty “Therapy” and in the same year – professional retraining in gastroenterology.
Since 2021, he has been holding the position of gastroenterologist at Klinka Expert Kursk LLC.
Conservative methods of therapy
To identify cholelithiasis, determine the degree of inflammation in the wall of the gallbladder, as well as select the correct individual tactics for surgical treatment, you can send me a complete description of an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, preferably a gastroscopy, to my personal email address, you must indicate your age and main complaints. In rare cases, if stones in the ducts are suspected, it is necessary to perform an endoscopic ultrasound examination of the ducts and pancreas. If I provide the above research, I will be able to advise you by email.
In the absence of pronounced manifestations, or in case of a single attack of biliary colic, conservative treatment is carried out aimed at reducing inflammation, improving the motility of the bile ducts and bladder, and the outflow of bile. In addition, it is necessary to correct metabolic processes, as well as eliminate concomitant diseases. However, the tactics of therapy depend on the phase of the process, whether it is an exacerbation, biliary colic or remission. The patient can receive treatment either on an outpatient basis or in a hospital (therapeutic department or surgery). During the period of remission, patients are recommended drug therapy, diet, physiotherapy, and sanatorium-resort treatment is also indicated.
For repeated attacks of biliary colic, which are accompanied by pain, surgical methods for the treatment of cholelithiasis are recommended - only in this way can the development of complications be prevented: peritonitis when the gallbladder ruptures, the development of obstructive jaundice and biliary pancreatitis when the stone enters the hepatic duct, which will lead to obstruction of the biliary tract .
Some categories of patients use traditional medicine methods in the treatment of cholelithiasis. As a result, according to the patients themselves, stones come out of the gallbladder with feces. However, the opening of the sphincter of Oddi, which separates the small intestine from the common bile duct, is no more than 3 mm in diameter. In this case, stones visible to the naked eye simply cannot enter the intestinal lumen. In fact, the patient may find “stones,” which are nothing more than clots of bile that enter the intestines in large quantities. Stone-like formations the size of a walnut, greenish-yellow in color can come out under the influence of various choleretic agents: decoctions and infusions of St. John's wort, flaxseed, immortelle flowers, dandelion root, stelina, peppermint, trefoil, etc. Thus, folk remedies have only a choleretic effect, but the stones are still in the patient’s gall bladder. It should be borne in mind that uncontrolled use of folk remedies can lead to undesirable consequences. Thus, as a result of increased peristalsis, stones in the gallbladder can move, blocking the duct, which will lead to edema, the development of an attack of acute cholecystitis, which, in turn, will cause obstructive jaundice and the development of acute pancreatitis.
In cases where the inflammatory process is pronounced, as well as with long-term stones, with the development of reactive changes in organs located nearby (duodenitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis, hepatitis), as well as with stone obstruction of the neck of the gallbladder, conservative treatment may be useless.
Treatment
The goal of treatment for gallstones is to relieve the condition and prevent complications. With the help of conservative treatment, you can only reduce the clinical manifestations; we are talking about taking drugs that improve the motility of the gallbladder, the outflow of bile, and anti-inflammatory therapy. It is important to prevent attacks by following a diet, combating inactivity and excess weight.
However, gallstones can only be removed through surgery. Indications for intervention are:
- recurrent attacks;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- constant pain;
- the presence of pathological changes in neighboring organs (pancreatitis, duodenitis, hepatitis);
- the appearance of complications.
Surgical methods of treatment
Today there are two main methods of surgical treatment for cholelithiasis:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- with this method, the intervention is performed using laparoscopic equipment through small incisions on the anterior wall of the peritoneum, through a puncture in the umbilical area or transvaginally. Today, laparoscopy is recognized as the “gold” standard in abdominal surgery. Among the advantages of this method, it is worth noting the excellent cosmetic result: only small incisions remain on the skin. The rehabilitation period is much shorter than with traditional surgical treatment. The patient begins to walk on the first day, and on the second day he is allowed to take liquid food. The operated patient usually leaves the clinic on the 2nd or 3rd day after the operation. A person can usually start work within 10-14 days. - Traditional cholecystectomy
is an open operation, performed manually, with a 15-20cm incision made on the anterior abdominal wall. Currently, surgical intervention using this method is performed only for complications of cholelithiasis (peritonitis, gallbladder perforation).
These operations are performed under general anesthesia, and the gallbladder is removed along with the stones according to the same procedure. If there is a single large or several small stones, the gallbladder is completely removed. Some patients ask about the possibility of removing only stones while preserving the gallbladder. It is possible to perform such surgical intervention. However, at this time there is no definite guarantee that the stones will not reappear. Today, specialists from all over the world are working on this problem, but stones often reappear within six months.
Watch a video of operations performed by Professor K.V. Puchkov. You can visit the website “Video of operations of the best surgeons in the world.”
Operation
Today there are two methods of surgical treatment, but in any case, during the operation the gallbladder is removed, since while methods for removing stones without removing the organ itself are not effective, after 6 months they form again
- Open cholecystectomy is an operation during which the stones along with the gallbladder are removed through one 15-20 cm incision in the abdominal wall. This technique is recommended only for complicated processes.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a low-traumatic operation for gallstones, performed through small punctures in the peritoneal wall, the size of which is no more than 10 mm. This technique is recognized as the “gold” standard in the treatment of gallstone disease. There are several types of laparoscopy; surgery for gallstones can be performed transvaginally (NOTES technology), through a single puncture in the paraumbilical area (single-port SILS technology), and mini-laparoscopy is also performed in our clinic using miniature instruments.
Transvaginal laparoscopic cholecystectomy using the NOTES method
Rice. 6. Scheme of laparoscopic transvaginal cholecystectomy using NOTES technology
Rice. 7. View of the anterior abdominal wall during laparoscopic cholecystectomy using SILS technology.
Since 2007 in France, and since 2008 in the Russian Federation, a unique method of removing the gallbladder has been practiced - transvaginal cholecystectomy using NOTES technology. The operation is performed without any punctures of the abdominal wall, therefore, there are no postoperative scars. The essence of the surgical intervention is access to the affected organ through a small puncture (1 cm) of the posterior vaginal fornix. The intervention is performed using laparoscopic instruments and optics introduced into the peritoneal cavity through this access. After removing the gallbladder through the same access, one suture is placed on the puncture. The synthetic suture material used in this case dissolves within 3-4 weeks.
The advantages of this method are:
- in the absence of pain after surgery;
- the patient's motor activity is not impaired;
- short rehabilitation period, patient hospitalization lasts only one day;
- excellent cosmetic effect;
After 7-10 days after surgery, a person can begin to work, and they can play sports on the 14th day. Among the restrictions in the postoperative period should be the need to exclude intimate relationships for a month. At the same time, the genital organs (uterus, appendages, etc.) are not affected during transvaginal cholecystectomy, so their functionality remains unchanged.
Complications
Complications of cholelithiasis are often observed due to blockage of any part of the biliary tract by a stone. Let's look at the most common of them.
Choledocholithiasis is the presence of stones in the bile ducts. This condition may be asymptomatic if the stones do not interfere with the patency of the bile ducts. If they obstruct (clog) the bile ducts, obstructive jaundice develops. Since bile does not flow from the liver into the duodenum, it enters the blood, turning the skin yellow.
Stones located in the bile ducts not only block them, but also, by injuring them, cause inflammation - cholangitis. Stagnation of bile also contributes to inflammation. A dangerous form of cholangitis is purulent cholangitis. With the progressive rapid course of purulent cholangitis, small ulcers form not only in the bile ducts, but also in the thickness of the liver itself, which leads to the formation of multiple liver abscesses. The prognosis in such cases is unfavorable.
Acute obstructive cholecystitis develops when the cystic duct, through which bile flows from the gallbladder, is blocked by a stone. The outcome of obstructive cholecystitis can be hydrocele of the gallbladder, if the body’s strength is high enough, and blockage of the cystic duct by a stone persists. If the strength of the bacteria present in the bile exceeds the strength of the body, either empyema of the gallbladder or gangrene of the gallbladder occurs. With empyema of the gallbladder, its lumen contains pus, which can break into the abdominal cavity with all the ensuing consequences. With gangrene of the gallbladder, the death of its wall occurs, which can provoke perforation (the formation of a hole), which, as in the case of empyema, leads to diffuse peritonitis.
Large gallbladder stones can form a bedsore in the gallbladder wall. And since the wall of the gallbladder often comes into contact with the wall of the duodenum, a bedsore can form in it. Once in the intestinal lumen, the stone usually blocks the intestinal lumen, and intestinal obstruction develops, requiring emergency surgical intervention.
If a stone blocks the pancreatic duct, pancreatitis develops, i.e. inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis can progress to pancreatic necrosis - death of pancreatic tissue, which often leads to death.
We tried to characterize the main complications of gallstone disease so that you understand how important it is to see a doctor in a timely manner.
Single-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy SILS
The use of the NOSE technique is technically impossible in cases where patients have undergone many surgical interventions on the pelvic organs in the past. Therefore, an equally effective method of minimally invasive cholecystectomy was developed, which has been used in America since 2008, and since 2009 such operations have been performed by domestic surgeons. We are talking about removing the gallbladder through a puncture in the navel area (SILS technology).
Single-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy
consists of performing an operation using a special device (port), which is a soft plastic apparatus that is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a puncture. Port diameter 23-24 mm. It is through this that laparoscopic instruments are inserted; the diameter of the laparoscope does not exceed 5 mm. Upon completion of the operation, a cosmetic suture is applied to the small wound. Surgical intervention using SILS technology (single-port surgery), in contrast to conventional laparoscopic access (multi-puncture), has a number of advantages:
- fewer punctures on the abdominal wall;
- less pain after surgery;
- shorter rehabilitation period;
- better cosmetic effect;
The advantages of this method of surgery are especially noticeable when there are multiple stones in the gallbladder - with the usual method, the surgeon must increase the puncture to remove stones and the diseased organ.
The choice of the appropriate surgical treatment method depends on the individual characteristics and health status of the patient. Visiting a clinic with qualified and experienced specialists guarantees the highest possible treatment results.
Forecast
With stones in the gall bladder, there are no obvious clinical manifestations at first. But sooner or later a person is forced to see a doctor. Repeated attacks indicate the need for surgery, otherwise there is a high risk of complications. With a timely cholecystectomy, a complete cure is possible, and in the future the person, subject to simple recommendations, can lead a life without any special restrictions.
Every patient who contacts me can count on complete and high-quality treatment. I always strive to perform a low-traumatic operation. But to choose the optimal treatment tactics, an examination is necessary; in our clinic, all effective diagnostic methods are available to patients. We have developed a special program, registered in the Russian Federation, which allows us to improve diagnostics and select the most appropriate treatment method, avoiding unnecessary trauma and the risk of intraoperative complications.
Having personally performed more than 6,000 laparoscopic cholecystectomies, the experience gained over more than 30 years of work allows me to find the solution that is most suitable for the patient, taking into account his medical condition. The results of the operations performed are summarized in 30 scientific papers published in academic Russian and foreign publications. I described in detail the indications and technique of all types of operations for cholelithiasis in a monograph published in 2021 - SURGERY FOR GALLSTONES: laparoscopy, minilaparoscopy, single port, transvaginal access, simultaneous operations. -M.: Publishing House "MEDPRACTICA-M", 2021, 312 p.
I also regularly conduct seminars where issues of treatment of the abdominal organs, including cholelithiasis, are discussed. They are attended by both postgraduate cadets and leading specialists from large scientific centers.