Traumatologist-orthopedist (adults and children)
Bogatov
Victor Borisovich
21 years of experience
Highest qualification category. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, First Moscow Medical University. I.M. Sechenov.
Make an appointment
Arthrosis is a disease that affects human joints. First, the disease affects the articular cartilage, and then becomes chronic and spreads to nerves, ligaments, muscles and bone.
general information
Arthrosis is a chronic, long-term process that affects not only the joints. As it progresses, dystrophic and degenerative changes and auxiliary apparatus occur. In the process, the patient faces inflammation of the cartilage and bone tissue, joint capsule and periarticular bursa, as well as the muscles, ligaments and subcutaneous tissue in contact with them.
Regardless of the location, the pathological process follows a single pattern. First, in the thickness of the tissue, the balance between the processes of growth and destruction of cartilage is disturbed, and the balance shifts in favor of dystrophy and reverse development (degeneration). At this time, invisible changes occur in the microstructure of the cartilage, which leads to its thinning and cracking.
As the disease progresses, the joint loses its elasticity and becomes more dense. This reduces its ability to absorb shock; the rate of tissue damage is constantly increasing due to vibration and microtrauma during movements. The thinning of the cartilage layer provokes the active growth of bone structures, as a result of which spines and protrusions appear on the smooth surface of the joint - osteoarthritis develops. Movement becomes increasingly limited and painful. Spasms of the muscles surrounding the affected area develop, which aggravates the pain and deforms the limb.
Make an appointment
Drug therapy
The prescription of medications is aimed at relieving pain, suppressing its progression and restoring joint function. To combat pain, the following are used:
- Painkillers from the NSAID group. The type of medication, its release form and dosage are selected by the doctor individually. The choice depends on the severity of pain, age, gender and other factors. The most commonly prescribed medications include Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Ketorol, etc. They are usually taken orally in tablet form, but injections or ointments may be used.
- Muscle relaxants. They are necessary to relieve spasm from the periarticular muscles. This way it is also possible to reduce pain and restore normal blood circulation in the joint.
- Neurotropic B vitamins. This is a sociable component of basic therapy. B vitamins help normalize the functioning of the peripheral nervous system and also inhibit pain.
- Painkiller blockades. As a rule, they are used for pronounced acute pain that cannot be eliminated by taking the drugs described above. In this case, solutions of Novocaine or Lidocaine are used, which are injected into the most painful places.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee or any other joint is not complete without taking medications that help restore joint function. For this purpose the following are appointed:
- Chondroprotectors. Taking them restores cartilage tissue and improves blood circulation in it. It is taken in the form of ointments, injections and tablets.
- Hyaluronic acid. The medicine is injected directly into the joint cavity, ensuring the fastest possible onset of the therapeutic effect. Its main purpose is to improve the viscosity of the synodal fluid and prevent trauma to the articular surfaces of the bones.
Stages of the disease
Arthrosis of the joints develops gradually and in the process goes through three successive stages that determine the severity of the disease:
- Stage 1: the pathology is not detected on X-ray or ultrasound, but the destruction processes have already started; the composition of the joint fluid changes, as a result of which the tissues receive fewer nutrients and become more sensitive; increased stress on the affected area causes inflammation (arthritis) and pain;
- Stage 2 is characterized by active destruction of cartilage tissue, and bone spines and growths appear along the edges of the articular platform (the area of contact of surfaces); at this time, the pain becomes habitual, and the inflammatory processes become stronger and weaker; spasms of the muscles associated with the joint are periodically observed;
- Stage 3: areas of destruction affect almost the entire surface of the cartilage, the articular area is deformed, the affected limb deviates from its axis; range of motion decreases and ligaments weaken and become short.
Some experts also distinguish stage IV of the development of arthrosis. It is characterized by almost complete immobility of the joint.
Arthrosis of the upper extremities
This localization of the disease is less common than in the lower extremities. This:
- Arthrosis of the shoulder joint. As a rule, it occurs after injury and against the background of microtrauma in professional athletes. Sometimes diagnosed in individuals whose profession involves physically demanding work. The acromial type of disease is a consequence of injury and inflammation. Initially it goes unnoticed, but as it progresses, painful sensations appear in the area of the injured shoulder. Patients note limited mobility, as well as a crunching sound when moving. In the absence of timely treatment, partial ankylosis may occur.
- Elbow - diagnosed much less frequently. In most cases, this diagnosis is detected in certain professions: miners, blacksmiths and people working with vibrating tools. The symptomatic picture includes pain in the elbow when flexing and extending the upper limb and limited mobility.
- Arthrosis of the joints of the hand. As a rule, it is diagnosed in the carpometacarpal joint of the 1st finger (it is this joint that is most susceptible to injury in everyday life). It is characterized by a dull pain in the outer surface of the palm, which can radiate to the thumb.
- Arthrosis of the finger joints. Most often found in people doing small work (embroidery, knitting, etc.). Overgrowth of bone tissue is observed, leading to the formation of Heberden's and Bouchard's nodes. Patients rarely report joint pain (sometimes when the weather changes) and stiffness in movement.
Kinds
Depending on the cause of the disease, primary and secondary arthrosis are distinguished. In the first case, the pathology occurs independently against the background of the complex influence of predisposing factors. The secondary form is a consequence of other diseases and is divided into the following groups:
- joint damage resulting from metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases (gout, diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, hyperparathyroidism);
- destruction associated with congenital pathologies (Paget's disease, congenital hip dislocation, scoliosis, hemophilia, etc.);
- post-traumatic arthrosis, which arose against the background of fractures, cracks, necrotic processes or surgical operations, as well as due to the characteristics of the profession.
The most popular classification of osteoarthritis is depending on the location of the pathological process:
- gonarthrosis: damage to the knee, one of the varieties of which is palletofemoral arthrosis - destruction of the joint between the femur and the patella);
- arthrosis of the ankle joint: occurs against the background of heavy load and frequent injuries;
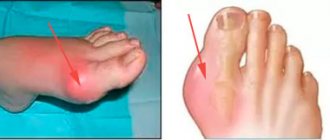
- arthrosis of the foot joints: the big toe most often suffers at the junction with the foot; the lesion develops against the background of gout or hallux valgus;
- shoulder arthrosis is characterized by damage to the shoulder and often occurs at a young age against the background of increased physical activity (loaders, athletes, construction workers);
- coxarthrosis: damage to the hip joint; can be both unilateral and bilateral and is one of the common causes of disability in people over 50 years of age;
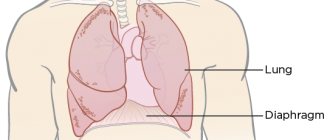
- vertebral arthrosis: destruction of the cartilage discs between the vertebrae, most often affecting the cervical and lumbar spine;
- arthrosis of the joints of the hand: the joints of the fingers are most often affected; women in menopause are especially susceptible to pathology;
- arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint: it is quite rare, most often against the background of chronic inflammation due to malocclusion or improper prosthetics;
- Arthrosis of the elbow joint: a rare form of the disease, most often associated with injuries to this area.
General information
Arthrosis is diagnosed in approximately 1/5 of the world's population, but the disease is more common among older people. This is proven by the statistics of its distribution among different ages:
- youth under 40 years old – no more than 6-7%;
- persons of mature age after 45 years – up to 20-25%;
- after 70 years – up to 80%.
The disease affects tissues that are under constant stress: small joints of the hands and metatarsals of the feet, hip and knee joints, areas in the cervical and thoracic spine, and, a little less often, the ankle and shoulder joint.
On a note! Damage to the interphalangeal joints of the hands occurs 10 times more often in women than in men.
In many Western countries, the term “arthrosis” is not used, replacing it with the concept “arthritis”. Such a substitution is completely justified, since inflammatory processes in most cases precede arthrosis or accompany it. In domestic medicine, the terms “arthrosis” and “arthritis” essentially mean the same disease, but with a different etiology of the process. Additionally, the concepts osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, and deforming osteoarthritis are used to denote pathology.
On a note! The difference between arthritis and arthrosis lies in the cause of the disease. In the first case, these are inflammatory processes (the suffix -itis means inflammation), in the second - metabolic disorders (protein, mineral).
Reasons for development
The main factor in the development of arthrosis is the discrepancy between the load experienced and the ability of the joint to withstand this load. Acute or chronic, this process inevitably leads to tissue destruction.
The list of reasons that increase the risk of developing arthrosis of any localization includes:
- heredity;
- endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus);
- injuries of the articular apparatus: bruises, dislocations, fractures or cracks of bones inside the joint capsule, complete or partial ruptures of ligaments, penetrating wounds;
- regular increased load on the joints associated with the profession);
- obesity;
- hypothermia;
- previous inflammatory diseases of the joints: acute arthritis, tuberculosis, etc.;
- blood diseases in which bleeding into the joint often occurs (hemophilia);
- sudden changes in hormonal levels (pregnancy, menopause);
- local circulatory disorders due to atherosclerosis, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, etc.;
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.);
- connective tissue dysplasia (congenital pathology, accompanied, among other things, by excessive joint mobility);
- congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal system (flat feet, dysplasia or congenital dislocation of the hip joint, etc.);
- age over 45-50 years (increased risks are associated with a decrease in collagen synthesis);
- osteoporosis (bone loss);
- chronic intoxication of the body (including salts of heavy metals, drugs, alcohol);
- surgical interventions on joints.
Preventive measures
The basis for preventing arthrosis is reducing the risk of injury. The main measures include:
- a competent training regimen (if the sick person plays sports);
- getting rid of excess weight;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic and endocrine diseases;
- in the case of a genetic predisposition, be attentive to your health and not overexert yourself physically, and ensure moderate physical activity.
Symptoms
Symptoms of arthrosis practically do not depend on its cause and location, since changes in the joints follow the same scenario. The disease develops gradually and begins to manifest itself when the cartilage is quite seriously damaged.
One of the first signs of trouble is a crunching sound in the problem area when moving. It most often occurs when the knee or shoulder is affected. At the same time, a person may feel a slight decrease in mobility after prolonged inactivity, for example, in the morning.
When asked what symptoms appear with arthrosis, most patients name pain first. At first insignificant and weak, it gradually gains strength, preventing normal movement. Depending on the stage and location of the pathology, a person may feel:
- starting pain: occurs during the first movements after prolonged inactivity of the joint and is associated with the formation of a thin film of destroyed tissue on the surface of the cartilage; after starting work, the film moves and the discomfort disappears;
- pain during prolonged physical activity (standing, walking, running, etc.): appears due to a decrease in the shock-absorbing properties of the joint;
- weather pain: provoked by low temperature, humidity, changes in atmospheric pressure;
- night pain: associated with venous stagnation and increased blood pressure inside the bones;
- joint blockade: sharp, severe pain associated with pinching of a piece of cartilage or bone located in the joint cavity.
As arthrosis develops, the symptoms become more noticeable, the patient notes the following signs:
- increase in morning stiffness;
- intensification and increase in duration of pain;
- decreased mobility;
- joint deformation due to bone growths;
- deformation of bones and surrounding tissues: the process is clearly visible on the limbs and fingers, which become noticeably curved.
When inflammation occurs, the affected area swells, turns red and becomes hot to the touch. Pressing on it causes a sharp increase in pain.
Arthrosis of the lower extremities
- Arthrosis of the hip joint is the most dangerous and severe type. Due to the anatomical features of the structure of this joint, it is here that the rapid development of degenerative-dystrophic disorders occurs with damage to the musculo-ligamentous apparatus. When inflammation occurs, the effect of complete or partial immobility develops. Often this pathology occurs due to the presence of congenital dysplasias, dislocations and osteochondropathy. It manifests itself in the form of pain (at first it appears in the late afternoon and night, but later it becomes permanent, radiating to the groin and gluteal region) and forced position of the lower extremities.
- Ankle - occurs quite often, since the ankle is forced to withstand a large load every day. As a result, it is often injured, leading to degeneration. Ankle arthrosis often occurs without significant symptoms, but as it progresses, pain appears during physical activity. Then the pain becomes constant, stiffness of movements and complete immobility are added (rarely, in the absence of timely and adequate treatment).
- Arthrosis of the knee joint is the most common type. It is the knee that bears the greatest load, which is why it is more susceptible to injury than others. There are several types: patellefemooal and tibiofemoral. The first occurs after injury to the patellofemoral joint. At the initial stages, it is asymptomatic, since the joint has a large amount of cartilage responsible for shock absorption. Their presence prevents bone injury. Later, the patient begins to notice pain in the knee after physical activity, which gradually becomes permanent (often intensifies when the weather changes). Synovitis, characterized by severe, almost unbearable pain, is often associated with the pathology. The tibiofemoral type is diagnosed extremely rarely and has a more favorable prognosis. It is characterized by pain sensations radiating to the lower part of the body (usually to the feet).
- Heel - degenerative-dystrophic changes can be observed in the area of the subtalar or talocalcaneal-navicular joints after injury or illness. It also does not manifest itself clinically for a long time, but over time it begins to become painful and aching in nature.
Tests and diagnostics
An orthopedic surgeon diagnoses arthrosis. He conducts a detailed interview with the patient to identify complaints and medical history. The doctor asks in detail about the time of the first signs and the speed of their development, previous injuries and illnesses, and the presence of similar problems in relatives.
A general blood test can reveal the inflammatory process that often accompanies arthrosis.
The main diagnostic method is radiography. The following signs are clearly visualized in the image:
- narrowing of the joint space;
- change in the contours of contacting bones;
- impaired bone structure in the affected area;
- bone growths (osteophytes);
- curvature of the axis of a limb or finger;
- subluxation of the joint.
For a more detailed diagnosis, the following may be prescribed:
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Ultrasound of the joint;
- arthroscopy (internal examination of the joint cavity using a camera inserted through a small puncture);
- scintigraphy (assessment of the condition of bones and metabolism in them using the introduction of radiopharmaceuticals).
If a secondary nature of the disease is suspected, appropriate tests and consultations with specialists are prescribed.
What does the examination procedure include?
To diagnose arthrosis, a medical examination with anamnesis is sufficient. To determine the extent of damage, an instrumental examination is performed. The main ways to obtain a clear picture of the disease:
- radiography;
- CT, MRI;
- ultrasonography;
- scintigraphy;
- diagnostic arthroscopy with biopsy of cartilage tissue and synovial fluid.
In case of an acute inflammatory process, the doctor prescribes additional tests: a general blood test, rheumatic tests, biochemistry (levels of glucose, protein compounds, electrolytes).
Treatment of joint arthrosis
The choice of treatment for joint arthrosis depends on the cause of the disease, its stage and symptoms. In the arsenal of doctors there are:
- medications;
- non-drug treatment;
- surgical techniques.
In addition, the patient is required to strictly follow a diet and adjust their lifestyle to minimize further damage to the joints.
Drug treatment
Prescribing medications for arthrosis has two main goals:
- relieving pain and inflammation;
- restoration of cartilage tissue or, at least, stopping further degeneration.
To alleviate the patient's condition, various types of drugs are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: ibuprofen, ketorolac, diclofenac and their analogues in the form of tablets, injections, ointments or suppositories; they relieve pain and inflammation well;
- hormones (corticosteroids): indicated for severe pain and, most often, injected directly into the joint cavity;
- other analgesics, for example, antispasmodic (mydocalm): help reduce pain by relaxing muscles;
It is important to remember: all types of painkillers are used only to alleviate the patient’s condition. They do not affect the condition of cartilage, but when taken for a long time, they accelerate its destruction and cause serious side effects.
The main drugs for joint restoration today are chondroprotectors. They help saturate the cartilage with nutrients, stop degeneration and initiate cell growth processes. The most common remedy in this group is glucosamine and its analogues. They have an effect only at the early and middle stages of the disease and with regular long-term use.
Drugs that improve microcirculation in tissues and antienzyme agents help enhance the effect of chondroprotectors. The former provide a good supply of oxygen and nutrients to the affected area, while the latter slow down the processes of tissue destruction.
The doctor selects specific medications, their dosage and regimen.
Non-drug treatment
Non-drug treatment includes the following methods:
- physiotherapy: shock wave therapy: destroys bone growths and stimulates blood circulation due to ultrasound;
- automated electromyostimulation: exposure to electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contraction;
- ultraphonophoresis: exposure to ultrasound combined with the use of medications;
- ozone therapy: introduction of a special gas mixture into the joint capsule;
Surgery
Most often, the help of a surgeon is required in severe stages of the disease. Depending on the localization of the pathological process and the degree of damage, the following may be prescribed:
- puncture: puncture of the joint with removal of part of the fluid and, according to indications, administration of drugs;
- corrective osteotomy: removal of part of the bone followed by fixation at a different angle to relieve the load on the joint;
- endoprosthetics: replacement of a damaged joint with a prosthesis; used in extremely advanced cases.
Make an appointment
Types of disease
In modern orthopedics, the diagnosis of arthrosis begins with determining its type. Thus, according to localization, diseases of the ankle, elbow, shoulder and other joints are distinguished.
At the appointment, the stage of spread of the disease is determined:
- the first implies the absence of pronounced changes. The cartilage tissue lacks nutrients, and the cartilage itself becomes less resilient. Primary inflammation leads to unpleasant pain;
- the second stage of arthrosis involves the destruction of the cartilage structure and the spread of bone growths. The patient suffers from regular pain, which either subsides or reappears;
- in the third degree of arthrosis, the cartilage becomes especially thin and deformed, and joint mobility is sharply limited due to shortening of the ligaments.
Are you experiencing symptoms of arthrosis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Arthrosis in children
Arthrosis is considered a disease of older people, but it can also occur in children. The most common causes of pathology are:
- congenital pathology of connective tissue;
- severe injuries;
- heredity;
- metabolic disorders and functioning of the endocrine glands;
- orthopedic disorders (flat feet, scoliosis, etc.);
- overweight.
Children's arthrosis is rarely accompanied by severe symptoms: the pain is aching, and there is virtually no stiffness or limitation of function. Degenerative changes are detected on x-rays, MRI and ultrasound. The treatment process uses the same means as for adults. Maximum attention is paid to exercise therapy and physiotherapy, since they are especially effective at a young age. Without treatment, the disease sooner or later goes into an advanced stage with complete loss of mobility.
Categories of people most susceptible to disease
Despite the fact that absolutely anyone can get arthrosis, there are a number of categories of people who are especially susceptible to this disease. These include:
- elderly people suffering from disorders of the endocrine system;
- obese persons;
- athletes and people whose work involves excessive physical activity, often abnormal;
- patients who have undergone joint surgery in the past;
- people with a genetic predisposition: if parents or grandparents suffered from arthrosis, then there is a high probability that it can also be passed on to their children (grandchildren);
- patients with dystrophic disorders in the lumbar and cervical spine.
Diet
Diet is one of the most important factors in the treatment of arthrosis. If you are overweight, you need to reduce it to reduce the stress on your joints. In this case, a balanced diet with a calorie deficit is prescribed. Regardless of body mass index, doctors recommend completely avoiding:
- fast carbohydrates (sugar, desserts, flour);
- alcoholic drinks;
- spices;
- legumes;
- strong tea and coffee;
- excessively fatty and spicy foods.
Canned food and offal are not excluded, but are significantly limited, as is salt. An ideal diet for osteoarthritis includes:
- lean meats;
- fish and seafood;
- eggs;
- dairy products;
- flaxseed and olive vegetable oils;
- vegetables and fruits, a large amount of greens;
- cereals in moderation, durum wheat pasta;
- products with a high content of collagen (jellied meat, jellied meat, jelly).
Complications
In the absence of timely or correct treatment of arthrosis, various complications and consequences can develop, most of which cause significant harm to health and disrupt normal daily life. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to promptly consult a doctor at the MedArt diagnostic and treatment center, where they carry out modern diagnostics that make it possible to diagnose pathology even in the early stages. The main complications of this disease are:
- Chronic pain syndrome , which intensifies with physical activity of varying intensity (from sports to simple walking).
- Deformation of the joint , as a result of which the gait changes (if the lower smoked meats are affected).
- Dysfunction of the limb - stiffness, followed by complete or partial immobility.
- Loss of ability to work and disability.
Prevention
Arthrosis is easier to prevent than to treat. To maintain healthy joints for many years, it is recommended:
- to live an active lifestyle;
- do exercises regularly and visit the pool;
- eat right, consume enough omega-3 and collagen;
- do not exceed the BMI norm;
- wear comfortable shoes.
If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, it is recommended to undergo regular spa treatment, as well as to exclude occupational risk factors: prolonged standing, heavy lifting, vibration.
First signs
A person begins to experience pain in the area of the damaged joint after physical activity (playing sports, jogging, walking without stopping, climbing stairs, and much more). In the morning, after a long stay in a motionless state, the first “starting pain sensations” appear, combined with slight stiffness. To eliminate limited mobility, you need to warm up for a certain amount of time. The pain is aching or dull in nature and is not very intense. Due to the lackluster clinical picture, patients rarely seek medical advice in the early stages. Many people begin to self-medicate and try out different treatment methods, which can only worsen the current situation. However, it is in the early stages that this disease has the most favorable prognosis and a high chance of a full recovery without consequences. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that you make an appointment with a doctor at the MedArt clinic if you notice any sensations in your joints.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Medical orthopedists invite everyone to check the condition of the joints and, if necessary, begin treatment. We use modern effective techniques:
- full-fledged drug therapy in accordance with indications;
- physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage;
- diagnostic and therapeutic punctures of the joint with the introduction of a synovial fluid substitute or medications;
- drug blockades for complete pain relief and other techniques.
You can view the full list of services on the website or by phone.
Exacerbation
All degenerative diseases are characterized by a slow, often asymptomatic (especially in the first stages) course. An increase in pain is observed when weather conditions change (dampness, wind or drop in temperature) and when the inflammatory process begins. Inflammation is characterized by swelling, hyperemia of the skin, pain and swelling. As a rule, such inflammation is aseptic in nature, but in the presence of foci of infection and chronic diseases there is a risk of infection. Therefore, if signs of an inflammatory process appear, you must immediately seek qualified medical help. provide independent first aid using the following methods:
- Take any painkiller medication.
- Apply ointment or gel with an anesthetic effect to the skin.
- Keep the limbs in a stationary position (until the pain is eliminated).
Advantages of the clinic
“Health Energy” is a multidisciplinary medical center equipped in accordance with modern standards. We offer patients:
- consultations with experienced doctors;
- examination using high-quality diagnostic equipment;
- individual approach to treatment selection;
- regular monitoring and performance monitoring.
The joints of our body can withstand enormous loads, but there are situations when they need help. Don’t let arthrosis change your life, sign up for a consultation at Health Energy.
Non-drug therapy
It is important to understand that taking medications is not a panacea and not the only way to recover. To eliminate pain, increase joint mobility and improve quality of life, you will need to devote a sufficient amount of time to non-drug treatment methods. The most important among them is physical therapy. Experts recommend not to forget about physical activity, which should be adequate and safe for a particular patient. It is necessary to maintain the correct balance between adequate physical activity and proper rest. You can achieve this result by sticking to daily workouts. The training program is compiled by a qualified doctor who assesses the current state of health and capabilities of the patient’s body. To correctly perform exercises with a gradual increase in load, it is better to do them under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor. Only after receiving all the recommendations can you repeat the exercises at home. To get the desired result, you must adhere to the following training rules:
- Classes should be held every day , regardless of well-being, mood, weather, life circumstances and other factors.
- All movements are performed extremely smoothly and slowly.
- If pain intensifies during training, then stop training.
Regardless of the degree of arthrosis of the knee joint, the patient must avoid running (especially short distances at high speed), jumping, outdoor games (football, basketball, volleyball, etc.), lifting weights (barbell, etc.), long stays in stationary. The best option in this case would be swimming, yoga (preferably with an instructor who will know about problems with the joint) and Pilates.
If a relapse of pain occurs, you will need to give up any physical activity and exercise until the pain syndrome is completely relieved. During the day, you need to ensure complete immobility of the injured limb for 20-30 minutes. However, it is not recommended to overuse such rest, since a long stay in a motionless state causes severe pain when moving in the future. If the pain in the lower extremities becomes severe, then it is worth purchasing a cane or crutches, which will help reduce the load on the legs. Massage is no less effective in helping to reduce inflammation. Massage courses provide an opportunity to normalize blood circulation and metabolism in the joint, improve innervation and regeneration of joint tissue. In this way, it is possible to warm up the tissues, relieve muscle spasms and, accordingly, relieve pain.
For arthrosis, physiotherapy is indicated. It helps improve well-being and fights possible complications of the disease. Physiotherapeutic procedures include:
- Electrophoresis or phonophoresis with solutions of analgesic drugs.
- Warming applications with paraffin (carried out exclusively in the absence of an inflammatory process).
- Darsonvalidization - exposure to high and low frequency electrical currents to stimulate blood circulation and muscle relaxation.
- Magneto and laser therapy.
- Electrical stimulation . This is an effective physiotherapy aimed at restoring muscle volume and strength.
It is also possible to carry out hirudotherapy - treatment using leeches. The saliva of these animals contains a large number of enzymes that dilate blood vessels and normalize metabolic processes. In addition, it helps to dissolve necrotic tissue and cleanse joint cavities.
To improve the motor function of the limb, different methods of joint fixation are shown. Among them:
- Orthoses - fix and support the limb in an anatomically correct position.
- Taping is joint fixation using special adhesive tapes.
- Elastic knee pads to prevent joint injury.
A cane and crutches, thanks to which you can reduce the load on the lower smoked meats.
Modern developments and discoveries in the field of medicine make it possible to select the optimal treatment for arthrosis of the knee joint at any stage. Patients can live a full life, move around and not take a large number of medications on an ongoing basis. However, for this it is necessary to promptly contact qualified specialists who can provide professional assistance.
Stage 3 treatment
At stage 3 of arthrosis, surgery is performed; we will explain further why. Changes in the joint are very pronounced; at this phase, the disease extremely reduces the patient’s standard of living and performance. Osteochondral damage has reached a critical point at which the tissues of the bone junction do not represent any functional significance. The hyaline cover is almost completely destroyed. It is worth noting that this was one of the main structures of the knee, which in a healthy state was responsible for the coordinated and painless work of this part of the limb.
- Important cartilage does not repair itself, including through non-surgical methods.
- The exposed and flattened surfaces of the interacting bone ends exert unnatural pressure on each other, constantly rubbing against each other, seriously injuring nearby soft tissues and becoming even more deformed every day.
- The person feels terrible pain, not to mention the lost ability to walk normally. Patients experience daily torment, when sleep is not a joy, and during the day there is no rest from pain. Only a few people report a relatively tolerable condition.
- Anti-inflammatory analgesic drugs, as a rule, have a mild effect, but more often than not “work”. There is no point in using chondroprotectors, since strengthening and nourishing the scanty remnants of cartilage does not save the situation.
Sometimes they try to treat the consequences of grade 2-3 arthrosis with minimally invasive surgery (arthroscopy), during which marginal osteophytes can be removed, as well as torn osteochondral fragments can be removed from the joint cavity. Such manipulations, as evidenced by reviews, somewhat alleviate the patient’s condition and slightly improve motor function, but temporarily. Osteoarthritis in the knee joint remains active and will manifest itself again in the near future. Note that at 3 tbsp. Doctors mostly do not resort to minimally invasive approaches.
And this is an astroscope view of completely healthy surfaces, they are perfectly smooth.
Pathogenesis of 3-4 degrees is a very serious problem, which can only be solved with much more complex reconstructive and plastic surgical tactics. Domestic and foreign orthopedic surgeons unanimously agree that today there is no procedure that can be compared with endoprosthetics. Replacing the knee joint with a prosthesis that completely replicates the mechanical features, configuration of shapes and sizes of a natural organ will make it possible to say goodbye to both the ill-fated pathology and the disability with which it has “awarded” you.
The disease progresses quickly and can reach from the moderate-medium phase to stage 4 in a matter of months. Surgery should be performed as early as possible, before degenerative processes penetrate deep into the bone. Severely damaged bones can make it difficult to place an endoprosthesis.
Many, not fully realizing that the severity of the degenerations that have occurred are incomparable with conservative and unconventional tactics, try in every way to bypass the operation, swallowing pills by the handful, applying ointments to the sore area. Someone turns to osteopaths, private doctors who practice all kinds of alternative techniques. Unfortunately, you can’t go against nature, healing won’t come after them, and you need to come to terms with this fact. Therefore, discard senseless ideas and act prudently.
Very often the disease can develop at lightning speed.
Your physical fitness depends entirely on your decision! You can continue to suffer from stiffness and pain for life, vainly testing “empty” methods of treatment: drugs and non-standard remedies that have no evidence of effectiveness for your severity of illness. Or you can undergo surgical treatment and begin to live a full life, free from past suffering and support devices.
If you are young and only have one part of your joint damaged, a less traumatic procedure called partial joint replacement may be recommended.
There is no need to worry about surgical intervention; modern technologies have stepped far forward, and today knee joints are brilliantly replaced abroad with long-lasting implants. After such implantation, carried out in a good clinic, the risk of complications is minimal (1-2%), and restoration of mobility functions occurs in more than 95% of cases. After joint replacement, a rehabilitation course of 3-4 months will follow, including:
- physical recovery through special therapeutic exercises;
- taking medications (antibiotics, antithrombotics, etc.);
- a physiotherapy program including myostimulating, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and wound healing procedures;
- massage sessions (in the later stages of rehabilitation).
Good to know! At stage 1, the disease can be stopped and prevented conservatively. If you do nothing and start arthrosis of the knee, allowing it to move from stage 1 to stage 2, drug treatment will be much more problematic, but for a certain category of patients a non-surgical approach is still appropriate. The last two stages are always an operation.
Treatment 2 degrees
With gonarthrosis of moderate severity, the quality of life already becomes significantly spoiled. A sore knee worries more, the painful syndrome manifests itself more often and more intensely than it was at the beginning of the disease. The pain is especially pronounced immediately after waking up in the morning, while going up and down the stairs. There is often a feeling of unpleasant numbness that appears after prolonged walking or standing in one position for a long time. Flexion in the knee area is reduced, the patient is not able to bend the leg, as required by physiology. A person begins to spare his limb, trying almost not to step on it, which is why gradual muscle atrophy occurs.
It’s still tolerable, but often the knee makes itself felt.
It is strictly prohibited to undergo treatment at home without seeking medical help from a professional orthopedist! If the deformity becomes more complex, it will lead to immobilization and blocking of the joint. That is why adequate diagnosis and equally competent treatment in accordance with the nature of the disorders are extremely important, and not classes according to Bubnovsky. According to the well-known Bubnovsky method, you cannot train everyone, if only because it does not take into account the individuality factor of each individual medical problem. In addition, it can be useful only in the initial period, while physical rehabilitation should be carried out in conjunction with the main treatment program.
But the pool is always recommended to everyone; there are practically no contraindications to it, with the exception of open or fresh wounds.
We emphasize that treatment necessarily involves a qualified, comprehensive approach.
- If the doctor does not see an urgent need for surgery, the priority is to reduce the load on the problem area. If you are overweight, in order to ensure good relief for the joint affected by arthrosis, it is imperative to adjust your body weight by following the diet that your doctor recommends.
- All patients are prescribed the use of special orthopedic devices when moving. This, depending on the existing problem, may include knee braces, compression garments, elastic bandages, a cane, crutches, or a walker.
- Additionally, the orthopedic traumatologist will prescribe a unique set of exercises that will help strengthen and increase the endurance of the muscles of the affected limb.
- Also, arthrosis in moderate to moderate manifestations involves the use of medications that include substances present in the cartilaginous tissues of the knee. These include formulations based on chondroitin sulfate, injections of hyaluronic acid, and preparations with glucosamine. They cannot restore cartilage, but saturate it with nutritional components, so that remission of the disease can be achieved.
- Physiotherapy procedures are also recommended, but they are used only after all signs of inflammation have disappeared. Physical sessions, for example, laser, magnet or ultrasound, should take place within the medical facility. Thanks to physiotherapy, nutrition and metabolism in bone, muscle, and cartilage tissues improves. If you bought a Vitafon vibroacoustic device for home use, first ask a specialist about the possibility of using it for your diagnosis and the operating features of the device.
We have reviewed the basic principles on which the official treatment of arthrosis is based, meeting the standards of orthopedics. Since many people with stage 2 osteoarthritis. are very interested in alternative methods, looking for their salvation in them, we offer to get acquainted with the most popular of them. And let’s find out whether they are as unique as they are presented to us on the Internet.
Stem cells for knee treatment
We will talk about autotransplantation of mesinchemal stem cells to a patient with knee gonarthrosis, taken from the crest of the pelvic or femur. Cell therapy, according to interested sources, will achieve almost self-renewal of the entire joint by activating regenerative self-healing processes in the damaged segment. Thanks to this technology, it is theoretically possible to achieve improvement in the constituent units of the osteochondral organ. However, in practice, there is not yet a single “live” radiographic evidence that would confirm that after the introduction of stem cells into the affected area, the joint became healthy.
It is possible that this technology is the future, but as a rule, when introducing new methods, the percentage of failures of varying degrees is never announced, so at this stage it is better not to experiment.
The positive effect of stem cells on joints and bones has not been proven and is highly doubtful, since this technique has not yet been recognized in orthopedics. Scientists are just studying and experimenting with it. Moreover, there is information regarding the unsafe effect of stem cells on the human body, which, according to highly competent specialists, can provoke cancer. What about those people who paid for the procedure and were satisfied with the result? Here we can only say one thing: many patients will believe in eternal life for that kind of money, but the placebo effect does not last long, do not forget about this too.
Method according to Neumyvakin
Treatment of the knee joint according to the method of Neumyvakin, a professor of space medicine, involves the use of ordinary hydrogen peroxide orally (orally), by injection or locally (in the form of compresses, lotions on the knee). Traditional orthopedic doctors have an extremely, extremely negative attitude towards this method. But Neumyvakin assures that in order to restore your joint, you need to prevent oxygen starvation of cells and tissues, and everything will return to normal. For oral administration, peroxide is diluted in water and drunk according to a specific regimen.
Professor Neumyvakin.
Attention! Internal intake of peroxide leads to damage to the gastrointestinal tract, and is also often accompanied by all sorts of severe adverse reactions, ranging from gastritis to urticaria, diarrhea, cough, rhinitis and lethargy. It is difficult to predict how your body will react to this remedy, so it is better not to take risks. And remember that you cannot take any medications in parallel with oxygen therapy! As for any lotions and the like, applying a pharmaceutical solution to the skin, in principle, does not threaten life, but it will have no more than a mild analgesic effect.
Mud treatment
Therapeutic mud springs containing unique components (magnesium, chromium, iodine, bromine, calcium nitrate, etc.) help reduce painful symptoms, increase blood flow to diseased areas, and stimulate metabolism. They are of greatest value for people with a mild stage of the disease or patients who have already undergone surgery on the leg. It is also permissible to carry out mud therapy at level 2 if the doctor believes that a natural remedy in combination with the main treatment program will reduce the aggression of pathological phenomena (stop progression) and improve the overall clinical picture. Mud therapy is practiced in special health resort-type medical institutions. Natural healing muds based on peloids are used in the form of applications and in combination with the galvanization method (electrophoresis).
Uses of gelatin
Natural gelatin is a safe product that helps maintain joint structures in good condition. The jelly-like substrate, diluted in water, is recommended to be consumed internally. According to reviews of some doctors, gelatin will have a faster and more productive effect on bone, cartilage and muscle-ligamentous elements. Experts emphasize that this method does not have medicinal properties, it only helps prevent arthrosis. Consequently, if the pathogenesis has already taken place, gelatin treatment in the absence of pathology or at the earliest stages can be considered solely as a measure to prevent the appearance or progression of degenerative changes. When the disease is moderate and severe, this approach will not work for preventive purposes.
Gelatin is a good dietary supplement for keeping joints healthy, but not for treating them. The process of destruction of cartilage tissue is not reversible.
Ayurveda for joints
Modern alternative medicine is known for many extraordinary trends, including Ayurveda treatment of various parts of the musculoskeletal system. According to this unofficial theory, joint damage is associated with excess toxins accumulated in the body due to energetic disharmony. The damaging mechanism of disturbed energy balance (Vata) is primarily the weakening of Agni, or digestive fire, which leads to the accumulation of undigested food residues (Ama) in the intestines. They secrete toxins, which the blood transports to the joint, where harmful substances settle and inhibit metabolic processes.
Don't be fooled!
Let's be honest, this is not medicine, but pure philosophy, although it is possible that the emergence of a pathogenic environment in the knee joint in some patients developed according to this mechanism. According to Ayurveda, osteoarthritis is classified into several types, and each type has its own treatment system, each of which is based on diet, herbal medicine, taking Ayurvedic tablets and powders, yoga and breathing exercises, unconventional massage, auto-healing training, etc. Of course, all this sounds tempting, but if arthrosis cannot be reversed even through scientific high technologies, how can one believe that herbal powders, thought treatment and other Ayurvedic tactics will cure irreversible deformities?!
Salt compresses
We offer for consideration another common method - treatment of the knee joint with salt compresses. Salt (table and sea) is used to prepare a saturated saline solution used to impregnate compresses that are applied to the sore spot for several hours. Such therapy should not be considered as an independent remedy, much less as a panacea for gonarthrosis. Salt can temporarily soothe pain, relieve swelling of the soft tissues covering the bone structure, without harm to biological structures. But it will not cure the disease and will not put the patient back on his feet! Its effect is purely symptomatic. The solution is prepared at the rate of taking 100 g of salt per 1 liter of room temperature water.
For certain types of knee diseases, hot compresses can only do harm. Be careful.
Worth checking out! Sometimes salt is used in dry, heated form, which is placed in a bag, and local heating of the knee is performed. Sometimes as wet but hot dressings. Hot procedures are dangerous in case of purulent-inflammatory processes in the joint cavity; they will only aggravate the clinical picture to the utmost. Therefore, do not use such recipes without being sure that the lesion is not accompanied by a similar process.