Flu
– an acute viral infection caused by the influenza virus.
There are 3 types of the virus - A, B and C. Types A and B annually cause the development of seasonal epidemics, type C is rare and does not cause epidemics. Influenza type A is divided into different subtypes (H1N1, H3N2, H5N1, H7N9). The letters indicate the types of proteins on the surface of the virus (H - hemagglutinins, N - neurominedase), and the number indicates the order of their discovery. With the help of these proteins, the virus attaches to human cells. These H and N proteins are constantly changing, resulting in a different virus. If the type B virus affects only humans, then the type A virus circulates among people and many animals (waterfowl and poultry, horses, pigs). Currently, only 2 subtypes of the A virus are spread from person to person - H1N1 (swine flu) and H3N2. In 2015, the bird flu virus (H7N9) was identified; people were infected with it from domestic chickens, while the chickens themselves did not get sick and the virus was not transmitted from person to person. The avian influenza virus was characterized by a severe course in children.
Seasonal outbreaks are typical for places with a temperate climate during the transition to winter. Apparently, a decrease in ambient temperature leads to a decrease in immunity and a weakening of the body’s defenses, which is a predisposing factor in the development of the epidemic.
Main route of infection
– airborne. The influenza virus attaches to the surface cells of the respiratory tract, penetrates them and multiplies, leading to death. Massive cell death leads to local inflammation of the airways, weakening their protective properties. All this causes secondary complications with the development of deadly pneumonia. When you cough and sneeze, millions of viruses spread into the air and infect people.
During an epidemic, there is a high chance of getting sick while in public places. You can also become infected through household contact; the patient’s secretions on the hands and household items (table, pens and pencils, handrails in transport, door handles, telephone handsets and other gadgets) are dangerous. The virus remains active on these objects for 2 hours. That is why the basic rules for preventing infection are:
- Avoid crowded places during an epidemic;
- Wash your hands, face, and blow your nose more often and thoroughly;
- Use disposable disinfectant wipes;
- Ventilate the room;
- Wear individual disposable masks (it should be noted that the confined space they create can be a negative factor; it is recommended to replace masks every 4 hours)
Flu symptoms
Flu symptoms
are high temperature (
up to 38-39
), general weakness, lethargy, pain in muscles and joints. The so-called respiratory syndrome develops - coughing, sneezing, feeling of lack of air, sore throat. Symptoms of pneumonia (pneumonia) are rapid breathing (about 40 respiratory movements when the norm is 20), severe cough, shortness of breath, and blue discoloration of the skin. In these cases, hospitalization and inpatient treatment are recommended. To confirm pneumonia, an x-ray of the lungs is usually performed.
Flu symptoms usually last 7-10 days
, then pass on their own. Why most people have a mild form of the disease, and some have a severe form with the development of complications, scientists have not yet figured out.
Diagnosis is based on the presence of characteristic complaints (increase in temperature to 39 degrees and severe intoxication syndrome - general weakness, drowsiness, body aches, on the 2-3rd day respiratory syndrome - cough, runny nose) during the period of seasonal exacerbation. Laboratory diagnostics to determine the type of virus are not carried out in everyday life due to the lack of prognostic significance.
How the disease develops
There are 4 stages of development of classical fowl plague. The virus is primarily localized on the mucous membranes; no more than 4 hours pass from the moment it enters the bloodstream. Stages:
- The first is the reproduction and increase in the concentration of the virus.
- Second (viremia), the virus is easily detected in the blood.
- Third, the production of antibodies, the pathogen does not multiply.
- Fourth, the concentration of antibodies increases, immunity begins to form.
The pathogen destroys red blood cells. Virions are toxic, they secrete substances that are poisonous to the body, and this occurs most at stage 2. The likelihood of death at this time is high.
Flu treatment
It is advisable to adhere to home bed or semi-bed rest. This is especially true for “business” people who constantly work and prefer to endure the flu “on their feet.” Firstly, in doing so they infect their surroundings, and secondly, the chances of developing complications with further hospitalization increase significantly.
Drugs with proven antiviral activity against influenza are oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza). However, for their effective use, they should be taken in the first hours of the development of symptoms, maximum during the first 24 hours. The World Health Organization does not confirm the effectiveness of the domestic drug Arbidol and does not recommend its use as an antiviral agent.
The same can be said about a large group of immunostimulants and immunomodulators (cycloferon, amiksin, galavit, diucifon, imunofan, thymogen, viferon, kipferon, ribomunil, bronchomunal, oscillococcinum, etc.). Their effectiveness is zero and does not exceed the placebo effect. As a rule, all of them are not registered at all and are not used in European countries and the USA. Unfortunately, lubricating the nose with oxolinic ointment also does not protect us from the influenza virus.
The vast majority of people heal on their own at home within 5-10 days. Here you can remember the old saying: “If you treat the flu, it goes away within 7 days, if you don’t treat it, it will go away within a week.”
Thus, when the temperature rises above 38.0 degrees, it is recommended to give antipyretic drugs (paracetamol, ibuprofen). For children, there are forms of these drugs in rectal suppositories and powders.
For cough symptoms, drugs from the mucolytic group are used, which help thin and remove mucus. If you are bothered by a painful dry “barking” cough, you can use central antitussive drugs.
In general, in most cases of persistent cough, a symptom indicating the presence of bronchitis, in order to eliminate it and prevent the development of pneumonia, it is necessary to use penicillin or macrolide antibiotics. To do this, you need to consult a doctor.
General information
Bird flu is a rare, but very dangerous human disease that is caused by strains of influenza type A. As a rule, they affect domestic and wild birds.
But relatively recently, infections caused by these strains have also been recorded in humans. Most cases of this disease in humans have been caused by the Asian strains of influenza H5N1 and H7N9 . Interestingly, if wild birds become infected with these strains, the disease occurs without symptoms, while poultry may die.
Human infection with H5N1 was first identified in Hong Kong in 1997. However, people experienced severe respiratory symptoms and a high mortality rate. A few years later, cases were recorded again - mainly in Asia and the Middle East. There have been periodic outbreaks of bird flu in China.
How avian influenza manifests itself in humans and how this disease should be treated will be discussed in this article.
When to call a doctor if you have the flu?
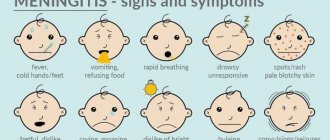
For children, the reason to call a doctor is frequent and difficult breathing, bluish skin tint, lethargy and drowsiness, refusal to drink and eat, repeated vomiting, high temperature (39 or more).
For adults – shortness of breath, worsening during the day, chest pain, repeated vomiting, severe weakness and dizziness, high fever.
In order for the efforts of doctors to be effective, you need to seek help from doctors in a timely manner, i.e. immediately when the above symptoms appear.
Pathogenesis
When infected with the influenza virus, selective damage to the epithelium of the respiratory tract occurs. When viruses multiply in columnar epithelial cells, they gradually cause their degenerative changes. Host cells are used to build new viral particles. Since the replication of the H5III virus occurs not only through epithelial cells of the respiratory tract, but also through intestinal epithelial cells. Therefore, the disease can manifest itself not only as catarrhal syndrome, but also as damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
The influenza virus causes cytopathic, vasopathic and immunosuppressive pathomorphological changes. The causative agent of influenza, virus type A, is more stable in the environment than the human virus. It can survive in bird droppings for about 3 months, can tolerate low temperatures well, but dies under the influence of disinfectants. It is characterized by high contagiousness and variability.
How to avoid getting the flu?
The most effective way to specifically prevent influenza is vaccination!!! Its safety and effectiveness have been confirmed by 50 years of use by progressive doctors around the world. 70-90% of those who got vaccinated in October-November (Influvac, Influenza) can rest easy during the seasonal epidemic; they will not get the flu. Even if the types of influenza virus in the vaccine do not match the type that caused the epidemic, the severity of the disease in the vaccinated person will be several times less, and the possibility of developing complications is sharply reduced.
WHO recommends that the following groups of people be vaccinated annually:
- pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy
- children from 6 months to 5 years
- seniors 65 years and older
- people with chronic illnesses
- healthcare workers
Summarizing all of the above, we can draw the following conclusions:
- The most effective way to reduce morbidity and mortality from influenza is to get vaccinated annually
- Immunostimulants and oxolinic ointment are ineffective against influenza
- If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, antipyretic drugs should be given
- You should call a doctor if: the temperature rises above 39.0 degrees, with a constant and debilitating cough, rapid and difficult breathing, shortness of breath, vomiting, dizziness, refusal to drink and eat in children.
What is the danger?
Bird flu has been diagnosed in all types of domestic birds: terns, parrots, quails, pheasants. All strains are capable of recombination, resulting in the formation of completely new, unexplored variations of the virus.
Often, when there is a massive mortality of poultry at poultry farms, and a diagnosis of avian influenza is established, laboratory tests reveal non-virulent strains of the virus. This indicates the serious importance of stress factors, existing infections (note: mycoplasmosis) and poor living conditions in the development of the disease.
Sources of the causative agent of classical bird plague:
- sick;
- recovered individuals (virus carriers).
The influenza virus is released through secretions and excreta; transmission route is airborne. You can bring it into the house with exchange containers, hatching eggs, and feed. In megacities, classic bird plague is carried by crows, jackdaws, pigeons, sparrows, rodents and cats. According to studies, virulent strains are more often diagnosed in short-lived birds.
Causes
In nature, the main reservoir of avian influenza is migratory wild migratory waterfowl, as well as domestic birds. The virus is found in the digestive tract of birds and is excreted in the feces.
Infection can occur in the following cases:
- If a person comes into contact with infected birds (in factories, households, zoos, etc.).
- From bird droppings - through contaminated objects and hands.
- From dead birds.
The disease is not transmitted from person to person.
Prevention
There is currently no vaccine for this virus. Therefore, preventive measures boil down to following the following rules:
- Always cook poultry meat and eggs thoroughly.
- Destroy all infected birds on farms. At the same time, people who do this work must wear appropriate protective clothing.
- Conduct regular sanitary and epidemiological control over birds kept on farms and in private yards.
- Do not allow children to come into contact with potentially infected birds.
- If birds die on your farm, always notify your veterinarian.
- If cold symptoms occur after contact with birds, consult a doctor immediately.
- Always wash your hands thoroughly after handling birds.
Is it possible to get the flu and coronavirus at the same time?
Every year more than 30 million cases of ARVI are registered in the Russian Federation. Most often, acute respiratory viral infections are recorded from September to April, and the peak of outbreaks occurs in February and March. With the beginning of the warm season, the incidence of ARVI decreases.
The COVID-19 pandemic has not affected the spread of ARVI, and therefore the combination of these two respiratory infections in one person is not excluded. It is important to remember that to make a diagnosis of COVID-19, only clinical symptoms (which are in many ways similar to the manifestations of ARVI) are not enough - laboratory confirmation is required.
Flu vaccination (flu shots)
Vaccination is an effective way to protect against influenza. As a rule, vaccination is recommended for people with weakened immune systems, as well as those with chronic diseases. Flu shots are often recommended for older adults and children because they help prevent the flu or alleviate the illness.
Immunity occurs 14 days after vaccination and lasts for 6-9 months. Therefore, it is recommended to get vaccinated every year.
Article on the topic
But the horns didn’t grow! Truths and myths about vaccinations
Flu vaccines come in three types:
- Live vaccines
The vaccine is administered nasally. Children from 3 to 14 years old need to be vaccinated twice, with an interval of 3-4 weeks;
- Inactivated whole virion vaccines
The vaccine is administered intranasally (twice, with an interval of 3-4 weeks) or once subcutaneously (in the upper-outer part of the shoulder). Suitable for children over 7 years old and adults;
- Subunit and split vaccines (third generation influenza vaccines). The vaccine is administered intramuscularly or deeply subcutaneously (children twice, adults once). Children from 6 months of age, adolescents and adults are subject to vaccination.
Vaccination reactions and complications.
- It is rarely possible for the temperature to rise above 37.5 degrees C in the first three days after administration
- Sometimes there is painful swelling and mild tenderness at the injection site
- In some cases, muscle pain and joint pain are observed
Is there a runny nose with coronavirus?
Common symptoms that occur with COVID-19 include:
- increased body temperature - in more than 90% of cases;
- cough (dry or with a small amount of sputum) - in 80% of cases;
- shortness of breath - accompanies approximately 55% of cases of the disease;
- increased fatigue - this symptom is noted by approximately 44% of patients;
- feeling of chest congestion - in 20% of those who have had COVID-19;
- reduction or complete absence of smell and taste - have been found in many confirmed cases.
A runny nose is not a defining symptom. It can occur both with coronavirus infection and with ARVI.
Recommendations for the treatment of ARVI and COVID-19
It is quite difficult to carry out differential diagnosis at the initial stage of the disease. This is due to the fact that the primary clinical manifestations of ARVI and COVID-19 are similar: weakness, fever, catarrhal symptoms.
An equally significant factor of similarity is the seasonal course of many acute respiratory viral infections and (at the moment) the non-seasonal prevalence of the new coronavirus infection.
Today there is no universal treatment and prevention regimen for COVID-19, since there is no data on the effectiveness or ineffectiveness of various therapeutic regimens. That is why the decision to prescribe certain drugs is made by doctors and medical commissions, based on an assessment of the manifestations of the disease, the balance of risks and benefits for the patient.
According to the current recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, today patients with coronavirus infection are prescribed antiviral drugs, interferon drugs, antimalarials, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. Anti-inflammatory therapy is also carried out, antithrombotic drugs are administered, , , .
Since the clinical picture of mild forms of COVID-19 and the clinical picture of seasonal ARVI are similar, before making an etiological diagnosis, it is recommended to include in the treatment regimens for COVID-19 drugs that are used to treat seasonal ARVI: intranasal forms of interferon-α, interferon inducer drugs, which include Kagocel, .
Is bird flu dangerous for humans?
Avian influenza is one of the most common diseases in poultry.
Avian influenza is a dangerous subtype A disease caused by a virus. It affects not only poultry, but also humans (in 60% of cases, infected people die).
Often appears in winter and affects one bird population and then the rest. Ducks, geese and chickens are most susceptible to the disease.
This type of flu is especially dangerous because it constantly changes and prevents the human immune system from fighting it. Because the virus is virulent, it is easily transmitted through the air.
Human infection occurs through contact with sick birds, during carcass cutting, assembling and packaging eggs and meat. It also occurs when cleaning up bird droppings and touching contaminated objects.
Bird flu is especially dangerous because it constantly changes and prevents the human immune system from fighting it
Rarely, a person becomes infected after eating eggs or meat.
Transmission of influenza from one person to another has not yet been proven. However, influenza is mutational and often changes in nature, so there is a risk of infecting other people.
Prevention of influenza, coronavirus infection and ARVI
Prevention of new coronavirus infection and other acute respiratory viral infections is divided into specific and nonspecific.
Specific prevention - vaccination
Currently, influenza vaccination is being carried out in Russia, for which several vaccines of domestic and foreign production are used. The antigenic composition in influenza vaccines is updated annually in accordance with WHO recommendations, depending on the prevalence of certain influenza strains.
A vaccine against the new coronavirus infection SARS-CoV-2 has been registered in the Russian Federation. It was developed by the Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology named after Academician Gamaleya of the Russian Ministry of Health, and is now at stage III of clinical trials. It is planned that in 2021, after completion of phase III studies and receipt of reliable data on effectiveness and safety, the vaccine will go on the market and will be available for immunization of the population.
First of all, it will be used for the specific prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection among workers in the healthcare system, education, law enforcement, public transport, food and trade, social protection, as well as everyone who comes into contact with a large number of people. Nonspecific prevention of COVID-19 and other acute respiratory viral infections
Nonspecific prevention primarily includes:
- A set of measures aimed at strengthening the body’s defenses (charging, hardening, maintaining a healthy lifestyle).
- Taking medications that help increase immune defense. Interferon drugs and their inducers and antiviral drugs are considered as means for this.
Nonspecific prevention also includes adherence to personal hygiene rules, which are aimed at preventing infection with a viral infection:
- frequent hand washing with soap, use of disinfectants, avoiding touching your face and mucous membranes with your hands;
- use of disposable napkins and handkerchiefs when sneezing and coughing;
- the use of masks by the population and protective suits by health workers;
- washing the nasal mucosa to reduce the viral and bacterial load.
If you experience symptoms of the flu or coronavirus infection, do not delay visiting your doctor and getting tested. Timely treatment can contribute to the mild progression of respiratory viral infections, reduce the risk of complications, and facilitate and accelerate the recovery process.
Diet
Diet for influenza, ARVI, colds
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 4-7 days
- Terms: 5-12 days
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles per week
- The diet of a patient infected with this disease should be light, but at the same time rich in vitamins.
- It is extremely important to drink plenty of fluids to replenish fluid losses and prevent dehydration.
- You should eat in small portions, doing this 5-6 times a day.
- The menu should contain protein products (poultry, rabbit), fish, stewed and fresh vegetables, and fruits.
- It is recommended to drink fruit drinks and compotes, decoctions of dried fruits.
What is the difference between COVID-19 and ARVI?
The differences between COVID-19 and ARVI begin during the incubation period - from the moment of infection until the appearance of clinical symptoms. With COVID-19, the latent period lasts from two to fourteen days, on average 5–7 days, and the development of symptoms with other acute respiratory viral infections usually takes 3 days.
Weakness during ARVI is rare, as is severe fever. For ARVI, the appearance of shortness of breath (30%) and difficulty breathing (>20%), which are observed with COVID-19, is also atypical.
If the clinical picture of ARVI is characterized by catarrhal symptoms - redness of the throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, cough, quickly turning from dry to wet, then the main clinical sign of coronavirus infection is respiratory failure (in mild cases of the disease), in moderate and severe cases - rapid increasing respiratory failure. In this case, the mucous membranes change slightly or moderately, a runny nose may be absent.
A typical complication of COVID-19 is viral interstitial pneumonia, while ARVI is more characterized by complications such as the development of acute bronchitis or exacerbation of chronic bronchitis.
Clinical observations have also shown that the onset of a new coronavirus infection in some patients is accompanied by the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes (conjunctivitis) and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, manifested in the form of diarrhea, while these symptoms are not typical for ARVI.
How to improve your health?
- Timely diagnosis of health conditions
- Avoid self-medication and recommendations from dubious sources
- Maximize the use of non-drug methods of prevention and treatment: Physiotherapy (exceptional safety and fantastic effectiveness)
- Climatotherapy (and in Moscow - halotherapy)
It is necessary to sanitize chronic lesions, especially for ENT organs:
- Strengthening the “Pirogov’s lymphoid ring” is important to reduce the risk of severe infection and prevent infection from penetrating into internal organs (kidneys, joints, heart, lungs).
Tests and diagnostics
- After the patient contacts the doctor, the specialist must determine whether the patient has had contact with potentially infected birds or traveled to regions with an increased risk of disease transmission.
- When listening to the patient, wheezing and harsh breathing are detected.
- An X-ray examination is carried out, where instantly spreading infiltration is determined.
- Laboratory tests are also carried out. A blood test demonstrates a decrease in lymphocytes , leukocytes , and platelets .
- An RT-PCR analysis is carried out, for which a swab is taken from the nose or throat.
- Sputum and endotracheal aspirate samples can also be taken for analysis.
If a case of avian influenza is confirmed or suspected during the diagnostic process, it is reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The first signs and symptoms in chickens
The first signs after infection appear the next day.
The reason for the mass death of chickens is low immunity
In acute poultry form:
- sharply reduce egg production;
- refuse to take food (even to the point of anorexia);
- secrete thick mucus that clogs the respiratory organs and nasopharynx;
- wheeze heavily and breathe intermittently;
- have a hot body (their body temperature reaches 44 degrees);
- excrete brown and greenish droppings;
- experience neurosis and convulsions, their neck and wings become bent;
- suffer from incoordination of movements, stagger, fall;
- feel very thirsty.
In the last stage, pulmonary edema and damage to the nervous system are observed, a general deterioration in health and death.
WHO activities
WHO, as a leader in global health, closely monitors avian and other zoonotic influenza viruses through its Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS). WHO, in collaboration with the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE), conducts human-animal contact surveillance, assesses risks and coordinates responses to zoonotic influenza outbreaks and other human health threats. WHO provides risk-based recommendations, develops and adjusts surveillance, preparedness and response strategies for influenza – seasonal, zoonotic and pandemic – and communicates risk assessments and recommended interventions to Member States in a timely manner to improve preparedness and strengthening the national and global response.
Bibliography
(1)
Control of Communicable Diseases Manual 20th Edition. American Public Health Association (2015). APHA Press, Washington DC. ISBN: 978-0-87553-018-5
(2)
Monthly Risk Assessment summaries at the Human Animal Interface
(3) WHO Manual for the laboratory diagnosis and virological surveillance of influenza, 2011
How to treat and can it be cured at all?
Important! It is currently impossible to cure acute influenza. All sick chickens and potentially infected individuals in contact with them are destroyed.
The poultry house is quarantined. All items located in the chicken coop or near sick birds are destroyed. Meat, eggs, feathers and other products are disposed of.
With a mild form of the disease, birds with good immunity cope with the disease on their own.
H5N1 is the most dangerous variant of the virus
To stimulate the development of immunity and ensure its active work in the fight against the virus, birds are given medications (antibiotics and vitamins). When quarantine is established in the region, birds are also given antibiotics and vitamins.
What to do with a sick bird
If pronounced symptoms of the disease appear, veterinarians in the region are informed. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the diseased birds are destroyed.
The poultry house is quarantined. Sick birds are killed and sent to the laboratory for examination.
Important! Birds located near infected individuals are also exterminated to prevent the spread of the infectious disease. All products of infected individuals are disposed of.