Every mother dreams of giving birth and raising a healthy baby. Unfortunately, there are many dangers along the way of pregnancy, and one of them is the herpes virus, which is familiar to many. The virus can manifest itself in different ways: from itchy sores on the lips, poisoning a comfortable life, to the development of serious health-threatening conditions. In pregnant women, relapses can occur especially often, which is due to a natural decrease in immunity during pregnancy. During this difficult period, the expectant mother's immunity levels decrease. This condition is called physiological immunosuppression, which, on the one hand, helps to bear a child without rejecting him, and on the other, makes the body susceptible to various infections. Despite the fact that herpes on the lips is not considered a serious disease by most, herpes viruses can have an adverse and even fatal effect on the course of pregnancy and childbirth, leading in some cases to damage to the fetus.
- Herpes on the lips during pregnancy
- Why is herpes dangerous during pregnancy?
- An important aspect of protecting the body from viruses and germs
- Herpes during pregnancy. Is it possible to resist him?
- How to behave if the disease manifests itself
- How does the virus enter the body and why is it activated?
- Herpes zoster during pregnancy
- Who needs a herpes diagnosis?
- Herpes treatment regimen
- Effects of therapy with VIFERON
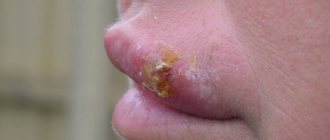
Herpes on the lips during pregnancy
The herpes simplex virus (Herpes simplex virus) of the first and second types is constantly present in the body in most people after infection in early childhood and under unfavorable conditions can be activated. It is known that by the age of fifteen, 80% of children and adolescents are infected with one or another herpes virus, and by the age of 30, 90% of people have antibodies to different types of this virus. The most common sites for infection are the genital area and surrounding skin, such as the buttocks, perineum, and face. Single or grouped itchy blisters appear on/on the nose, lips, cheeks, mouth, and on the mucous membrane of the eyelids. Recurrences of herpes during pregnancy are a very common occurrence, since a woman’s immune system during this period may not be able to cope with the virus that has once settled in the body.
Symptoms (manifestations)
The two types of herpes described above give rashes in different places of the body. But the symptoms are similar:
- rashes that look like blisters
- burning and itching of the mucous membranes of the genital organs
- headache
- muscle pain
- weakness in the body
- temperature is about 38 - 39 degrees
In the place through which the pathogen entered the woman’s body, burning and itching first begins. But only after a while a rash appears. Blistering rashes are called "vesicles." They are filled with serous contents that have no color. The blisters of labial herpes are found mainly on the lips, sometimes on the nose. With genital herpes, accordingly, the rash will be on the labia, in the vagina, on the cervix and even in the anus area.
Several days pass before the bubbles open and their contents come out. Small ulcers remain at the site of the rash. If you touch them, pain will occur. Wounds take a long time to heal. With genital herpes, pregnant women may experience vaginal discharge of a watery consistency for 5-7 days. This is one of the symptoms of genital herpes.
Recurrent genital herpes during pregnancy is clinically similar to primary herpes, but the symptoms are not so obvious. As we know, during pregnancy a woman’s immunity decreases (so that she can carry a child without the body rejecting it), so the disease recurs. Doctors call such relapses relapses. After an exacerbation, a stage of remission usually follows.
Remission means that the pathogen remains in the body, but there are no longer typical obvious symptoms. Relapses are similar in symptoms to the clinical picture of primary herpes.
Why is herpes dangerous during pregnancy?
The greatest danger is posed by primary infection with herpes during pregnancy. Due to the absence of antibodies protecting against herpes in the mother’s body, the situation is characterized by more pronounced manifestations. For the fetus, the risk is especially high when infected with genital herpes in the first and third trimesters. Infection of the fetus in the first trimester leads to severe consequences, but such cases are extremely rare, since with the primary infection of a pregnant woman up to 10 weeks, as a rule, spontaneous termination of pregnancy occurs. The situation is considered extremely unfavorable in the case of primary infection in the second and third trimesters. However, primary infection in the second half of pregnancy almost always has a clear manifestation, which allows immediate action to be taken. HSV, while in the body, certainly reduces the “reserve” of health originally provided by nature. However, in the process of interaction with the virus, antibodies are formed that are passively transmitted to the newborn from the mother. With recurrent herpes or carriage of the virus, the risk to the fetus is assessed as minimal, since maternal antibodies help cope with the infection even in the event of an active relapse. With this form of infection, the virus is released less than with the primary one.
Eppstein-Barr virus
The Epstein-Barr virus predisposes to premature termination of pregnancy, fetal malnutrition, and in newborn children it causes damage to the nervous system, visual organs, recurrent chroniosepsis, hepatopathy and respiratory distress syndrome. However, this virus provokes the listed pathologies only under certain conditions, under which it becomes dangerous during pregnancy. It is very bad if a pregnant woman has not previously encountered the Eppstein-Barr virus, which is why she does not have antibodies to this virus in her body. If there was contact, and antibodies were detected after treatment, then this is a good sign, because in this case there is nothing to be afraid of. This serves as evidence that if a woman’s body becomes infected again, she will cope with this dangerous disease on her own. This means that a pregnant woman will not have to take medications that are heavy and quite dangerous for the development of the fetus.
An important aspect of the body's defense system against viruses and microbes
In the process of evolution, humans have developed various defense mechanisms that allow them to resist various infections. Thus, the interferon system IFN is one of the most important factors of the body’s resistance, participating in various immunological reactions. Interferons are a group of biologically active proteins or glycoproteins synthesized by the cell in the process of a protective reaction to foreign agents, which include viral infection. Currently, the concept of “interferon system” (SI) has emerged. It does not belong to any specific organ, but exists in every cell, so all of them can be infected with a virus and must have a system for recognizing and eliminating foreign genetic information. SI is configured to recognize “self and foe” and is “built-in” into almost all cells of the body, which allows it to actively influence the entire cascade of the body’s defense reactions from phagocytosis to inflammation, which makes it an important factor in nonspecific resistance. As a result of the study of interferons, their role was determined: control and self-regulation of processes in the body. The main effects of interferon protection: antiviral, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, preventing excessive cell proliferation, protection against radiation and others. Herpesvirus infections cause an imbalance in the interferon system, inhibit the cellular and phagocytic reactions of the body (prevent the detection, absorption and removal of viral particles). Restoration and normalization of the body’s defense mechanisms is the preventive task of antiviral therapy.
Asymptomatic herpes
Asymptomatic herpes is not at all uncommon. The absence of visible manifestations of genital herpes does not guarantee the absence of the infection itself. Inflammation of the vagina, cervical canal, endometrium, and uterine appendages does not exclude HS. Not so long ago, it was believed that only clinically pronounced forms of HS pose a serious threat to the health of a modern woman and her child. The absence of clinical manifestations of HSV infection in a pregnant infected woman does not prevent transmission of the virus in the perinatal period to the child. This statement is supported by data that in 60-80% of cases, children with neonatal herpes are born to mothers with atypical or asymptomatic forms of HSV infections (Bursrein DN 2003).
In asymptomatic cases, the herpes virus can be determined by cultural and immunohistochemical methods, which means timely action can be taken.
- Culture method (growing the virus in cell culture)
- PCR – diagnostics for the presence of viral DNA in the ejaculate and its fractions
- Spermogram (determines the number of sperm, their motility, the number of normal sperm)
- Study of the population of immature germ cells in the ejaculate
In fertile men, active HSV is detected in 6-10% of cases using the culture method and up to 47% when using PCR diagnostics, i.e. PCR is a more informative technique.
Herpes during pregnancy. Is it possible to resist him?
What can be advised to those who, with the help of approved medications, seek to stop herpes during pregnancy? VIFERON is an antiviral drug that can be taken by expectant mothers. One of its properties is a wide range of antiviral activity due to the presence of interferon in the drug. That is, you can start using it already at the beginning of symptoms. This can stop the disease at the very beginning, while the virus has not yet multiplied and affected healthy cells. Doctors prescribe VIFERON for herpes during pregnancy to compensate for the lack of its own interferon and enhance antiviral protection. Already from the 14th week of pregnancy, VIFERON Suppositories are allowed in a dosage of 500,000 IU. It is prescribed for primary or recurrent herpetic infection of the skin and mucous membranes, with a localized form, mild and moderate course, including the urogenital form of infection.
Diagnostics
Enzyme immunoassay is a very reliable diagnostic method. It allows you to detect both labial and genital herpes in a woman. ELISA detects immunoglobulins G and M in the patient’s blood. After infection, Ig M first appears in the blood. And after 2-4 weeks, Ig G can be detected (after primary infection or resumption of a pre-existing disease).
Types of ELISA:
- qualitative
- quantitative
The last of these provides information about the titer of immunoglobulins, that is, their quantity. Quantitative ELISA allows you to assess whether the patient has immunity to the herpes pathogen.
In addition to ELISA, diagnosis is carried out using PCR or virological culture. The fact that a woman has herpes is indicated to the doctor by symptoms that point specifically to this disease.
Laboratory diagnostic methods:
- serology
- culture method
- immunofluorescent reaction
- microscopic examination
In 80 women of reproductive age out of 100, antibodies to the causative agent of herpes simplex type 1 are detected during testing. Antibodies in the same patients to the second type virus are found in 30 women out of 100. Those who want to conceive a child, and those who are already pregnant, worry when ELISA detects herpes in the body. But there is no need to worry, because a herpes test shows whether there are protective antibodies in the blood.
If you have IgG, then the fetus is not in danger. This is even good, because herpes will not be passed on to the child, because the mother has immunity. If (IgM) is detected, this may indicate a recurrence of herpes, which the woman was once infected with and which was latent.
IgM remains in the body for only one or maximum two months. IgG antibodies will remain in the blood throughout your life, which in medical language is called seropositivity. If a primary infection has occurred, then IgM and a 4-fold increase in IgG are detected, which are detected during studies with a break of 12 days.
A relapse of the disease in a woman is indicated by a large amount of IgG and the appearance of IgM. If questionable results regarding IgM were obtained, you need to take the test again after 10 or 12 days.
How to behave if the disease manifests itself
Speaking about household habits, it is worth noting that hand hygiene during a relapse of herpes is very important. Do not touch the affected area with your hands, because the infection can be transferred from the face to the genital area. Infection of the birth canal before childbirth may lead to a caesarean section. Herpetic infection in pregnant women requires mandatory treatment under the supervision of a specialist. If a pregnant woman is surrounded by someone with signs of infection, close contacts should be avoided: kissing, sex, and you should not share dishes, linen, or towels with the patient.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HERPES SIMPLE
Key Facts
There are two types of herpes simplex virus: herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-I) and herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-II).
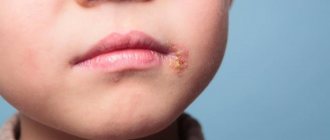
HSV-I herpes on the lips and facial area
transmitted primarily through oral contact and causes oral herpes (symptoms of which may include a “fever sore”), but can also cause genital herpes.
HSV-II herpes in the genital area
is one of the sexually transmitted infections and causes genital herpes.
More than 90% of the world's population are carriers of the herpes virus. Infection with both HSV-I and HSV-II lasts for life.
The frequency of herpes on the lips varies from person to person and can recur from 2 to 12 times a year. Most cases of herpes are oral and genital.
Typically, the virus settles in the body at 3-5 years of age, but does not appear until puberty.
Transmission routes:
- Autoinfection.
The virus is transmitted from infected areas of the body to uninfected areas. For example, contact lens wearers can transfer the herpes virus to the eye area by wetting the lenses with infected saliva instead of a solution.
- When contacting another person through a kiss
For infection to occur through a kiss, the virus needs 2 conditions:
so that the carrier has an active phase of herpes (moreover, it can be asymptomatic)
so that the partner has a predisposition to infection: an abundance of saliva, small wounds.
- Upon contact with a contaminated surface
The virus is able to survive for some time outside its host: in a humid environment, at a temperature of 37°. That is, it is possible to become infected by drinking from the same glass or using the same lipstick. It is theoretically possible, but rare, to become infected with genital herpes when sitting on plastic surfaces (toilet, locker room bench), because On plastic surfaces under favorable conditions, the virus survives for about 4 hours.
Stages of herpes
Precursor stage
It usually begins with a tingling, itching and burning sensation on the lips. Duration from several hours to 1 day.
Hyperemia stage
Literally on the same day as the tingling sensation, swelling and redness of the lip occurs. The condition is usually accompanied by itching and lasts on average 1-2 days.
Bubble stage
A group of several bubbles is formed, which merge with each other into one painful bubble filled with lymph. This usually happens on the second day and is accompanied by very painful sensations.
Stage of erosion formation
On day 3, the blisters transform into ulcers and pustules, which then form a sore. Usually it is gray in color with a bright red ring around it. The liquid released from the sore contains virus particles in a concentration of 1 million per 1 ml. and is highly contagious
Crust formation stage
From days 4 to 9, the sore dries out and crusts over. In this case, the pain becomes less, but severe itching appears. The sore may fall off in parts and bleed. Herpes begins to heal from the inside, the sore becomes smaller.
Healing stage
On days 9-11, the wound heals and heals. However, redness may persist for another two days. During this period, the virus returns to a dormant state, in which it can remain until it is activated again by risk factors.
Treatment
The most effective medications for people infected with HSV are antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, famciclovir and valacyclovir. They help relieve symptoms and reduce the frequency of their occurrence, but do not lead to a complete cure.
Prevention
HSV-I herpes on the lips and facial area
HSV-I is most contagious during the onset of oral herpes symptoms, but it can also be transmitted when no symptoms are felt or observed. Individuals with active symptoms of oral herpes should avoid oral contact with others and sharing objects that have come into contact with saliva. They should also abstain from oral sex to prevent herpes from spreading to their partner's genitals. People with symptoms of genital herpes should avoid sexual intercourse while they are experiencing symptoms.
Consistent and correct use of condoms can help prevent the spread of genital herpes. However, condoms can only reduce the risk of infection, since symptoms of genital herpes can appear in areas not protected by a condom.
Individuals already infected with HSV-I cannot become infected again, but they remain at risk of infection with HSV-2, which affects the genital area.
Pregnant women with symptoms of genital herpes should inform health care providers. Preventing new infections with genital herpes virus is especially important for women in late pregnancy, since this is the period when the risk of developing neonatal herpes is highest.
HSV-II herpes in the genital area
People with a genital infection caused by HSV should abstain from sexual activity while symptoms of genital herpes appear. HSV-II is most contagious when lesions appear, but it can also be transmitted when no symptoms are felt or observed.
Systematic and correct use of condoms can help reduce the risk of spreading genital herpes. However, condoms provide only partial protection because HSV can be found in areas not protected by a condom. Medical male circumcision can provide men with lifelong partial protection against HSV-II, as well as HIV and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Individuals with symptoms suggestive of genital HSV infection should be tested for HIV infection, and those living in areas with high HIV prevalence should be offered more focused HIV prevention interventions, such as pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Pregnant women with symptoms of genital herpes should inform health care providers. Preventing new infections with genital herpes virus is especially important for women in late pregnancy, since this is the period when the risk of developing neonatal herpes is highest.
How does the virus enter the body and why is it activated?
Of the eight types of herpes viruses known today, the cause of rashes on the lower part of the face and genitals are usually HSV-1 (mainly herpes labialis) and HSV-2, which has more dangerous consequences. Transmission of HSV-2, as a rule, occurs through sexual intercourse, but vertical transmission is also possible - from mother to child during childbirth. Moreover, if a pregnant woman is infected for the first time, then the risk of neonatal herpes in the baby is 50 to 50, and in case of relapse, only 3-5% of children are born with signs of herpes infection. With the vertical mechanism of infection, the fetus is infected through maternal blood during childbirth, or the virus enters the pregnant woman’s uterine cavity from the cervix. At the same time, a high level of immunoglobulin proteins in the blood (antibodies) can protect the fetus from intrauterine infection. Cellular immunity also plays an important role in preventing the recurrence of herpes. In turn, the frequency and intensity of relapses depends on the state of local (mucosal) immunity. When there is a malfunction in the immune system, there are exacerbations of herpes infection. Injuries, surgeries, cosmetic procedures, sexual contacts that injure the mucous membrane, and taking certain medications can trigger a relapse. With reduced levels of T-cell immunity, conditions are created for the virus to multiply in cells. Interferon deficiency plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of herpes. In foci of herpetic lesions, local suppression of interferon formation is noted. VIFERON for herpes during pregnancy in the form of Suppositories can be taken starting from the 14th week, however, local forms such as Gel and Ointment have no restrictions on the duration of pregnancy. They are used directly on the affected areas: skin and mucous membranes.
Ways of spreading the disease
HSV-1 is transmitted in the following ways:
- contact-household
- airborne
Airborne transmission means that the virus is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person through touching (only through those areas where there are rashes), kissing, etc. By using the personal belongings of an infected person, you have every chance of becoming infected. Therefore, a pregnant woman should only use her own cosmetics, toothbrush, body washcloth, towels and dishes.
HSV-2, that is, the genital type of herpes infection, is transmitted through sexual contact (coitus). In half of the cases, a woman becomes infected from a partner who currently has no significant symptoms, but may only have a small rash, mild pain and a slight burning sensation, nothing more. Such symptoms often seem not to threaten a man’s health, and he does not go to the doctor, infecting his partners through kissing, touching and unprotected sexual intercourse.
If a pregnant woman becomes infected with herpes for the first time, the fetus will become infected in 50-60 cases out of 100. These are very high chances of getting sick. Vertical transmission of genital herpes is also possible (through the placenta or during childbirth). During the birth process, the baby passes through the birth canal, where the virus is localized and there are rashes. His immunity is still too weak to resist such an infection, and infection occurs literally in minutes.
Most of the population suffers from herpes due to the fact that it is very easily transmitted. Therefore, those who are expecting a child need to be tested before pregnancy and monitor their immune status for all 9 months.
Herpes zoster during pregnancy
Herpes zoster (herpes zoster, herpes zoster) is a viral disease of the skin and nervous tissue that occurs due to reactivation of the herpes virus type 3. Primary infection with the Varicella-zoster virus usually manifests itself as chickenpox. People with immunosuppression have a much higher risk of getting the disease than those with normal immunity. The main symptom is severe, prolonged pain, which may precede the rash. Pregnant women may experience severe complications. Infection in the first trimester will most likely lead to primary placental insufficiency and miscarriageii.
Prevention
The main measures to prevent herpes in pregnant women are:
- testing for the herpes virus when planning to conceive (before you become pregnant)
- rejection of bad habits
- strengthening the immune system (hardening, balanced nutrition, physical activity and healthy lifestyle in general)
If you know about your recurrent herpes, you need to be treated before pregnancy with multivitamin complexes and immunomodulatory drugs as prescribed by your doctor. Laser therapy may also be recommended to help make the virus less active. You should also avoid contact with those who have recurrent herpes. Health to you and your baby!
Diagnosis of herpes, who needs it
When planning a pregnancy, it is recommended to be tested for this infection, which is dangerous for the fetus, since herpes can have an atypical form, in which there is no itching and burning, and there are no vesicles. The reason for diagnosis may also be a history of herpetic rashes of any localization, erosive or vesicular rashes on the skin, buttocks, thighs, mucopurulent discharge from the vagina, or sexual contact with a partner who has this disease, as well as frequent changes of partners. Particular attention is required for women with a burdened obstetric history, those who have already suffered perinatal losses or have given birth to a child with congenital defects. Pregnant women with signs of intrauterine infection determined by ultrasound should undergo testing.
What is herpes? Types of infection
The disease is incurable. The virus can “sleep” in the body for years. But, as soon as for some reason the body’s defenses weaken, the clinical picture of the disease will appear. There are 2 types of herpes virus:
- HSV-1 (so-called labial)
- HSV-2 (genital: rashes appear on a person's genitals)
The second type of herpes is very dangerous for those who are pregnant. This is a TORCH infection. A woman should definitely be checked for a number of such infectious diseases at the stage of pregnancy planning, because they can harm the development of the fetus.
Treatment regimen:
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from the 14th week of gestation) are recommended to use the drug VIFERON® 500000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours for 10 days, then for 9 days 3 times with an interval of 3 days (on the fourth day) 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours. Then every 4 weeks until delivery VIFERON® 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, before delivery (from the 38th week of gestation), the use of the drug VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days. Ointment for local and external use (interferon content 40,000 IU) is applied in a thin layer to the lesions 3-4 times a day and rubbed in gently. Duration of therapy – 5 – 7 days. You can also use Gel (interferon content 36,000 IU). A 0.5 cm strip is applied using a spatula or a cotton swab/cotton swab to a previously dried affected surface 3–5 times a day for 5–6 days; if necessary, the duration of the course is increased until the clinical manifestations disappear. It is advisable to start therapy at the first signs of relapse: tingling, redness, itching.
Effects of therapy with VIFERON
“The use of the drug VIFERON® from the 14th week of pregnancy contributed to:
– exclusion of signs of hematogenous infection;
– reducing the frequency of ascending infection by 4.5 times;
– reducing the incidence of pathology in newborns (infectious and non-infectious);
– exclusion of structural changes in the central nervous system in newborns;
– increasing the frequency of births of healthy children by 2 times [1];
According to available data: “The inclusion of the drug VIFERON® in complex therapy helps reduce:
– threats of termination of pregnancy 2 times;
– polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios by 3 times;
– gestosis by 2.5 times;
– the frequency of replicative forms of the virus is 2 times (HSV from 79.3% to 45%, CMV – from 62.2% to 33.3%);
– the frequency of relapses of concomitant bacterial vaginosis is more than 1.5 times (mycoplasma and ureaplasma);
– the total number of non-infectious complications of the perinatal period by 2.5 times (from 28.6% to 12%)
– the total number of cases of IUI in newborns increased 5 times (from 26.7% to 5.2%);
– the incidence of severe forms of IUI doubled (from 25% to 11.3%) [2].
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Sources:
- Bocharova I.I., Novikova S.V., Malinovskaya V.V., Vyzhlova E.N., Parfenov V.V. Perinatal aspects of herpesvirus infections // Medical Advisor. Gynecology. 2021.1/(41).
- IN AND. Krasnopolsky, T.G. Tareeva, V.V. Malinovskaya. Monitoring of pregnant women with viral infections of the herpes family // Medical technology. – M. 2021. – 40 p.
i https://www.lvrach.ru/
ii https://medi.ru/
Loading...
Take other surveys
Getting pregnant with herpes - pros and cons
Is herpes dangerous during pregnancy? - probably one of the most common questions asked by women when visiting a doctor. Of course, the presence of HSV infection requires more careful examination and monitoring of such patients. With GG (genital herpes), damage to the placenta and fetus can occur at any stage of pregnancy and lead to malformations, immunodeficiency states and fetal death, miscarriages, premature birth due to severe changes in all three membranes of the placenta and umbilical cord vessels. Intrauterine HI is an uncontrollable cause of perinatal mortality, morbidity and early childhood disability.
The importance of the problem is due to the fact that HSV, unlike other infectious diseases, has a destructive effect on the tissues and organs of the fetus. A study before IVF in women with HSV showed a more than 2-fold decrease in the ability of the embryo to implantation compared to healthy women.