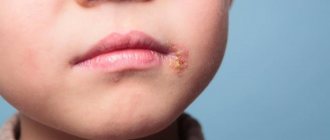
Manifestations of the virus are characteristic blistering rashes on the mucous membranes and skin. After some time, small ulcers form in their place, then crusts. In the area where the rash should appear, burning and itching first occurs. Herpes is characterized by severe pain in the area of the rash.
The herpes virus spreads along the nerve endings and is not completely removed from the body even after a course of drug therapy. It is able to exist in an active and “sleeping” state.
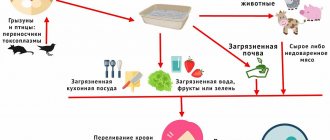
Herpes simplex viruses types 2 and 1 are transmitted sexually and through contact, even when the symptoms of the disease in the carrier are not yet noticeable. In the early stages of infection, there are usually no symptoms at all, so diagnosis can only be made in the initial stages through laboratory testing. Primary infection with the virus most often occurs in childhood, even in preschool age.
In women, genital herpes usually appears on the labia and cervix, less often in the perineal area. In men, blisters appear on the skin and mucous membrane of the penis, as well as inside the urethra and rectum.
Why do tests for herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2?
Herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 not only cause cosmetically unpleasant rashes. It also causes severe pain (for example, along the nerve trunks in the area of the rash), general weakness and damage to the central nervous system.
Therefore, it is important to know about the presence of this virus in the body in order to ensure the necessary prevention of exacerbations of infection and timely, comprehensive treatment. These measures will prevent complications associated with the active progression of herpes infection.
The danger of herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 is that against the background of decreased immunity, from which no person is immune at different periods of life, the infection is activated. The activity of the virus can lead to serious complications such as damage to the facial, auditory and other cranial and spinal nerves.
Herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 can seriously threaten a pregnant woman and her unborn child. Intrauterine infection occurs with serious consequences for the nervous system. Reactivation of the infection during pregnancy can lead to its pathological course or premature termination.
Herpes treatment regimen
If mild symptoms of HSV are detected, treatment can be carried out at home; for generalized forms, hospitalization is necessary. There are two treatment regimens for treating exacerbations. In the first, which is used on demand, various herpes treatments are used at the first manifestations, even before the appearance of blistering rashes. It is recommended to take loading doses of herpes medications in tablets throughout the day. This allows you to prevent relapse without the appearance of typical skin rashesSource: Approaches to immunotherapy for recurrent herpes simplex. Shulzhenko A.E., Zuikova I.N. Science of life and health, 2014. p. 130-131.
The second regimen is a long course of anti-relapse treatment if herpes worsens every 1-2 months or more often. Oral medications for herpes are indicated for daily use for up to a year. During this period, immune function, which is responsible for suppressing infection, is restored.
The use of local remedies - cream, ointment for herpes on the area of the rash, has a very limited effect.
Etiotropic therapy is supplemented with drugs to stimulate the immune system and vitamin preparations.
To prevent frequent relapses, a herpes vaccine is necessary. It is administered outside the period of exacerbation according to the scheme and protects against severe and complicated forms. Source: Modern prospects for the treatment of genital herpes. Khryanin A.A., Reshetnikov O.V. Medical Council, 2021. p. 80-84.
When should you test for antibodies to herpes simplex?
It is advisable to carry out an analysis for antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (IgG, IgM), as well as an analysis for the DNA of the virus in the following cases:
• If small blisters appear on the skin or mucous membranes;
• With HIV infection or immunodeficiency of unknown origin;
• The appearance of burning, swelling and rashes in the genitourinary area may indicate herpes simplex virus type 2. Determination of antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 2 IgG class and other methods can help in the differential diagnosis of genitourinary tract infections;
• In preparation for pregnancy (it is advisable for both partners to be tested for antibodies to herpes simplex);
• If there are signs of intrauterine infection of the child or feto-placental insufficiency, etc.
Diagnostics
Tests for antibodies to herpes simplex virus 2 and 1: IgG, IgM
Given the high frequency of infection, antibodies to the herpes simplex virus are found in the vast majority of people (more than 90%) around the world. However, the antibody titer and its change over a certain period can provide much more information important for the treatment of herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1.
Antibodies to herpes simplex Ig M and Ig A do not remain in the blood for long - approximately 1-2 months. The only type of antibodies to herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 that persist in the blood throughout life is IgG.
Antibodies to herpes simplex Ig M are markers of primary infection. During primary infection with herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1, the IgG titer may increase. If the tests were taken at an interval of 10-12 days, the titer of IgG antibodies to the herpes virus can increase fourfold.
In the case of recurrent infection, antibodies to herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 IgG are very high. This indicates constant antigenic stimulation of the body. The exacerbation of the disease is also indicated by the appearance of IgM in the blood serum.
Causes
The main cause of the disease is infection with one of the types of viruses listed above. However, clinical signs of herpes do not appear in all people infected with viruses. This largely depends on immunological reactivity and the influence of provoking factors. These include the following influences:
- frequent and prolonged overwork of the body;
- systemic hypothermia or overheating, excess UV radiation;
- physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- insomnia, sleep problems;
- sudden changes in climate, region of residence, time zone;
- colds, decreased immune defense.
The severity of manifestations and the form of the disease depend on age, general condition of the body, and associated factors.
Interpretation of tests for antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
• IgG is elevated in chronic herpes infection. If antibodies to herpes IgG increase by more than 30% when repeated testing after a time interval of 10 days, you can think about activation of the infection. If the titer of IgG antibodies to the herpes virus decreases during repeated studies, this indicates the success of treatment and the “extinction” of the infection.
Elevated IgG antibodies to herpes may indicate an intrauterine infection or the likelihood of its development. If the study was first performed during pregnancy, then it is not worth judging the probability until repeated studies are carried out. If IgG antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 were detected in the blood before pregnancy, then the likelihood of intrauterine infection is low.
• IgA appears in the blood 14 or more days after infection with the herpes virus and is not critical in diagnosis.
• IgM class - the first antibodies that appear after infection with herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1 within two weeks. A positive test result makes one think about an acute herpetic infection or the activation of a chronic one. In the latter case, IgM does not always appear in the blood serum; here the concentration of IgG antibodies to herpes is of greater importance.
A negative test result may indicate no infection. However, the same test result occurs in the first days of herpes infection or with a chronic inactive infection.
Prevention
Particular importance in preventing exacerbations is given to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. A rational, healthy diet, moderate physical activity, treatment of all infections, concomitant pathologies, elimination of stress and hypothermia are necessary.
When rashes appear, no special measures are taken; it is important to provide the patient with separate dishes and hygiene items, and avoid close contact and kissing until complete recovery. For HSV type 2, the use of condoms is important.
Taking medications for herpes or vaccination can reduce the risk of exacerbations. Source: Prospects for vaccine prevention of herpes simplex. Isakov V.A., Isakov D.V. Bulletin of Hematology No. 3, 2021. p. 4-10.
Sources:
- Features of herpes viruses. Peradze Kh.D., Sukhoruk A.A. Pediatrician, 2010. p. 78-80
- Viruses of the herpes family and immunity. Kharlamova F.S., Egorova N.Yu., Guseva L.N., Guseva N.A., Novosad E.V., Chernova E.V., Uchaikin V.F. Children's infections, 2006. p. 3-10
- Prospects for vaccine prevention of herpes simplex. Isakov V.A., Isakov D.V. Bulletin of Hematology No. 3, 2021. p. 4-10
- Approaches to immunotherapy for recurrent herpes simplex. Shulzhenko A.E., Zuikova I.N. Science of life and health, 2014. p. 130-131
- Modern prospects for the treatment of genital herpes. Khryanin A.A., Reshetnikov O.V. Medical Council, 2021. p. 80-84
- Some information about the morphology of herpes viruses and their properties. Lutsenko M.T., Gorikov I.N. Bulletin of physiology and pathology of breathing No. 38, 2010. p. 74-77
Determination of DNA of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
The study is carried out using a highly sensitive PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique. The DNA of the virus is determined by examining a scraping from the urethra, collecting morning urine or cerebrospinal fluid. If the analysis revealed DNA fragments of herpes simplex virus type 2 or 1, this indicates the presence of a herpes infection. If viral DNA is not detected, it means that it is not present in the sample taken, or is still present there in a concentration below the sensitivity limit of the test.
In Lab4U, using laboratory methods, you can accurately determine the presence of herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1, as well as get an impression of the course of the infectious process and possible complications. All this provides the doctor with valuable information that helps in diagnosis and choice of treatment regimen.
A study to identify the causative agent of herpes viral infection types 1 and 2 (Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2), during which the genetic material (DNA) of the simplex virus is determined using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method herpes.
Synonyms Russian
Herpes virus, herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2), determination of herpes by DNA.
English synonyms
Herpes Simplex Virus, Type 1 and Type 2, HSV-1 or HSV-2 IgM or IgG, HSV-1, HSV-2, HHV1, HHV2.
Research method
Real-time polymerase chain reaction.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
A swab from the pharynx (oropharynx), prostate secretion, the first portion of morning urine, scraping from the rectum, saliva, scraping from erosive and ulcerative elements, urogenital scraping, ejaculate, venous, capillary blood, cerebrospinal fluid.
General information about the study
The PCR method can detect even a small amount of viral particles in biological material. It allows you to identify herpes viruses regardless of the period of infection, even during the period when antibodies have not yet formed.
The most common are types 1 and 2 of herpes. Both are contagious and contribute to the appearance of small bubbles (vesicles) on the mucous membranes, which burst, forming open wounds. With HSV-1, blisters appear around the mouth and in the oral cavity, while HSV-2 usually affects areas around the genital area.
The herpes simplex virus can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact when there are vesicles on the skin, and sometimes even when there are no visible lesions on it. HSV-2 is often classified as a sexually transmitted disease, but infection with HSV-1 herpes can also occur, for example, through oral sex. According to WHO, from 50% to 80% of the adult population of developed countries are infected with type 1 herpes and about 20% with type 2. Because the symptoms of type 2 are subtle, 90% of those infected with it may be unaware of their infection.
In the case of primary infection, painful blisters usually form at the site of infection after two weeks, which usually resolve after four weeks. They appear on the genitals, around the anus, on the buttocks or thighs, after which they can burst. You may also experience flu-like symptoms, such as chills and sore throat.
However, blisters with herpes do not always form. Sometimes symptoms of the disease are so mild that they go unnoticed or are mistaken for something else, such as insect bites or allergies. After the infection enters the body and spreads, the herpes virus remains in a latent form. With stress or other diseases that lead to a decrease in immunity, it can become active again. In most cases, herpes simplex is not dangerous to health, but it can cause serious illnesses: neonatal herpes (if a child becomes infected during childbirth from a mother infected with genital herpes) and encephalitis. They can lead to serious incurable neurological diseases and even death. The following factors increase the risk of contracting herpes:
- diseases that suppress the immune system (for example, HIV/AIDS),
- organ transplantation.
Currently, a cure for herpes is not possible, however, there are antiviral drugs that suppress its spread, and also shorten the duration of the acute phase of the viral infection and mitigate the symptoms of the disease.
What is the research used for?
- To detect herpes viral infection of the genital organs in men and women and monitor its treatment.
- To test a woman for herpes before and during pregnancy (if there is a risk of infection).
When is the study scheduled?
- If necessary, confirm or deny the fact of genital herpes infection.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Positive result
- The body is infected with a virus. The result is indicated in crosses depending on the amount of genetic material identified during the study.
| «+» | 2 copies of DNA |
| «++» | 102-103 copies of DNA |
| «+++» | 103-104 copies of DNA |
| «++++» | 104-105 copies of DNA |
| «+++++» | >105 copies of DNA |
Negative result
- Most often, there is no infection of the genitals with the herpes virus.
What can influence the result?
- Antiviral therapy can reduce the amount of virus in epithelial cells, however, due to the high sensitivity of the PCR method, this rarely leads to false negative results.
- Errors at the stage of taking biological material, when a sufficient number of virus-infected cells do not enter the sample for research, can lead to false negative indicators.