Photo source freepik
Tuberculosis, in the old days called consumption, has been known to mankind since ancient times. And for centuries it remained one of the most formidable diseases along with plague and typhus. There were cases when the disease wiped out entire families, because medicine knew nothing about the methods of transmission, as well as identifying the disease in the early stages.
Only towards the end of the 19th century was the infectious nature of the disease proven, and then scientific research began to be carried out on the development of immunity to the disease. The first vaccine against tuberculosis was created only at the beginning of the twentieth century, and they learned to reliably diagnose the disease only with the invention of fluorography.
Based on the accumulated knowledge about tuberculosis, modern phthisiology arose. However, today's TB doctor deals not only with the treatment of tuberculosis, but also with other infectious diseases, including, for example, leprosy.
What does a TB doctor treat?
The diversity and complexity of medicine lead to the emergence of extremely narrow specialties. And a TB doctor is a good example of this. Initially, the duties of this specialist included the examination and treatment of patients with tuberculosis. But as human knowledge about microorganisms, as well as the infections that can be transmitted through them, has developed, the number of diseases has increased.
Today these include the following:
- all forms and types of tuberculosis;
- leprosy;
- sarcoidosis
In addition, the specialty is also divided into narrower areas:
- a phthisiopulmonologist specializes in lung diseases;
- a phthisiogynecologist is involved in the treatment of tuberculosis that has affected the genital area, reproductive organs of a woman or a pregnant woman;
- a phthisiourologist works when the male genital organs, as well as the urinary system, are infected;
- a phthisiosurgeon performs surgical interventions;
- A phthisio-otolaryngologist treats the larynx, ears and nasopharynx;
- a phthisiodermatologist specializes in the treatment of affected skin;
- a phthisioculist is hired to treat the eyes;
- A phthisio-orthopedist, using special products, eliminates the resulting deformation of the musculoskeletal system;
- The phthisiopeliatrist provides vaccinations and medical examinations for patients under 18 years of age.
Quite often, ordinary people confuse the profession of a phthisiatrician with another specialty, which is also aimed at treating lung diseases - a pulmonologist. Although in essence these are two equal medical professions. The fact is that if a pulmonologist diagnoses a patient with tuberculosis, he will immediately refer him to a phthisiatrician, who will become the attending physician. In other words, although tuberculosis affects the lungs, it is entirely under the control of another specialist.
Although it should be noted that the phthisiatrician works quite a lot and actively with other medical specialists:
- infectious disease specialist;
- surgeon;
- oncologist;
- gynecologist;
- pediatrician;
- urologist;
- neurologist;
- gastroenterologist
It should also be noted that the work of a phthisiatrician is very dangerous, since the doctor always runs the risk of becoming infected through airborne droplets, as well as through direct contact with an infected person. In this regard, doctors of this profile are entitled to some benefits. These include:
- half-holiday;
- additional days of vacation;
- payments to wages.
Photo source: pressfoto/freepik
Diagnostic methods
After the first consultation, the TB specialist issues directions for tests. Before the next visit, it is necessary to do a general blood test, chest x-ray, and tuberculin skin test (depending on the patient’s age).
Additionally, the doctor may need microbiological culture of various materials (pus/urine/sputum), liver tests (blood biochemistry), and an examination of the visual organs by a highly specialized doctor. Also, if necessary, you need to undergo computed tomography, MRI, cerebrospinal fluid diagnostics and other manipulations.
Do not expose your body to additional stress; undergo only those diagnostic methods prescribed by your TB doctor.
Responsibilities of a phthisiatrician
The functional list of a specialist of this profile should include:
- carrying out diagnostics and examinations;
- prescription of treatment taking into account the individual characteristics of the body;
- carrying out vaccinations;
- work with documents.
In order to fulfill all the requirements presented, the phthisiatrician must know:
- anatomy and physiology;
- features of infectious diseases;
- principles of vaccination and medical examination;
- methods for drawing up treatment plans.
T-SPOT.TB
T-SPOT.TB is a modern method of immunological diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection using a blood test.
T-SPOT TEST FOR TUBERCULOSIS METHOD IS RECOMMENDED:
- If the patient refuses to undergo skin tests and fluorography;
- If extrapulmonary forms of TV are suspected;
- If the patient is found to have an allergy to tuberculin (according to the medical history), allergic diseases, skin diseases, epilepsy, acute and exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- Patients for whom subcutaneous tests are contraindicated or difficult due to exacerbation of the underlying disease.
- When a false positive Mantoux reaction is detected in children vaccinated with the BCG vaccine.
- In people who have visited countries with high incidence of tuberculosis (Africa, Asia)
- In pregnant women in case of contact with a patient with tuberculosis or presence of symptoms;
- Patients with HIV infection, especially those with a reduced level of CD4 protein cells;
- For tumor diseases, if a person is undergoing radiation or chemotherapy treatment
- For autoimmune and other pathologies leading to immune suppression;
Requirements for a phthisiatrician
Working in such a dangerous profession requires meeting the following requirements:
- completed higher medical education;
- a valid certificate in the field of Phthisiology;
- medical record with all necessary examinations;
- knowledge of safety precautions when working with tuberculosis;
- leadership skills;
- ability to work in special programs on a PC.
How does a pulmonologist treat?
A pulmonologist prescribes different treatments. In some cases, conservative treatment is sufficient, in which the use of antibacterial and expectorant drugs can be combined with inhalations and physiotherapeutic procedures. In some cases, endoscopic methods are used, for example, when there is no other way to clear the bronchi of mucus and pus.
In our clinic, patients are seen by pulmonologist Maria Yuryevna Tsapaeva, an experienced specialist. She will conduct a diagnosis, prescribe treatment, help you choose breathing exercises or create a preventive program.
You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling 8(83159) 9-22-10.
Phthisiatrician's place of work
A phthisiatrician can build his career in the following healthcare institutions:
- municipal and commercial clinics;
- multidisciplinary hospitals;
- tuberculosis dispensaries.
As previously mentioned, TB doctors have a shortened working day, but this fact does not in any way affect the density and intensity of their daily work. Therefore, young professionals need to be prepared for the fact that they need to work with large volumes of information, as well as devote significant time to working with documentation.
From the first sneeze?
– If a person with tuberculosis coughs on a child, does this mean that the child will get sick?
– After the first contact, no one gets sick. Tuberculosis is a disease of the weak and unprotected. But if a child has a cold or is weakened, he has a greater chance of getting sick. Therefore, close contact with a carrier of tuberculosis (for example, at home or at school) is a very alarming situation. The risk group includes frequently ill children, toddlers and adolescents who are obese, receiving immunosuppressive therapy (prescribed for autoimmune diseases), and children with congenital HIV infection.
tuberculosis
Question answer
What professions are people required to undergo fluorography annually?
– Can a healthy lifestyle protect against tuberculosis?
– A healthy lifestyle is a good help in the fight against infection. However, it cannot be considered 100% protection. No country has yet declared itself a tuberculosis-free zone. Mycobacterium is a very smart infection that can adapt to any living conditions. We must not forget about this!
Where can I study to become a phthisiatrician?
Photo source: pressfoto/freepik
Phthisiatricians are trained at medical universities. To do this, you should enroll either in the “General Medicine” department or in the “Pediatrics” department. The training will take six years if it is full-time. After receiving a diploma, a young doctor can choose his specialty in residency. It is there that “Phthisiology” is presented. You will have to study for another two years.
When to see a pulmonologist
Cough is a symptom that is often associated with a sore throat, flu or ARVI. Of course, if we are talking about a seasonal respiratory infection, it is not necessary to contact a pulmonologist. But a cough can be a manifestation of a much more serious illness.
You should make an appointment with a pulmonologist if you have the following symptoms:
- A dry or wet cough that does not stop for several weeks.
- A characteristic cough that bothers the patient mainly in the morning and is accompanied by viscous discharge. Although it is believed that such a cough is mainly characteristic of smokers, in fact it occurs in anyone who suffers from a chronic form of bronchitis (for example, people who work in hazardous industries).
- The cough is accompanied by shortness of breath, which occurs even with minor physical exertion and at rest. If shortness of breath itself is accompanied by difficulty in exhaling, this should also be a reason to consult a doctor.
- A prolonged cough in which the sputum changes color (for example, it becomes distinctly yellow, pinkish, or green). An even more alarming symptom is the appearance of blood clots in it.
- Drowsiness during the day, which is accompanied by dry mouth and larynx immediately after waking up.
- The cough is accompanied by pain in the chest, which intensifies with deep inhalation and exhalation, etc.
Very often, an appointment with a pulmonologist is recommended by a therapist who either detects some changes in fluorography or finds it difficult to interpret the study data.
Allergy sufferers should also make an appointment with a pulmonologist if they have symptoms of bronchial asthma: the cough is paroxysmal in nature, accompanied by sneezing, lacrimation, and itching in the eyes. In such cases, the patient may experience a feeling of lack of air, which causes headaches and disturbed sleep.
Consultation with a pulmonologist is also recommended for expectant mothers. During pregnancy, many women experience worsening chronic diseases, including those of the respiratory system. In addition, changes in the hormonal system can lead to impaired lung function. At the same time, an experienced doctor in such cases will help get rid of unpleasant symptoms by selecting medications that are safe for mother and child or recommending physiotherapeutic procedures.
People who work in hazardous industries, as well as smokers, are recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations by a pulmonologist 1-2 times a year.
In addition, in international practice there are a number of other criteria under which a consultation with a pulmonologist is considered necessary. In addition to the already mentioned cough and shortness of breath, these are also frequent ARVI - more than 3 times a year.
Personal qualities of the TB profession
In order to work as a doctor in this category, you must have the following qualities:
- responsibility;
- diligence;
- Analytical mind;
- caution;
- stress resistance;
- organization;
- accuracy;
- the ability to weigh all risks and make sound decisions.
Short description
There are many subsections, TB specialists actively collaborate with pediatricians, surgeons, endocrinologists, bacteriologists and infectious disease specialists, as well as pulmonologists. Pulmonologists and phthisiatricians should not be confused. The first are general medical staff working with diseases of the respiratory tract and lungs. The second are narrow-profile, whose field of interest includes only patients affected by Koch’s bacillus, suffering from leprosy and sarcoidosis. The doctor works with both children and adults, which depends on the specialization received.
Observation by a TB specialist for healthy children
As a rule, in healthy children, prevention, control of vaccine administration and revaccination, and control of samples are carried out by a pediatrician. Children are referred to a phthisiatrician if a decision is made about revaccination if there is a medical outlet or if tuberculin tests are positive.
It is important to know that having a vaccination (BCG) primarily protects your child. Since 1962, Russia has carried out comprehensive vaccination of children, a practice that continues to this day. Today, BCG is the only tuberculosis vaccine available, and WHO considers it as a life-saving element of measures to protect against the disease.
Each parent has the right to decide whether to vaccinate their child with one vaccine or another. But world practice in the fight against tuberculosis has proven that the disease is tens of times more dangerous than post-vaccination complications.
Organs for which a phthisiatrician is responsible
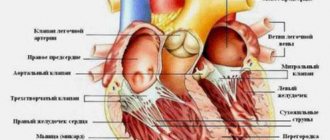
Most often, the disease affects the pulmonary system, but it is possible that other organs may be involved in the pathological process. To be more precise, there is not a single organ in the human body that cannot be affected by tuberculosis: bones and joints, peritoneal organs, intestines, lymph nodes, adrenal glands, genitourinary system - everything is vulnerable to the disease.
The way pathological agents are released into the external environment will depend on which organ was affected: feces, urine, sputum, blood, sperm, tears, breast milk, etc.